Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Term Paper
Uploaded by
zaityzakeryOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Term Paper
Uploaded by
zaityzakeryCopyright:
Available Formats
CBB 4233: Industrial Effluent Engineering Term Paper Title: Wastewater Treatment System in Dutch Lady Milk Industries
Berhad
Nor Zaity Che Mat Zakery 12121 Chemical Engineering
1.0 1.1
INTRODUCTION Companys profile Incorporated in 1963, Dutch Lady Milk Industries Berhad is currently the leading dairy
company in Malaysia. Its holding company is Royal FrieslandCampina NV, a Dutch multinational corporation and one of the largest dairy cooperatives in the world. Dutch Lady Malaysia manufactures and sells a wide range of quality dairy products for the home and export market, with all products enjoying a strong following with its Dutch Lady and Friso brands. Overall, there are five plants producing different type of dairy products in Dutch Lady Milk Industries Berhad. Sterilised Milk (STM) plant producing sterilized milk, Ultra-high temperature (UHT) plant producing UHT milk, Chilled plant (CHP), producing chilled products, Powder plant producing powder-based product and Milk Reception (MLR) plant functioned as to store, cook and deliver milk to all plants.
1.2 Wastewater Treatment System
According to Environmental Quality Act (EQA) 1974 (Industrial Effluent) Regulations 2009, industrial effluent is defined as any liquid waste or wastewater generated from manufacturing process. Wastewater treatment system functions as to treat the industrial effluent so that the final effluent is safe before it is being discharged to the river. Previously, there are two methods in which the contaminants are removed which are either by chemical or biological treatment (Metcalf and Eddy, 1991). Today, the processes or unit operations are group together to provide the methods known as primary, secondary and tertiary treatment. The methods involved are screening, sedimentation, biological, chemical treatment etc.
In Dutch Lady, the liquid waste coming from milk processing is sent to wastewater for further treatment before it is being discharged to the river. This is to comply with Malaysia law, Environmental Quality Act (EQA) 1974 (Industrial Effluent) Regulations 2009. The wastewater treatment in Dutch Lady is activated sludge treatment type in which air is bubbled in biological tank with the presence of microorganism. The treatment chosen is basically based on factors such as the type of influent, availability of the area and cost.
2.0
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS Before the treatment method is discussed, it is important to know the typical
characteristics and sources of wastewater. In Dutch Lady, the source of wastewater basically coming from three types of categories which are processing waters, cleaning wastewaters and sanitary wastewater. Table 2.1 summarized the type and sources of wastewater in Dutch Lady. Table 2.1: Type and sources of wastewater in Dutch Lady Type Processing waters Sources of wastewater Processing waters include water used in the cooling and heating process. Basically, these effluents are free from pollutant. The wastewater coming from processing water can be straightly discharged into the monsoon drain or reused. Cleaning wastewater basically coming from the cleaning of equipment in contact with milk or milk product, spillage of milk, CIP cleaning process and water resulting from malfunction and operational control. In Dutch Lady, wastewater is coming from five different plant producing different products such as yogurt, chilled products, powder-based product, UHT and sterilized milk product. The sanitary wastewater is normally piped directly to sewage works
Cleaning wastewater
Sanitary wastewater
The usages of CIP chemical such as caustic soda for dairy cleaning cause the pH variation in wastewater. Apart from that, other concern which related to CIP is the effect to biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD). Therefore, a proper treatment strategy is required.
2.1 Treatment Strategy As the major wastewaters are coming from milk processing, biological wastewater treatment is the best option due to biodegradable properties of the liquid waste. In Dutch Lady, the equalization tank and biological tank is a type of sequential batch reactor (SBR). Basically, SBR uses five stages of treatment which are filling, reacting, settling, decanting and idle. Details for the treatment process are described in the next chapter.
3.0 DESCRIPTION AND JUSTIFICATION OF THE PROCESS
This chapter will explain step by step process of biological treatment which implemented in Dutch Lady. Figure 3.1 to 3.5 summarized the process.
Figure 3.1 Collection Sump
Figure 3.2 Equalization Tank
Figure 3.3 Biological Tank
Figure 3.6 Sampling Sump
Figure 3.5 Sludge cake
Figure 3.4 Belt Press
Figure 3.7Final Discharge Point
a)
Collection Sump
Influent coming from processing units will be channeled to the wastewater treatment through pipeline. Overall, there are five pipelines which indicate the influent coming from five plants. The pipelines are equipped with flow meter. The influents with different flow rates will enter the collection sump in order to mix them altogether before entering the equalization tank.
b) Equalization Tank Equalization tank functioned as the damping of flowrate variations so that a constant or nearly constant flow rate is achieved. There are two types of equalization tank, in-line arrangement or off-line arrangement. Basically, for in-line arrangement, all of the flow will pass through the equalization tank meanwhile for off-line arrangement; only the flowrate above the specified limit is diverted into the equalization tank. In Dutch Lady, in-line arrangement is used since all the influent will enters the equalization tank before it is treated in biological tank. According to Metcalf and Eddy (1991), biological treatment is enhanced through the application of flow equalization tank. The reasons are: 1) Shock loading are eliminated or can be minimized 2) Inhibiting substances can be diluted 3) Stabilized the pH
Figure 3.8: Equalization tank Sometimes, air is supplied in equalization tank to control odor. c) Biological Tank
As the major wastes are mainly coming from milk processing which categorized under organic matter, therefore biological treatment is used. Generally, there are five major groups of biological processes such as aerobic processes, anoxic processes, anaerobic process, combined aerobic, anoxic and anaerobic processes and pond processes. According to Arrun (2011),
biological treatment using aerobic activated sludge process has been in practice for well over century. The wastewater treatment in Dutch Lady uses aerobic activated sludge process in which the biological treatment requires the presence of oxygen. The term biological treatment means that bacteria or microorganism are involved in degradation of organic impurities and the operating condition of the bioreactor. Therefore, the activated sludge process will take place in the presence of air and microorganism is used to eat the organic matter and convert it into carbon dioxide, water and biomass. The organic matter will act as food to microorganism and oxygen is required for respiration process. Figure 3.8 shows the activated sludge process in Dutch Lady
Figure 3.9: Biological tank Photo is taken during the sedimentation process. It is observed that clear water at the top and sludge settle at the bottom. d) Conditioning and Belt Press
Sludge settled at the bottom of biological tank is then conveyed to the belt press using pump. The function of belt press is remove water from sludge, thicken the sludge and thus reducing the volume of sludge. In order to ensure the thin sludge does not break apart, polymer is used and mix with the sludge in the conditioning tank before it is conveyed to the belt press. Thickened sludge forming the sludge cake is rolled out to the sludge container while the separated water decants to the equalization tank.
Belt press
Polymer dosing
Figure 3.10: Belt press e) Final discharged point
Treated water or effluent is channeled to the sampling sump before it is being discharged to the river. This is where the water is test to ensure that the parameters do not exceed the limit set by DOE. The six parameters are: 1) Temperature 2) pH 3) Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) 4) Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) 5) Suspended Solid (SS) 6) Oil and Grease (O&G) Sample collected is sent to Permulab for analysis.
Following the standard set by Department of Environment (DOE), Dutch Lady has ensured that the parameters do not exceed the standard. Figures below summarized the result obtained from Permulab.
Figure 3.11: pH monitoring of effluent
Figure 3.12: Temperature monitoring
Figure 3.13: COD monitoring
Figure 3.14: BOD monitoring
Figure 3.14: Suspended solid monitoring
Figure 3.15: Oil and grease monitoring
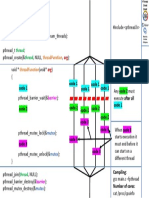
4.0 BLOCK DIAGRAM OF THE WASTEWATER TREATMENT PROCESS
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF WASTEWATER TREATMENT IN DUTCH LADY
5.0 CONCLUSION As conclusion, the wastewater treatment process in Dutch Lady Milk Industries is a type of activated sludge system. Regular monitoring to the pH, BOD, COD, temperature, suspended solid and oil and grease has ensured that the parameters does not exceed the limit as required by DOE. The results obtained shows that the overall effluent quality of Dutch Lady is fairly excellent. However, a few recommendation is proposed to improve the treatment performance such as: 1) To reduce blower time so that cost can be reduced 2) To fix polymer dosing 3) To install primary clarifier to reduce suspended solid loading .
REFERENCES Environmental Quality Act (EQA) 1974 (Industrial Effluent) Regulations 2009 Tchobanoglous G, Burton L.F,(1991). Wastewater engineering:treatment disposal and reuse/Metcalf& Eddy
You might also like
- VuHaiNam - Assignment 7Document4 pagesVuHaiNam - Assignment 7Nam VuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 CarboxylicDocument8 pagesAssignment 1 CarboxylicYu HuiNo ratings yet
- Secondary TreatmentDocument14 pagesSecondary TreatmentNasirNo ratings yet
- L 31Document12 pagesL 31RadhaAnanthalekshmiNo ratings yet
- Eceboardlouie: Front BackDocument7 pagesEceboardlouie: Front BackJoaquin GonzalezNo ratings yet
- A New Approach To The Design of Super-DirectiveDocument12 pagesA New Approach To The Design of Super-DirectiveAnonymous P2ZN8X100% (1)
- SAP Basis Questions AnsDocument5 pagesSAP Basis Questions AnsSantanu Kar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Functional DescriptionDocument20 pagesGas Turbine Functional Descriptioncbmanaus100% (1)
- Performance Evaluation of Effluent Treatment Plant of Dairy Industry PDFDocument6 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Effluent Treatment Plant of Dairy Industry PDFMortezaNo ratings yet
- Dairy Waste N ManagementDocument11 pagesDairy Waste N ManagementMudit MisraNo ratings yet
- 1.1 GeneralDocument18 pages1.1 GeneralPravinAlbdusMathewNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Faiz Rizwan Bin Kifriazrin 2017631978 Mid Term AssessmentDocument10 pagesMuhammad Faiz Rizwan Bin Kifriazrin 2017631978 Mid Term AssessmentAzizrin AzaliNo ratings yet
- Water Jar TestDocument8 pagesWater Jar TestNurin Adlina100% (1)
- Plant Based Coagulant For Waste Water TreatmentDocument9 pagesPlant Based Coagulant For Waste Water TreatmentInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & Management100% (1)
- Okoye - A - I - PG - M.SC - 07 - 42985 (JURNAL PENTING 15062017) PDFDocument134 pagesOkoye - A - I - PG - M.SC - 07 - 42985 (JURNAL PENTING 15062017) PDFKartika Anggraeni100% (1)
- Lab Report 1Document11 pagesLab Report 1Mohamed SaeedNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument18 pagesThesisKadiwa Carig Cagayan South100% (2)
- Uitm Lab Report Plug Flow ReactorDocument15 pagesUitm Lab Report Plug Flow ReactorNabilah SyaheeraNo ratings yet
- Small Renewable Energy Power Programme (SREP) - STDocument6 pagesSmall Renewable Energy Power Programme (SREP) - STMohd Asri TaipNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Enzyme KineticsDocument3 pagesQuiz On Enzyme KineticsHens Christian FuentesNo ratings yet
- Full Lab 1 Mai 2014Document19 pagesFull Lab 1 Mai 2014Kairu Nichkhun HorvejkulNo ratings yet
- Subic Water and Sewerage CoDocument4 pagesSubic Water and Sewerage CoNicole Anne BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Cob Project ReportDocument8 pagesCob Project ReportrituNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For Determining Oil and Grease For Raw and Treated EffluentDocument3 pagesLaboratory Manual For Determining Oil and Grease For Raw and Treated EffluentAnas YuzairiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - After-Tax Economic AnalysisDocument28 pagesChapter 17 - After-Tax Economic AnalysisBich Lien Pham0% (1)
- CLB21003 Process Heat Transfer Experiment 1: Heat Conduction (Discussion) Lab ReportDocument3 pagesCLB21003 Process Heat Transfer Experiment 1: Heat Conduction (Discussion) Lab ReportSiti Hajar Mohamed100% (1)
- FULL Plate and Frame Filter Press PDFDocument16 pagesFULL Plate and Frame Filter Press PDFMuhammad Asyraf IINo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3Anonymous Vx9KTkM8nNo ratings yet
- CEV633 - ASGN 1 - Mar2018 - QuestionDocument2 pagesCEV633 - ASGN 1 - Mar2018 - Questionbotakmbg6035No ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument3 pagesWaste Water TreatmentSana Saleem100% (1)
- CHE 413 Momentum TransferDocument4 pagesCHE 413 Momentum TransferMaria Cecille Sarmiento GarciaNo ratings yet
- CSTR Design For Propylene Glycol Chemical ProductionDocument13 pagesCSTR Design For Propylene Glycol Chemical ProductionMeilani Kusuma WatiNo ratings yet
- CPE 655 Solid Waste Management: Report: MSW Treatment by Incineration Is Not Relevant For MalaysiaDocument2 pagesCPE 655 Solid Waste Management: Report: MSW Treatment by Incineration Is Not Relevant For Malaysiaafiqahanuwar0% (1)
- Three Types of Paints and CoatingsDocument6 pagesThree Types of Paints and CoatingsberchardNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Phenolic Water Using AdsorptionDocument74 pagesTreatment of Phenolic Water Using AdsorptionShubham JainNo ratings yet
- Chem-E-Car Sefter Conception: Muhammad Miftahur Rahman Habib Al Aziz Fitri Handayani ArcodheaDocument16 pagesChem-E-Car Sefter Conception: Muhammad Miftahur Rahman Habib Al Aziz Fitri Handayani ArcodhearahmanNo ratings yet
- Properties of ShellDocument15 pagesProperties of ShellJay-Ar S. SungaNo ratings yet
- University Life Purpose: VisionDocument7 pagesUniversity Life Purpose: VisionMaria Cecille Sarmiento GarciaNo ratings yet
- 1R16 - Project StudyDocument27 pages1R16 - Project StudyRenzo Cadag MacasilNo ratings yet
- Detail DesignDocument108 pagesDetail DesignChoon Zhe ShyiNo ratings yet
- FR Experiment 3Document7 pagesFR Experiment 3m kimNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 Batch Evaporative Crystallization PDFDocument9 pagesExp 4 Batch Evaporative Crystallization PDFmirza farhanNo ratings yet
- Bioproduct Exp4 g1Document20 pagesBioproduct Exp4 g1JivashiniBalasupurManiamNo ratings yet
- Foundation Design AssignmentsDocument2 pagesFoundation Design Assignmentssomesh dubeyNo ratings yet
- Food Research International: Aline R.A. Silva, Marselle M.N. Silva, Bernardo D. Ribeiro TDocument17 pagesFood Research International: Aline R.A. Silva, Marselle M.N. Silva, Bernardo D. Ribeiro TNikolett NagyNo ratings yet
- BKF3731 Lab Manual Edited 26 Jan 2012Document38 pagesBKF3731 Lab Manual Edited 26 Jan 2012Sharifah Nur FasihahNo ratings yet
- Final Proposal PDFDocument59 pagesFinal Proposal PDFColeen TorresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Cost Concept: Haslina Abdullah. Haslinaa@uthm - Edu.myDocument43 pagesChapter 2 - Cost Concept: Haslina Abdullah. Haslinaa@uthm - Edu.myLau Siong KwongNo ratings yet
- Microbial Leaching 1Document30 pagesMicrobial Leaching 1manmithNo ratings yet
- Leaching (Coconut Oil)Document2 pagesLeaching (Coconut Oil)Maria Hazel AbayaNo ratings yet
- "Production of Ethanol From Bagasse PDFDocument64 pages"Production of Ethanol From Bagasse PDFGimei Benedict100% (1)
- Assignment Fluid 2 UitmDocument19 pagesAssignment Fluid 2 UitmFirdaus AsryNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Assessment CPD30302 July18Document12 pagesLab Report Assessment CPD30302 July18Fikri IlyasNo ratings yet
- Seasoning of TimberDocument2 pagesSeasoning of TimberKrishnaSahNo ratings yet
- Kepong IiDocument15 pagesKepong IiShahiera ShafieNo ratings yet
- List of Tables List of Figures List of Abbreviations 1Document75 pagesList of Tables List of Figures List of Abbreviations 1AlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- Result and Discussion CrystallisationDocument4 pagesResult and Discussion CrystallisationAdiel AdrieNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (Part A and Part B)Document8 pagesAssignment 1 (Part A and Part B)botakmbg6035No ratings yet
- NOTA STUDENT Buku SAB4943 Mod3Document62 pagesNOTA STUDENT Buku SAB4943 Mod3Muhamad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Dustbin - LiteratureDocument25 pagesDustbin - LiteratureChandini ChandiniraoNo ratings yet
- Dairy Wastewater Treatment Using Orange Peel As AdsorbentDocument10 pagesDairy Wastewater Treatment Using Orange Peel As Adsorbentadarsh sNo ratings yet
- ChE 180 Alternative Paper Version2Document6 pagesChE 180 Alternative Paper Version2Emmanuel CristobalNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Disposal and Pollution Control in DairyDocument14 pagesWaste Water Disposal and Pollution Control in Dairy19 CH 056 Vaishali Vivek100% (1)
- Result 20121022Document1 pageResult 20121022zaityzakeryNo ratings yet
- Aim For Operation ManagementDocument1 pageAim For Operation ManagementzaityzakeryNo ratings yet
- Aim For Operation ManagementDocument1 pageAim For Operation ManagementzaityzakeryNo ratings yet
- CalculationDocument1 pageCalculationzaityzakeryNo ratings yet
- Compiled Report v3Document145 pagesCompiled Report v3zaityzakeryNo ratings yet
- Managing People and OrganizationDocument8 pagesManaging People and Organizationzaityzakery100% (1)
- Result For Progress ReportDocument3 pagesResult For Progress ReportzaityzakeryNo ratings yet
- Calculation Cost Distillation ColumnDocument2 pagesCalculation Cost Distillation ColumnzaityzakeryNo ratings yet
- Gaseous and Solid WasteDocument6 pagesGaseous and Solid WastezaityzakeryNo ratings yet
- Gas ChromDocument23 pagesGas ChromMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles and Processes in The Operation of Incineration TechnologyDocument6 pagesBasic Principles and Processes in The Operation of Incineration TechnologyzaityzakeryNo ratings yet
- Bio-Oil Using Acetic AcidDocument2 pagesBio-Oil Using Acetic AcidzaityzakeryNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger: Area 36.67 M Type Fixed-Tube Heat Exchanger Material Stainless SteelDocument1 pageHeat Exchanger: Area 36.67 M Type Fixed-Tube Heat Exchanger Material Stainless SteelzaityzakeryNo ratings yet
- Aim For Operation ManagementDocument1 pageAim For Operation ManagementzaityzakeryNo ratings yet
- Gaseous WasteDocument3 pagesGaseous WastezaityzakeryNo ratings yet
- Calculation Cost Distillation ColumnDocument2 pagesCalculation Cost Distillation ColumnzaityzakeryNo ratings yet
- The Biological Basis of Waste Water TreatmentDocument20 pagesThe Biological Basis of Waste Water TreatmentRadulescu EugenNo ratings yet
- Metrology Lab 2 FinalDocument8 pagesMetrology Lab 2 Finalgoutham dkNo ratings yet
- Wake Up and Roar Satsang With H.W.L. PoonjaDocument1 pageWake Up and Roar Satsang With H.W.L. PoonjaIrina MTrNo ratings yet
- Voided Biaxial Slabs - State of Art: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental ScienceDocument10 pagesVoided Biaxial Slabs - State of Art: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental ScienceShinde vishalNo ratings yet
- Bmaxx 4400 JindalDocument76 pagesBmaxx 4400 JindalRakesh Karan Singh0% (1)
- CVV CableDocument7 pagesCVV CableNopNo ratings yet
- EN VEGASWING 63 Two WireDocument48 pagesEN VEGASWING 63 Two WireLucas FiordelisiNo ratings yet
- (L2) - Mole Concept JEEDocument19 pages(L2) - Mole Concept JEEHYDRA CLAN100% (1)
- Beam-Column Self Study Report by Othman and HaniDocument29 pagesBeam-Column Self Study Report by Othman and Haniozzieastro100% (2)
- M04 - L01 - Student GuideDocument9 pagesM04 - L01 - Student GuideShreyasNo ratings yet
- Seismic: VvinuDocument528 pagesSeismic: VvinuLucas ScartonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Gas Supply SystemDocument28 pagesLecture 1-Gas Supply SystemMuhammad FakhriNo ratings yet
- Peugeot 206Document1 pagePeugeot 206Sergio Hernandez0% (1)
- Work With Linked ServersDocument44 pagesWork With Linked ServersioiNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study and Static Analysis of Piston Using Solid Edge and AnsysDocument23 pagesComparative Study and Static Analysis of Piston Using Solid Edge and AnsysIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- حالات تحميل الرياح والزلازل للكود الجديد PDFDocument3 pagesحالات تحميل الرياح والزلازل للكود الجديد PDFmohamedmararNo ratings yet
- The Chattering Problem in Sliding Mode SystemsDocument8 pagesThe Chattering Problem in Sliding Mode SystemsBhaskar BiswasNo ratings yet
- Panaray 802 Series III Loudspeaker: General DescriptionDocument4 pagesPanaray 802 Series III Loudspeaker: General Descriptionadibecha100% (1)
- Design Simulation Manufacture and Testingof A Free-Piston Stirling Engine - Ivan Niell Deetlefs PDFDocument138 pagesDesign Simulation Manufacture and Testingof A Free-Piston Stirling Engine - Ivan Niell Deetlefs PDFJorge ValianteNo ratings yet
- Damco Cambodia Corporate BrochureDocument9 pagesDamco Cambodia Corporate BrochureSok HengNo ratings yet
- JM at - 20040129Document11 pagesJM at - 20040129wreckedweaselNo ratings yet
- Fxe-400s Control PC: ApparatusDocument2 pagesFxe-400s Control PC: ApparatusCristian Gabriel CordaryNo ratings yet
- Hydro Static Interlocks and Pins in Lifeboat Hook SystemsDocument2 pagesHydro Static Interlocks and Pins in Lifeboat Hook Systemsdwad82No ratings yet
- Mbackpaper 18Document6 pagesMbackpaper 18Aakash PathakNo ratings yet
- HVAC Dampers Installation Method StatementDocument3 pagesHVAC Dampers Installation Method StatementDong VanraNo ratings yet
- CONTENTSDocument9 pagesCONTENTSESRANo ratings yet
- M Ishaq Electrical SupervisorDocument7 pagesM Ishaq Electrical SupervisorMuhammad IshaqNo ratings yet
- The Chengdu Jian-20Document20 pagesThe Chengdu Jian-20Cat CrysisNo ratings yet