Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Measles: Communicable Disease Causative Agent Signs & Symptoms Core, Prevention & Control Bacteria
Uploaded by
Wilma BundangOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Measles: Communicable Disease Causative Agent Signs & Symptoms Core, Prevention & Control Bacteria
Uploaded by
Wilma BundangCopyright:
Available Formats
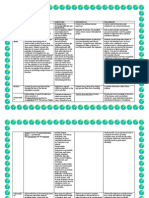
COMMUNICABLE DISEASE Disease BACTERIA Measles Causative Agent Virus Signs & Symptoms High fever, rashes Core,
Prevention & Control Vaccination/ proper hygiene, sanitation
Cholera
Tuberculosis
Vibrio Cholerae * severe diarrhea (watery stools) * acute abdominal pain * frequent vomiting * severe dehydration owing to the large amount of water lost in feces. Mycobacterium Prolonged illness with tuberculosis fever, cough, nightsweats, weight loss and may occasionally cough up blood. As the disease progresses, symptoms get worse and shortness of breath ensues. Streptococcus pneumoniae
Water that has been boiled, water that has been chemically disinfected, or bottled water.
Drug treatment requires that a number of antibiotics be taken for a prolonged period of time, usually six to nine months.
VIRUS Pneumonia
Cough Rusty or green mucus (sputum) coughed up from lungs Fever Fast breathing and shortness of breath Shaking chills Chest pain that usually worsens when taking a deep breath (pleuritic pain) Fast heartbeat Fatigue and feeling very weak
In addition to vaccinations, physicians recommend that people wash hands, refrain from smoking, eat healthfully, exercise, and stay away from sputum or cough particles from others with pneumonia.
Nausea and vomiting Diarrhea Sweating Headache Muscle pain Confusion or delirium Dusky or purplish skin color (cyanosis) from poorly oxygenated blood Common sense measures such as frequent hand washing and keeping children away from crowds and sick individuals are only partially effective.
Bronchiolitis
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
Stomach flu
E. coli
A one to seven day prodrome of mild fever, coryza and cough is common with bronchiolitis. Disease can rapidly progress to deepening cough, tachypnoea, restlessness, chest wall retraction, nasal flaring and grunting. Audible wheezing is a characteristic feature. It can be accompanied by paroxysms of coughing, vomiting, dehydration, otitis media and diarrhoea. Abdominal cramps Stomach pain Nausea Vomiting Diarrhea
Wash your hands thoroughly after going to the toilet and before eating or preparing food. Clean the toilet, including the seat and handle, with disinfectant after each bout of vomiting or diarrhea. Don't share towels, flannels, cutlery and utensils with other household members.
Don't return to work until 48 hours have passed since your last bout of vomiting or diarrhea.
MOSQUITO CARRIER Dengue
Flavivirus
Fever, frontal headache, retro orbital pain or pain in the back of the eyes, nausea and vomiting. Dengue fever is also commonly known as breakbone fever because it also causes arthralgia, which is pain of the joints. Chills, back pain and swelling of the lymph nodes are also common symptoms of dengue fever. The most noticeable sign of the disease is a maculopapular or scarlatiniform rash that appears on the trunk or extremities such as the hands
The best method for the prevention of this disease is vector control. The use of insecticides is strongly urged as well as the elimination of water holding containers that are perfect breeding grounds for Aedes aegytpi.
Chikungunya
Alpha virus
Muscle pain, headache, nausea, fatigue and rash. The joint pain is often very debilitating, but usually lasts for a few days or may be prolonged to weeks.
No vaccine is available for prevention of Chikungunya Fever. So measures for prevention and control are the avoidance of mosquito bites and reduction in density of vector.
FUNGI Candidiasis
Candida albicans
Redness, itching and discomfort, though complications may be severe or even fatal if left untreated in certain populations
Some practitioners of alternative medicine have promoted a fictitious condition called "candidiasis hypersensitivity" and sold dietary supplements as a supposed cure; a number of them have been prosecuted. Use of ethanol solution application, though it is not advisable for all versions of the disease, depending on afflicted region and progression and because of pain complications. The use of diuretics concerning infection of genitalia may also be employed to stop and eliminate the infection, though the process may take several weeks. In addition, the fungal yeast spores are notorious for recurring in more than a quarter of patients.
Zeaspora
Fungus
Zeaspora can, however, be manifested as color ranging anywhere from white to dark gray in later stages[2] and feeling from smooth and damp to rough and irregular in later stages.
You might also like
- Firearm Registration Application Form PDFDocument1 pageFirearm Registration Application Form PDFWilma Bundang71% (7)
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument7 pagesAcute GastroenteritisCherr NollNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Bacteria of Medical ImportanceDocument12 pagesGram Positive Bacteria of Medical ImportanceGeorge C. KasondaNo ratings yet
- Environmental EngineeringDocument38 pagesEnvironmental EngineeringPrakash Maurya100% (1)
- DENGUEDocument34 pagesDENGUEjerson.panopio1329No ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis Is A Condition That Causes Irritation and Inflammation of The Stomach andDocument4 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis Is A Condition That Causes Irritation and Inflammation of The Stomach andChrisette Cenizal LoreñaNo ratings yet
- Botulism: Physical ExamDocument13 pagesBotulism: Physical ExamAlexandria P. OrcajadaNo ratings yet
- Typhoid FeverDocument7 pagesTyphoid FeversakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document12 pagesAssignment 1Ilhaashini krishnanNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Pneumonia Education EnglishDocument9 pagesMicrosoft Word - Pneumonia Education Englishjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- TyhpoidDocument8 pagesTyhpoidTanor YansaNo ratings yet
- TyhpoidDocument8 pagesTyhpoidTanor YansaNo ratings yet
- Dengue OutlineDocument6 pagesDengue OutlineLouie George NeriNo ratings yet
- Applied Microbiology and Infection Control AssignmentDocument17 pagesApplied Microbiology and Infection Control AssignmentNader OsmanNo ratings yet
- Symptoms of TyphoidDocument6 pagesSymptoms of TyphoiddebasishroutNo ratings yet
- Strointestinal / GastroenterologyDocument6 pagesStrointestinal / GastroenterologyLeizel ApolonioNo ratings yet
- DiseasesDocument13 pagesDiseasesJaypee SaturnoNo ratings yet
- NSTP AssignmentDocument9 pagesNSTP AssignmentDiana Ruth ElizagaNo ratings yet
- Causes: GastroenteritisDocument5 pagesCauses: Gastroenteritispragna novaNo ratings yet
- TH THDocument4 pagesTH THdhen2_kyzluvdenNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument19 pagesDiarrheaShaffy UngaNo ratings yet
- Health Advisory For VolunteersDocument4 pagesHealth Advisory For VolunteersHerbert Q. CarpioNo ratings yet
- Bibliography: NCERT - TextbookDocument10 pagesBibliography: NCERT - TextbookjothiNo ratings yet
- DysenteryDocument7 pagesDysenterymukulpjrNo ratings yet
- DiseasesDocument3 pagesDiseasesBarani KingNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Nursing Considerations and Nursing Care ManagementDocument5 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever Nursing Considerations and Nursing Care Managementjanns tumanengNo ratings yet
- Common Cold: SymptomsDocument13 pagesCommon Cold: Symptomsjesjay mimayNo ratings yet
- Viral Fever Management With HomoeopathyDocument6 pagesViral Fever Management With HomoeopathyTarakanta PatraNo ratings yet
- Common ColdDocument3 pagesCommon Coldyantiee-frieska-situmeang-peank-7585No ratings yet
- Dengue Fever EngDocument21 pagesDengue Fever EngAminul Islam MithuNo ratings yet
- DENGUEDocument5 pagesDENGUEHpu JogindernagerNo ratings yet
- High Fever Headaches Eyes Muscle PainDocument4 pagesHigh Fever Headaches Eyes Muscle PainMol maharjanNo ratings yet
- Polio: Bacteria Clostridium TetaniDocument6 pagesPolio: Bacteria Clostridium TetaniLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNo ratings yet
- Information For Patients - LeptospirosisDocument10 pagesInformation For Patients - LeptospirosistravelbeeNo ratings yet
- TyphoidDocument26 pagesTyphoidLiya Mary ThomasNo ratings yet
- 18 Common Infections: Matthew DrydenDocument17 pages18 Common Infections: Matthew Drydenprerakdhawan95No ratings yet
- Whooping CoughDocument72 pagesWhooping Coughwengie100% (1)
- BHW Training Adult CareDocument123 pagesBHW Training Adult CareWilma BeraldeNo ratings yet
- Health and Disease OrganismsDocument59 pagesHealth and Disease OrganismsAlian WilliansNo ratings yet
- Dengue: Signs and SymptomsDocument5 pagesDengue: Signs and SymptomsMary Charlotte PableoNo ratings yet
- Reporting Draft For PPT InputsDocument2 pagesReporting Draft For PPT InputsPhaestus ReverseNo ratings yet
- Recent Health ProblemsDocument13 pagesRecent Health ProblemsKatie CraneNo ratings yet
- Disease Caused Due To Climate ChangeDocument32 pagesDisease Caused Due To Climate ChangeHari BaluNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseasesDocument13 pagesInfectious DiseasesRavneetKalkatNo ratings yet
- The AppendixDocument4 pagesThe AppendixAmik, Aila H.No ratings yet
- Nat Csi FinalsDocument31 pagesNat Csi FinalsPaola ParkerNo ratings yet
- Typhoid PDFDocument3 pagesTyphoid PDFZ3usNo ratings yet
- MSN I 20.4.2020 FN TyphoidDocument20 pagesMSN I 20.4.2020 FN TyphoidDr. DhaneshNo ratings yet
- Bio Project EtaDocument2 pagesBio Project EtaClaresta Puspa MelatiNo ratings yet
- Common Communicable Disease in The CommunityDocument5 pagesCommon Communicable Disease in The CommunityMaristelaMolinaNo ratings yet
- Symptoms, Complications and Prevention of Typhoid FeverDocument3 pagesSymptoms, Complications and Prevention of Typhoid Feverhasandsome100% (1)
- Common Diseases: Posted byDocument4 pagesCommon Diseases: Posted byChin ChanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation On ADDDocument39 pagesClinical Presentation On ADDSREEDEVI T SURESHNo ratings yet
- Vulnus SclopectariumDocument1 pageVulnus SclopectariumNurnazila HariviskaNo ratings yet
- GERMAN MEASLES and HEPATITISDocument51 pagesGERMAN MEASLES and HEPATITISatienza02No ratings yet
- Sectionsfor Typhoid FeverDocument6 pagesSectionsfor Typhoid FeverDennis NjorogeNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesLesson PlanLynn QuinatadcanNo ratings yet
- Illness Symptoms Reasons Solutions Homemade Solutions Ways To Avoid Such Health IssuesDocument9 pagesIllness Symptoms Reasons Solutions Homemade Solutions Ways To Avoid Such Health IssuessunilviniNo ratings yet
- FWBD - Major Health ProblemDocument3 pagesFWBD - Major Health ProblemDez TabiosNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases: Samantha Mihalovich Northern Kentucky University Bachelors of Science in NursingDocument38 pagesCommunicable Diseases: Samantha Mihalovich Northern Kentucky University Bachelors of Science in NursingSamantha MihalovichNo ratings yet
- 5 Diseases To Be Wary of This MonsoonDocument3 pages5 Diseases To Be Wary of This MonsoonTejas DesaiNo ratings yet
- User's Guide to Echinacea and Other Cold & Flu FightersFrom EverandUser's Guide to Echinacea and Other Cold & Flu FightersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- National Book Store: Iba, ZambalesDocument1 pageNational Book Store: Iba, ZambalesWilma BundangNo ratings yet
- I. Identification. Stictly No ErasuresDocument1 pageI. Identification. Stictly No ErasuresWilma BundangNo ratings yet
- Watercolor PaintDocument3 pagesWatercolor PaintWilma Bundang100% (2)
- Lawrence Always Works Hard To Achieve SomethingDocument1 pageLawrence Always Works Hard To Achieve SomethingWilma BundangNo ratings yet
- Importance of IctDocument1 pageImportance of IctWilma BundangNo ratings yet
- ApplicationDocument1 pageApplicationWilma BundangNo ratings yet
- Marketing StrategiesDocument15 pagesMarketing StrategiesWilma BundangNo ratings yet
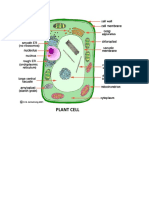
- Plant CellDocument5 pagesPlant CellWilma BundangNo ratings yet
- Coffee Jelly Ice CandyDocument1 pageCoffee Jelly Ice CandyWilma BundangNo ratings yet
- COMPOUND MICROSCOPE Consists Essentially of Two or More Double ConvexDocument1 pageCOMPOUND MICROSCOPE Consists Essentially of Two or More Double ConvexWilma BundangNo ratings yet
- Pinoy Fruit Salad RecipeDocument3 pagesPinoy Fruit Salad RecipeWilma Bundang100% (1)
- Driver ApplicationDocument1 pageDriver ApplicationWilma BundangNo ratings yet
- Environmental EffectsDocument1 pageEnvironmental EffectsWilma BundangNo ratings yet
- Annual Improvement PlanDocument2 pagesAnnual Improvement PlanWilma Bundang100% (3)
- Fundamental Rules For Indirect SpeechDocument1 pageFundamental Rules For Indirect SpeechWilma BundangNo ratings yet
- Visual Texture Is A Visual Quality of A Surface. It Is The Result From Painting or Drawing As The RealDocument1 pageVisual Texture Is A Visual Quality of A Surface. It Is The Result From Painting or Drawing As The RealWilma BundangNo ratings yet
- Probiotics & Prebiotics (Dr. Minidian)Document15 pagesProbiotics & Prebiotics (Dr. Minidian)Khairunnisa10inNo ratings yet
- Sugarcane DiseasesDocument6 pagesSugarcane DiseasesNkanyisoNo ratings yet
- What's The Best Antibiotic For A Staph Infection - Treatments and RisksDocument3 pagesWhat's The Best Antibiotic For A Staph Infection - Treatments and RisksSundaramoorthy SelvanathanNo ratings yet
- Jl. Pulo Mas Timur K No.2 RT4/RW.14, Kayu Pu H, Kec. Pulo Gadung, Kota Jakarta Timur, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta 13210Document1 pageJl. Pulo Mas Timur K No.2 RT4/RW.14, Kayu Pu H, Kec. Pulo Gadung, Kota Jakarta Timur, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta 13210suherman paleleNo ratings yet
- Microbiological Risk AssessmentDocument30 pagesMicrobiological Risk AssessmentJosé SalazarNo ratings yet
- Medical Questionnaire PDFDocument3 pagesMedical Questionnaire PDFChristan CepedaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing FK 2012Document32 pagesAntimicrobial Susceptibility Testing FK 2012Sheryl Elita100% (1)
- MicrobiologyDocument108 pagesMicrobiologyHampson Malekano100% (1)
- Cholera: Presenter: Dr. Sohani Bajracharya Date: 26 February 2018Document32 pagesCholera: Presenter: Dr. Sohani Bajracharya Date: 26 February 2018Bajracharya SohaniNo ratings yet
- Typhidot AssayDocument16 pagesTyphidot Assaychocoholic potchiNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Project YSU (1) FINAL EDITION 2016 2017-1Document28 pagesAhmed Project YSU (1) FINAL EDITION 2016 2017-1Yakubu Adamu JajereNo ratings yet
- BMW Rules, 2016Document13 pagesBMW Rules, 2016Pabhat KumarNo ratings yet
- Blood Culture TV RaoDocument61 pagesBlood Culture TV RaoLavina D'costaNo ratings yet
- GiardiaDocument17 pagesGiardiaYaw BoatengbNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable DiseasesDocument476 pagesEpidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable Diseasesegregious100% (1)
- Coipars ColombiaDocument12 pagesCoipars Colombiaduverney.gaviriaNo ratings yet
- Role of Probiotics in AquacultureDocument24 pagesRole of Probiotics in AquacultureGopi NuthalapatiNo ratings yet
- Microbial Keratitis Royal College of OphthalmologistDocument2 pagesMicrobial Keratitis Royal College of OphthalmologistmahadianNo ratings yet
- Ciliates and Flagellates HardDocument4 pagesCiliates and Flagellates HardLizaNo ratings yet
- Impose Strict PunishmentDocument1 pageImpose Strict PunishmentNurnajihahNo ratings yet
- Virus Patogenik: Hishamuddin Bin AhmadDocument26 pagesVirus Patogenik: Hishamuddin Bin AhmadShareall RazhiftNo ratings yet
- Rosemary AntibacterialDocument5 pagesRosemary AntibacterialNurul Izzah Wahidul AzamNo ratings yet
- CONCLUSION Questions 1.4.1-Yoshi Nakachi-2 - 8 - 21Document2 pagesCONCLUSION Questions 1.4.1-Yoshi Nakachi-2 - 8 - 21Yoshi NNo ratings yet
- Anexa CORECTA UbisoftDocument19 pagesAnexa CORECTA UbisoftClaudia DumitriuNo ratings yet
- 2nd MAPEH 4Document2 pages2nd MAPEH 4Edmar MejiaNo ratings yet
- Ks Hospital, Hospital Road, Distt Mandi, Himachal Pradesh MANDI, 175001Document2 pagesKs Hospital, Hospital Road, Distt Mandi, Himachal Pradesh MANDI, 175001Anurag UniyalNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Macromycets in MacedoniaDocument5 pagesMedicinal Macromycets in Macedoniaapi-3718255No ratings yet
- WW1 and DisseasesDocument9 pagesWW1 and DisseasesmariavillaresNo ratings yet