Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hormones Table
Uploaded by
spica25Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hormones Table
Uploaded by
spica25Copyright:
Available Formats
Josell Mary Engelee M.
Lim 2-BMT
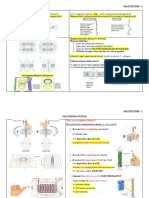
Hormone Insulin
Source Pancreatic Islets(Beta-cells) Pancreas(alpha cells)
Glucagon
Stimulus for release high blood glucose concentrations low levels of glucose in the blood
Inhibitor
Effects
PTH
Parathyroid Gland
low blood Ca2+ levels
Calcitonin
Thyroid gland (parafollicular cells)
elevated Ca2+
Vitamin D
Skin, Liver and Kidneys
PTH and Prolactin
ADH/AVP
Posterior pituitary gland
low blood volume, low blood pressure, high osmotic pressure
GH-IH like hormones Increases glucose and amino acid intake high levels of Increases glucose in the breakdown of blood; Amylin and glycogen and GHIH release of glucose into the circulatory system calcitonin Increase rate of bone breakdown by osteoclast; increase in Vitamin D synthesis PTH Decrease rate of bone breakdown; prevents large increase in blood Ca2+ levels following a meal Serum phosphate maintain serum calcium concentrations by increasing absorption of calcium and phosphate in the intestines and reabsorption of calcium and phosphate in the kidneys; mobilizes calcium from bone in response to parathyroid hormone activity Alcohol and caffeine Conserves water; constricts blood vessels
Oxytocin
Posterior pituitary gland
in the blood nipple stimulation, drug pitocin, and start of labor
After child birth
GH
Anterior pituitary gland
high levels of somatomedins (compounds stimulating tissue growth; released by liver)
inhibited by high levels of somatomedins
ACTH
Anterior pituitary gland
arrival of corticotropinreleasing hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus
somatostatin
Cortisol
Adrenal Cortex
ACTH
Insulin
Aldosterone
Adrenal Cortex
Adrenal Androgen
Adrenal Cortex
Deficiency of sodium, loss of blood or dehydration that lowers BP or elevated potassium levels Puberty: ACTH
Normalized Potassium Level
Melatonin
LH
Anterior pituitary gland
Stimulated by GnRH
GnRH antagonists GnRH analogues
Increases uterine contractions(if target tissue is the uterus) increases milk letdown for mammary glands Increases gene expression, breakdown of lipids and release of fatty acids form cells; increases blood glucose levels Increases secretion of glucocorticoid hormones like cortisol; increases skin pigmentation at high concentrations Increases fat and protein breakdown; increase glucose synthesis for amino acids; increases blood nutrient levels Increase rate of sodium transport into body; increase rate of K+ excretion; secondarily favor water retention Increase female sexual drive, growth of pubic and axillary hair Promotes ovulation and progesterone production in ovary; promotes
FSH
Anterior pituitary gland
gonadotropinreleasing hormone (GnRH)
inhibin
Progesterone
Ovaries
pituitary tropin LH
none
Estrogen
Ovaries
FSH
Aromatase; Melatonin
Testosterone
Testis
Stimulated by LH
Melatonin
Prolactin
Anterior pituitary gland
TRH
estrogens and dopamine
TSH
Anterior pituitary
arrival of
arrival of
testosterone synthesis and support for sperm cell production in testis Promotes follicle maturation and estrogen secretion in ovary; promotes sperm cell production in tetsis Increased size of cells lining the uterus; Aids in uterine and mammary gland development; for secondary sexual characteristics and menstrual cycle Increased cell division in the lining of the uterus; Aids in uterine and mammary gland development; for secondary sexual characteristics and menstrual cycle Development of the reproductive structures and development of male secondary sex characteristics; Aids in sperm cell production initiates milk production following pregnancy Increases thyroid
gland
T3/T4
Thyroid Gland
thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) from the hypothalamus binding of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH; also known as thyrotropin) to transmembrane receptors at the cell surface.
somatostatin from the hypothalamus
hormone secretion
Decrease in TSH
increased basal metabolic rate; essential for protein synthesis, glucose catabolism, fat mobilization; promotes normal nervous system function, cardiac function; promotes muscular and skeletal development and function; promotes GI motility, F reproductive ability, hydration of skin
Thymosin
Thymus Gland
TSH
sex hormones
Erythropoietin
Kidneys
MSH
Anterior pituitary gland
Stimulated when oxygen becomes scarce like in stroke Pregnancy
Renin
Kidneys
Angiotensin ANP
Liver Heart
Decreased arterial blood pressure; Angiotensin Renin Atrial stretch, sympathetic
Promotes immune system development and function High levels of blood Signals production oxygen of RBC; powerful vasoconstrictor Dopamine Increases melanin production in melaocytes to make skin darker in color Melatonin/Inhibiting Regulates blood drug/ANP pressure and blood flow ACE inhibitor Maintains Blood Pressure Shortening of vessel Reduces BP; blood walls, volume, and
stimulation, raised sodium concentration Leptin Adipose tissue Increased appetite; increased number of adipocytes Egg fertilization
parasympathetic stimulation, lower sodium concentration Decreased number of adipocytes
blood Na concentration
Sensation of satiety (fullness)
HCG
Ovaries
Child delivery
Melatonin
Pineal Gland
Darkness
Light: gonadal/adrenal testosterone; gonadal estrogen Aspirin
prevents the deterioration of the corpus luteum at the end of the fourth week and enables pregnancy to continue beyond the end of the normal menstrual cycle Helps regulate seasonal reproductive cycles Induces labor; Inflammation, Pain mechanisms, blood clotting, vasoconstriction and vasodilatation
PG/LT
Seminal Vesicle
Pregnancy
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Logic of English - Spelling Rules PDFDocument3 pagesLogic of English - Spelling Rules PDFRavinder Kumar80% (15)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- A Beautiful Mind - Psychology AnalysisDocument15 pagesA Beautiful Mind - Psychology AnalysisFitto Priestaza91% (34)
- Seatwork 10152014Document4 pagesSeatwork 10152014spica25No ratings yet
- Info 8 MationDocument23 pagesInfo 8 Mationspica25No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Formal Lab ReportDocument3 pagesCarbohydrates Formal Lab Reportspica25No ratings yet
- Amino Acids Formal Lab ReportDocument4 pagesAmino Acids Formal Lab Reportspica2520% (5)
- HemophiliaDocument31 pagesHemophiliaspica25No ratings yet
- Amino Acids Formal Lab ReportDocument4 pagesAmino Acids Formal Lab Reportspica2520% (5)
- Microbiology ReportDocument45 pagesMicrobiology Reportspica25No ratings yet
- Book Report On The Constant Princess by Anne BoleynDocument9 pagesBook Report On The Constant Princess by Anne Boleynspica25No ratings yet
- Gastric Emptying PresentationDocument8 pagesGastric Emptying Presentationrahul2kNo ratings yet
- Project TitleDocument15 pagesProject TitleadvikaNo ratings yet
- Government by Algorithm - Artificial Intelligence in Federal Administrative AgenciesDocument122 pagesGovernment by Algorithm - Artificial Intelligence in Federal Administrative AgenciesRone Eleandro dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in ContextDocument31 pagesOral Communication in ContextPrecious Anne Prudenciano100% (1)
- Sarcini: Caiet de PracticaDocument3 pagesSarcini: Caiet de PracticaGeorgian CristinaNo ratings yet
- Q3 Lesson 5 MolalityDocument16 pagesQ3 Lesson 5 MolalityAly SaNo ratings yet
- Claim &: Change ProposalDocument45 pagesClaim &: Change ProposalInaam Ullah MughalNo ratings yet
- Pon Vidyashram Group of Cbse Schools STD 8 SCIENCE NOTES (2020-2021)Document3 pagesPon Vidyashram Group of Cbse Schools STD 8 SCIENCE NOTES (2020-2021)Bharath Kumar 041No ratings yet
- Samsung LE26A457Document64 pagesSamsung LE26A457logik.huNo ratings yet
- Steven SheaDocument1 pageSteven Sheaapi-345674935No ratings yet
- TEsis Doctoral en SuecoDocument312 pagesTEsis Doctoral en SuecoPruebaNo ratings yet
- Security Questions in UPSC Mains GS 3 2013 2020Document3 pagesSecurity Questions in UPSC Mains GS 3 2013 2020gangadhar ruttalaNo ratings yet
- Matthew DeCossas SuitDocument31 pagesMatthew DeCossas SuitJeff NowakNo ratings yet
- K3VG Spare Parts ListDocument1 pageK3VG Spare Parts ListMohammed AlryaniNo ratings yet
- APICS-Houston Newsletter Sept 2012Document16 pagesAPICS-Houston Newsletter Sept 2012Christopher SeifertNo ratings yet
- Final ReflectionDocument4 pagesFinal Reflectionapi-314231777No ratings yet
- Skype OptionsDocument2 pagesSkype OptionsacidwillNo ratings yet
- APA CitationsDocument9 pagesAPA CitationsIslamNo ratings yet
- Purposeful Activity in Psychiatric Rehabilitation: Is Neurogenesis A Key Player?Document6 pagesPurposeful Activity in Psychiatric Rehabilitation: Is Neurogenesis A Key Player?Utiru UtiruNo ratings yet
- Dummies Guide To Writing A SonnetDocument1 pageDummies Guide To Writing A Sonnetritafstone2387100% (2)
- List of Vocabulary C2Document43 pagesList of Vocabulary C2Lina LilyNo ratings yet
- Magnetism 1Document4 pagesMagnetism 1krichenkyandex.ruNo ratings yet
- Name: Kartikeya Thadani Reg No.: 19bma0029Document4 pagesName: Kartikeya Thadani Reg No.: 19bma0029Kartikeya ThadaniNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Methodsin ImmnunologyDocument58 pagesLaboratory Methodsin Immnunologyadi pNo ratings yet
- Contoh RPH Ts 25 Engish (Ppki)Document1 pageContoh RPH Ts 25 Engish (Ppki)muhariz78No ratings yet
- EMI - Module 1 Downloadable Packet - Fall 2021Document34 pagesEMI - Module 1 Downloadable Packet - Fall 2021Eucarlos MartinsNo ratings yet
- PEG Catalog Siemens PDFDocument419 pagesPEG Catalog Siemens PDFrukmagoudNo ratings yet
- Meike SchalkDocument212 pagesMeike SchalkPetra BoulescuNo ratings yet