Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 11 - Mitral Stenosis
Uploaded by
Indra HebatCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 11 - Mitral Stenosis
Uploaded by
Indra HebatCopyright:
Available Formats
Principles
Causes Causes
NOTE:
Prevalence
depends on
socioeconomic
status of the
country
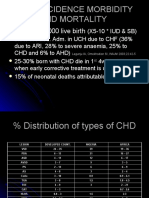
Rheumatic (85,4%)
NOTE:
Prevalence
depends on
socioeconomic
status of the
country
Rheumatic fever (75% valvular
involvment)
NOTE:
Prevalence
depends on
socioeconomic
status of the
country
Stenotic annular calcication
(12,5%)
NOTE:
Prevalence
depends on
socioeconomic
status of the
country
Congenital (0,6%)
NOTE:
Prevalence
depends on
socioeconomic
status of the
country
Rheumatic fever Rheumatic fever
Group A streptococcal
(GAS) tonsillopharyngitis
Arthritis joints
Chorea minor Subcutaneous nodules
Pancarditis
Congenital Mitral Stenosis Congenital Mitral Stenosis
Rare (0,6% of CHD)
Combined with other cong. defects
Forms: Annulus hypoplasia, parachute, double
orice
NOTE: Shone complex is an association of congenital mitral stenosis and
other left-sided in and outow obstruction (coarctation, valvular/
subvalvular aortic stenosis)
NOTE: Shone complex is an association of congenital mitral stenosis and
other left-sided in and outow obstruction (coarctation, valvular/
subvalvular aortic stenosis)
011 // Mitral Stenosis
1
Pressure Tracing LV/LA Pressure Tracing LV/LA
LA-LV gradient Elevated pressure in LA
Elevated pressure pulm.
capillaries
Pulm. cong. / edema
PHT / reactive PHT Tricuspid regurgitation
Right heart failure Atrial brillation
Echocharacteristics of MS Echocharacteristics of MS
Doming (diastolic
buldging of the AMVL)
Reduced valve opening
Commisural fusion Leaet tip thickening
Secondary calcication
Subvalvular involvement
(thickend and fused
tendinae)
Associated problems Associated problems
Thickened aortic valve
Reduced LVF (rheumatic
myocarditis)
Enlarged LA Pulmonary hypertension
Other valve involvement Aortic regurgitation
Tricuspid stenosis Thrombus
Risk of Thrombus Risk of Thrombus
NOTE:
Most thrombi are
seen in the left
atrial appendage.
Thus you will miss
them with
transthoracic
Echo!!
Systemic embolism in 20% of
all MS patients
NOTE:
Most thrombi are
seen in the left
atrial appendage.
Thus you will miss
them with
transthoracic
Echo!!
80% of patients are in Ab
NOTE:
Most thrombi are
seen in the left
atrial appendage.
Thus you will miss
them with
transthoracic
Echo!!
45% have spontaneous left
atrial contrast
NOTE:
Most thrombi are
seen in the left
atrial appendage.
Thus you will miss
them with
transthoracic
Echo!!
011 // Mitral Stenosis
2
Quantication
MV Area Reference Values MV Area Reference Values
Normal (cm) 4 6 cm
Mild (cm) > 1,5 cm
Moderate (cm) 1 1,5 cm
Severe (cm) < 1 cm
Problems with MV Planimetry (PSAX) Problems with MV Planimetry (PSAX)
NOTE:
Nevertheless, if
feasible,
planimetry is the
most exact
method to
evaluate MV
area
Image quality Alignment
NOTE:
Nevertheless, if
feasible,
planimetry is the
most exact
method to
evaluate MV
area
Timing Calcication
NOTE:
Nevertheless, if
feasible,
planimetry is the
most exact
method to
evaluate MV
area
Atrial brillation Incompl. comm. fusion
NOTE:
Nevertheless, if
feasible,
planimetry is the
most exact
method to
evaluate MV
area
Operator experience
NOTE:
Nevertheless, if
feasible,
planimetry is the
most exact
method to
evaluate MV
area
Forms of Mitral Stenosis Forms of Mitral Stenosis
Classic form Funnular form
011 // Mitral Stenosis
3
MS Gradients Reference Values MS Gradients Reference Values
Mild (mmHg) < 5 < 8
Moderate (mmHg) 5 10 8 15
Severe (mmHg) > 10 > 15
NOTE: Gradients are higher in the setting of additional MR! NOTE: Gradients are higher in the setting of additional MR! NOTE: Gradients are higher in the setting of additional MR!
PHT Pitfalls PHT Pitfalls PHT Pitfalls
Diastolic dysfunction Aortic regurgitation
Following valvuloplasty
Concave shape of
tracing
Degenerative calcic MS
Color Doppler , PISA and Continuity Equation Color Doppler , PISA and Continuity Equation Color Doppler , PISA and Continuity Equation
Candle ame MR
PISA for quantication PISA for quantication
MVA = Mitral volume ow/ Peak velocity of
diastolic mitral ow
MVA = Mitral volume ow/ Peak velocity of
diastolic mitral ow
Continuity Equation ( doesnt work if AR and MR
present)
Continuity Equation ( doesnt work if AR and MR
present)
Quantication of Mitral Stenosis in Atrial Fibrillation Quantication of Mitral Stenosis in Atrial Fibrillation
Planimetry Several diferent measurements
Mean gradients
Average 5 cycles with small variation of R-R intervals
close to normal HR
PHT
Avoid mitral ow from short diastoles/ average
diferent cardiac cycles
011 // Mitral Stenosis
4
Valvuloplasty
Indication and Results Indication and Results
Indication
Clinically signicant MS (valve area < 1,5 cm or <
1,8 cm in unusually large patients)
Results
Good immediate results (valve area > 1,5 cm with
no regurgitation) can be obtained in over 80%
NOTE: PHT method is not reliable immediately after valvuloplasty! NOTE: PHT method is not reliable immediately after valvuloplasty!
Prevalvuloplastic Echoevaluation Prevalvuloplastic Echoevaluation
Mobility Subvalvular thickening
Valve thickening Calcication
Calcication of
commissures
Thrombus
Mitral regurgitation Tricuspid regurgitation
011 // Mitral Stenosis
5
You might also like
- Tte and Tee Assessment For Asd Closure 2Document88 pagesTte and Tee Assessment For Asd Closure 2Avinash GutheNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease BDocument38 pagesCongenital Heart Disease BDr Richard AnekweNo ratings yet
- CMR Guide CHD 2014 PDFDocument105 pagesCMR Guide CHD 2014 PDFBasemAlharbiNo ratings yet
- Achd LectureDocument48 pagesAchd LecturedrmdsaeedNo ratings yet
- By: Dr. Shkar R. SaeedDocument45 pagesBy: Dr. Shkar R. SaeedSimon JosanNo ratings yet
- Narrow Complex TachcyardiaDocument32 pagesNarrow Complex Tachcyardiamanak_18No ratings yet
- Atrial Septal Defects: Imaging Conference December 10, 2008 Angela Morello, M.DDocument49 pagesAtrial Septal Defects: Imaging Conference December 10, 2008 Angela Morello, M.Dkiritokazuto35No ratings yet
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument10 pagesValvular Heart DiseaseEzyan SyaminNo ratings yet
- Guidelines - Assessment of ASD and PFO and Evaluation of A Cardiac Source of Embolism - 2Document50 pagesGuidelines - Assessment of ASD and PFO and Evaluation of A Cardiac Source of Embolism - 2Sebastian ChandraNo ratings yet
- ASD For TKV Sem-4Document35 pagesASD For TKV Sem-4Aulia SriyantiNo ratings yet
- Tachycardia Approach and ManagementDocument41 pagesTachycardia Approach and ManagementChadi Alraies100% (5)
- Microsoft PowerPoint - ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE PDFDocument51 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE PDFHanafieHeluthNo ratings yet
- Tetrology of FallotDocument55 pagesTetrology of FallotShravani ShagapuramNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument51 pagesCongenital Heart Diseaseelsa prima putri100% (2)
- Asd - TheDocument40 pagesAsd - TheguidanceNo ratings yet
- Transposition of The Great Arteries: Eric Osborn January 27, 2010Document35 pagesTransposition of The Great Arteries: Eric Osborn January 27, 2010Soad ShedeedNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseasesDocument47 pagesCongenital Heart Diseasesfrenee aradanasNo ratings yet
- Aortic Valve DiseaseDocument63 pagesAortic Valve DiseaseFaridOrahaNo ratings yet
- Adult Congenital Heart Disease Board ReviewDocument79 pagesAdult Congenital Heart Disease Board ReviewKhajornsak Som-UnNo ratings yet
- Aortic Aneurysm-Dr AbhishekDocument90 pagesAortic Aneurysm-Dr Abhisheksarath chandranNo ratings yet
- Cme Atrial FibrillationDocument43 pagesCme Atrial FibrillationAlex Matthew100% (1)
- PB12 7839 R3 PDFDocument9 pagesPB12 7839 R3 PDFStephanie BecerraNo ratings yet
- L-R ShuntDocument88 pagesL-R ShuntnanohaniwiekoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pathology: Professor Mircea BuruianDocument174 pagesCardiovascular Pathology: Professor Mircea BuruianDiana PopoviciNo ratings yet
- 7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraDocument57 pages7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraSurya ArhNo ratings yet
- Restrictive CardiomyopathyDocument15 pagesRestrictive CardiomyopathyJing CruzNo ratings yet
- Ilmu Dan Seni Pengabilan KeputusanDocument17 pagesIlmu Dan Seni Pengabilan KeputusanMuhammad Khoirul SodiqNo ratings yet
- Neonatal and Pediatric Guidelines Arrhythmia ManagementDocument16 pagesNeonatal and Pediatric Guidelines Arrhythmia ManagementAkhmad HidayatNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument61 pagesTetralogy of FallotHanya BelajarNo ratings yet
- Kindermann Aneurysm May2014Document14 pagesKindermann Aneurysm May2014cystanarisaNo ratings yet
- DR Sutarmawan Acute Presentation of Valve SletnosisDocument33 pagesDR Sutarmawan Acute Presentation of Valve SletnosisArniNo ratings yet
- Mitral StenosisDocument17 pagesMitral StenosisMuhammad Alauddin Sarwar100% (8)
- Chad ScoreDocument5 pagesChad ScoreakochaNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Katup Jantung: Dr. Tjatur Winarsanto SPPD Rs CiremaiDocument59 pagesPenyakit Katup Jantung: Dr. Tjatur Winarsanto SPPD Rs CiremaianisamayaNo ratings yet
- Mitral StenosisDocument48 pagesMitral StenosiskornbergwiNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DeseasesDocument54 pagesCongenital Heart DeseasesAntony100% (1)
- Board Review: Vikram Chhokar MD University of Tennessee Division of CardiologyDocument79 pagesBoard Review: Vikram Chhokar MD University of Tennessee Division of CardiologyFernando SalimNo ratings yet
- Cctga PcicsDocument9 pagesCctga PcicsAdrian KhomanNo ratings yet
- 7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraDocument57 pages7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraSurya Ashri Rahman HNo ratings yet
- Mitral StenosisDocument29 pagesMitral Stenosisrameshbmc100% (4)
- Tachyarrhythmias When Should I Refer?Document25 pagesTachyarrhythmias When Should I Refer?Cindy Seow Sieng TengNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Assessment: Sickkids Advanced Paediatric Cardiology ProgramDocument61 pagesCardiac Assessment: Sickkids Advanced Paediatric Cardiology Programmadimadi11No ratings yet
- Mitral Stenosis-RarestDocument9 pagesMitral Stenosis-RarestWen Jie LauNo ratings yet
- 5a. Echo Evaluation of Mitral Stenosis, DR AzriDocument37 pages5a. Echo Evaluation of Mitral Stenosis, DR AzriJalu PanjongkoNo ratings yet
- Echocardiographic Assessment of Aortic Valve Stenosis DR RanjitDocument93 pagesEchocardiographic Assessment of Aortic Valve Stenosis DR RanjitNavojit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 14 Clauss Pediatric Echocardiography PDFDocument159 pages14 Clauss Pediatric Echocardiography PDFSergiu NiculitaNo ratings yet
- Sao Subvalvulara: Cmho Sao Discreta: RV CMH, LVNC, CMR, Channel 2020 3Document39 pagesSao Subvalvulara: Cmho Sao Discreta: RV CMH, LVNC, CMR, Channel 2020 3Andreea ŞtefănescuNo ratings yet
- Aortic Stenosis:: Updates in Diagnosis & ManagementDocument48 pagesAortic Stenosis:: Updates in Diagnosis & ManagementCuca PcelaNo ratings yet
- Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) : Presenter Dr. Maimuna Sayeed Resident (Phase A) Paediatric Gastroenterology & NutritionDocument50 pagesAtrial Septal Defect (ASD) : Presenter Dr. Maimuna Sayeed Resident (Phase A) Paediatric Gastroenterology & NutritionIrving H Torres LopezNo ratings yet
- Echocardiography General Principles and ExamplesDocument135 pagesEchocardiography General Principles and Examplesroseneels9No ratings yet
- Doing Coronary Angiogram IndependentlyDocument127 pagesDoing Coronary Angiogram IndependentlySyed WaheduzzamanNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart Disease-1Document38 pagesValvular Heart Disease-1Taufiq RamadhanNo ratings yet
- TUGAS Ventricular Septal DefectDocument8 pagesTUGAS Ventricular Septal DefectMohammad NafisNo ratings yet
- Echocardiographic Assessment of ASD: Chairperson: Assoc. Prof. Naveen SheikhDocument53 pagesEchocardiographic Assessment of ASD: Chairperson: Assoc. Prof. Naveen SheikhWyahmp WyahmpNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Imaging of Pulmonary Embolism: Shane BezzantDocument109 pagesDiagnostic Imaging of Pulmonary Embolism: Shane Bezzantdrqazi777No ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument31 pagesTetralogy of FallotDevipriya MajumderNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Subarachnoid HaemorrhageDocument6 pagesLecture 5 Subarachnoid HaemorrhageEmily MurrayNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: Cabg - OpcabDocument49 pagesCoronary Artery Bypass Grafting: Cabg - OpcabdeNo ratings yet
- P Cefalico Varones 0-36Document1 pageP Cefalico Varones 0-36RONALDNo ratings yet
- WHO - Haemoglobin Level For Anemia 2011Document6 pagesWHO - Haemoglobin Level For Anemia 2011Adhi SanjayaNo ratings yet
- GRCHRT Boys 24HdCirc-L4W Rev90910Document1 pageGRCHRT Boys 24HdCirc-L4W Rev90910jjys29No ratings yet
- Jurnal MDR TBDocument7 pagesJurnal MDR TBIndra HebatNo ratings yet
- Game ConfigDocument1 pageGame ConfigIndra HebatNo ratings yet
- m1 e PDFDocument5 pagesm1 e PDFIndra HebatNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument1 pageReadmeIndra HebatNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2b4rra51No ratings yet
- Aldrete Score SheetDocument1 pageAldrete Score SheetBoston GunawanNo ratings yet
- God of WarDocument27 pagesGod of WarIndra HebatNo ratings yet
- Aldrete Score SheetDocument1 pageAldrete Score SheetBoston GunawanNo ratings yet
- God of WarDocument27 pagesGod of WarIndra HebatNo ratings yet
- Trajenta Tablets: What Is in This LeafletDocument4 pagesTrajenta Tablets: What Is in This LeafletIndra HebatNo ratings yet
- Trajenta Tablets: What Is in This LeafletDocument4 pagesTrajenta Tablets: What Is in This LeafletIndra HebatNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Ecg Survival Guide: MacpedsDocument21 pagesPediatric Ecg Survival Guide: MacpedsMohd KhalilNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease and Vascular AbnormalityDocument19 pagesCongenital Heart Disease and Vascular AbnormalityCai TabalocNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Disorders in ChildrenDocument41 pagesCardiac Disorders in ChildrenB AuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Adult Resuscitation v3 1Document16 pagesLesson 2 Adult Resuscitation v3 1Michels Garments S.H Nawaz HosieryNo ratings yet
- Benefit of Atrial Septal Defect Closure in Adults: Impact of AgeDocument8 pagesBenefit of Atrial Septal Defect Closure in Adults: Impact of AgeraisNo ratings yet
- Membaca Ekg Untuk PemulaDocument15 pagesMembaca Ekg Untuk PemulaChristopher NjotokusgitoNo ratings yet
- Susila Wahiddiyah, Alfi Ari Fahrul RizalDocument10 pagesSusila Wahiddiyah, Alfi Ari Fahrul RizalNandha PuspitaSariNo ratings yet
- Cor Pulmonale IkaDocument19 pagesCor Pulmonale IkaIka Lukita SariNo ratings yet
- 2020 SCA InfographicDocument1 page2020 SCA InfographicThe National DeskNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiac Surgery - Nursing Care and ManagementDocument225 pagesAdult Cardiac Surgery - Nursing Care and ManagementOsama Elsayed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Materi Pelatihan Code Blue WUFDocument81 pagesMateri Pelatihan Code Blue WUFBoby GeaNo ratings yet
- Emergency EchocardiographyDocument62 pagesEmergency Echocardiographyansarijaved100% (1)
- 2021 ACLS Study GuideDocument20 pages2021 ACLS Study GuideShane Brown83% (12)
- MCQ Cardio 2Document54 pagesMCQ Cardio 2Dian Paramita100% (1)
- Nama Sex Tgl-Lahir RujukanDocument23 pagesNama Sex Tgl-Lahir RujukanFACHRIZAL AMRIENo ratings yet
- PhDthesisAASL PDFDocument168 pagesPhDthesisAASL PDFmuhammad alamNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrestDocument30 pagesCardiac ArrestTommy NainggolanNo ratings yet
- Mitral RegurgitationDocument43 pagesMitral Regurgitationraissasafitry100% (1)
- Backwell's 5 Min Veterinary ConsultDocument120 pagesBackwell's 5 Min Veterinary ConsultAndra Elena Pricop100% (2)
- Heart FailureDocument1 pageHeart FailureTrisha VergaraNo ratings yet
- Ekg QuestionsDocument7 pagesEkg Questionsdayumthatsalonguser nameNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument15 pagesApproach To The Patient With Cardiovascular DiseaseJanel EnriquezNo ratings yet
- CRFDocument27 pagesCRFNatalie WNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmias in Africa: Epidemiology, Management Challenges, and PerspectivesDocument10 pagesCardiac Arrhythmias in Africa: Epidemiology, Management Challenges, and PerspectivesmahsusiyatiNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorDocument28 pagesDefibrillatorAnish H DaveNo ratings yet
- ECG Definition: - PurposeDocument2 pagesECG Definition: - PurposeJustine Karl Pablico100% (1)
- Ventricular Septal DefectDocument4 pagesVentricular Septal DefectMarina RotaruNo ratings yet
- Ecg Essentials 2 PDFDocument45 pagesEcg Essentials 2 PDFjaikishan marathe 69No ratings yet
- Cardiopatias Congênitas: Ac. Alex André Ferreira Queiroz Ac. João Victor Lima DantasDocument25 pagesCardiopatias Congênitas: Ac. Alex André Ferreira Queiroz Ac. João Victor Lima DantasJoão Victor Lima DantasNo ratings yet
- Preemptive Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy To Prevent Cardiac Arrest in Peripartum Cardiomyopathy: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesPreemptive Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy To Prevent Cardiac Arrest in Peripartum Cardiomyopathy: A Case Reportvanilla wottledNo ratings yet