Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Crowded Coasts Case Studies Explored
Uploaded by
debbie96Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Crowded Coasts Case Studies Explored
Uploaded by
debbie96Copyright:
Available Formats
Crowded Coasts Case Studies Coastalisation
Bournemouth. People move b/c of climate, accessibility, environment quality. Industries move b/c of accessibility, cheaper wages, graduates, cheaper land, land available Population has retirees and youth from university
Florida.75% live along coast Spain1.2% increase per year of people along coast since 2000
Impacts of tourism
Kimmeridge Bay Fossil collecting causes trampling and stone turning Removes fossils Limpet Protection Zone educates visitors on how to reduce impacts
Studland Baydanger to people, animals and plants Congestion Pollution Litter Trampling Noise from motors Water traffic
Conflict on the coast
Studland Beach.tourism vs. social/environment Land development ruins dunes Cliffs eroded by tourists walking Traffic congestion disturbs residents Boats damage marine ecosystems
Southampton Watersindustry vs. social/environment Good for industry as sheltered from storms, deep waters for boats, land nearby available Conflicts of oil refinery which gives income etc. but pollution Conflict of new housing as provides large amounts of sewage Conflict of popular sailing area but creates pollution, water traffic
Dibden Bay.economic vs. social/environment For development: Provide 300 jobs Increase economy
Improve transport
Against development: Cost 700 million Ruins views Traffic increase SSSI ruined
Pollution
Southampton Metal pollution especially tin very high levels Oil spills e.g. 1989- 800 birds effected, sand dunes, beaches Liquid waste ruins food webs Sewage discharge of 300 million litres a day
Environments at Risk
Southampton Salt Marshes (SSSI) Valuable for animal habitats, sea defence Ruined by refinery which reduces its size
Studland Beach Sand Dunes (SSSI) Habitat for animals and the heath is rare greenery Ruined by tourists trampling and land developments
Impact of Industry
Southampton Pollution Scenery ruined Natural land lost Increased traffic
Coastal Erosion
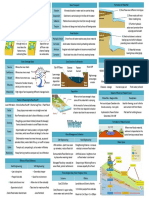
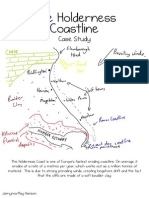
Holderness Fastest rate of erosion in Europe Over 2000 years, cliff retreated 4km Reasons for erosion: o Geology- boulder clay (soft) and chalk o Fetch- receives very strong waves due to current, pressure, deep sea floor o Longshore drift- lack of beach so cliff erodes more
Managing coastal erosion
Holderness Hard and Soft engineering techniques Hard: Soft: Beach nourishment at Hornsea Coastal zoning Managed retreat Wooden groynes at Hornsea Rock groynes at Mappleton Revetments at Easington Sea walls at Withernsea
Flood risks
Holdernesssea levels expected to rise by 30cm by 2050 Venicefloods 200 days of the year Thames Estuary Rising levels due to storms, sea levels rise, amplitude Risk of flooding increasing due to Thames Gateway as less surface run off Without Gateway, 1.25 million people at risk
Sustainable Management
Thames Estuarydeveloping but they want to protect the salt marshes and extend them as benefits nature and act as sea defence Abbot Farmthey retreated the line to create 84 hectares of farmland into salt marshes which benefits animals and acts as sea defence-may not be sustainable as could bring disadvantages for future people Integrated Coastal Management and Shoreline Management Planssustainable as deals with more than one place, but takes into consideration independent needs Holdernesshard engineering not as sustainable as soft engineering Kentretreating line is controversial and easy way out so not sustainable
You might also like
- Crowded CoastsDocument12 pagesCrowded Coastsdebbie96No ratings yet
- Crowded Coasts AS Notes.Document7 pagesCrowded Coasts AS Notes.ultimop34No ratings yet
- Geog Investigations Case StudiesDocument14 pagesGeog Investigations Case StudiesZeynep AkıNo ratings yet
- Increasing RisksDocument5 pagesIncreasing Risksdebbie96No ratings yet
- Case Study For Coastal Erosion Holderness Revision NotesDocument3 pagesCase Study For Coastal Erosion Holderness Revision NotesRahil BhavanNo ratings yet
- Holderness Case StudyDocument2 pagesHolderness Case Studymrstone77No ratings yet
- Andros Barrier Reef Case StudyDocument3 pagesAndros Barrier Reef Case StudyaNo ratings yet
- Coasts Case StudiesDocument6 pagesCoasts Case StudiesEricka AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Coastal Processes and ManagementDocument28 pagesCoastal Processes and ManagementJoshuaHortonNo ratings yet
- Coral Reefs: Types of Coral Reefs in The Caribbean, There Are Three Basic Types of Coral Reefs Such AsDocument4 pagesCoral Reefs: Types of Coral Reefs in The Caribbean, There Are Three Basic Types of Coral Reefs Such AsMercedes AlexisNo ratings yet
- IB Geography Oceans Case StudiesDocument6 pagesIB Geography Oceans Case StudiesMarc Wierzbitzki0% (1)
- Interference With Coastal Structures: o o o oDocument6 pagesInterference With Coastal Structures: o o o oROSALIE AGMALIWNo ratings yet
- Interference With Coastal Structures: o o o oDocument6 pagesInterference With Coastal Structures: o o o oROSALIE AGMALIWNo ratings yet
- As Level GeographyDocument9 pagesAs Level GeographyWill TeeceNo ratings yet
- Case Studies - iGCSE GeographyDocument21 pagesCase Studies - iGCSE GeographyAmalia Korakaki100% (1)
- Global Warming NotesDocument4 pagesGlobal Warming NotesPatrice DavisNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Pollution on Marine-Coastal and Inland EcosystemsDocument12 pagesImpacts of Pollution on Marine-Coastal and Inland EcosystemsMalay SarkerNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Coasts (Module Overview)Document2 pagesModule 2 - Coasts (Module Overview)Claudia MuirNo ratings yet
- Case Study PDFDocument7 pagesCase Study PDFnarayananNo ratings yet
- Formation of Oxbow Lakes: A Concise GuideDocument10 pagesFormation of Oxbow Lakes: A Concise GuideSandy SaddlerNo ratings yet
- Geography Notes-Half Yearly 2011.: Coastal ManagementDocument6 pagesGeography Notes-Half Yearly 2011.: Coastal ManagementannieaterNo ratings yet
- Geography IGCSE Case StudiesDocument23 pagesGeography IGCSE Case StudiesGaara aishiteruNo ratings yet
- Synthesis: Thematic Paper: Synthesis of The Protective Functions of Coastal Forests and Trees Against Natural HazardsDocument10 pagesSynthesis: Thematic Paper: Synthesis of The Protective Functions of Coastal Forests and Trees Against Natural HazardsHaryo ArmonoNo ratings yet
- Active recall answers for coastal processes and landforms examDocument5 pagesActive recall answers for coastal processes and landforms examDcsantosNo ratings yet
- EUROSION Case Study of Rostock Coastline Erosion in GermanyDocument16 pagesEUROSION Case Study of Rostock Coastline Erosion in GermanyGogo1111No ratings yet
- 3.9 - Coastal FloodingDocument2 pages3.9 - Coastal Floodingemzspooner11No ratings yet
- Tuan Hung ProjectDocument2 pagesTuan Hung Projectnguyen quoc tanNo ratings yet
- Guyana Water Management and Flood Control Chapter Provides InsightDocument48 pagesGuyana Water Management and Flood Control Chapter Provides InsightHanniel MadramootooNo ratings yet
- Case StudiesDocument10 pagesCase StudiesMiguel Oubiña SánchezNo ratings yet
- 08 Coastal ManagementDocument3 pages08 Coastal ManagementAlexandra ChapmanNo ratings yet
- Eng Project PDFDocument5 pagesEng Project PDFHarshini VNo ratings yet
- Coral Reefs: A Fragile Ecosystem Under ThreatDocument10 pagesCoral Reefs: A Fragile Ecosystem Under Threatapi-26554515No ratings yet
- Alevel - AS Geography World at Risk RevisionDocument36 pagesAlevel - AS Geography World at Risk RevisionAttiyaNo ratings yet
- Coastal Flooding & Environmental Refugees Case Study - MaldivesDocument2 pagesCoastal Flooding & Environmental Refugees Case Study - Maldivesaugust1929No ratings yet
- Coastal Management Case Study: Lyme Regis, Dorset, UKDocument3 pagesCoastal Management Case Study: Lyme Regis, Dorset, UKTugas PWKNo ratings yet
- 2015 Case Studies BOOKLET With DetailDocument28 pages2015 Case Studies BOOKLET With DetailGrace KamauNo ratings yet
- Coasts Under ThreatDocument9 pagesCoasts Under Threatapi-258813608No ratings yet
- Coastal Landforms Class 8 (2022-2023)Document55 pagesCoastal Landforms Class 8 (2022-2023)As 54bdNo ratings yet
- 3a. The Coastal ZoneDocument140 pages3a. The Coastal Zoneb_osborne100% (1)
- Water Management and Flood Control in GuyanaDocument47 pagesWater Management and Flood Control in GuyanaRyan BoodramlallNo ratings yet
- Geography NotesDocument7 pagesGeography NoteshelloNo ratings yet
- MunroethuruthuDocument40 pagesMunroethuruthuAkhil S KumarNo ratings yet
- GCSE Revision GuideDocument86 pagesGCSE Revision GuideJamie WeeksNo ratings yet
- Outline Examples of Coastal Management Strategies in The UKDocument2 pagesOutline Examples of Coastal Management Strategies in The UKDesign_for_LifeNo ratings yet
- Holderness Case StudyDocument9 pagesHolderness Case StudyJamyma-May HansonNo ratings yet
- SFA Newsletter Summer Autumn 2016Document22 pagesSFA Newsletter Summer Autumn 2016Sandringham Foreshore AssociationNo ratings yet
- The State of Pollution of The Mediterranean SeaDocument7 pagesThe State of Pollution of The Mediterranean SeaROHIT SaiNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources GuideDocument61 pagesNatural Resources GuidePandiya RajanNo ratings yet
- Battle For The Biosphere RevisionDocument15 pagesBattle For The Biosphere RevisionMrs MitchellNo ratings yet
- Shoreline ErosionDocument11 pagesShoreline ErosionTushar PandeNo ratings yet
- Ow It Formed (Geograp Ical Processes)Document3 pagesOw It Formed (Geograp Ical Processes)Jaimie DonovanNo ratings yet
- Ocean Resources: Fishing FactsDocument16 pagesOcean Resources: Fishing Factskartik_rajaniNo ratings yet
- The Impacts of Beach PollutionDocument4 pagesThe Impacts of Beach Pollutionnagendra yanamalaNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Biodiversity 8Document70 pagesAquatic Biodiversity 8jomo1155No ratings yet
- Marine Biology: A Threat To Polar PteropodsDocument9 pagesMarine Biology: A Threat To Polar PteropodswendihiNo ratings yet
- Holderness SMHWDocument14 pagesHolderness SMHWpoopNo ratings yet
- The Great Barrier Reef Rose Beck 9SG: Background InfoDocument3 pagesThe Great Barrier Reef Rose Beck 9SG: Background Info박찬우No ratings yet
- SandDocument2 pagesSandBilLy OlLabisNo ratings yet
- Crowded Coasts RevisionDocument5 pagesCrowded Coasts RevisionLaura2611No ratings yet
- New Welsh Reader 130 (New Welsh Review Autumn 2022): Restored MemoryFrom EverandNew Welsh Reader 130 (New Welsh Review Autumn 2022): Restored MemoryNo ratings yet
- Replication of DNADocument1 pageReplication of DNAdebbie96No ratings yet
- MitosisDocument1 pageMitosisdebbie96No ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in InsectsDocument1 pageGas Exchange in Insectsdebbie96No ratings yet
- Circulatory System of A MammalDocument1 pageCirculatory System of A Mammaldebbie96No ratings yet
- Managing Rural RebrandingDocument2 pagesManaging Rural Rebrandingdebbie96No ratings yet
- Haemoglobin: Higher The Partial Pressure, The Higher The AffinityDocument2 pagesHaemoglobin: Higher The Partial Pressure, The Higher The Affinitydebbie96No ratings yet
- Rebranding PlacesDocument4 pagesRebranding Placesdebbie96No ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument1 pageMeiosisdebbie96No ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle Interphase Divided Into: G1Document1 pageThe Cell Cycle Interphase Divided Into: G1debbie96No ratings yet
- Blood Vessels and Their FunctionsDocument2 pagesBlood Vessels and Their Functionsdebbie96No ratings yet
- Urban RebrandingDocument2 pagesUrban Rebrandingdebbie96No ratings yet
- Transport: Globalisation How Is It Happening? What Types?Document1 pageTransport: Globalisation How Is It Happening? What Types?debbie96No ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in FishDocument1 pageGas Exchange in Fishdebbie96No ratings yet
- London OlympicsDocument2 pagesLondon Olympicsdebbie96No ratings yet
- Tissue Fluid: Hydrostatic Pressure: Pressure of Blood From Heart ContractionsDocument1 pageTissue Fluid: Hydrostatic Pressure: Pressure of Blood From Heart Contractionsdebbie96No ratings yet
- Changes in RelationDocument1 pageChanges in Relationdebbie96No ratings yet
- Global GroupingsDocument1 pageGlobal Groupingsdebbie96No ratings yet
- Urban Fieldwork and ResearchDocument1 pageUrban Fieldwork and Researchdebbie96No ratings yet
- Trade BlocsDocument2 pagesTrade Blocsdebbie96No ratings yet
- Population Change Ways To Collect DataDocument2 pagesPopulation Change Ways To Collect Datadebbie96No ratings yet
- Global Hubs Areas Providing Focal Points For Activities That Have Global InfluenceDocument1 pageGlobal Hubs Areas Providing Focal Points For Activities That Have Global Influencedebbie96No ratings yet
- TNC (Transnational Company)Document2 pagesTNC (Transnational Company)debbie96No ratings yet
- Ageing PopulationDocument1 pageAgeing Populationdebbie96No ratings yet
- Global NetworksDocument2 pagesGlobal Networksdebbie96No ratings yet
- Megacities Case Studies - LA and MumbaiDocument2 pagesMegacities Case Studies - LA and Mumbaidebbie96No ratings yet
- Polish Migration To UKDocument1 pagePolish Migration To UKdebbie96No ratings yet
- Migration PatternsDocument2 pagesMigration Patternsdebbie96No ratings yet
- European MigrationDocument2 pagesEuropean Migrationdebbie96No ratings yet
- Effects of GlobalisationDocument2 pagesEffects of Globalisationdebbie96No ratings yet
- World Cities Vs MegacitiesDocument2 pagesWorld Cities Vs Megacitiesdebbie96No ratings yet
- Narimat PRDocument2 pagesNarimat PRF Anton NicolasNo ratings yet
- McArthur-Burney Falls Memorial State Park Campground MapDocument2 pagesMcArthur-Burney Falls Memorial State Park Campground MapCalifornia State ParksNo ratings yet
- Silviculture systemDocument34 pagesSilviculture systemSunil Singh TomarNo ratings yet
- Darwin and The World'S First Ecological ExperimentDocument2 pagesDarwin and The World'S First Ecological ExperimentlulugovindaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Ecosystem Unit CurriculumDocument3 pagesBiodiversity and Ecosystem Unit CurriculumMa'am Angeli ArgenteNo ratings yet
- What Is Conservation?Document2 pagesWhat Is Conservation?laNo ratings yet
- Kaziranga National ParkDocument15 pagesKaziranga National Parkamityalwar100% (1)
- Soil ErosionDocument23 pagesSoil ErosionFanuel MsangiNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Population Welfare and Environmental Resource BaseDocument10 pagesRelationship Between Population Welfare and Environmental Resource BasePreetam PandeyNo ratings yet
- History of OceanographyDocument22 pagesHistory of OceanographyAgus SatriadiNo ratings yet
- Uwadiae 2011Document19 pagesUwadiae 2011davidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1Gia Joyce Ancheta100% (1)
- Aquatic ArchitectureDocument43 pagesAquatic ArchitectureLevi Rachil TTGI191315No ratings yet
- Economic Impacts of WildfireDocument4 pagesEconomic Impacts of WildfireSouthern Fire ExchangeNo ratings yet
- Cane ToadDocument4 pagesCane ToadDbaltNo ratings yet
- CivilDocument3 pagesCivilraj9914032325No ratings yet
- Reflection EssayDocument4 pagesReflection Essayapi-359141130No ratings yet
- Green Infrastructure in IndonesiaDocument3 pagesGreen Infrastructure in IndonesiaNida HumaidaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Akhir SemsterDocument90 pagesTugas Akhir SemsterDyah AliaNo ratings yet
- Environment Speech 1Document4 pagesEnvironment Speech 1edwardbasteNo ratings yet
- Opportunities For The Critical Decade: Enhancing Well-Being Within Planetary Boundaries. Australia New Zealand Society For Ecological Economics 2013 Conference ProceedingsDocument295 pagesOpportunities For The Critical Decade: Enhancing Well-Being Within Planetary Boundaries. Australia New Zealand Society For Ecological Economics 2013 Conference Proceedingsmegcevans100% (1)
- ENVS 1301 - Written Assignment Unit 8Document6 pagesENVS 1301 - Written Assignment Unit 8Saiful IslamNo ratings yet
- The Feasibility of Plastic Bottles As ChairDocument2 pagesThe Feasibility of Plastic Bottles As ChairRalph Filio75% (4)
- Ecological Pyramids Pogil Key 1617 PDFDocument3 pagesEcological Pyramids Pogil Key 1617 PDFTaylor Ibach0% (2)
- Sloth Bear Habitat Akhtar Bargali 15 2Document9 pagesSloth Bear Habitat Akhtar Bargali 15 2Sabyasachi RathNo ratings yet
- Overpopulation Underpopulation and Optimum PopulationDocument13 pagesOverpopulation Underpopulation and Optimum Populationapi-230294264100% (1)
- Natural Science 2Document8 pagesNatural Science 2Manyaim ShahNo ratings yet
- The Importance of BiodiversityDocument2 pagesThe Importance of BiodiversityLily Sharma100% (1)
- Lesson 2. Seven Principles of Environment and Environmental LawsDocument10 pagesLesson 2. Seven Principles of Environment and Environmental LawsAllysa Shane Paningbatan RascoNo ratings yet
- Drone Based Geomorphological and Landscape Mapping of Bolata Cove Bulgarian CoastDocument6 pagesDrone Based Geomorphological and Landscape Mapping of Bolata Cove Bulgarian Coastsebastian tejadaNo ratings yet