Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Theory of Machines - Sheet1
Uploaded by
Dr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Theory of Machines - Sheet1
Uploaded by
Dr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyCopyright:
Available Formats
South Valley University Faculty of Engineering Dept.
of Mechanical Engineering Question One:
Theory of Machine Code: ENM222 2013/2014
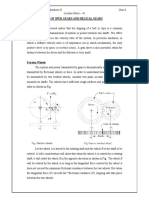
1. What is the main purpose of gears? 2. Explain the terms : Module, Pitch circle, Circular pitch, Clearance, Face of a tooth, Flank of a tooth, Backlash, Dedendum and Addendum. 3. What is the main advantage and disadvantage of: spur, helical, double helical, bevel , worm, Rack and pin Gears. 4. what are the main Factors considered in gear selection 5. What do you understand by gear train? Discuss the various types of gear trains. 6. Explain briefly the differences between simple, compound, and epicyclic gear trains. What are the special advantages of epicyclic gear trains ? 7. Explain the procedure adopted for designing the spur wheels. 8. How the velocity ratio of epicyclic gear train is obtained by tabular method? 9. Explain with a neat sketch the sun and planet wheel. 10. What are the various types of the torques in an epicyclic gear train ?
Question Two:
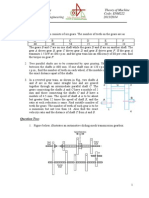
1. In a simple gear train, if the number of idle gears is odd, then the motion of driven gear will (a) be same as that of driving gear (b) be opposite as that of driving gear (c) depend upon the number of teeth on the driving gear (d) none of the above 2. The train value of a gear train is (a) equal to velocity ratio of a gear train (b) reciprocal of velocity ratio of a gear train (c) always greater than unity (d) always less than unity 3. When the axes of first and last gear are co-axial, then gear train is known as (a) simple gear train (b) compound gear train (c) reverted gear train (d) epicyclic gear train 4. In a clock mechanism, the gear train used to connect minute hand to hour hand, is (a) epicyclic gear train (b) reverted gear train (c) compound gear train (d) simple gear train 5. In a gear train, when the axes of the shafts, over which the gears are mounted, move relative to a fixed axis, is called (a) simple gear train (b) compound gear train (c) reverted gear train (d) epicyclic gear train 1
South Valley University Faculty of Engineering Dept. of Mechanical Engineering
Theory of Machine Code: ENM222 2013/2014
6. A differential gear in an automobile is a (a) simple gear train (b) epicyclic gear train (c) compound gear train (d) none of these 7. A differential gear in automobilies is used to (a) reduce speed (b) assist in changing speed (c) provide jerk-free movement of vehicle (d) help in turning 8. The two parallel and coplanar shafts are connected by gears having teeth parallel to the axis of the shaft. This arrangement is called a. spur gearing (b) helical gearing (c) bevel gearing (d) spiral gearing 9. The type of gears used to connect two non-parallel non-intersecting shafts are a. spur gears (b) helical gears (c) spiral gears (d) none of these 10. An imaginary circle which by pure rolling action, gives the same motion as the actual gear, is called a. addendum circle (b) dedendum circle (c) pitch circle (d) clearance circle 11. The size of a gear is usually specified by a. pressure angle (b) circular pitch (c) diametral pitch (d) pitch circle diameter 12. The radial distance of a tooth from the pitch circle to the bottom of the tooth, is called a. dedendum (b) addendum (c) clearance (d) working depth 13. The module is the reciprocal of a. diametral pitch (b) circular pitch (c) pitch diameter (d) none of these 14. If the module of a gear be m, the number of teeth T and pitch circle diameter D, then (a) m = D/T (b) D = T/m (c) m = D/2T (d) none of these
With my best wishes Dr. Nouby M. Ghazaly
You might also like
- Toothed Gearing Types and ApplicationsDocument35 pagesToothed Gearing Types and ApplicationsSomnath Somadder100% (1)
- M&M MCQDocument18 pagesM&M MCQGgfgNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines - Final Report 2014Document5 pagesTheory of Machines - Final Report 2014Dr-Nouby Mahdy Ghazaly100% (1)
- Question Bank (MCQS) : Q, Then It Would Result in Grashof's Linkage Provided ThatDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank (MCQS) : Q, Then It Would Result in Grashof's Linkage Provided ThatPrasad Govind KumbharNo ratings yet
- Machine DesignDocument20 pagesMachine DesignHabibUllah0% (2)
- Kom MCQ With 2 Marks and 16 MarksDocument20 pagesKom MCQ With 2 Marks and 16 MarksMushini Nagabhushan0% (1)
- Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines Assignment QuestionsDocument2 pagesKinematics and Dynamics of Machines Assignment QuestionsvishalNo ratings yet
- Me III II DMM II LnotesDocument33 pagesMe III II DMM II LnotesChandu MallamNo ratings yet
- Ars and CamsDocument85 pagesArs and CamsHariharan MNo ratings yet
- Module-5 Toothed GearingDocument4 pagesModule-5 Toothed Gearingonkarlamkane4No ratings yet
- Assignment Unit - 1: 2) .A Pair of Involute Gears Is in Mesh. The Application Restricts The Space To Accommodate TheseDocument4 pagesAssignment Unit - 1: 2) .A Pair of Involute Gears Is in Mesh. The Application Restricts The Space To Accommodate TheserahulNo ratings yet
- 9A14402 Theory of MachinesDocument8 pages9A14402 Theory of MachinessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Parametric Modelling of Straight Bevel Gearing System and Analyze The Forces and Stresses by Analytical ApproachDocument5 pagesParametric Modelling of Straight Bevel Gearing System and Analyze The Forces and Stresses by Analytical ApproachseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - 1 - Design of Spur and Helical GearsDocument41 pagesUnit 3 - 1 - Design of Spur and Helical GearsY20me135 V.LokeshNo ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering: Objective Questions and AnswersDocument121 pagesAutomobile Engineering: Objective Questions and AnswersAjin Sadanandan100% (2)
- Mod-3B-Helical GearDocument2 pagesMod-3B-Helical GearSharthak GhoshNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachinesDocument2 pagesKinematics of Machinessameer_m_daniNo ratings yet
- 18mec201t CT 2 QP and Ak Batch 1Document6 pages18mec201t CT 2 QP and Ak Batch 1SREEJAUN T J (RA2111025010015)No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityKrinal AdakiNo ratings yet
- Design of A Two-Stage Cycloidal Gear Reducer WithDocument14 pagesDesign of A Two-Stage Cycloidal Gear Reducer WithAlejandro ChavezNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 - GearsDocument2 pagesTutorial 5 - GearsAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery UNIT 4Document4 pagesKinematics of Machinery UNIT 4MugilNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Total Marks: 70: Printed Pages: Sub Code: Paper Id: Roll NoDocument3 pagesTime: 3 Hours Total Marks: 70: Printed Pages: Sub Code: Paper Id: Roll NoAwanish SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document9 pagesUnit 5Sachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Problems s3Document3 pagesProblems s3zangue billy james67% (3)
- Kinematics of Machinery Question BankDocument92 pagesKinematics of Machinery Question BankNatesha Sundharan100% (2)
- CH 8Document3 pagesCH 8أحمد عبدالجليلNo ratings yet
- KDMDocument3 pagesKDMDeep RavalNo ratings yet
- ME-352 (Machanics of Machinery Sessional)Document5 pagesME-352 (Machanics of Machinery Sessional)Ali NowrozNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Straight Line Mechanism Gate BitsDocument9 pagesUnit 3 Straight Line Mechanism Gate BitsVenkateswar Reddy MallepallyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: MCQ BankDocument7 pagesUnit 1: MCQ BankrishitNo ratings yet
- QBDocument8 pagesQBrahulNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Mechanisms Key ConceptsDocument39 pagesUnit 4 Mechanisms Key ConceptsYUVARAJAN DNo ratings yet
- TOM Question BankDocument10 pagesTOM Question BankMadhan Kumar GovindarajuNo ratings yet
- Sheet1Document4 pagesSheet1Mahmoud salahNo ratings yet
- New Friction Mechanical TransmissionDocument5 pagesNew Friction Mechanical TransmissionInternational Journal of Engineering Inventions (IJEI)No ratings yet
- Knee Power Generation: An Overview of Hardware and Working PrincipleDocument93 pagesKnee Power Generation: An Overview of Hardware and Working PrincipleSRL MECHNo ratings yet
- MCQ Tom Chap. 2Document11 pagesMCQ Tom Chap. 2AdityaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Fof KOMDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank Fof KOMPriyajyoti sarkarNo ratings yet
- Unit-1: Introduction: Question BankDocument12 pagesUnit-1: Introduction: Question BankAmit BharadwajNo ratings yet
- 154 Top Theory of Machines MCQDocument26 pages154 Top Theory of Machines MCQRajpalsinh JadejaNo ratings yet
- 154 Top Theory of Machines - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument26 pages154 Top Theory of Machines - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answersahmish kabbaxeNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Theory of Machines MCQDocument23 pagesMechanical Engineering Theory of Machines MCQwalunjmayur45275No ratings yet
- Subjective Questions (Any Three) :-: Univ. Roll NoDocument3 pagesSubjective Questions (Any Three) :-: Univ. Roll NoSonukNo ratings yet
- Gears: Classification, profiles, advantagesDocument18 pagesGears: Classification, profiles, advantagesSharthak GhoshNo ratings yet
- Upto 2010 KomDocument36 pagesUpto 2010 KomRajueswarNo ratings yet
- Class Test 4 & 5 Cams - Gears - Assignment Questions KomDocument10 pagesClass Test 4 & 5 Cams - Gears - Assignment Questions KomVenkateswar Reddy MallepallyNo ratings yet
- Sheet 5Document3 pagesSheet 5Fouad MohamedNo ratings yet
- 6 Gear TrainDocument3 pages6 Gear TrainAnuj ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Design, Analysis & Fabrication of Shaft Driven Bicycle: Dandage R.V. Patil A.A., Kamble P.NDocument10 pagesDesign, Analysis & Fabrication of Shaft Driven Bicycle: Dandage R.V. Patil A.A., Kamble P.Nsrihariharan dhandapaniNo ratings yet
- KOM Question BankDocument10 pagesKOM Question Banknsubbu_mitNo ratings yet
- W - 6 - Mce 3513 - Lo2Document19 pagesW - 6 - Mce 3513 - Lo2Muhammed RazaNo ratings yet
- 133BB112017Document3 pages133BB112017prempragupta123No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1ankursolanki13No ratings yet
- Ii Me6401 ADocument2 pagesIi Me6401 AananthakumarNo ratings yet
- Upto 2010 KomDocument36 pagesUpto 2010 KompsnasabariNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Differential Geometry and Saddle Synthesis of LinkagesFrom EverandKinematic Differential Geometry and Saddle Synthesis of LinkagesNo ratings yet
- High Speed Off-Road Vehicles: Suspensions, Tracks, Wheels and DynamicsFrom EverandHigh Speed Off-Road Vehicles: Suspensions, Tracks, Wheels and DynamicsNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines - Final Exams2015Document2 pagesTheory of Machines - Final Exams2015Dr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Vibration3 Exam MiniaDocument2 pagesVibration3 Exam MiniaDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibration 3rd Years 2015Document1 pageMechanical Vibration 3rd Years 2015Dr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Contact Stress Distribution of Deep Groove Ball Bearing Using AbaqusDocument13 pagesContact Stress Distribution of Deep Groove Ball Bearing Using AbaqusDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Power Management Strategies For HybridDocument5 pagesPower Management Strategies For HybridDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of Drum Brake Performance For Passenger CarDocument4 pagesExperimental Investigation of Drum Brake Performance For Passenger CarDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Influence of Misalignment and Backlash On Spur Gear Using FemDocument4 pagesInfluence of Misalignment and Backlash On Spur Gear Using FemDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Applications of Finite Element Stress Analysis of HeavyDocument5 pagesApplications of Finite Element Stress Analysis of HeavyDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- A Novel Approach For The Effect of The Housing Height of Anti-Friction Bearings On The Generated Vibration Using Dynamic ModelDocument15 pagesA Novel Approach For The Effect of The Housing Height of Anti-Friction Bearings On The Generated Vibration Using Dynamic ModelDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Fatigue Analysis of Heavy Duty Truck FramesDocument6 pagesA Review of The Fatigue Analysis of Heavy Duty Truck FramesDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- The Future Development and Analysis of Vehicle ActiveDocument7 pagesThe Future Development and Analysis of Vehicle ActiveDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Thermal Analysis of Both Ventilated and Full Disc Brake Rotors With Frictional Heat GenerationDocument20 pagesThermal Analysis of Both Ventilated and Full Disc Brake Rotors With Frictional Heat GenerationDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Mid Term ExamDocument2 pagesMid Term ExamDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Answer ALL Questions.: Question OneDocument1 pageAnswer ALL Questions.: Question OneDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations - Lecture1Document20 pagesMechanical Vibrations - Lecture1Dr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Brake SheetDocument1 pageBrake SheetDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibrations - Sheet1Document1 pageMechanical Vibrations - Sheet1Dr-Nouby Mahdy Ghazaly100% (1)
- Answer ALL Questions.: Question OneDocument1 pageAnswer ALL Questions.: Question OneDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Answer ALL Questions.: Question OneDocument1 pageAnswer ALL Questions.: Question OneDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines - Lecture1Document30 pagesTheory of Machines - Lecture1Dr-Nouby Mahdy Ghazaly100% (1)
- MAEM 421 Automotive Electronics1Document47 pagesMAEM 421 Automotive Electronics1Dr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- DR - Nouby Ghazaly CV 2014Document9 pagesDR - Nouby Ghazaly CV 2014Dr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines - Sheet2Document2 pagesTheory of Machines - Sheet2Dr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines - Lecture2Document25 pagesTheory of Machines - Lecture2Dr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Machine Theory Bachelor in Mechanical Engineering: Gear TrainsDocument16 pagesMachine Theory Bachelor in Mechanical Engineering: Gear TrainsDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Geometric Parameters of A New Wedge Brake Using Taguchi ApproachDocument13 pagesOptimization of Geometric Parameters of A New Wedge Brake Using Taguchi ApproachDr-Nouby Mahdy GhazalyNo ratings yet
- A Review of Automotive Brake Squeal MechanismsDocument5 pagesA Review of Automotive Brake Squeal MechanismsDr-Nouby Mahdy Ghazaly100% (1)
- New Scientific IdeasDocument10 pagesNew Scientific IdeasRaageshwori PradhanNo ratings yet
- Cuspal Inter Link Theory.Document6 pagesCuspal Inter Link Theory.Gopal krishna PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- 13 Rotational Dynamics v2Document5 pages13 Rotational Dynamics v2Hubert YuanNo ratings yet
- Occasionalism: God as the Sole CauseDocument3 pagesOccasionalism: God as the Sole CauseSibghat ShahNo ratings yet
- Mekanika Benda Langit - Gerak Dalam Orbit & Transfer OrbitDocument14 pagesMekanika Benda Langit - Gerak Dalam Orbit & Transfer OrbitmarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Interpretative Methodology From Literary Criticism: Carnivalesque Analysis of Popular Culture: Jackass, South Park and 'Everyday' CultureDocument15 pagesInterpretative Methodology From Literary Criticism: Carnivalesque Analysis of Popular Culture: Jackass, South Park and 'Everyday' CultureIvana VujićNo ratings yet
- Dicks, D. R. - Solstices, Equinoxes, & The Presocratics - JHS, 86 - 1966!26!40Document16 pagesDicks, D. R. - Solstices, Equinoxes, & The Presocratics - JHS, 86 - 1966!26!40the gatheringNo ratings yet
- CognizantDocument75 pagesCognizantShaiwal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Normi Na EmpiDocument2 pagesNormi Na EmpiEdriel TibonNo ratings yet
- Star David SymbolDocument2 pagesStar David Symbollangvirag100% (2)
- Nature, Scope and Method of EthicsDocument24 pagesNature, Scope and Method of Ethicsolive100% (1)
- Lit21st 1 Semester (1 Quarter) Social Innovation Fundamental: Global Issues I. The Universe Some Terminologies & Points To PonderDocument13 pagesLit21st 1 Semester (1 Quarter) Social Innovation Fundamental: Global Issues I. The Universe Some Terminologies & Points To PonderRoie Andrae ArayonNo ratings yet
- Statistical Mechanics Homework 1Document2 pagesStatistical Mechanics Homework 1JungHyunParkNo ratings yet
- Kalapurusha Concept by Astrologer Rakesh AroraDocument7 pagesKalapurusha Concept by Astrologer Rakesh ArorakuberastrologyNo ratings yet
- The Idol of SaturnDocument6 pagesThe Idol of SaturnDAVIDNSBENNETTNo ratings yet
- PhysciDocument402 pagesPhysciRosielyn Fano CatubigNo ratings yet
- Diffusion PlasmaDocument34 pagesDiffusion PlasmaPriyanka Lochab100% (1)
- OliverCage ElectronicMeasurementsAndInstrumentationt PDFDocument749 pagesOliverCage ElectronicMeasurementsAndInstrumentationt PDFSubhajit Saha100% (1)
- The Secrets of AstrologyDocument192 pagesThe Secrets of Astrologyskballenm92% (26)
- Aristotle'S Criticism On Theory of FormsDocument2 pagesAristotle'S Criticism On Theory of FormsGhina SaleemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LinguisticsDocument16 pagesIntroduction To LinguisticsWagdi Bin-HadyNo ratings yet
- Rendezvous With Rama by Arthur C. Clarke ExtractDocument17 pagesRendezvous With Rama by Arthur C. Clarke ExtractOrion Publishing Group38% (8)
- Guidelines To Determine ProfessionDocument5 pagesGuidelines To Determine Professionsurinder sangarNo ratings yet
- The A.P.R.O. Bulletin May-Jun 1972Document9 pagesThe A.P.R.O. Bulletin May-Jun 1972Nicholas VolosinNo ratings yet
- StsDocument5 pagesStsNoemie Opis0% (1)
- Atkinson - Practical Mental Influence and Mental FascinationDocument94 pagesAtkinson - Practical Mental Influence and Mental Fascinationmuzicoterapie1092No ratings yet
- Astrology and MarriageDocument32 pagesAstrology and MarriagedrjperumalNo ratings yet
- The Egyptian View of First Principles and the Nature of RealityDocument4 pagesThe Egyptian View of First Principles and the Nature of RealityJoão Pedro FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Yu-Zhang 2005 - Three Parameter ALDDocument14 pagesYu-Zhang 2005 - Three Parameter ALDApoorva KhandelwalNo ratings yet