Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 12,1-2 Dan 13 Capacity Planning
Uploaded by
Fadhila KhairunnisaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 12,1-2 Dan 13 Capacity Planning
Uploaded by
Fadhila KhairunnisaCopyright:
Available Formats
12/9/2013
Week 12,1-2 dan 13
Capacity Planning
Capacity definition
2
Capacity is the amount of work that can be done in a specified time period. capacity is defined as the capability of a worker, machine, work center, plant, or organization to produce output per time period. Capacity is a rate of doing work, not the quantity of work done.
12/9/2013
Basic Capacity Definitions
produce a desired output in a given time period Capacity Planning determining the resources and methods needed to meet the priority plan Capacity Control monitoring production, comparing with the capacity plan, and taking appropriate corrective actions Capacity Management determining capacity needed as well as providing, monitoring, and controlling the capacity
Capacity Required capacity needed to
Capacity versus Load
12/9/2013
Capacity Planning Levels
Resource Planning Long range resource
requirements linked to the production plan
Rough-cut Capacity Planning Used to check
feasibility of MPS
Capacity Requirements Planning Detailed
work center capacity plans linked to MRP
Capacity Planning Levels
12/9/2013
Capacity Requirements Planning (CRP) Inputs
Open Order File found as scheduled receipts on
MRP
Planned order releases from MRP Potential
future orders
Work Center file
Information
on capacity in the work center Move, wait, and queue time information
Capacity Requirements Planning Inputs - Continued
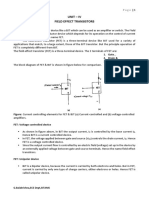
Routing file the path that the work will follow
Operations
to be performed Operation sequence Work centers used Potential alternative work centers Tooling needed Standard setup times and run times
12/9/2013
Sample Routing File
Figure 5.3 Routing file
Capacity Available
Impacted by:
Product
specification Product mix Methods used to make product Pace of work
12/9/2013
Planning calender
11
Finding Capacity Available
Rated Capacity = (available time) x (utilization) x (efficiency)
Available
time number of hours a work center can be
used Utilization = [(hours worked)/(available hours)] x 100% Efficiency = [(actual production rate)/(standard production rate)] x 100%
12/9/2013
Soal (rated capacity)
13
A work center consists of 4 machines and is operated 8 hours per day for 5 days a week. Historically, the utilization has been 85% and the efficiency 110%. What is the rated capacity?
Demonstrated capacity
14
Over the previous 4 weeks, a work center produced 120, 130, 150, and 140 standard hours of work. What is the demonstrated capacity of the work center?
12/9/2013
Capacity required (load)
15
Capacity required (load)
16
12/9/2013
Capacity Load Sum of all time required for orders on a work center - Example
Example Load Profile
12/9/2013
Scheduling Orders
Back scheduling (the typical approach) Start
with the due date, use lead time to find the proper start date for each operation
Forward scheduling Launch the order into
the first (gateway) work center, then use the lead times to find when the order will be completed at each work center
Back Scheduling Example
An order for 150 of a component is due on day 135 An order starts at the beginning of a day and finished at the end of a day Operation times for the 150 ordered:
Operation 10 4 days in work center 12 Operation 20 5 days in work center 14 Operation 30 1 day in work center 17 Operation 40 2 days in work center 03
10
12/9/2013
Data from the work center file
The resulting work schedule
11
12/9/2013
The work schedule shown graphically
Making the plan
12
12/9/2013
Managing the Plan Adjusting Capacity
Use Overtime or Undertime Adjust the number of workers Shift workers from other work centers Use alternative work centers to shift load Subcontract work
26
13
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- SystemDesk - EB Tresos Studio Workflow DescriptionsDocument23 pagesSystemDesk - EB Tresos Studio Workflow DescriptionsAmalkumar V GNo ratings yet
- Design and Control of A Three-Phase Active Rectifier Under Non-Ideal Operating ConditionsDocument8 pagesDesign and Control of A Three-Phase Active Rectifier Under Non-Ideal Operating Conditionsrakeshee2007No ratings yet
- Parallel Rubik's Cube Solver: Abstract-This Report Investigates Parallel Processing ForDocument3 pagesParallel Rubik's Cube Solver: Abstract-This Report Investigates Parallel Processing ForTejas LadheNo ratings yet
- Edc 4 UnitDocument26 pagesEdc 4 UnitAnonymous 6Ts3r7dwNo ratings yet
- Baker Campbell FormulaDocument3 pagesBaker Campbell FormulaArkayan LahaNo ratings yet
- Mba Time Table Updated On 1st Nov 2021Document4 pagesMba Time Table Updated On 1st Nov 2021KNRavi KiranNo ratings yet
- Ford OBD2 MonitorDocument282 pagesFord OBD2 MonitorAnonymous 4IEjocNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. Chemistry Honours-2022: 1 ListDocument4 pagesB.Sc. Chemistry Honours-2022: 1 ListSrijaNo ratings yet
- 2015 03 21a Mba Self-StudyDocument8 pages2015 03 21a Mba Self-Studyapi-265932575No ratings yet
- Compiler Lab VivaDocument6 pagesCompiler Lab VivaGaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics: What Is An Application?Document4 pagesComputer Basics: What Is An Application?Ser Crz JyNo ratings yet
- PHP BitsDocument24 pagesPHP BitskarunakarNo ratings yet
- Apa Flyer - CFDDocument2 pagesApa Flyer - CFDSantiago UrgilesNo ratings yet
- JDSU TrueSpeed Automated RFC-6349 TCP TestingDocument36 pagesJDSU TrueSpeed Automated RFC-6349 TCP TestingTakisNo ratings yet
- Xpac 2004 Release NotesDocument11 pagesXpac 2004 Release NotesAgustinus YosefNo ratings yet
- Continua SQ Wall LEDDocument7 pagesContinua SQ Wall LEDneuvoNo ratings yet
- Cat CDVRDocument8 pagesCat CDVRAdeel AfzalNo ratings yet
- On Chip Networks - Second EditionDocument212 pagesOn Chip Networks - Second EditionAditya Nair100% (3)
- Manual ETANK2000Document73 pagesManual ETANK2000Ever BriceñoNo ratings yet
- LogDocument2 pagesLogjwadey21No ratings yet
- SEC08-20 Rehabilitation TechnologyDocument2 pagesSEC08-20 Rehabilitation TechnologyJuliana Orjuela Garcia100% (1)
- ERP OverviewDocument29 pagesERP OverviewLupsoiuCosmin100% (1)
- BS en 00054-1-2021Document26 pagesBS en 00054-1-2021Mike DluNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Project All Numerates Grade 6 Table of SpecificationsDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Project All Numerates Grade 6 Table of Specificationsian bondocNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 7 Discussing Online Privacy - AnswersDocument9 pagesACTIVITY 7 Discussing Online Privacy - AnswersAdrian VSNo ratings yet
- Suzuki GSXR 1000 2007 - 08 Anular EscapeDocument6 pagesSuzuki GSXR 1000 2007 - 08 Anular EscapeBj BenitezNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Resume WritingDocument29 pagesThe Basics of Resume WritinglolaNo ratings yet
- B.SC Computer Science 2020-2021 SylabusDocument67 pagesB.SC Computer Science 2020-2021 SylabusKrithika SKNo ratings yet
- Radio Trimble Trimark 3Document2 pagesRadio Trimble Trimark 3Robinson VargasNo ratings yet