Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Putting BOTOX Facial Fillers Into Practice
Uploaded by
Vinisha Vipin SharmaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Putting BOTOX Facial Fillers Into Practice
Uploaded by
Vinisha Vipin SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
Putting Botulinum Toxins and Facial Fillers into Practice
Sirtaz S. Sibia, , D.O., , FAOCO
Orlando, Florida May 2013
Approach to the cosmetic patient
Anatomic areas of concern to the patient
Give the patient a mirror and have them point out what bothers them
History of previous treatment D Document t patients ti t anatomy t Educate the patient about treatment options
Botox Cosmetic, Dysport, Xeomin, Restylane, Perlane, Juvederm, Radiesse, etc.
Basic Physician Knowledge of Botulinum toxins
Botulinum toxins Indications Temporary improvement in the appearance of moderate to severe glabellar lines g Corrugator and/or procerus activity Adults 65 years
Administering physicians Be well trained Have knowledge of muscles controlling facial expression Understand the dynamics g g of aging Be qualified to evaluate and determine individual treatment
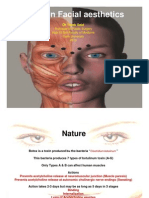
Botulinum Toxin Overview
BOTOX
Cosmetic, Xeomin and Dysport are purified natural proteins derived from the purified, bacterium Clostridium botulinum. toxins works by blocking acetylcholine impulses that trigger hyperactive muscle l contractions. i
Botulinum
Botulinum Toxin vs. The Aging Face
Glabellar frown lines H i t l forehead Horizontal f h d lines li Periorbital lines (Crows feet) Lateral brow lift
BOTOX Cosmetic Packaging
Store vacuum-dried product in refrigerator (2-8 (2-8C) C). Administer within 4 hours after reconstituting product. Store reconstituted product at 2C to 8C. BOTOX Cosmetic should be clear, colorless and free of particulate matter. Supplied in a single patient use vial.
Dysport Packaging
Store vacuum-dried product in refrigerator (2-8 (2-8C) C). Administer within 4 hours after reconstituting product. Store reconstituted product at 2C to 8C. Dysport should be clear, colorless and free of particulate matter. Supplied in a single patient use vial.
Botulinum systemic side effects
Rare
Usually not associated with cosmetic indications
Generalized weakness Fl lik symptoms Flu-like t Diffuse skin rash Headache
Botulinum Contraindications
Pregnancy and breast feeding Di d of Disorders f th the neuromuscular l junction j ti
Myasthenia gravis M Myopathies thi
Aminoglycoside therapy
May i M impair i neuromuscular l transmission t i i and d are a theoretical th ti l contraindication
Botox/Dysport yp Preparation p
1 cc syringes
Insulin syringe y g with p preattached 30 guage needle vs. separate syringe and needle
30 gauge needle Digital camera Consent form Postop instructions
Anesthesia for Injections
None I ethyl Ice, th l chloride hl id Emla, ELA-Max, Betacaine
Botox/Dysport Preparation
Botulinum toxin needs to be reconstituted with sterile, preservative free saline Refer to Botulinum toxin by units not volume
Botox: Vial Dilutions
Saline 2.0 ml 2.5 ml 4.0 ml 5.0 ml U/ml 50 40 25 20 U/0.1 ml 5.0 4.0 2.5 2.0
Dysport: yp Vial Dilutions
Saline 1.5 ml 2.0 ml 2.5 ml 3.0 ml U/ml 200 150 120 100 U/0.1 ml 20.0 15.0 12.0 10.0
Documentation of Botox treatments
Botulinum toxin injection worksheet B f Before and d after ft photographs h t h Make good notes on how many units injected for each site to help improve results for future Botox/Dysport / Xeomin treatments
BOTOX R Injection Worksheet
Patient Name: _______________________________ DOB: _________ Treatment Areas: glabella forehead periorbital Date: _________ perioral other
BOTOXR: Lot __________
Expiration ___________
Concn ___________
The risks, benefits, and alternatives of Botox injections were discussed with patient. BotoxR was administered after alcohol skin prep and topical anesthesia placement. Patient tolerated procedure well and there were no complications. Return appointment: ___________________
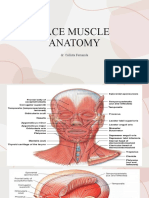
Key Muscles of the Upper Face
Corrugator Supercilii
Frontalis
Procerus
Orbicularis Oculi
Discussing BOTOX Cosmetic, Xeomin or Dysport with your Patients
BOTOX Cosmetic/ Dysport/ Xeomin is a natural, purified protein that relaxes wrinkle-causing muscles, creating a smoothed and improved appearance. BOTOX Cosmetic/ Dysport/ Xeomin is administered via a few tiny injections of purified protein into the muscle to block nerve impulses that trigger wrinkle-causing muscle contractions. BOTOX Cosmetic/ Dysport/ Xeomin is a simple and quick, minimally invasive treatment that delivers dramatic results with no downtime.
Discussing BOTOX Cosmetic, Xeomin, and d Dyport D t with ith your Patients P ti t
Dont fixed fixed , frozen frozen , paralyzed paralyzed , deaden deaden , needles Do smooth, th relax, l refresh, f h tiny ti injection, soften
Botulinum Toxin Marketing g
Internal marketing
Botox/Dysport/Xeomin brochures Treat office staff with left over Botox/Dysport
External marketing g
Traditional advertising Spas, salons, gyms, health clubs
Pricing
Botox Days
Glabellar Frown Lines
Rhytids (wrinkles) between the brows Produced by
corrugator g procerus orbicularis oculi depressor supercilli
Before and After: Glabella
Glabellar line treatment
injection sites:
1 in procerus 2 in each corrugator
Total
dose:
Botox/Xeomin: 20 U (4U/injection site) Dysport: 50 U (10 U/injection site)
Decrease in Glabellar Lines after Treatment with BOTOX Cosmetic
Baseline
Day 30
Unretouched clinical trial photos taken while frowning before BOTOX Cosmetic and after BOTOX Cosmetic. Individual results lt may vary.
Potential complications p of g glabellar treatments
Bruising B Brow Pt i Ptosis Diplopia Eyelid Ptosis
Treat with Naphcon A or Iopidine, the alpha agonistic activity stimulates ti l t Muellers M ll muscle l which hi h lifts lift the th lid and d compensates t for f the th loss of the levator
Why y use Botulinum in glabella g vs. fillers
Occlusion of cutaneous vessels (Zyplast) Bli d Blindness (C (Collagen, ll f fat, t t triamcinolone) i i l ) Cerebrovascular occlusion (fat)
Forehead Lines
Rhytids (wrinkles) across the forehead Produced by
frontalis muscle
Before and After:Forehead
Forehead line treatment
Botox/Xeomin: 2 U/ site Dyport: 5U/ site
to prevent eyelid ptosis, injections should be at least 1 cm above the supraorbital p rim and away from the area above the lateral eyebrow
Potential complications p of forehead treatments
Bruising B Brow Ptosis Pt i Eyelid Ptosis
Periorbital Lines (Crows (Crow s Feet)
Rhytids (wrinkles) radiating di i from f the h lateral canthus, especially when a person smiles Produced by
orbicularis oculi
Before and After: p periorbital lines
Periorbital line treatment
Botox/Xeomin: 3 U per site Dysport: 8 U per site
Inject 1 cm away from orbital rim To prevent bruising in this area use intradermal or subcutaneous injections
Potential complications p of p periorbital treatments
Diplopia K titi Keratitis Ectropion Epiphora Weakness of zygomaticus muscle
Lateral Brow Lift
Performed mainly for female patients Treat the lateral brow depressors p so the brow elevators work unopposed
Before and After:lateral brow lift
Lateral Brow Lift Treatment
4 units Botox/Xeomin 3 units Botox/Xeomin 2 units Botox/Xeomin
treat just like you do the glabellar lines add an additional 2 units into the orbicularis oculi 1 1-2 2 cm lateral to the orbital rim and at the tip of the eyebrow
Postop p Instructions
Do not lie down for the next 4 hours D not Do t lean l over for f the th next t 4 hours h Do not touch or massage the treated areas in any fashion for at least 4 hours Immediately y after the injections, j frown and smile repeatedly for the next 15 to 30 minutes
Fillers: Temporary, Semipermanent, and Permanent
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Temporary Fillers
Less durable and enduring Biodegradable Bovine Collagen: Zyderm and Zyplast Human dollagen: Cosmoderm and Cosmoplast p Hyaluronic acid: Restylane, Perlane, Captique, Hylaform, Juvederm Ultra Fat fillers
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Semipermanent fillers
Slowly biodegradable Liquid Silicone: Silikon 1000 Polylactic acid: Sculptra Calcium Hydroxylapatite: Radiesse Fat fillers
1. 2. 3.
Permanent fillers:
Nonbiodegradable Polymethylmethacrylate: Artefill, Artecoll Fat fillers
6.
Collagen Implants: Z d Zyderm and dZ Zyplast l t
FDA approved in 1981 and 1985, respectively Bovine collagen implant Pros: safe, reliable, user-friendly, contains lidocaine Cons: allergic reaction, redness, swelling, skin test is required, and a second skin test is recommended Recommended use: fine to deep wrinkles, frown lines, smile lines, crows feet, lip border acne and other scars border,
Collagen Replacement: Cosmoderm and Cosmoplast
FDA approved in 2003 Pros: immediate rsults with no down time Cons: short-lived correction Recommended use for Cosmoderm: superficial papillary dermis for correction of wrinkles and acne scars Recommended use for Cosmoplast: mid to deep dermis for correction of wrinkles and acne scars
Synthetic Calcium: R di Radiesse
FDA approved in 2006 Volume composition p made up p of 70% carboxymethylcellulose and 30% calcium hydroxylapatite Pros: no allergy testing testing, long shelf life life, longevity once injected Cons: nodules common, , especially p y in lips, p , mistakes no easily forgiven Recommended use: nasolabial folds, d depressed d scars, oral l commissures i
Synthetic Poly Poly-L-Lactic L Lactic Acid: Sculptra
FDA approved in 2004 Synthetic y poly-L-lactic p y acid Pros: long-lasting, long safety record as an implant/suture material Cons: approved for HIV lipodystrophy only; granulomas have been reported Recommended use: filler for HIV lipodystrophy-related atrophy; and mild volume loss
Polydimethylsiloxane: Silik Silikon 1000
FDA approved in 1997 Purified polydimethylsiloxane p y y Pros: low biological toxicity potential, inert material Cons: approved for retinal tamponade during vitreoretinal surgery only, requires multiple p treatments Recommended use to treat facial lipoatrophy in patients with HIV
PMMA/Bovine Collagen: A t Artecoll ll and dA ArteFill t Fill
FDA approved in 2006(Artefill) Made up of 20% precision-filtered polymethylmethacrylate microspheres and 80% purified bovine collagen Pros: long-lasting, g g, must be injected j correctly Cons: skin testing required, contraindicated with allergies, thin skin surgical excisions required for removal, multiple treatments required Recommended use: nasolabial folds
Hyaluronic Acid: Captique
FDA approved in 2004 Bacterial fermentation-derived hyaluronic y acid Pros: safe, reliable, user-friendly, predictable results, results no allergy testing Cons: rare allergic reactions, postinjection j swelling, g, p pain Recommended use: moderate to severe facial wrinkles
Hyaluronic Acid: R t l Restylane
FDA approved in 2003 Bacterial-cultured stabilized hyaluronic y acid Pros: safe, reliable, user-friendly, predictable results, results no allergy testing Cons: rare allergic reactions and particles may y lead to uneven distribution Recommended use: superficial defects, lips, lines, contouring for moderate to severe wrinkles i kl
Hyaluronic Acid: Perlane
FDA approved in 2007 High-viscosity g y bacterial-cultured hyaluronic acid Pros: excellent for deeper folds requiring a thicker filler filler, fills deep folds with less material than Restylane Cons: rare allergic g reactions Recommended use: shaping facial contours, defining cheeks, eliminating d deep f ld and folds d enlarging l i li lips
Hyaluronic Acid: Juvederm Ult and Ultra d Ultra Ult plus l
FDA approved in 2006 Bacterial-cultured stabilized hyaluronic y acid Smooth-consistency gel Pros: safe, reliable, user-friendly, no allergy testing Cons: temporary injection-site redness and tenderness Recommended use: lips, lines, contouring moderate wrikles
Importance of HA fluid retention Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring polysaccharide(sugar) The most important characteristics of hyaluronic acid relevant to its performance as a dermal filler is its fluid retention, i.e., water binding capabilities
Possible side effects and complications with fillers
1. 2. 3. 4 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
Early
Bruising g Swelling Pain Herpes Overcorrection Undercorrection Necrosis Hematoma
Late
Allergic g reaction Asymmetry Scarring Nodules Granulomas Elevations Migration Lumping
Before and After Fillers
Before and After Filler
Filler for tear troughs
Before and After Fillers in Lips
Before and After Fillers in Lips
Before and After Fillers in Lips
Removal of Fillers from Lips
Removal of Fillers from Lips
Removal of Fillers from Lips
Latisse for hypotrichosis
Latisse is FDA approved to grow eyelashes, making them longer, thicker and darker. Applied at night to the upper eyelid margins at the base of the lashes. Patients with a history of abnormal intraocular pressure need to be supervised by their ophthalmologist.
Latisse: Side Effects
May cause darkening of the eyelid skin. May cause increased brown pigmentation of the iris. May y cause itching g sensation or redness of the eyes. May cause dry eyes.
You might also like
- Botulinum Toxins: Cosmetic and Clinical ApplicationsFrom EverandBotulinum Toxins: Cosmetic and Clinical ApplicationsJoel L. CohenNo ratings yet
- Neurotoxins and Fillers in Facial Esthetic SurgeryFrom EverandNeurotoxins and Fillers in Facial Esthetic SurgeryBradford M. TowneNo ratings yet
- Elite Botox TrainingDocument169 pagesElite Botox Trainingcarolina100% (4)
- AMET Botox and FillerDocument186 pagesAMET Botox and Fillerhesham100% (2)
- Cosmetic Uses of Botulinum ToxinDocument28 pagesCosmetic Uses of Botulinum Toxineby_3tamaNo ratings yet
- BOTOX LectureDocument74 pagesBOTOX LectureAnonymous 8hVpaQdCtr100% (6)
- Age-less: The Definitive Guide to Botox, Collagen, Lasers, Peels, and Other Solutions for Flawless SkinFrom EverandAge-less: The Definitive Guide to Botox, Collagen, Lasers, Peels, and Other Solutions for Flawless SkinRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- CelluliteDocument8 pagesCelluliteAdityaNo ratings yet
- MesobotoxDocument12 pagesMesobotoxNiculae Bogdan Dimitrie100% (1)
- BoTox Injection Technique.15Document8 pagesBoTox Injection Technique.15mickey_hayden67% (3)
- Botox FillerDocument42 pagesBotox Fillermeiranty NingrumNo ratings yet
- Botox Training Courses, Dermal Filler, PDO Threads CoursesDocument39 pagesBotox Training Courses, Dermal Filler, PDO Threads CoursesSkinoza Academy67% (3)
- Holistic Microneedling: The Manual of Natural Skin Needing and Derma Roller UseFrom EverandHolistic Microneedling: The Manual of Natural Skin Needing and Derma Roller UseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Hypo-Pigmentation Of The Skin A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypo-Pigmentation Of The Skin A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Anti-Aging Therapeutics Volume XIVFrom EverandAnti-Aging Therapeutics Volume XIVRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Cosmetic Dry Needling: Using Acupuncture for Cosmetic Gains for Those Not Trained in Traditional Acupuncture TheoryFrom EverandCosmetic Dry Needling: Using Acupuncture for Cosmetic Gains for Those Not Trained in Traditional Acupuncture TheoryNo ratings yet
- Botox EbookDocument15 pagesBotox Ebookdoraemon100% (2)
- The Face of the Future: Look Natural, Not Plastic: A Less-Invasive Approach to Enhance Your Beauty and Reverse Facial AgingFrom EverandThe Face of the Future: Look Natural, Not Plastic: A Less-Invasive Approach to Enhance Your Beauty and Reverse Facial AgingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Your Complete Guide to Facial Rejuvenation Facelifts - Browlifts - Eyelid Lifts - Skin Resurfacing - Lip AugmentationFrom EverandYour Complete Guide to Facial Rejuvenation Facelifts - Browlifts - Eyelid Lifts - Skin Resurfacing - Lip AugmentationNo ratings yet
- 10-28 InjectablesDocument31 pages10-28 Injectablessalibagustavo60% (5)
- Safety Injectables WorkbookDocument110 pagesSafety Injectables Workbookgeraffe94% (17)
- Botox in Facial AestheticsDocument27 pagesBotox in Facial AestheticsTip Piraya100% (5)
- Injectable ChartDocument2 pagesInjectable ChartAlejandro De La Cerda100% (2)
- Shaping Lips With FillersDocument4 pagesShaping Lips With FillersElaine Medeiros75% (4)
- BotulinumDocument151 pagesBotulinumisabel90% (10)
- Z Hãng Algeness dermal filler training manual 2019 - Giới thiệu sản phẩm PDFDocument156 pagesZ Hãng Algeness dermal filler training manual 2019 - Giới thiệu sản phẩm PDFLe Dung100% (1)
- TreadliftDocument39 pagesTreadliftanggraini100% (5)
- Upper Face BotoxDocument32 pagesUpper Face Botoxyaseer arafat67% (3)
- Facial Lifting With Aptos ThreadsDocument9 pagesFacial Lifting With Aptos ThreadsAlejandro Saldarriaga OchoaNo ratings yet
- The Dermal Filler Approach FinalDocument32 pagesThe Dermal Filler Approach FinalhenkyNo ratings yet
- Module 1, Course B - A Practical Guide To Botulinum Toxin Type A - The Scientific Art of Softening Lines and Wrinkles 2Document97 pagesModule 1, Course B - A Practical Guide To Botulinum Toxin Type A - The Scientific Art of Softening Lines and Wrinkles 2Heather Marie Mathis100% (1)
- 2012 @dentallib Rebecca Small A Practical Guide To Dermal Filler PDFDocument193 pages2012 @dentallib Rebecca Small A Practical Guide To Dermal Filler PDFДмитрий Матвеев75% (8)
- 12 Filler PointsDocument15 pages12 Filler PointsSripada Lk Kingjorn100% (1)
- 2018 Hassan Galadari (Auth.) - Soft Tissue Augmentation - Principles and PracticeDocument92 pages2018 Hassan Galadari (Auth.) - Soft Tissue Augmentation - Principles and PracticeMohan100% (3)
- Simplified Facial RejuvenationDocument627 pagesSimplified Facial RejuvenationDicu Ovidiu100% (6)
- CanulaDocument3 pagesCanulaCatalina Soler Lioi100% (1)
- V LIFT PRO PDO Threads Brochure EnglishDocument24 pagesV LIFT PRO PDO Threads Brochure EnglishMichele Carvalho100% (3)
- 2 5283002287399110242 PDFDocument190 pages2 5283002287399110242 PDFAndra Larisa Ciolpan100% (7)
- Introductory Botulinum PresentationDocument113 pagesIntroductory Botulinum Presentationprontaprintpottersbar100% (5)
- Cog Thread LiftDocument5 pagesCog Thread Liftemilly vidya71% (7)
- Understanding Thread Lifting (History)Document5 pagesUnderstanding Thread Lifting (History)Anonymous LnWIBo1G100% (1)
- Nonsurgical Lip and Eye Rejuvenation Techniques: Gabriella Fabbrocini Maria Pia de Padova Antonella TostiDocument125 pagesNonsurgical Lip and Eye Rejuvenation Techniques: Gabriella Fabbrocini Maria Pia de Padova Antonella Tostikleidi8586% (7)
- Facial MesotherapyDocument3 pagesFacial Mesotherapydanielagonzalezt5No ratings yet
- Mesoglow y MesoliftDocument2 pagesMesoglow y MesoliftPablo BaudinoNo ratings yet
- Polydioxanone Thread LiftingDocument4 pagesPolydioxanone Thread LiftingGLORIANo ratings yet
- Botulinum Toxins in Clinical Aesthetic Practice 3rd Edition Volume Two - Functional Anatomy and Injection Techniques 2018Document237 pagesBotulinum Toxins in Clinical Aesthetic Practice 3rd Edition Volume Two - Functional Anatomy and Injection Techniques 2018Dogukan Demir75% (4)
- Laser / IPL Technology for Skin Care: A Comprehensive Technical and Informative TextbookFrom EverandLaser / IPL Technology for Skin Care: A Comprehensive Technical and Informative TextbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Module 2, Course B - FillersDocument120 pagesModule 2, Course B - FillersHeather Marie Mathis100% (2)
- The Art of Threads A Comprehensive ReviewDocument17 pagesThe Art of Threads A Comprehensive Reviewalejandro Gonzàlez80% (5)
- Cosmetic Dermatology: Products and ProceduresFrom EverandCosmetic Dermatology: Products and ProceduresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Dermal Filler 4Document59 pagesDermal Filler 4Ahmed Sad100% (1)
- Flawless Skin: Skin Resurfacing Guide for Acne Scarring - Ageing Lines - Sun Damage - PigmentationFrom EverandFlawless Skin: Skin Resurfacing Guide for Acne Scarring - Ageing Lines - Sun Damage - PigmentationNo ratings yet
- Thread Lift Classification Technique and How To Approach To The PatientDocument9 pagesThread Lift Classification Technique and How To Approach To The PatientErick SimbolonNo ratings yet
- Skin Beauty InjectionsDocument12 pagesSkin Beauty Injectionst3kla100% (1)
- Criteria of SelectionDocument12 pagesCriteria of SelectionVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Non Surgical Management of Periapical Lesions Using Calcium HydroxideDocument6 pagesNon Surgical Management of Periapical Lesions Using Calcium HydroxideVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Op Dent MCQDocument11 pagesOp Dent MCQammarstein89No ratings yet
- EditorialDocument2 pagesEditorialVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Diff Betwn Inlay and Amalgam CavityDocument7 pagesDiff Betwn Inlay and Amalgam CavityVinisha Vipin Sharma100% (1)
- All CeramicsDocument8 pagesAll CeramicsVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- 10 1002@sca 21331Document6 pages10 1002@sca 21331Vinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Preparation Updated May2017 Prof Marco VersianiDocument159 pagesMechanical Preparation Updated May2017 Prof Marco VersianiVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- 24CE09 Enamel Therapy THPM HODocument8 pages24CE09 Enamel Therapy THPM HOVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Some Basics of LasersDocument102 pagesSome Basics of LasersVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Challenges in Working Length DeterminationDocument101 pagesChallenges in Working Length DeterminationVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Content ServerDocument6 pagesContent ServerVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Acupuncture in Dentistry PDFDocument73 pagesAcupuncture in Dentistry PDFVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- NatlJMaxillofacSurg7110-8069052 222450Document7 pagesNatlJMaxillofacSurg7110-8069052 222450Vinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Content ServerDocument6 pagesContent ServerVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Eaat 14 I 1 P 217Document6 pagesEaat 14 I 1 P 217Vinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- 172/pdf/dt July 14 NPR Ruddle FNLDocument11 pages172/pdf/dt July 14 NPR Ruddle FNLVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Content ServerDocument5 pagesContent ServerVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aprd 2 (3) 60-62 PDFDocument3 pagesAprd 2 (3) 60-62 PDFVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Glide Path PreparationDocument5 pagesGlide Path PreparationVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Content ServerDocument6 pagesContent ServerVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Laser in Conservative Dentistry & EndodonticsDocument75 pagesLaser in Conservative Dentistry & EndodonticsVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Content ServerDocument17 pagesContent ServerVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Show TextDocument1 pageShow TextVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Content ServerDocument6 pagesContent ServerVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dentin HypersensitivityDocument62 pagesDentin HypersensitivityVinisha Vipin Sharma100% (1)
- EchsDocument20 pagesEchsVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Practice: Radiographic Evidence of Postoperative Healing 12 Years Following Root Canal Treatment - A Case ReportDocument5 pagesPractice: Radiographic Evidence of Postoperative Healing 12 Years Following Root Canal Treatment - A Case ReportVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Restorations: Bonded Porcelain Veneers - Part 1: PerspectiveDocument5 pagesCeramic Restorations: Bonded Porcelain Veneers - Part 1: PerspectiveVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Jced 6 E230Document7 pagesJced 6 E230Vinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- RSC Article Template-Mss - DaltonDocument15 pagesRSC Article Template-Mss - DaltonIon BadeaNo ratings yet
- The Body Shop Case Analysis. The Challenges of Managing Business As Holistic ConfigurationDocument28 pagesThe Body Shop Case Analysis. The Challenges of Managing Business As Holistic ConfigurationHanna AbejoNo ratings yet
- MS Lync - Exchange - IntegrationDocument29 pagesMS Lync - Exchange - IntegrationCristhian HaroNo ratings yet
- William Hallett - BiographyDocument2 pagesWilliam Hallett - Biographyapi-215611511No ratings yet
- (Isaac Asimov) How Did We Find Out About AntarcticDocument24 pages(Isaac Asimov) How Did We Find Out About AntarcticDrBabu PSNo ratings yet
- Hw10 SolutionsDocument4 pagesHw10 Solutionsbernandaz123No ratings yet
- LEMBAR JAWABAN CH.10 (Capital Budgeting Techniques)Document4 pagesLEMBAR JAWABAN CH.10 (Capital Budgeting Techniques)Cindy PNo ratings yet
- Stonehell Dungeon 1 Down Night Haunted Halls (LL)Document138 pagesStonehell Dungeon 1 Down Night Haunted Halls (LL)some dude100% (9)
- 2022 Tony Elumelu EntrepreneursDocument10 pages2022 Tony Elumelu EntrepreneursOladosu EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- MCQ Floyd ElexDocument87 pagesMCQ Floyd ElexnicoleNo ratings yet
- Java Complete Collection FrameworkDocument28 pagesJava Complete Collection FrameworkkhushivanshNo ratings yet
- Camless EnginesDocument4 pagesCamless EnginesKavya M BhatNo ratings yet
- E-Mobility and SafetyDocument77 pagesE-Mobility and SafetySantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Inorganic PolymersDocument24 pagesTerm Paper Inorganic PolymersCasey Karua0% (1)
- UAV Design TrainingDocument17 pagesUAV Design TrainingPritam AshutoshNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Urja Vikas Nigam LTD., Vadodara: Request For ProposalDocument18 pagesGujarat Urja Vikas Nigam LTD., Vadodara: Request For ProposalABCDNo ratings yet
- UFO Yukon Spring 2010Document8 pagesUFO Yukon Spring 2010Joy SimsNo ratings yet
- Principles of Supply Chain Management A Balanced Approach 4th Edition Wisner Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesPrinciples of Supply Chain Management A Balanced Approach 4th Edition Wisner Solutions Manualoutlying.pedantry.85yc100% (28)
- Aribah Ahmed CertificateDocument2 pagesAribah Ahmed CertificateBahadur AliNo ratings yet
- De Thi Chon Hoc Sinh Gioi Cap Tinh Mon Tieng Anh Lop 12 So GD DT Thanh Hoa Nam Hoc 2015 2016Document11 pagesDe Thi Chon Hoc Sinh Gioi Cap Tinh Mon Tieng Anh Lop 12 So GD DT Thanh Hoa Nam Hoc 2015 2016Thuy LinggNo ratings yet
- International Freight 01Document5 pagesInternational Freight 01mature.ones1043No ratings yet
- European Construction Sector Observatory: Country Profile MaltaDocument40 pagesEuropean Construction Sector Observatory: Country Profile MaltaRainbootNo ratings yet
- Refutation EssayDocument6 pagesRefutation Essayapi-314826327No ratings yet
- Galman V PamaranDocument7 pagesGalman V PamaranChow Momville EstimoNo ratings yet
- Soundarya Lahari Yantras Part 6Document6 pagesSoundarya Lahari Yantras Part 6Sushanth Harsha100% (1)
- Table of Specification 1st QDocument5 pagesTable of Specification 1st QVIRGILIO JR FABINo ratings yet
- Analytics Designer - Comment Deletion - SAP CommunityDocument6 pagesAnalytics Designer - Comment Deletion - SAP CommunityARPITA BISWASNo ratings yet
- Outline Calculus3Document20 pagesOutline Calculus3Joel CurtisNo ratings yet
- Inventions Over The Last 100 YearsDocument3 pagesInventions Over The Last 100 YearsHombreMorado GamerYTNo ratings yet
- DR S GurusamyDocument15 pagesDR S Gurusamybhanu.chanduNo ratings yet