Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Surface Treatment
Uploaded by
Sreedhar Patnaik.MCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Surface Treatment
Uploaded by
Sreedhar Patnaik.MCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIT-VIII-MECHANICAL SURFACE TREATMENT AND COATING
� DIFFERENTSURFACETREATMENTPROCESSES
After Manufacturing a product , some of its surfaces have to be processes further to ensure certain required properties and characteristic. The following are the different surface engineeringprocesses. 1.Mechanicalsurfacetreatmentandcoating 2.Casehardeningandhardfacing 3.Thermalspraying 4.Vapourdeposition 5.Diffusioncoating 6.Electroplating 7.Anodizng 8.Conversioncoating 9.Hotdipping 10.Porcelainenamelling,ceramiccoatingandorganiccoating 11.Painting 12.Ionimplantation
Characteristicswhichimprovethroughsurfaceengineering
Surface engineering is an important aspect of all manufacturing processes/It is used to impartspecificphysicalandmechanicalpropertiessuchasappearance,corrosion,friction,wear and fatigue resistance. Many techniques are applied for modifying surfaces .It may be necessarytoperformsurfaceengineeringinorderto,
1. Improve resistance to corrosion and oxidation in gas turbine components, sheet metals for automobilesetc., 2.Improvefatigueresistancesuchasbearings,shaftsetc. 3.Improvelubrication(suchasretainlubricationproperly) 4.Reduceadhesion. 5.Modifysurfacetexture. 6.Impartdecorativefeaturesetc. � Surfacepreparationtechniquesforcoatings Surfacepreparation Surface preparation of the substrate is very essential in order to ensure good electrodeposits.Thefollowingstepsareusuallyfollowedforefficientelectrodepositing 1.Removaloforganicimpuritiesandgreasefromthesurface This is done by employing organic solvents like trichloroethylene ,methylene chloride and hot aqueous alkali,pH increase and catalysis the hydrolysis of fatty impurities.Alkai treatmentcanalsobecarriedoutbymakingthesurfaceofarticlecathodicbyusingacurrentof 30to80oC.Theliberatedhydrogenontheelectrodehelpsintheremovaloforganicimpurities. Acidpickling The excess alkali from above process is now removed by dipping the articles in a10 % h2so4 solution. This treatment also removes scales or rust from the surface. Pickling in dilute h2so4 and simultaneously making the surface anodic by using about 100 mA cm^2 current density.Itismoreeffectivemethodofremovingoxidesscalesfromthesurface. Polishing This is done in order to obtain a lustrous surface. The articles are polished by using siliconcarbidewheels,followedbysandblastingandmechanicalbuffing.
� Thermalormechanicalmodificationofsurfacesofsurfaceengineering. Several techniques are used to mechanically improve the surfaces properties of finished components.Thecommonmethodsare, 1.shotpleening 2.Waterjetpleening 3Laserpeening 4.Rollerburnishing 5.Explosivehardening 6.Cladding 7.Mechanicalplating
In thermal modification surface treatment, coatings are applied to metal surfaces by spray gun with a stream of oxyfuel flame, electric arc or plasma arc. The coatings are various metals and alloys, carbides and ceramics. The coating materials are in form of wire rod or powder or in droplets or particles impact the surface at high speeds. Several thermal spraying processes are used.Theseareasfollows,
1.thermalwirespraying 2.Thermalmetalpowderspraying 3.Plasma 4.Detonation 5.Highvelocityoxyfuelgasspraying 6.Wirearc The surface to be sprayed are first cleaned and roughened to improve bond strength .The coating has a a layered structure deposited material and may have porosity due to entrapped airandoxideparticlesbecauseofthehightemperaturesinvolved.
� Thevariousmechanicalcleaningprocesses. Thedifferentmechanicalcleaningprocessesareasfollows 1.tumbling 2.powerbrushing 3.wirebrushing 4.precleaning 1.Tumbling
Tumbling is a process of cleaning or eliminating the slurry of abrasive agent such as sand,granite chips or aluminium oxide pallet that are present along with the workpieces.In the process,workpiecesareplacedinalargebarrelordrum.Theendsofabarrelareclosedbycast iron lids. Horizontal trunnious are employed for the support of barrel .The barrel is charged with work pieces and slurry of abrasive agents. It is then rotated at a speed ranges from 2550 rpm .Due to repeated rubbing against each other resulting in the elimination of sand and fins fromtheworkpieces. The process of tumbling is performed only for the parts which withstand the action of tumbling. The rotation of the barrel also cause elimination of sharp edges and fins due to continuouspeeningactiontherebyrelievingtheinternalstressesintheworkpieces. 2.PowerBrushing
For eliminating light sand, rust or loosely adhering scale from casting ,manual wire brushingisused.Butforbetterproductivemethodspowerbrushingmachinesareemployed.In power brushes. Large range of fills materials are available which not only eliminates the scale .rust ,sand ,sand but also develop a finished surface. It is also used to remove excessive plastic residue.Inindustries,powerbrushesareemployedforedgeblending,polishingandeliminating contaminantsfromthesurfacewhichareoperatedbyhorsepower. The power brushes are made of wire, fibre cord etc.The brushes used on these machinesaregenerallyofrotarytypeandaremadeindifferentshapessuchaswheel,cup,roller typeetc. � VariouschemicalcleaningprocessesindetailandWhysurfacecleaningisrequired? Thevariouschemicalcleaningprocessesarefollows a)Solventcleaning
It is used to remove oils,greases,buffing compounds chlorinated or fluorinated hydrocarbons ,toulenes,xylene,acetone etc.This is followed by cleaning with stream and hot watercontainingwettingagentsandalkalis/ b)Alkalicleaning Trisodium phosphate along with soaps and caustic soda is used for the removal of old paint Coating from metal surface .This method can be made more effective by the application of an electrodecurrentandmakingthemetalcathodicinalkalimedium.Analkalitreatmentisalways followed by thorough rinsing with water and then immersion in slightly acidic to remove alkali traces. c)Picklingandetching
Itisgenerallyusedtoremovethescalesonmetalsurfacesbyimmersingthemetalsand in an acid pickling solution ,aluminium is pickled in alkaline solution .Acid pickling of steel is accompaniedbydippinginwarmdiluteH2SO4towhishsomeinhaitorhasbeenadded. Surface cleaning is required for smooth bright and strong deposit surface and to secure long life services of protective coatings on a metal surface. Maximum coating adhesion can be obtained only if the base metal is free from any dirt extraneous matter such as grease and combustionproducts. EXAMPLES:Oxides,sulphidesetc. � Differentdegreasingmethodsindetailswiththehelpofneatsketches. Vapourdegreasing It is a simple process. The equipment consists of condensing coils and cooling jackets heater boiling solvent .Generally the solvent used is a halocarbon solvent such as trichloroethylene. Heaterraisethetemperatureoftheliquidsolventstoitsboilingpoint.Whenthesolvent starts boiling it produces hot, heavy vapours that rise to an established vapour line .As the solvent vapours line. Parts ambient temperature are now introduced into the solvent vapour andthecondensesonthepartsurface.Theliquidsolventcondensate,anddissolvesthegreases cleaned,morevapoursareproducedintheboilingsumptoreplacethosethatwerecondensed.
2.Immersiondegreasing Thepartsaresuccessivelyimmersedintwotanksofthesamesolventinliquidform,the firsttankactingasawashandthesecondasrinse. 3.SteamCleaning The application of detergent and alkaline cleaners using steam cleaners is an effective degreasing method. Heavy greases and waxes are dissolved and flushed away by the impingement of steam and the action of chemicals. Hot water spray cleaning using chemicalsisalmostaseffectiveassteamcleaning.
4.Wiping The surface are degreased using a clean brush for cloth soaked in halo carbon or other degreasingsolvent.
5.DetergentDegreasing The surfaces are scrubbed in a solution of liquid detergent and then washed with clean hotwater,followedbydryinginair.
PART-2
� Surfaces Coating and Casehardening, Thermal Spraying, Vapour Deposition, Ion Implantation, Diffusion Coating, Electroplating, Electroless Plating and Electro Forming,CeramicOrganicandDiamondCoating Whatissurfacecoating?Whyitisprovidedonvariousproducts: SurfaceCoating Surface coating or surface treatment is defined as a process in which surface layer of materials are applied to the original metal surface of the part with the help of different methodslikemechanical,electrochemicalthermalordiffusion. Surfacecoatingisprovidedonvariousproductsduetothefollowingreasons
1.Tochangethesurfacepropertieswithrespecttotherequirements.
2.Toapplytheexpectedcolourstothesurfacesoftheproduct. 3.Forsmooth,attractiveandpleasantappearanceoftheworkpieceorproduct. 4.Forprovidingtheworkpiecewithsomeexpectedfunctionalpropertieslike, (i)Corrosionresistance (ii)Abrasivewearresistance (iii)Transmithardness (iv)Forprovidinghighdurability (v)Improvementofelectricalandtemperatureresistances. Thus, with the help of surfaces coating technology, a manufacturer can select a low gradematerialandmadeitcorrespondingtotheneed. Diffusioncoating&varioustypesofdiffusioncoating: Diffusioncoating Aprotectivecoatingobtainedbydiffusingthecoatingmetalintoabasemetaliscalled asdiffusioncoating.Itisalsotermedascementation. Diffusioncoatingareobtainedbyheatingthebasemetalinarevolvingdrumcontaining apowderofthecoatingmetal.Thecoatingmetalgetsdiffusedintothebasemetalandresults intheformationoflayersofalloyofvaryingcomposition.Theouterlayersarericherinthe coatingmetalandthelayeradjacenttothebasemetalmaybeanintermediatecompounda solidsolution.Thethicknessofthecoatingiscontrolledbyvaryingthetimeoftreatmentand temperature.Itissuitableforcoatingmetalscanbeusedasanalloyofiron. EXAMPLE:Zn,chromiumandaluminium Typesofdiffusioncoatingare 1.Sheradizing 2.Colourizing 3.Chromizing
1.Sheradizing
Sheradizingisatypeofcementationordiffusioncoatinginwhichthebasemetalis heatedinarevolving,containingzincpowderascoatingmetal.Asaresult,diffusionofcoating metaltakesplaceforminglayersofalloyofvaryingcomposition.Itisusedforcoatingiron articles;thesearticlesarefirstcleanedandthenplacedwithzincdustinadrum.Toavoid oxidationofzinc,thedrumistightlypackedorsealed.Nowthedrumisrotatedslowlyfor2to3 hoursandthetemperatureismaintainedbetween350oCand370oCbyusinggasheatingor electricity.ThezincetsdiffusedintotheironsurfaceformingalayerofFeZnallot.Athinfilmof FeZnalloyisobtainedoverthesurfaceofironattheendoftheprocess.Sheradizingisusedfor smallsteelarticleslikebolts,nuts,washersetc. 2.Colorizing Colorizingisacementationordiffusioncoatingsdoneusuallyonmetalobjectssuchas steelparts.Themetalsobjectssurfaceiscleanedbysandblastingandthentheobjectissealed tightlyinadrumwithamixtureofaluminiumpowderandaluminiumoxidetogetherwitha traceofNH3actingasflux.Theprocessismadetooccurintheabsenceofairinareducing atmosphereofhydrogenbymaintainingthetemperaturetoabout8001000degrees.Atthe endoftheprocessalayerofAl3Fe3isobtainedwhichcorrespondstoabout25%ofAlby weight.Thecoatingisemployedforprotectionoffurnaceparts. CHROMIZING Chromozingisatypeofcementationordiffusioncoatingsobtainedbyheatingabase metalwithamixtureof55%chromiumpowderand45%aluminainasealeddrumat temperaturemaintainedbetween1300to1400degreecentigradeforabout3to4 hours.Aluminahelpsinpreventingthecoalescenceofchromiumparticles.Thisprocessis carriedoutinthreestages 1. Fe+ 2.CrCl2+H2Cr+2HCl(REDUCTION) 3.CrCl2Cr+Cl2(DECOMPOSITON) CrCl2FeCl2+Cr(DISPLACEMENTREACTION)
ACorrosionresistantchromizedcoatedsurfaceisobtainedwithchromiumcontentindiffusion layervaryingfrom10%to20%. Q10.Briefoutvariousinorganiccoatings.Discusstheirimportanceandapplications. Ans:
Inorganiccoatings Theseareproducedbychemicalactionwithorwithoutelectricalassistance.The treatmentschangetheimmediatesurfacelayerofmetalintoafilmofmetallicoxideor compoundwhichhasbettercorrosionresistancethanthenaturaloxidefilmandprovidesan effectivebaseforsupplementaryprotectionsuchaspaints. ANODIZING Itinvolvestheelectrolyticoxidationofasurfacetoproduceatightlyadherentoxide scalewhichisthickerthanthenaturallyoccurringfilm.Itisanelectrochemicalprocess,during whichaluminiumistheanode.Theelectriccurrentpassingthroughanelectrolyteconvertsthe metalsurfacetoadurablealuminiumoxide.Theoxidizedsurfaceishardandabrasionresistant whichprovidessomedegreeofcorrosionresistance.Anodiccoatingprovidesanexcellent surfaceforbothpaintingandadhesivebonding.Anodizingiswidelyusedwith7000series alloys,magnesiumandtitaniumalloys. CHROMATEFLIMING Thetreatmentinvolvesshorttimeimmersioninstronglyacidicchromatesolutions. However,sprayingorapplicationbybrushingorswabbingcanalsobeusedfortouchupof Variousinorganiccoatingsare 1.Anodizing 2.Chromatefilming 3.Phosphatising 4.Nitriding 5.Passivefilms 6.Cladding 7.Electroplating 8.Packcementation 9.Electrolessplating 10.Physicalvapourdeposition
parts.Theirmainpurposeistoprovideasuitablesurfaceforsealingresinsorpaints.These treatmentsareavailableforaluminium,magnesium,cadmiumandzincalloyssolution. Austeniticstainlesssteelsandhardenablestainlesssteelssuchasmartensitic,precipitation hardeningandmaragingstainlesssteelsareoftencoatedwiththisprocess. CLADDING Thecorrosionresistanceofasubstratecanbeimprovedbymetallurgicallybindingto thesusceptiblecorealloyandasurfacelayerofametaloranalloywithgoodcorrosion resistance.Claddingisselectedsuchthatifitgetsdamaged,itprovidescathodicprotectionby corrodingsacrificially.Claddingisdominantlyappliedinthemanufacturingofsheet,plateor tubing.Theapplicationoftheprocessislimitedtosimpleshapedarticlesthatdonotrequire muchsubsequentmechanicaldeformation. ELECTROPLATING Itisobtainedbypassinganelectricalcurrentthroughasolutioncontainingdissolved metalionsandthemetalobjecttobeplated.Themetalobjectservesasthecathodeinan electrochemicalcell,attractingmetalionsfromthesolution.Ferrousandnonferrousobjects areplatedwithavarietyofmetalsincludingAl,brass,bronze,cd,cu,cr,fe,pb,ni,tinandznaswell aspreciousmetalsuchasAg,Auandpt.Theprocessisregulatedbycontrollingvarietyof parameters,includingthevoltageandamperage,temperatureandpurityofbothsolutions. PACKCEMENTATION Diffusioncoatingsareformedbydepositingalayerofaluminiumonthe,metalsurface andthenheatingthecomponentinafurnaceforaperiodoftime.Duringthisheattreatment, theAlandmetalatomsmitigateordiffuseintoeachotherasaresultthesecoatingsarecalled diffusioncoatings.Thisprocessisusuallyperformedbyapackcementationprocess,inwhichAl depositionandtheheattreatmentoccursimultaneously.Itiswidelyusedtoconferoxidation resistanceonferrousalloys. ELECTROLESSPLATING Electrolessnickelplatingisachemicalreductionprocesswhichdependsuponthe catalyticreductionprocessofnickelionsinanaqueoussolutionandthesubsequentdeposition ofnickelmetalwithouttheuseofelectricalcorrosionresistanceandhighhardness.Applicable inmakingvalves,pumppartsetc PHYSICALVAPOURDEPOSITON
Itreferstoaprocessinwhichmaterialsinavapourstatearecondensedthrough condensation.Chemicalreactionorconversationtoformasolidmaterial.Theseprocessesare usedtoformcoatingstoalterthemechanical,electrical,thermal,potical,corrosionresistance andwearpropertiesofthesubstrates.Itisusedtoformfreestandingbodiesfilmsandfibres andtoinfiltratetoformcompositematerials. PART3 � Listvariousoforganicandinorganiccoatingsandbetweenorganicandorganic coatingswiththeirapplications. Organiccoatings Organiccoatingsareinertorganicbarriersappliedonmetallicsurfacesandother constructionalmaterialsforcorrosionprotectionaswellasdecoration Variousorganiccoatingsare 1.Paints 2.Varnishes 3.Enamels 4.Lacquers 5.Emulsionpaints Inorganiccoatings Theseareproducedbychemicalactionwithorwithoutelectricalassistance.The treatmentchangetheimmediatesurfacelayerofmetalintoafilmofmetallicoxideor compoundwhichhasbettercorrosionresistancethanthenaturaloxidefillandprovidesan effectivebaseofsupplementaryprotectionsuchaspaints 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Anodizing Chromatefilming Phosphating Nitriding Passivefilms
6. Cladding 7. Electroplating 8. Packcementation 9. Electrolessplating 10. Vapourdeposition 11. Hotdipgalvanizing 12. Thermalspraying ORGANICCOATINGS 1.Thesearetheorganicbarriersovera metalsurface 2.coatingdoesnotreactwiththebase metal 3.Surfacecharacteristicsofthebasemetal arenotchanged 4.Noelectricalassistancerequired. 5.Theyprovidecorrosionresistanceand aestheticappearance. ApplicationsofOrganicCoatings 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Automobileindustry. Polishingwoodenfurniture. Lustrous,glossyandhardsurfacecanbeachieved. Interiordecoration. Coatingcottonfabricswhichareusedinpreparingartificialleathers. Externalsurfacesofbricksworks,concreteetc.,afteraddingaweatherresisting compound. 7. Corrosionresistantpaintingofelectricandtelegraphpolesandtowers. 8. Forpaintinghotwaterpipes,tanks,oiltanksandgasstoragetanksetc. ApplicationsofInorganicCoatings (a) Protectionofironfromatmosphericcorrosionintheformofroofingsheets,wires, pipes,nails,bolts,screwsetc. (b) Coatingsteel,copperandbrasssheets. (c) Coatingintricateshapes. INORGANICCOATINGS 1.Ametalsurfaceiscoatedbyanother metal. 2.Coatedmetalreactswiththebasemetal andformsalayer 3.Surfacecharacteristicsofthebasemetal change 4.Electricalassistanceisrequiredforsome processes. 5.Theyprovidecorrosionresistanceand sometimesformabaseforpaints.
Protectionoffurnaceparts. Protectionofgasturbineblades. Digitalandelectronicinstruments. CoatingPrintedCircuitBoards(PCB) Decorativeandfunctionalpurposes. Jewellarycoatings. � Dipcoatingandspraycoating.Distinguishbetweenthesetwoprocess.Comparethe meritsanddemerits. SprayCoating Inthisprocess,thecoatingmetalinthemoltenstatefromasprayinggunissprayedon theroughsurfaceofthebasemetal.Themetalsthussprayandadherestothebasemetal surface.Asealeroilisappliedtothespraycoating,becausetheyarecontinuousbutsome porous.Thisprovidesthemetalasmoothsurface. DipCoating Thisprocessingeneralconsistsofimmersingthebasemetalinabathofmoltencoating metal,coveredbyamoltenfluxlayer.Thefluxcleansthebaseofmetalsurfaceandprevents theoxidationofmoltencoatingmetal. ComparisionofSprayandDipCoating Theprocessofspraycoatingofferscertainadvantagesoverdipcoatingmethodssuchas (i) (ii) (iii) Greaterspeedofworking. Applicabletothelargersurfaces Easyapplicationofeventhickcoatingtorestrictedareas.
(d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i)
Theadvantagesofdipcoatingoverspraycoatingare Thecoatingproducedhavegoodadhesivestrength Providesgoodprotectionfromatmosphericcorrosion. � Diffusioncoatingapplicationofsurfaceengineering. (i) (ii)
DiffusioncoatingIsaprocessinwhichanalloyingelementisdiffusedintothesurfaceofthe metal.Italtersthesurfaceproperties.Thealloyingmetalscanbesuppliedinsolid,liquid, gaseousstate. Diffusioncoatingprocesshasdifferentnamesdependingonthediffusedmetal, diffusionprocessarecarburizing,Nitridingandboroninzingetc. Carburizing Inthisdiffusionprocess,carbonistheelementaddedtothesurfaceforthelowcarbon steelandalloysteels.Heatthesteelsat870oto950oinanatmosphereofcarbonaceousgases andthenquench.Ahardhighcarbonsurfacesproducedtypicalapplicationsaregears,cams, shafts,pistonpins,pistons,sprockets,clutchplatesandbearings. Nitriding Inthisdiffusionprocess,nitrogenistheelementaddedtothesurfaceofsteels,alloy steels,stainlesssteelsandhighspeedtoolsteels.Heatthesteelat500oto600oCinan atmosphereofammoniagas.Coredepth0.10.66mmcanbeobtained.Typicalapplicationsare gears,cuttersandvalves. Boronizing Intheprocess,boronistheelementaddedtosteelsurfaces.Thepartisheatedusing boroncontaininggas(or)solidincontactwithpart,anextremelyhardandwearresistant surfacecharacteristicareobtained.Coredepth0.025to0.075mmcanbeobtained.Typical applicationsarediesteelsandtoolsetc. � Mechanicalcoatingprocesses. (i) Galvanizing Galvanizationisaprocessinwhichtheironarticleisprotectedfromcorrosion bycoatingitwithathinlayerofzinc.Nthisprocess,firstironorsteeliscleaned bypicklingwithdilutesulphuricacidsolution(H2SO4)atatemperaturerangeof 60to90oCfor15to20minutes.Therefore,itremovesscale,rustandother impuritiespresentifanyandthenwashedwellanddried.Thenafter,dippedin thebathmoltenzincwhichisat425to450oC.Topreventitfromoxide formation,thesurfaceofbathiscoveredwithaflux(ammoniumchloride). Whentheironpieceistakenoutitiscoatedwithathinlayerofzinc.Andto removeexcesszinc,itispassedthroughapairofhotrollers.Lastly,itis annealedatatemperatureof450oCandthencooledslowly.
(ii)
Itismostwidelyusedfortheprotectionofironandsteelproductssuch aswires,pipes,nails,bolts,screws,buckets,tubes,roofing,sheets,etc. ElectrostaticPainting
Electrostaticpaintingisthemechanicalcoatingprocessinwhichthepaintparticlesare chargedelectrostaticallybyapplyingD.Cvoltagebetweenthepaintbooth(cathode)and workpiece(anode).TheparticlesarecontrolledinthepathofelectrostaticfieldwhichIs formedbetweentheworkpieceandpaintboothasshowninfigure. Thepaintparticlesstickstotheworkpieceandgetsaccumulatedonit.Thenthework pieceisremovedfromthepaintboothandtreatedthermallybybakinginanoversoasto completetheprocessofcoating. Applications. (a) Electroplating Electroplatingistheprocessormethodofcoatingmetals,tochangetheir surfacepropertiessastoimproveappearance,increasethehardnessandtoimprove resistancetocorrosionandwearorchemicalattack. Electroplatingistheelectrodepositionofmetal,bymeansofelectrolysisover thesurfaceofmetals,alloysornonmetals. Thewearresistanceofametalpartcanbeimprovedbyelectroplatingaharder metalonitssurface.Themetalsmostoftenplatedonbasemetalsormaterialsare chromium,nickelandrhodium.Forexamplemetalslikeironwhichareeasilycorroded byatmosphericair,moistureandCO2arecoatedelectrolyticallywithbasemetalssuch asnickelorchromiumwhicharemoreresistanttowearorchemicalattack. Someoftheapplicationsofelectroplatingare. Platingforprotectionfromcorrosionandchemicalattack. Platingfordecoration. Platingforspecialsurfaceandengineeringeffects. Electroforming. Platingonnonmetallicmaterials. Therefore,thisprocessiswidelyusedinautomobiles,aircraft,refrigerators, radios,cameras,typewriters,umbrellas,watches,etc. (b) Parkerizing
� Variouschemicalcoatingprocessesandphosphatecoating. ChemicalCoatingProcess Theprocessofcoatingathinlayerofmaterialovertheoriginalmetalsurfacesofcomponent bymeansofcomponentbymeansofchemicalprocessisknownaschemicalcoatingprocess. Thisprocessisappliedoncomponentstoimprovethesurfacepropertiessuchascorrosion resistance,strengthstability,durability,appearanceetc. Thedifferenttypesofchemicalprocessareasfollows, Anodizing Chromecoating Electroplating Parkerizing Phosphatecoating.
PhosphateCoating Phosphatecoatingisobtainedbythechemicalreactionofaqueoussolutionof phosphateofiron,manganeseandzincwithbasemetalssuchasiron,steelandzinc.The chemicalreactionproducesasurfacefilmconsistingofmanganeseironphosphatesorzinciron phosphates.Forincreasingthereactionrate,acceleratorssuchasnitrites,chloratesornitrates arealsoadded.Applicationofphosphatecoatingonthebasemetalsurfacecanbedoneby brushingorspraying.Thiscoatingdoesnotoffercorrosionresistancebutoffersexcellentbases forpainting,impregnationwithoilsetc.Ironandmanganesecoatingsaregenerallyusedto reducewearcausedbyfriction.Phosphatecoatingcanbedoneonothermetalssuchas aluminum,cadmiumandtin.Thecolorofphosphatecoatingisusuallygrey. Theobjectivesofphosphatecoatingsareasfollows, 1. 2. 3. 4. Togivebetterresistancetocorrosion. Toprovidesurfaceaswearresistance. Togivedecorativeappearancebydifferentshadesofcoloredcoatings. Togiveadhesionsurfaceforpaints,oil(or)wax. Tofulfilltheaboveobjectivesdifferentphosphatecoatingareappliedonmetal surfacesofcomponents.Theyareasfollows, IronPhosphateCoating Thiscoatingactsasacleaner,andisbasicallyappliedonsteelcomponentsasbase coatfortheprocessofpainting. LeadPhosphateCoating
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Thiscoatingisappliedonironandsteelcomponentsforbettercorrosionresistance. ManganesePhosphateCoating ThiscoatingisappliedonInternalCombustion(IC)enginepartsandgearstoavoid gallingeffect.Thecoatofthismaterialincreasesfrictionandalsoactsaslubricant. Zinc(or)ZincironPhosphateCoating Thiscoatingisappliedoniron,steel,cadmium(or)zincplatedcomponentsto Increasetheadhesionpropertyofmetalsurfacesforconsequentfinishes, specificallywhensurfacesareexposedtoenvironment.
� Porcelainenameling&Ceramiccoatings.&itstheirapplications: (a) PorcelainEnameling Porcelainenamelingisalsocalledasvariousenameling.Porcelainenamelisan inorganiccoatingwithvitreousorglossywhichisappliestothesurfaceofthemetal atextremelyhightemperature.Therearetwoprocessesthroughwhichporcelain enamelcoatingcanbeapplied.Theyare, (i) WetProcess (ii) DryProcess. (i) WetProcess Inwetprocessofporcelainenameling,slurryisappliedonthesurfaceofthe metal.Theinitialstepinwetprocessisthatslurryoftheporcelainenamel mixtureistobeprepared.Thensiliconoxideandborax,titaniumoxideand zirconiumoxideasopaquematerials,astabilizer,coloredmetaloxidesand potassiumorsodiumoxideasfluxarecompletelymixedtogether.Thecomplete mixtureissmeltedtogether,groundandthencooled.Theadditionofsodium silicatewaterandclaytothemixtureformsamasswhichismilledtogetherto formaslurry.Themetalsurfaceisthencoatedwithaslurrybyaprocessofclip coating,flowcoatingorspraying.Finally,thecoatingisdriedandheatedata temperaturebetween500oCto800oC. (ii) DryProcess Indryprocessofporcelainenameling,theinitialstepistoheatthecomponent toanappropriatetemperature.Thesurfaceofthearticleisappliedwithdry powderofporcelainenamel.Duetothestickynature,thesurfaceofthe componentgetsfusedwithpowder.Forcompletelyfusedpowderonthesurface ofthecomponentitisreheatedtoasuitabletemperature.Finally,thepowderis fusedinthesurfaceofthecomponent.
Applications 1. Porcelainenamelingiswidelyusedinvarioususedinvariouscoatingapplicationswhich includewaterheaters,heatexchangers,outdoorarchitecturalpanelsandsigns. 2. Itactsasaprotectivesurfaceforcookingutensils,kitchenandbathroomfixturesand applicationssuchasdishwashers,refrigeratorsanddryers. 3. Porcelainenamelsarealsousedinchemicalprocessingvessels,agriculturalpanels, storagetanks,pipingandpumpcomponents.Italsoactsasaacidresistant. (b) CeramicCoatings Aceramiccoatingisdefinedasaninorganic,nonmetallicandprotectivecoating onthesurfaceofametalwhichisappropriateforuseatredheatoraboveredheat. Ceramiccoatingsaremorepreferableduetotheirstabilityatboththeroom temperatureaswellasatimmenselyhightemperatureandalsoinbetweenthese twolimits.Thewidelyusedmaterialsforceramiccoatingsaresilicidesand aluminides. Sandblastingisusedforthepreparationofbasemetalsurfacesforceramic coating.Onthepreferredsurfaces,thematerialrequiredforcoatingissprayedand thendriedthroughairandfinallybakedatatemperatureofabout540oC.Thetime thatistakenforbakingusuallydependsuponthesizeofthecoatingcomponent. Silicidecoatingsoffermoreprotectionwhencomparedtoaluminitecoatings. Theprotectionofferedbysilicidecoatingsareupto1928oCwhileitisrestrictedto below165oCinaluminitecoatings.Ceramiccoatingsarecorrosionresistantand increasethestrengthandrigidityofthemetalparts.Itprovidesgreaterresistanceto chemicalattackandincreasedresistancetomechanicalabrasion.Duetoincreased thermalstability,largevarietiesofthermalandelectricalinsulatorspossessceramic coatings. Applications Ceramiccoatingshaveawiderangeofapplicationsinaircrafts,rockets, satellites,gasturbines,steelindustries,textileindustries,chemicalindustries,dataprocessing industries,kitchenwares,sanitarywares,jewelleryetc. � Metalizing&itsapplications: (a) Wiremetalizing (b) Powdermetalizing Metalizing Itistechniqueofcoatingmetalonthesurfaceofnonmetallicobjects.Itisalso knownasmetalspraying.
(a)
WireMetalizing Inwiremetalizing,themetallicgunusesametalintheformofwire.Initially,the surfaces,tobecoatedarecleanedandroughenedtoimprovebondstrength.The coatingmaterialissprayedonthemetalsurfacebyusingaspraygun(metallicgun), whichcomprisesof, (i) Agastorchwithaholeatthecentreofthetipforthewire. (ii) Agearandasmallairturbineinordertofeedinthewirethroughthetop intotheflameasfastasitmelts. (iii) Anaircaparoundthetorchtipand (iv) Anozzletosupplyablastofairtoatomizethemoltenmetalanddeposit itonthepreparedsurface. Inthisprocessthewireisfedintothemetallicgunataspecificrate,meltedbyan oxyacetyleneflameandthenitisblownontothesurface,beingcoatedby compressedair.However,wiremetalizingismostcommonlyusedbecauseofthe followingreasons, (a) (b) (c) Themetalusedislessexpensive Itcanbehandledveryeasilyand Easyavailability. PowderMetalizing Inthismethod,coatingmaterialisintheformofpowder.Thepowderedmetalis fedthroughrubberhosetospraygunfromacontainerandoutthroughthecenter oftheflame. Inthiscase,asmallamountofairissufficienttodepositthemoltenmetalonthe surfacebeingcoated,sincethemetalisalreadyintheatomizedform.Thepowder gunhasnogearsorturbine,costslessandislightertohandle. Applications Themetalizingisused, 1. Incorrosionprotection. 2. Toobtainhardandnoblesurfaces. 3. Insolderingthesurfaces. 4. Toincreasetheelectricalconductivityofpoorconductors. 5. Toincreasethermalconductivityoftheconductors. 6. Themetalizingisalsoemployedinreflectingsurfaces,decorativefilms andspecialmetalforms.
(b)
You might also like
- Electro PlatingDocument47 pagesElectro Platingajuthottungal100% (2)
- OAU Post UTME Past Question and AnswerDocument17 pagesOAU Post UTME Past Question and AnswerCharles Obaleagbon86% (28)
- List of Steel Products Made in The UK PDFDocument120 pagesList of Steel Products Made in The UK PDFAntonio MarrufoNo ratings yet
- Gas Processing Fundamentals Manual1Document12 pagesGas Processing Fundamentals Manual1Ahmed Khamees ShatlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Casting Processes: Proses TuanganDocument76 pagesChapter 2: Casting Processes: Proses TuanganhizanorhudaNo ratings yet
- 2b-CASTING PROCESSESDocument42 pages2b-CASTING PROCESSESIzzat IkramNo ratings yet
- Surface Finishing OperationsDocument88 pagesSurface Finishing OperationsKodeboyina Chandramohan100% (1)
- Ammonia Based Refrigeration SystemsDocument19 pagesAmmonia Based Refrigeration SystemsHoainam NguyenNo ratings yet
- Guide Managing Risks Foundry WorkplaceDocument56 pagesGuide Managing Risks Foundry WorkplaceMohsin KhanNo ratings yet
- Powder Coating ProcessDocument4 pagesPowder Coating ProcessPraveen Verma DatlaNo ratings yet
- Scaled Up Process DirectlyDocument8 pagesScaled Up Process DirectlyAnonymous 1XHScfCINo ratings yet
- Surface TreatmentDocument34 pagesSurface TreatmentnagarajNo ratings yet
- Hand Book-GalvanizingDocument9 pagesHand Book-GalvanizingSreedhar Patnaik.M100% (1)
- 7 Cleaning & Surface TreatmentsDocument70 pages7 Cleaning & Surface Treatmentssakali ali100% (1)
- TALAT Lecture 5201: Aluminium Surface PretreatmentDocument12 pagesTALAT Lecture 5201: Aluminium Surface PretreatmentCORE Materials100% (1)
- Galva ParametersDocument3 pagesGalva ParametersSreedhar Patnaik.M100% (1)
- Chemical Analysis Procedures For Galvanizing PlantsDocument32 pagesChemical Analysis Procedures For Galvanizing PlantsSreedhar Patnaik.M100% (2)
- BLOWENGINEERING PLASTIC MACHINES Blow Molding Machine Manufacturer PDFDocument6 pagesBLOWENGINEERING PLASTIC MACHINES Blow Molding Machine Manufacturer PDFJoenetDarmawanNo ratings yet
- Electroplating FacilitiesDocument241 pagesElectroplating FacilitiesMike Joya100% (3)
- Investment Casting ProcessesDocument10 pagesInvestment Casting ProcessesPragyan Kumar PradhanNo ratings yet
- TM 1-1520-237-10 CH2-1Document784 pagesTM 1-1520-237-10 CH2-1willy90309No ratings yet
- Flux ControlDocument2 pagesFlux ControlSreedhar Patnaik.M50% (2)
- Flux - InformationDocument9 pagesFlux - InformationSreedhar Patnaik.M0% (1)
- Zinc Chloride Determination ProcedureDocument13 pagesZinc Chloride Determination ProcedureSreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- Grinding WheelsDocument54 pagesGrinding WheelsvelavansuNo ratings yet
- HydrometallurgyDocument80 pagesHydrometallurgyFanni Bayta100% (3)
- Iso 3210 2010Document9 pagesIso 3210 2010Jigar GalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 Surface Treatments, Coatings, and CleaningDocument13 pagesChapter 34 Surface Treatments, Coatings, and CleaningTrí NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Powder CoatingDocument6 pagesPowder CoatingJonathan Cecil FernandoNo ratings yet
- Inar Profiles Pvt. LTD., Kotturu, Industrial Area, Visakhapatnam, Andhrapradesh, IndiaDocument14 pagesInar Profiles Pvt. LTD., Kotturu, Industrial Area, Visakhapatnam, Andhrapradesh, IndiaSreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- BGAS-CSWIP-BG-22-12 BGAS-CSWIP 2nd Edition April 2019 PDFDocument30 pagesBGAS-CSWIP-BG-22-12 BGAS-CSWIP 2nd Edition April 2019 PDFEjazNo ratings yet
- Manganese PhosphatingDocument9 pagesManganese PhosphatingGopalakrishnan KuppuswamyNo ratings yet
- Industrial Chemical Cleaning MethodsDocument29 pagesIndustrial Chemical Cleaning MethodsTEZ ANALYSIS AND STORIESNo ratings yet
- X Ray of CastingDocument2 pagesX Ray of CastingBhupesh MulikNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and PaintingDocument13 pagesCorrosion and PaintingManeet GogiaNo ratings yet
- Salt Spray TestDocument13 pagesSalt Spray TestSreedhar Patnaik.M100% (1)
- Duplex SystemDocument9 pagesDuplex Systemnightmanmx100% (1)
- Surface Coating ProcessesDocument7 pagesSurface Coating ProcessesSailabala ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Engineering Specification: 1.0 Initial Bath PreparationDocument2 pagesEngineering Specification: 1.0 Initial Bath PreparationKamatchiNo ratings yet
- Sand Additives & BindersDocument20 pagesSand Additives & BindersNilesh Bhandari100% (1)
- Tile UnitDocument11 pagesTile UnitVikas M MatamNo ratings yet
- Preventive Maintenance - PFDocument6 pagesPreventive Maintenance - PFAnurag SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Preheating of Crucible - InstallationDocument1 pagePreheating of Crucible - Installationravindra kumarNo ratings yet
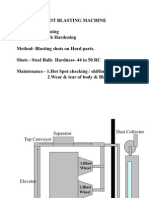
- 3.shot BlastingDocument12 pages3.shot BlastingVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (1)
- Group 1 Lost Foam Casting PDFDocument14 pagesGroup 1 Lost Foam Casting PDFRazlin Abd Rashid100% (1)
- Lathe Machine (Machining)Document12 pagesLathe Machine (Machining)faizan997No ratings yet
- U-4 Surface Finishing ProcessDocument38 pagesU-4 Surface Finishing Processapi-271354682100% (1)
- Water Pollution From Smelting, Metal Plating & Metal FinishingDocument37 pagesWater Pollution From Smelting, Metal Plating & Metal Finishingsuneetiscribed0% (1)
- Surface Engineering NotesDocument16 pagesSurface Engineering Notesdarksiderruv100% (2)
- CleaningDocument60 pagesCleaningvenkat4No ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes: International Islamic University IslamabadDocument21 pagesManufacturing Processes: International Islamic University IslamabadHassan AliNo ratings yet
- Machining Process-Ii: (Assignment)Document5 pagesMachining Process-Ii: (Assignment)Sobia JamilNo ratings yet
- NAME 345 Lecture-15 Surface PreparationDocument29 pagesNAME 345 Lecture-15 Surface PreparationBob SteinerNo ratings yet
- Surface Treatments and CoatingsDocument4 pagesSurface Treatments and Coatingsmightym85No ratings yet
- Surface EngineeringDocument43 pagesSurface Engineering10rajNo ratings yet
- Sector Specific Best Practice Guide: Best Practices in Metal Plating and FinishingDocument18 pagesSector Specific Best Practice Guide: Best Practices in Metal Plating and Finishingchemikas8389No ratings yet
- Internship Report On In-Plant Training at Mythri Metallizing PVT LTD FirmDocument19 pagesInternship Report On In-Plant Training at Mythri Metallizing PVT LTD Firmsagare prasadNo ratings yet
- Kap2 2Document25 pagesKap2 2Daniela MateiNo ratings yet
- Surface EngineringDocument23 pagesSurface EngineringPoorna SravanNo ratings yet
- 04-Diff Surface Conditions Info SheetsDocument14 pages04-Diff Surface Conditions Info SheetsRony Prayitno SimeonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document2 pagesChapter 3vinayakNo ratings yet
- Production TechnologyDocument60 pagesProduction Technology2mohan7100% (2)
- Foundary OverviewDocument8 pagesFoundary OverviewPradeep Pandurang JadhavNo ratings yet
- Wikipedia - FoundaryDocument7 pagesWikipedia - Foundaryshovit singh100% (1)
- BTI1133 Ch34Document42 pagesBTI1133 Ch34ACC SHNo ratings yet
- Surface Treatments & Coatings Ref: S. KalpakjianDocument22 pagesSurface Treatments & Coatings Ref: S. KalpakjianjojoNo ratings yet
- Abstract & IntroductionDocument11 pagesAbstract & Introductionafnanhanany50% (2)
- Thermal Spray V4Document24 pagesThermal Spray V4eitvasNo ratings yet
- FabricationDocument9 pagesFabricationAnilkumar HatkarNo ratings yet
- Surface EngineeringDocument20 pagesSurface EngineeringBrandt GadorNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Heat Treatment On The Microstructure of SteelDocument9 pagesThe Effect of Heat Treatment On The Microstructure of Steelilya danisyahNo ratings yet
- ME6352 Manufacturing Technolgy: Unit I Casting 8Document54 pagesME6352 Manufacturing Technolgy: Unit I Casting 8Aravind PhoenixNo ratings yet
- Final Assignment AMPDocument9 pagesFinal Assignment AMPMebrahtom LuelNo ratings yet
- Die Casting ReportDocument11 pagesDie Casting ReportFaria KhanNo ratings yet
- Boost ConvertorDocument5 pagesBoost ConvertorFaizan MalikNo ratings yet
- Material Check LestDocument2 pagesMaterial Check LestSreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- Galvanizing and Mechanical Preparation of Steel - 1Document4 pagesGalvanizing and Mechanical Preparation of Steel - 1Saurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Galvanizing SpcsDocument8 pagesGalvanizing SpcsSreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
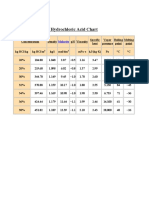
- Physical Properties of Hydrochloric Acid Chart: MolarityDocument1 pagePhysical Properties of Hydrochloric Acid Chart: MolaritySreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Guideline - Adjusting PH of Flux SolutionDocument4 pagesTroubleshooting Guideline - Adjusting PH of Flux SolutionSreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- HDG Steel Combined With Al-AlloyDocument9 pagesHDG Steel Combined With Al-AlloySreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- Anti-Blast Preparation and Adding Procedure: Startup QuantitiesDocument2 pagesAnti-Blast Preparation and Adding Procedure: Startup QuantitiesSreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- B-Gas-Question & Answer PaparsDocument62 pagesB-Gas-Question & Answer PaparsSreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- Flux Skimming PDFDocument6 pagesFlux Skimming PDFpbp2956No ratings yet
- Avoid Surprises at The Kettle & Vents & Holes Desigine GuideDocument27 pagesAvoid Surprises at The Kettle & Vents & Holes Desigine GuideSreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- Directory of Galvanizing Association DirectoryDocument8 pagesDirectory of Galvanizing Association DirectorySreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- p09s128 PDFDocument8 pagesp09s128 PDFAndiniPermanaNo ratings yet
- Surface Engineering For CorrosionDocument24 pagesSurface Engineering For CorrosionSreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- Materials: Development of Bath Chemical Composition For Batch Hot-Dip Galvanizing-A ReviewDocument24 pagesMaterials: Development of Bath Chemical Composition For Batch Hot-Dip Galvanizing-A ReviewkhurshedlakhoNo ratings yet
- Hot Dip GalvanizeDocument9 pagesHot Dip GalvanizeSreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- Cattle Feed: 1.process of ManufacturingDocument5 pagesCattle Feed: 1.process of ManufacturingMd RaihanNo ratings yet
- p09s128 PDFDocument8 pagesp09s128 PDFAndiniPermanaNo ratings yet
- HDG Steel Combined With Al-AlloyDocument9 pagesHDG Steel Combined With Al-AlloySreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- Procedures For Preparation of Galva Solutions - SreedhrDocument5 pagesProcedures For Preparation of Galva Solutions - SreedhrSreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- Inspection & Testing of Galva-Products-Prepared by SreedharDocument5 pagesInspection & Testing of Galva-Products-Prepared by SreedharSreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Hot-Dip Galvanized Reinforcing BarsDocument6 pagesFrequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Hot-Dip Galvanized Reinforcing Barsali tahaNo ratings yet
- Dhulian FinalDocument50 pagesDhulian FinalShams Sardar100% (1)
- Deal AMA NAMA 14.04.23Document26 pagesDeal AMA NAMA 14.04.23Afif SetiawanNo ratings yet
- PHYSIO ReviewerDocument3 pagesPHYSIO ReviewerPHILYP EPHRAIM PARANGALANNo ratings yet
- Soil Color and Texture MeaningDocument9 pagesSoil Color and Texture MeaningTinashe KatsuroNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLSDocument5 pagesExperiment 2 - ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLSFroz ChickenNo ratings yet
- SERIES 7000 Paste Slakers: Fully Automated Lime Slaking SystemsDocument4 pagesSERIES 7000 Paste Slakers: Fully Automated Lime Slaking Systemssoumyarm942No ratings yet
- MSD Group 1 Compiled Final ReportDocument168 pagesMSD Group 1 Compiled Final ReportAzwan AwalludinNo ratings yet
- Mausritter Adventure Tower of SootDocument2 pagesMausritter Adventure Tower of SootInshal ChenetNo ratings yet
- Ver 3.0 - Test Series - NEET - Schedule (XII & RM) - Code-A - BDocument3 pagesVer 3.0 - Test Series - NEET - Schedule (XII & RM) - Code-A - BCorona virusNo ratings yet
- Class Ii Composite Cavity PreparationDocument62 pagesClass Ii Composite Cavity PreparationShahid HameedNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Regulator Gas Feed Systems Theory and MaintenanceDocument62 pagesVacuum Regulator Gas Feed Systems Theory and Maintenancezhigang dingNo ratings yet
- APEG Polyester Fabric Belt EPDocument1 pageAPEG Polyester Fabric Belt EPmuhammad IhsanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Trihalomethanes: and Related Pentane-Extractable Organic HalidesDocument33 pagesAnalysis of Trihalomethanes: and Related Pentane-Extractable Organic HalidesaviantaraNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice LachingDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Lachingraghu_iict100% (1)
- EBT 335 Polymer Blends: Presented By: PL TehDocument23 pagesEBT 335 Polymer Blends: Presented By: PL TehTarani TharanNo ratings yet
- Goldmix PC110 TDS PDFDocument1 pageGoldmix PC110 TDS PDFRafael Obusan IINo ratings yet
- CE8005 QB Air Pollution and Control Engineering PDFDocument13 pagesCE8005 QB Air Pollution and Control Engineering PDFRohini meeraNo ratings yet
- NuHeat AR500 Datasheet 2 2014Document2 pagesNuHeat AR500 Datasheet 2 2014paul ArcosNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument23 pages6.1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsShadow MartinNo ratings yet
- TecamidDocument2 pagesTecamidTejas HuddarNo ratings yet
- 10 OBAT TERBANYAK YANG DIGUNAKAN November 21Document5 pages10 OBAT TERBANYAK YANG DIGUNAKAN November 21MutemjNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Tissues-Full NotesDocument12 pagesChapter-6 Tissues-Full NotesAdithya VinodNo ratings yet
- Compression Lab ReportDocument8 pagesCompression Lab ReportfatinzalilaNo ratings yet
- Colloid Chemistry and Phase Rule 4022146-1: (Essentials of Physical Chemistry - Arun Bahl & B.S. Bahl) Chapter 19 and 22Document51 pagesColloid Chemistry and Phase Rule 4022146-1: (Essentials of Physical Chemistry - Arun Bahl & B.S. Bahl) Chapter 19 and 22Razan khalidNo ratings yet