Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Web & Post-Conflict Governance Building in Fragile States by Jen Welch
Uploaded by
Leslie CarrOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Web & Post-Conflict Governance Building in Fragile States by Jen Welch
Uploaded by
Leslie CarrCopyright:
Available Formats
Web Science
jrw1g08@soton.ac.uk @jenwelch15 Jen_welch15
The Web & Post-conflict Governance Building in Fragile States
Case studies
1. The web for conflict prevention
Jennifer Welch Prof Susan Halford Dr Mark Weal Prof Gerry Stoker
Related work
[i]f the Internet can provide a canvas upon which nations can paint their social, linguistic,
cultural, and political beliefs, then perhaps the physical struggle for safe cultural havens and borders may no longer be as necessary for their preservation or evolution
McCormick (2002) The role of the Web in post-conflict governance building is at present widely underresearched, mainly due to the perceived lack of relevance of such technologies in places where infrastructure is severely lacking and where the prospects for connectivity seem implausible. So to answer the research question, we need to understand the debate in the field of peacebuilding, evaluate current policy and practice, and gather insights from close conceptual neighbours. Only academic work on the topic is on digital diasporas (Brinkerhoff 2007) and their use of the Web to affect the processes of peacebuilding on the ground in conflict-affected states. A review of policy and practice of five main actors in post-conflict governance building on a global scale provided the following results:
This case study covers a wide range of projects related to the use of ICTs and the web for conflict prevention. Most were perceived as disappointments, mainly due to the use of inappropriate technology, in terms of sustainability and capability (Musila 2013). There were also several unintended consequences of the use of ICTs, such as increased community participation from the workshops organised to teach local populations about the platforms and nefarious uses of the technology introduced (Puig Larrauri 2013).
2. The web for governance building
Again this case study covers a wide range of projects related to the use of ICTs and the web for governance building in developing countries. Project outcomes were deemed mainly positive, citing for example the computerisation of electoral lists as having increased citizens confidence in the [] system (UNDP 2013a: 37). However project reports highlighted that the beneficiaries of these initiatives were the upper and middle classes, rather than those who might need it the most.
Stabilisation Guiding Best practice Recognise Recognised Unit Principles on the potential and embrace Strategic Strategic transparency of ICT in potential of Comms only Comms only Broadcasting fragile states ICT in fragile states
How is the Web used The UN, in particular the UNDP was the most advanced in terms of perspective and practice of ICT use in fragile and conceptualised in settings. Notable in conflict prevention and governance building, which form the case studies of this research. post-conflict settings and with what Analysis & conclusions impacts?
From the academic literature, policy and practice review and insights gained from the case studies on closely related fields of conflict prevention and governance building in developing countries, we start to see the various ways in which the Web is used and conceptualised for post-conflict peacebuilding:
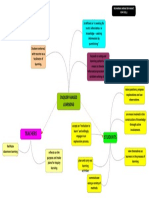
1 Six Webs identified in
academic, policy and case studies literature and pilot projects with different assumptions, risks and opportunities.
(Big) Data Agent of social change
Here the Web is conceptualised as a way of generating data, both in terms of specific location or as Big Data. Indicators Access Representativeness Ranging from the purely Prevalent in mainstream media, Sensitivity broadcasting perspective of especially in the Arab Spring Ownership strategic communications to more discourse, where the transformative Scope innovative crowdseeding effects of the Web are being techniques heralded. Unintended consequences Technologically deterministic Authenticity of information Agency Control of the message
2
Six Webs always co-exist, though not every type is actualised in a given context. Any could be actualised with their emergent properties.
Info sharing tool
Six Webs
Empowerment
Management tool
An alternative to the Increased efficiency for spoilers physical, geographical Control of the system inhabited by the victims and perpetrators of the violence experienced in conflict. Digital traces of interactions Security Used as a platform to organise, coordinate and to increase efficiency.
4 Juxtaposition of these
Webs can help explain intended & unintended consequences of actual projects and wider impacts.
Web seen as a catalytic enabler (UNDP 2013a) or a mobilising tool (UNDP 2013b). Agency Digital traces Security Power for whom?
3 This research shows that
understanding these conceptualisations is essential for a more effective understanding of success or failure in conflict-affected, fragile settings.
Alternative space
References: Brinkerhoff, J. M. (2007) Contributions of the digital diasporas to governance reconstruction in fragile states: potential and promise in Brinkerhoff, D. W. (ed.) (2007) Governance in Post-Conflict Societies: Rebuilding fragile states, Abingdon: Routledge Letouz, E., Meier, P. and Vinck P. (2013) 'Big Data for Conflict Prevention: New Oil and Old Fires' in 'New Technology and the Prevention of Violence and Conflict' in Mancini, F. (ed.) New Technology and the Prevention of Violence and Conflict, New York: International Peace Institute McCormick, G. M. (2002) Stateless Nations: I Pledge Allegiance To? in Mazarr, M. J. (ed.) Information Technology and World Politics, New York: Palgrave MacMillan, pp. 11-23 Musila, G. M. (2013) 'Early Warning and the Role of New Technologies in Kenya' in Mancini, F. (ed.) New Technology and the Prevention of Violence and Conflict, New York: International Peace Institute Puig Larrauri, H. (2013) 'New Technologies and Conflict Prevention in Sudan and South Sudan' in 'New Technology and the Prevention of Violence and Conflict' in Mancini, F. (ed.) New Technology and the Prevention of Violence and Conflict, New York: International Peace Institute UNDP (2013a) From Connectivity to Service Delivery: Case studies in e-governance, New York: UNDP UNDP (2013b) Issue Brief: Mobile Technology for Conflict Prevention - July 2013, New York: UNDP
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Writing Extraordinary EssaysDocument160 pagesWriting Extraordinary EssaysMica Bustamante100% (4)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Introduction To The Study of Literature in EnglishDocument331 pagesIntroduction To The Study of Literature in Englishmarta100% (2)
- Tourism Management/ProductDocument23 pagesTourism Management/ProductDurgesh Agnihotri100% (1)
- Cobern Camden - The New Archeological Discoveries and Bearing Upon The NT PDFDocument784 pagesCobern Camden - The New Archeological Discoveries and Bearing Upon The NT PDFFamSilverioIngarucaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society and Politics: Quarter 2 - Module 7 Cultural, Social and Political InstitutionsDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politics: Quarter 2 - Module 7 Cultural, Social and Political InstitutionsAnna Liza LingatNo ratings yet
- Spitzer y Auerbach PDFDocument197 pagesSpitzer y Auerbach PDFDiego Shien100% (1)
- Leena Eilitta, Liliane Louvel, Sabine Kim - Intermedial Arts - Disrupting, Remembering and Transforming Media (2012, Cambridge Scholars Publishing) PDFDocument242 pagesLeena Eilitta, Liliane Louvel, Sabine Kim - Intermedial Arts - Disrupting, Remembering and Transforming Media (2012, Cambridge Scholars Publishing) PDFCineclube do Chico100% (1)
- Teacher QuadrantDocument1 pageTeacher QuadrantMonikie Mala100% (8)
- Classifying Policing Social Machines by Maire Byrne-EvansDocument1 pageClassifying Policing Social Machines by Maire Byrne-EvansLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Web Forecasting by Lawrence GreenDocument1 pageWeb Forecasting by Lawrence GreenLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Memory Institutions and The Web - Nicole Beale - University of Southampton Web Science Institute Research Week, Royal Society.Document1 pageMemory Institutions and The Web - Nicole Beale - University of Southampton Web Science Institute Research Week, Royal Society.Nicole BealeNo ratings yet
- Web Science DTC Industry Forum: Opportunities and Challenges 2013Document18 pagesWeb Science DTC Industry Forum: Opportunities and Challenges 2013Leslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Visual Analytics by Paul BoothDocument1 pageVisual Analytics by Paul BoothLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Ontological Representation of Ancient Sumerian Literature Granularity Ontology Structure Formalise CONTENT Express Domain Knowledge Entities Relationships by Terhi NurmikkoDocument1 pageOntological Representation of Ancient Sumerian Literature Granularity Ontology Structure Formalise CONTENT Express Domain Knowledge Entities Relationships by Terhi NurmikkoLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Use of Mobile Technology To Support Dyslexic Learning in Higher Education by Katie SpiresDocument1 pageUse of Mobile Technology To Support Dyslexic Learning in Higher Education by Katie SpiresLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Online Collaborative Learning For Mathematics Education by Mandy LoDocument1 pageOnline Collaborative Learning For Mathematics Education by Mandy LoLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- The Virtual Body: Video Game Avatars As Self, Cipher, and Sex Object by Elzabi RimingtonDocument1 pageThe Virtual Body: Video Game Avatars As Self, Cipher, and Sex Object by Elzabi RimingtonLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Research Dissemination and Disaggregation by Will FysonDocument1 pageResearch Dissemination and Disaggregation by Will FysonLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Alison Knight Poster Industry Forum 2013 LatestDocument1 pageAlison Knight Poster Industry Forum 2013 LatestLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- The Role of Internet Intermediaries in Enhancing Cybersecurity by Evangelia PapadakiDocument1 pageThe Role of Internet Intermediaries in Enhancing Cybersecurity by Evangelia PapadakiLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Is The Web Corrupting The Values of Our Youth? by Huw DaviesDocument1 pageIs The Web Corrupting The Values of Our Youth? by Huw DaviesLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Engagement With Online Museums by Javier PeredaDocument1 pageEnhancing Engagement With Online Museums by Javier PeredaLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- The Web and Internet Piracy by Keiran RonesDocument1 pageThe Web and Internet Piracy by Keiran RonesLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- A Public Health Approach To Cybersecurity by Huw FryerDocument1 pageA Public Health Approach To Cybersecurity by Huw FryerLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Predicting Stock Prices With Online Information by Paul GaskellDocument1 pagePredicting Stock Prices With Online Information by Paul GaskellLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Personal Data and Transparency by Reuben BinnsDocument1 pagePersonal Data and Transparency by Reuben BinnsLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Privacy Choices and Informed Consent by Richard GomerDocument1 pagePrivacy Choices and Informed Consent by Richard GomerLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Skim Reading: An Adaptive Strategy For Reading On The Web by Gemma FitszimmonsDocument1 pageSkim Reading: An Adaptive Strategy For Reading On The Web by Gemma FitszimmonsLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Open Innovation Measurement and Optimisation by Gareth BeestonDocument1 pageOpen Innovation Measurement and Optimisation by Gareth BeestonLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- A Multi-Dimensional Framework of The ICT Innovation System by Chris HughesDocument1 pageA Multi-Dimensional Framework of The ICT Innovation System by Chris HughesLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Towards A Taxonomy For Web Observatories by Ian BrownDocument1 pageTowards A Taxonomy For Web Observatories by Ian BrownLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Orienting Within Complex Digital Environments Bridging The Gap Between The Inside and Out To Reduce Disorientation by Craig AllisonDocument1 pageOrienting Within Complex Digital Environments Bridging The Gap Between The Inside and Out To Reduce Disorientation by Craig AllisonLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Web For Environmental Sustainability: Identifying The Emerging Markets of The Cleanweb by Jack TownsendDocument1 pageWeb For Environmental Sustainability: Identifying The Emerging Markets of The Cleanweb by Jack TownsendLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- MOOCS in Higher Education Perspectives From HE Educators by Manual UrrutiaDocument1 pageMOOCS in Higher Education Perspectives From HE Educators by Manual UrrutiaLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- Charitable Use of Social Media by Christopher PhetheanDocument1 pageCharitable Use of Social Media by Christopher PhetheanLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- By Caroline HalcrowDocument1 pageBy Caroline HalcrowLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Social Software On Informal and Formal Learning by Robert BlairDocument1 pageThe Impact of Social Software On Informal and Formal Learning by Robert BlairLeslie CarrNo ratings yet
- International Relations PDFDocument65 pagesInternational Relations PDFJasiz Philipe OmbuguNo ratings yet
- Common English Errors and How to Overcome ThemDocument15 pagesCommon English Errors and How to Overcome ThemBharath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Melanie Walker Publications BooksDocument9 pagesMelanie Walker Publications BooksLuciano LimaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Eeuu Bil 2017Document6 pagesSyllabus Eeuu Bil 2017api-200062650No ratings yet
- Mohandas Karamchand GandhiDocument2 pagesMohandas Karamchand GandhiRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- An Advaita Story Explains Reincarnation as UnityDocument1 pageAn Advaita Story Explains Reincarnation as UnityJeremy WheelerNo ratings yet
- Understanding Essay Writing by DAWNDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Essay Writing by DAWNSyed Arsalan Tahir BukhariNo ratings yet
- العقل في الفكر الصوفي Mind in Sufi ThoughtDocument14 pagesالعقل في الفكر الصوفي Mind in Sufi Thoughtbahmalick650No ratings yet
- Philo 2nd Draft ExamDocument13 pagesPhilo 2nd Draft ExamJ R100% (1)
- Dap-Developmentally Appropriate PracticesDocument11 pagesDap-Developmentally Appropriate Practicesapi-59739555No ratings yet
- Functionalism and Formalism in LinguisticsDocument520 pagesFunctionalism and Formalism in LinguisticsBia CorrêaNo ratings yet
- An in-depth textual analysis of a rare Crimean Gothic language sourceDocument5 pagesAn in-depth textual analysis of a rare Crimean Gothic language sourceErnesto GarcíaNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Anthropological Literature in English On The Palestinian ®ham Ula and The Status of WomenDocument25 pagesA Review of The Anthropological Literature in English On The Palestinian ®ham Ula and The Status of WomendeepashajiNo ratings yet
- Strebel June2018 PDFDocument17 pagesStrebel June2018 PDFAdamNo ratings yet
- ArtsDocument31 pagesArtsmae nNo ratings yet
- Urban Open Spaces in Historical Perspective: A Transdisciplinary Typology and AnalysisDocument30 pagesUrban Open Spaces in Historical Perspective: A Transdisciplinary Typology and AnalysisSHUBHAM ARORANo ratings yet
- African LiteratureDocument9 pagesAfrican LiteratureRoshio Tsuyu TejidoNo ratings yet
- MOHSIN 2010culturalDocument6 pagesMOHSIN 2010culturalKaif MohammadNo ratings yet
- UNIFORM CIVIL CODE TOWARDS GENDER JUSTICE - Legal VidhiyaDocument7 pagesUNIFORM CIVIL CODE TOWARDS GENDER JUSTICE - Legal VidhiyaBBA LLBNo ratings yet
- Inquiry-Based Learning Mind MapDocument1 pageInquiry-Based Learning Mind MapNIKY LINSKYNo ratings yet
- Primer 2019-2020Document30 pagesPrimer 2019-2020Allen Lois LanuzaNo ratings yet
- Fashion Design in Prod Dev Using Telestia AB Tech-Dr Nor SaadahDocument9 pagesFashion Design in Prod Dev Using Telestia AB Tech-Dr Nor SaadahNick Hamasholdin AhmadNo ratings yet