Professional Documents
Culture Documents
VDRL Test
Uploaded by
Sai SridharOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
VDRL Test
Uploaded by
Sai SridharCopyright:
Available Formats
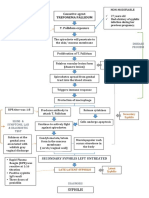
VDRL TEST: Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) Test is a slide flocculation test employed in the diagnosis of syphilis.
Since the antigen used in this test is cardiolipin, which is a lipoidal e tracted from beef heart, it is not a specific test. This test is also classified as non!specific or non!treponemal or standard test. The antibodies reacting with cardiolipin antibodies ha"e been traditionally (but incorrectly) termed #regain$. Principle: %atients suffering from syphilis produce antibodies that react with cardiolipin antigen in a slide flocculation test, which are read using a microscope. &t is not 'nown if the antibodies that react with cardiolipin are produced against some lipid component of Treponema pallidum or as a result of tissue in(ury following infection. Requirements: %atient)s serum, water bath, freshly prepared cardiolipin antigen, VDRL slide, mechanical rotator, pipettes, and hypodermic syringe with unbe"eled needle and microscope. *nown reacti"e and non!reacti"e serum controls are also re+uired. VDRL antigen: The cardiolipin antigen is an alcoholic solution composed of ,.,-. cardiolipin, ,./0. lecithin and ,.1. cholesterol. The cardiolipin antigen must be freshly constituted each day of test. The wor'ing antigen is a buffered saline suspension of cardiolipin. VDRL slide: This is a glass slide measuring / 2 - inch with 0/ conca"e depressions, each measuring 03 mm in diameter and 0.45 mm deep. Procedure: %atients) serum is inacti"ated by heating at 53o6 for -, minutes in a water bath to remo"e non!specific inhibitors (such as complement). The test can be performed both +ualitati"ely and +uantitati"ely. Those tests that are reacti"e by +ualitati"e test are sub(ected to +uantitati"e test to determine the antibody titres. Qualitative test: ,.,5 ml of inacti"ated serum is ta'en into one well. 073,th ml (or 0 drop from 08 gauge needle) of the cardiolipin antigen is then added with the help of a syringe (unbe"eled) to the well and rotated at 08, rpm for 9 minutes. :"ery test must
be accompanied with 'nown reacti"e and non!reacti"e controls. The slide is then "iewed under low power ob(ecti"e of a microscope for flocculation. The reacti"e and non!reacti"e controls are loo'ed first to "erify the +uality of the antigen. Depending on the si;e the results are graded as wea'ly reacti"e (<) or reacti"e (R). Reacti"e samples are then sub(ected to +uantitati"e test. Qualitative test: This is performed to determine the antibody titres. The serum is doubly diluted in saline from 0in / to 0=/53 or more. ,.,5 ml of each dilution is ta'en in the well and 073, ml of antigen is added to each dilution and rotated in a rotator. The results are then chec'ed under the microscope. The highest dilution showing flocculation is considered as reacti"e titre. Sometimes, due to "ery high le"el of antibodies in the serum (pro;one phenomenon) the +ualitati"e test may be non! reacti"e. &f the clinical findings are strongly suggesti"e of syphilis, a +uantitati"e test may be directly performed on the serum specimen. CSF VDRL: VDRL test may also be performed on 6S> samples in the diagnosis of neurosyphilis. ?uantitati"e VDRL is the test of choice on 6S> specimens. @owe"er, there are some "ariations in this test. The antigen is diluted in e+ual "olumes with 0,. saline, 6S> must not be heated (or inacti"ated), the "olume of antigen solution ta'en is ,.,0 ml (or 0 drop from /0 gauge needle) and rotation time is 8 minutes. Rest of the procedure remains same. Significance of VDRL test: VDRL test becomes positi"e 0!/ wee's after appearance of (primary lesion) chancre. The test becomes reacti"e (5,!45.) in the late phase of primary syphilis, becomes highly reacti"e (0,,.) in the secondary syphilis and reacti"ity decreases (45.) thereafter. Treatment in the early stages of infection may completely suppress production of antibodies and result in non!reacti"e tests. :ffecti"e treatment in the primary or secondary stages results in rapid fall in titre and the test may turn non!reacti"e in few months. Treatment in latent or late syphilis has "ery little effect on the titre and the titres may persist at low le"els for long periods. Since the titre
falls with effecti"e treatment, it can be used for assessment of prognosis. VDRL test is more suitable as a screening agent than a diagnostic tool. VDRL test is also helpful in the diagnosis of congenital syphilis. Since passi"ely transferred antibodies through placenta may gi"e false reacti"e test in serum of the infant, a repeat test after a month showing no increase in titre may help rule out congenital syphilis. Since the test employs a non!treponemal antigen, there are many chances of false positi"e results. >alse positi"ity (Ather than technical) may be due to physiological of pathological conditions. These are called biological false positi"es (B>%). &f the remain positi"e for less than 3 months it is considered acute and they remain positi"e for longer than 3 months it is called chronic B>%. The physiological reasons for B>% include pregnancy, menstruation, repeated blood loss, "accination, se"ere trauma etc while the reasons for pathological B>% include malaria, infectious mononucleosis, hepatitis, relapsing fe"er, tropical eosinophilia, lepromatous leprosy, SL:, rheumatoid arthritis etc. C reacti"e VDRL test does not necessarily imply that the person is syphilitic. The diagnosis must be made in con(unction with clinical findings. Cny reacti"e VDRL test must be confirmed with a specific or treponemal test such as T%@C, >TC!CBS test.
You might also like
- IVMS-Gross Pathology, Histopathology, Microbiology and Radiography High Yield Image PlatesDocument151 pagesIVMS-Gross Pathology, Histopathology, Microbiology and Radiography High Yield Image PlatesMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (2)
- Serological Diagnosis of SyphilisDocument81 pagesSerological Diagnosis of Syphilistummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiotechnologyDocument49 pagesIntroduction To BiotechnologyTanvi Jain100% (2)
- Role of Education in Conservation of BiodiversityDocument18 pagesRole of Education in Conservation of BiodiversitySai Sridhar100% (1)
- SPIROCHETESDocument11 pagesSPIROCHETESShujat Razaq100% (1)
- Common Teratogens and Their Effects: by GcespinoDocument49 pagesCommon Teratogens and Their Effects: by Gcespinokaycelyn jimenezNo ratings yet
- USMLE - BRS Pathology - Flash CardsDocument37 pagesUSMLE - BRS Pathology - Flash CardsJake ChuengNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Test, Values, and Interpretation Information On MedicineNetDocument5 pagesComplete Blood Count (CBC) Test, Values, and Interpretation Information On MedicineNetBabak BarghyNo ratings yet
- Scrub Typhus: The Re-Emerging Threat - Thesis SynopsisDocument17 pagesScrub Typhus: The Re-Emerging Threat - Thesis SynopsisRajesh PadhiNo ratings yet
- CHN Comprehensive Examination 2011-PrintDocument10 pagesCHN Comprehensive Examination 2011-PrintAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Neonatal SepsisDocument20 pagesNeonatal SepsisJustine Nyangaresi100% (1)
- ChromatographyDocument68 pagesChromatographythamizh555No ratings yet
- Mini Project On: Heart Disease Analysis and PredictionDocument26 pagesMini Project On: Heart Disease Analysis and PredictionKanak MorNo ratings yet
- Orientation To Blood Bank 2Document24 pagesOrientation To Blood Bank 2Darshita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Menular SeksualDocument83 pagesPenyakit Menular SeksualIvan Ho0% (1)
- Hema Ii Laboratory Week 7 - PT & PTT MethodsDocument37 pagesHema Ii Laboratory Week 7 - PT & PTT MethodsAl-hadad AndromacheNo ratings yet
- Infemax Infection Flusher - Infection Flusher PDFDocument2 pagesInfemax Infection Flusher - Infection Flusher PDFAnnabel JacksonNo ratings yet
- VDRL TestDocument2 pagesVDRL TestSajjadAhmad_QMCNo ratings yet
- Bleeding DisordersDocument39 pagesBleeding DisordersChelleyOllitroNo ratings yet
- Platelet ConcentratesDocument2 pagesPlatelet ConcentratesARIF AHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody Absorption FTA ABS TestDocument22 pagesFluorescent Treponemal Antibody Absorption FTA ABS TestMekar PalupiNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Report On Rapid Plasma Reagin Test (RPR)Document3 pagesComprehensive Report On Rapid Plasma Reagin Test (RPR)Kim RuizNo ratings yet
- Lab Report MicrobiologyDocument11 pagesLab Report Microbiologysalman ahmedNo ratings yet
- Pap Smear: Dr. Monika NemaDocument114 pagesPap Smear: Dr. Monika NemafadoNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Nanomaterials by Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approaches - An OverviewDocument5 pagesFabrication of Nanomaterials by Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approaches - An OverviewApexa SharmaNo ratings yet
- An Investegatory Project ReportDocument17 pagesAn Investegatory Project ReportKhushi kapseNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Results ReportingDocument7 pagesInterpretation of Results ReportingMerill Harrelson LibanNo ratings yet
- Hem - Lab 4 Retic - 09Document9 pagesHem - Lab 4 Retic - 09djebrutNo ratings yet
- Radioimmunoassay (Ria) 3Document21 pagesRadioimmunoassay (Ria) 3Sapna JainNo ratings yet
- Radial ImmunodiffusionDocument3 pagesRadial Immunodiffusionkiedd_04100% (5)
- Packed Cell Volume (PCV)Document24 pagesPacked Cell Volume (PCV)Eyasu demsewNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Project Report pdf3 PDFDocument35 pagesTuberculosis Project Report pdf3 PDFpari bNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)Document16 pagesEnzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)Kuzhandai VeluNo ratings yet
- Chemiluminescence As Diagnostic Tool A ReviewDocument26 pagesChemiluminescence As Diagnostic Tool A ReviewDian AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Susceptibility TestDocument5 pagesAntibiotic Susceptibility Testfarhanna8100% (3)
- Case Control StudyDocument6 pagesCase Control Studyphian0No ratings yet
- Role of Xray in OtolaryngologyDocument14 pagesRole of Xray in OtolaryngologysmcentNo ratings yet
- Sop 2001Document6 pagesSop 2001fedly100% (1)
- Coagulation TestsDocument25 pagesCoagulation Testsdave_1128No ratings yet
- 3-Differential WBC CountDocument11 pages3-Differential WBC CountdlerNo ratings yet
- Hematology Quick Facts Part1 PDFDocument10 pagesHematology Quick Facts Part1 PDFJohn Rhel DenqueNo ratings yet
- One Step Anti-HIV (1&2) TestDocument4 pagesOne Step Anti-HIV (1&2) TestGail Ibanez100% (1)
- Types of ImmunofluorescenceDocument2 pagesTypes of ImmunofluorescenceMuthiah RamanathanNo ratings yet
- Venous Blood CollectionDocument4 pagesVenous Blood CollectionSheila Mae BuenavistaNo ratings yet
- Pragya Project PDFDocument31 pagesPragya Project PDFShahnawaz khanNo ratings yet
- Mphil Bio-Chemistry ProjectDocument98 pagesMphil Bio-Chemistry ProjectBalaji Rao NNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Children 2016Document10 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemia in Children 2016Jorge Eduardo Espinoza RiosNo ratings yet
- Automation in Blood Banking - DR ShreyaDocument80 pagesAutomation in Blood Banking - DR ShreyaDr sakshiNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis: Ms - Deeptikukreti M.SC (N) 1 Year Student RconDocument20 pagesUrinalysis: Ms - Deeptikukreti M.SC (N) 1 Year Student RconDeepti KukretiNo ratings yet
- Handouts in Microtome PDFDocument10 pagesHandouts in Microtome PDFCANDELARIA ALMOROSNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3 White Blood CellDocument11 pagesLab Report 3 White Blood CellAlyaa AthiraNo ratings yet
- Manual For The Laboratory Diagnosis of Malaria.Document126 pagesManual For The Laboratory Diagnosis of Malaria.Mustafa Khandgawi100% (1)
- Blood Smears and The Use of Wrights StainDocument5 pagesBlood Smears and The Use of Wrights Stainkaleb16_2No ratings yet
- Term Paper ON: Correlation Between Rapid Test and Automated Methods in Diagnosing Infectious Disease Like TyphoidDocument22 pagesTerm Paper ON: Correlation Between Rapid Test and Automated Methods in Diagnosing Infectious Disease Like TyphoidSoniya DhyaniNo ratings yet
- MaleriaDocument41 pagesMaleriadeepak_143No ratings yet
- Chemiluminescence NotesDocument7 pagesChemiluminescence NotesSavarinathan Maria RayappanNo ratings yet
- Estimation of PCV by Wintrobe MethodDocument18 pagesEstimation of PCV by Wintrobe Methodjyoti singhNo ratings yet
- Assignment On: HepatitisDocument12 pagesAssignment On: HepatitisAbdallah KisswaniNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Diagnosis of MalariaDocument6 pagesLaboratory Diagnosis of MalariaRam Sharma PaudelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 42Document3 pagesChapter 42Soc Gerren TuasonNo ratings yet
- Blood Grouping ReagentsDocument7 pagesBlood Grouping ReagentsDominic EmerencianaNo ratings yet
- Rapid Plasma Reagin (RPR)Document7 pagesRapid Plasma Reagin (RPR)Gakwaya Jules CesarNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting HemolysisDocument6 pagesTroubleshooting HemolysisARIF AHAMMED PNo ratings yet
- Industrial Mini Project Report ON Alzheimer Disease Detection Using Support Vector Machine AlgorithmDocument10 pagesIndustrial Mini Project Report ON Alzheimer Disease Detection Using Support Vector Machine AlgorithmRahul RepalaNo ratings yet
- Workload Indicators (Staffing Norms)Document131 pagesWorkload Indicators (Staffing Norms)asimsiNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of HemostasisDocument5 pagesBasic Principles of HemostasisSean Matthew100% (1)
- VDRL/RPR: Dominic Edward Z. TomasDocument26 pagesVDRL/RPR: Dominic Edward Z. TomasDominic TomasNo ratings yet
- VDRL Test and Its InterpretationDocument11 pagesVDRL Test and Its InterpretationSauZen SalaZarNo ratings yet
- The Serological TestsDocument27 pagesThe Serological Testsalexbirhanu785No ratings yet
- Widal TestDocument8 pagesWidal Testhamadadodo7No ratings yet
- Classification of AnimalsDocument23 pagesClassification of AnimalsSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument12 pagesEnvironmental ScienceSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Consumer AttitudeDocument13 pagesConsumer AttitudeSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Consumer Buyer BehaviorDocument29 pagesConsumer Buyer BehaviorSai SridharNo ratings yet
- ConciliationDocument22 pagesConciliationSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Developmental BiologyDocument12 pagesDevelopmental BiologySai SridharNo ratings yet
- Water BathDocument5 pagesWater BathSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Bio ChemDocument3 pagesBio Chemsujithas0% (1)
- As A Man ThinkethDocument28 pagesAs A Man ThinkethSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Grif IthDocument9 pagesGrif IthSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Radio Immuno As SayDocument3 pagesRadio Immuno As SaySai SridharNo ratings yet
- Widal TestDocument3 pagesWidal TestSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Simple, Differential Staining and MotilityDocument8 pagesSimple, Differential Staining and MotilitySai SridharNo ratings yet
- Video Conferencing TechnologyDocument31 pagesVideo Conferencing TechnologySai SridharNo ratings yet
- Visible Spectro Photo Me TryDocument2 pagesVisible Spectro Photo Me TrySai SridharNo ratings yet
- UMLSDocument4 pagesUMLSSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Unit II - Fatty LiverDocument2 pagesUnit II - Fatty LiverSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Unit IIIDocument31 pagesUnit IIISai SridharNo ratings yet
- Selective, Differential, Enriched MediaDocument5 pagesSelective, Differential, Enriched MediaSai SridharNo ratings yet
- SDS - PageDocument5 pagesSDS - PageSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Types of CarcinogensDocument33 pagesTypes of CarcinogensSai SridharNo ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument2 pagesRadioactivitySai SridharNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Molar SolutionDocument1 pagePreparation of Molar SolutionSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Scientific Technique Molecular Biology Amplify DNA DNA Sequence Kary MullisDocument4 pagesScientific Technique Molecular Biology Amplify DNA DNA Sequence Kary MullisSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid HybridizationDocument2 pagesNucleic Acid HybridizationSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument4 pagesPaper ChromatographySai SridharNo ratings yet
- Mycoplasma and CoDocument58 pagesMycoplasma and Coobed cudjoeNo ratings yet
- Health Related Fitness TestDocument6 pagesHealth Related Fitness TestAimee HernandezNo ratings yet
- Neu N TORCH Infections Clinics in Perinatology 2015Document27 pagesNeu N TORCH Infections Clinics in Perinatology 2015vickyNo ratings yet
- Posterior Uveitis FinalDocument79 pagesPosterior Uveitis FinalNurul MasrurohNo ratings yet
- Sifilis Congénita - Seminars Perinatology 2018Document9 pagesSifilis Congénita - Seminars Perinatology 2018AlejandraMayaNo ratings yet
- Micro Bio Disease ListDocument168 pagesMicro Bio Disease Listspiff spacemanNo ratings yet
- Your Pregnancy PDFDocument72 pagesYour Pregnancy PDFPerpetua KamikadzeNo ratings yet
- Sana Loue - Textbook of Research Ethics - Theory and Practice-Springer (2000)Document276 pagesSana Loue - Textbook of Research Ethics - Theory and Practice-Springer (2000)Aastha TiwariNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone Compared With Benzylpenicillin in The Treatment of NeurosyphilisDocument7 pagesCeftriaxone Compared With Benzylpenicillin in The Treatment of NeurosyphilisJesus Alonso Campillo MoralesNo ratings yet
- Doxycycline Prophylaxis For Bacterial Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocument7 pagesDoxycycline Prophylaxis For Bacterial Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDini Permata SariNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Medical Research UGDocument35 pagesEthics in Medical Research UGPodBoogerNo ratings yet
- Path o Physiology of SyphilisDocument1 pagePath o Physiology of Syphilis3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Spirochetes and Curved RodsDocument54 pagesSpirochetes and Curved RodsDegee O. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Alfred Francois DonneDocument4 pagesAlfred Francois DonneFariha FirdausNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations and Treatment of Syphilis - UpToDateDocument2 pagesClinical Manifestations and Treatment of Syphilis - UpToDateCarmenDuganNo ratings yet
- Sample MCQ QuestionsDocument11 pagesSample MCQ QuestionsPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- ICD-10 CM All Diagnosis and Trigger Codes - Revised 9-17-2015Document6,507 pagesICD-10 CM All Diagnosis and Trigger Codes - Revised 9-17-2015Puskesmas MakaleNo ratings yet
- Aim: Determination of RPR or VDRL RPR: Rapid Plasma Reagin VDRL: - Venereal Disease Research LaboratoryDocument3 pagesAim: Determination of RPR or VDRL RPR: Rapid Plasma Reagin VDRL: - Venereal Disease Research LaboratoryMotherterrasa VocationalNo ratings yet
- Immunology and Serology Part 4Document108 pagesImmunology and Serology Part 4UnixoftNo ratings yet
- Notes MICROBIAL DISEASES and EPIDEMIOLOGYDocument12 pagesNotes MICROBIAL DISEASES and EPIDEMIOLOGYDaniella TupasNo ratings yet
- The Deadly Deception Produced By: Nova, WGBH Educational Foundation Release Information: Films For The Humanities and Sciences, (1993) VHS 60 MinDocument3 pagesThe Deadly Deception Produced By: Nova, WGBH Educational Foundation Release Information: Films For The Humanities and Sciences, (1993) VHS 60 MinGia LeNo ratings yet
- Abstracts: Brit. J. Vener. Dis. (1956), 32, 131Document5 pagesAbstracts: Brit. J. Vener. Dis. (1956), 32, 131Shaashi DamodaranNo ratings yet
- Icd 10 Baru P-CareDocument207 pagesIcd 10 Baru P-CareR Haruming PutriNo ratings yet