Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mathematics
Uploaded by
Asifrajar244Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathematics
Uploaded by
Asifrajar244Copyright:
Available Formats
Mathematics Summative Assessment 2
Linear equations in two variables
Q-1 Solve the linear equation
Q-2 The points (1,3), (2,3) and (4,3) form line a. Which is parallel to the x-axis. b. Which is parallel to the y-axis. c. Passing through the origin. Q-3 If the points (3,4) lies on the graph of the equation find the value of a.
Q-4 The distance between the graphs of the equation y = -1 and y = 3 is a. 2 b.4 c.3 d. 1
Q-5 The equation x 2 = 0 on the number line is represented by a. b. c. d. A line A point Infinitely many lines Two lines
Q-6 Solve the equation: 3x 2 = 2x + 3 Q-8 Find the temperature in degree Celsius for 95 Fahrenheit. Q-9 A three wheeler scooter charges Rs 10 for the first kilometer and Rs 4.5 each for every subsequent kilometer. For a distance of x km, an amount of Rs y is paid. Write the linear equation representing the above information. Q-10 4 years before, age of a mother was 3 times the age of her daughter. Write a linear equation to represent this situation.
Probability
Q-1 One card is drawn from a well shuffled deck of 52 cards. Calculate the probability that the card will be an ace. a. 4/52 Ans- (a) Q-2 Two teams, India and Australia, play a cricket match. It is known that the probability of Australia winning the match is 3/5. What is the probability of India winning the match. Ans- 2/5 Q-3 Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event a. 2/3 b. 3/2 c. 15% d. 0.7 b. 12/52 c. 1/52 d. 2/52
Ans- (b) Q-4 What is the probability of an impossible event. Ans- 0 Q-5 A four digit number is to be formed by using the digits 2,4,7 and 8. The probability that the number will start with 7 is a. 3/4 Ans- (b) Q-6 What is the probability of a number greater than 6 for a single throw of a die a. 0 Ans- (a) Q-7 A bag contains 5 whites, 4 red and 3 black balls. A ball is drawn from the bag, find the probability that it is not a black ball. Ans- 3/4 Q- 8 A coin is tossed 2 times what is the probability of getting at most 2 heads a. 3/4 Ans - (b) b. 1/2 c.1/4 d. 4/4 b. 1 c. 1/2 d. 1/6 b. 1/4 c. 1/3 d. 1/7
Q-9 The probability an event of a trial is a. 1 Ans- (c) Q-10 Outcome of an experiment are ________ if each has the same chance of occurring. Ans- equally likely b. 0 c. Between 0 and 1 d. More than 1
Quadrilaterals
Q-1 The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is a. 360 Ans- (a) Q-2 The bisectors of any two adjacent angles of a parallelogram intersect at a. 30 b. 45 c. 60 d. 90 b. Based on the type of the polygon c. 180
Ans- (d) Q-3 The point where the three medians of the triangle intersect is called a. Circumcentre Ans- (b) Q-4 ABCD is a rectangle. Diagonals AC and BD intersect at O. If angle OAB = 35, find the measure of angle DOC. a. 110 Ans- (a) Q-5 The diagonals AC and BD of quadrilateral ABCD are equal and are perpendicular bisector of each other then quadrilateral ABCD is a. Kite b. square c. Trapezium d. none of these b. 100 c. 55 d. 70 b. Centroid c. Incetre d. Orthocenter
Ans- (b) [square] Q-6 ABCD is a rhombus with angle ABC = 40. The measure of angle ACD is a. 90 Ans- (b) b. 20 c. 40 d. 70
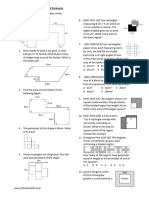
Q-7
a. 8.2 cm Ans- (d) Q- 8
b. 5.1 cm
c. 4.9 cm
d. 4.1 cm
a. 10 cm Ans- (b)
b. 5cm
c. 8 cm
d. 6 cm
Q- 9 If an angle of a parallelogram is two-third of its adjacent angle, find all the angles of the parallelogram. Ans- angle A = 108, angle B = 72, angle C = 108, angle D = 72. Q-10 ABCD is a square. AC and BD intersect at O. Find the measure of angle AOB. a. 45 Ans- (b) Q- 11 Diagonals necessarily bisect opposite angles in a a. Rectangle Ans- (d) b. parallelogram c. isosceles trapezium d. square b. 90 c. 50 d. 100
Q-1 A triangle and a rhombus are on the same base and between the same parallels. Then the ratio of area of triangle to that of rhombus is a. 1:1 Ans- (b) Q-2 Let ABCD be a parallelogram of area 124 cm2. If E and F are the mid-points of sides AB and CD respectively, then what is the area of parallelogram AEFD? Ans- 62 cm2 Q-3 Compute the area of trapezium PQRS. b. 1:2 c. 1:3 d. None of these
Ans- 180cm2 Q-4 In square ABCD, P and Q are mid-points of AB and CD respectively. If AB = 8cm and PQ and BD intersect at O, then find area of OPB. a. 8cm2 Ans- (a) Q-5 ABC is a triangle in which D is the mid-point of BC. E and F are mid-points of DC and AE respectively. If area of triangle ABC is 16 cm2, find the area of triangle DEF. Ans- 2 cm2 Q-6 ABCD is a parallelogram. P is the mid-point of AB, BD and CP intersect at Q such that CQ:QP = 3:1. If ar(PBQ) = 10 cm2, find the area of parallelogram ABCD. a. 160 cm2 Ans- (a) Q-7 Diagonal AC and BD of trapezium ABCD, in which AB II DC, intersect each other at O. The triangle which is equal in area of triangle AOD is a. Triangle AOB Ans- (b) Q- 8 ABCD is a rectangle with O as any point in its interior. If area of triangle AOD = 3cm 2 and area of triangle BOC = 6cm2, then area of rectangle ABCD is a. 9cm2 Ans- (d) b. 12cm2 c. 15cm2 d. 18cm2 b. Triangle BOC c. Triangle DOC d. Triangle ADC b. 100cm2 c. 130cm2 d. 155cm2 b. 10cm2 c. 15cm2 d. 6cm2
Circles
Q-1 If the length of a chord of a circle is 16 cm and is at a distance of 15 cm from the centre of the circle, then the radius of the circle is
a. 15 cm Ans- (c)
b. 16 cm
c. 17 cm
d. 34 cm
Q-2 The radius of a circle is 6 cm. The perpendicular distance from the centre of the circle to the chord which is 8 cm in length, is a. 5 cm Ans- (b) Q-3 One chord of a circle is known to be 10 cm. The radius of this circle must be a. 5 cm Ans- (b) Q-4 If O is the centre of a circle of radius r and AB is a chord of the circle at a distance r/2 from O, then angle BAO = a. 60 Ans- (c) Q-5 Two equal circle of radius r intersect such that each passes through the centre of the other. The length of the common chord of the circles is a. r Ans- (c) Q-6 angle CAB = 30 and angle CBO = 70, then find angle BCD b. 2r AB c. 3 r d. 3r/2 b. 45 c. 30 d. 15 b. Greater than 5 cm c. Less than 5 cm d. None of these b. 25 cm c. 27 cm d. 7 cm
Ans- angle BCD = 80 Q- 7 What is the degree measure of a semicircle? Ans- 180 Q- 8 An equilateral triangle ABC is inscribed in a circle with centre O. The measures of angle BOC is a. 30 Ans- (d) b. 60 c. 90 d. 120
Surface areas and Volumes
Q-1 If two cubes each of side 6 cm are joined face to face, then find the volume of the resulting cuboid Ans- 432 cm3 Q-2 If the sum of all the edges of a cube is 36 cm, then the volume of that cube is a. 9 cm3 Ans- (b) Q-3 On a particular day, the rain fall recorded in a terrace 6 m long and 5m broad is 15 cm. The quantity of water collected in the terrace is a. 300 liters Ans- (d) Q-4 What is the lateral surface area of a cuboid. Ans- 2h X (b+l) Q-5 If the volumes of two cubes are in the ratio 8:1, then the ratio of their edges is a. 8:1 Ans- (c) b. 22:1 c. 2:1 d. None of these b. 450 liters c. 3000 liters d. 4500 liters b. 27 cm3 c. 219 cm3 d. 729 cm3
Q-6 How many litres of water flow out of a pipe having an area of cross-section of 5 cm2 in one minute, if the speed of water in the pipe is 30 cm/sec? a. 9 L Ans- (a) Q-7 From a tap of inner radius 0.75 cm, water flows at the rate of 7 m per second. Find the volume in litres of water delivered by the pipe in one hour. a. 4455 L Ans- (a) Q-8 If the radii of two cylinders are in the ratio 2:3 and their heights are in the ratio 5:3, then find the ratio of their volumes. Ans- 20:27 Q-9 The number of surfaces of a hollow cylindrical object is a. 1 Ans- (c) Q-10 In a cylinder, if radius is halved and height is doubled, the volume will be b. 2 c.3 d. 4 b. 4400 L c. 4000 d. 4456 L b. 10 L c. 12 L d. 14 L
a. Same Ans- (c)
b. Doubled
c. Halved
d. Four times
Q-11 If the perimeter of one of the faces of a cube is 40 cm, then its volume is a. 6000 cm3 Ans- (c) Q-12 The surface area of cuboid is 3328 cm2; its dimensions are in the ratio 4:3:2. Find the volume of the cuboid. a. 12288 cm3 Ans- (a) Q-13 If the volumes of two cones are in the ratio 1:4 and their diameters are in the ratio 4:5, then the ratio of their heights, is a. 1:5 Ans- (d) Q-14 The radius of Jupiter is 11 times the radius of the earth. Calculate the ratio of volumes of Jupiter and the earth. How many earths can Jupiter accommodate? Ans- 1:1331; 1331 earths can Jupiter accommodate. Q-15 In a sphere the number of faces is a. 1 Ans- (a) Q-16 A cone and a hemisphere have equal bases and equal volumes the ratio of their heights is a. 1:2 Ans- (a) b. 2:1 c. 4:1 d. 2:1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 b. 5:4 c. 5:16 d. 25:64 b. 10000 cm3 c.11200 cm3 d. 12200 cm3 b. 1600 cm3 c. 1000 cm3 d. 600 cm3
Statistics
Q-1 The difference between the highest and lowest values of the observations is called a. Class intervals Ans- (b) Q-2 Find the range of the following data: 25,20,30,18,16,15 a. 15 Ans- (a) Q-3 Find the mean of the first five multiples of 3? b. 10 c. 5 d. 20 b. Range c. Frequency d. mean
a. 9 Ans- (a)
b. 12
c. 14
d. None of these
Q-4 What is the upper limit of the interval: 20 23 a. 20 Ans- (d) Q-5 What is the class mark of the interval 15-20 a. 15 Ans- (c) Q-6 The mean of 6 numbers is 30. If one number is excluded, their mean is 24. Find the excluded number. Ans- 60 Q-7 In a histogram, each class rectangle is constructed with base as a. Frequency Ans- (b) Q-8 If the difference of mode and median of a data is 24, then find the difference of median and mean. Ans- 12 b. Class-interval c. Range d. Size of the class b. 20 c. 17.5 d. None of these b. 21 c. 22 d. None of these
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Math 7 Week 5Document16 pagesMath 7 Week 5Rey Mark RamosNo ratings yet
- Geometry FlashCardsDocument26 pagesGeometry FlashCardsjcargs3100% (1)
- Finding Interior Angles 1Document2 pagesFinding Interior Angles 1mattNo ratings yet
- GCSE 3DTrigAndPythagorasDocument20 pagesGCSE 3DTrigAndPythagorasJean AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Ellem Silva Nascimento - 6.7 Applying Special Right Triangles PracticeDocument4 pagesKami Export - Ellem Silva Nascimento - 6.7 Applying Special Right Triangles PracticeEllem Silva nascimentoNo ratings yet
- Interior and Exterior AnglesDocument17 pagesInterior and Exterior AnglesDaisy100% (1)
- 2D ShapesssDocument4 pages2D ShapesssEdina BisićNo ratings yet
- Sections of SolidDocument2 pagesSections of SolidburaqsameerNo ratings yet
- Triangles - Geoemetry Worksheet - SAT Reasoning TestDocument9 pagesTriangles - Geoemetry Worksheet - SAT Reasoning TestGurukul24x7No ratings yet
- Digital Text BookDocument12 pagesDigital Text BookBindu Vinu100% (1)
- WLP Mathematics Q3 W1Document9 pagesWLP Mathematics Q3 W1Maestro Sonny TVNo ratings yet
- Digital Text BookDocument11 pagesDigital Text BookLekshmi LachuNo ratings yet
- Deductive Geometry: This Chapter at A GlanceDocument46 pagesDeductive Geometry: This Chapter at A Glancesquishyapply100% (1)
- Nota Chapter 6 3D Shapes F2Document3 pagesNota Chapter 6 3D Shapes F2Fatin MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Parallelogrames PDFDocument16 pagesParallelogrames PDFSyed Shoeb100% (1)
- Quadrilateral Properties Quiz: I Am A TrapeziumDocument7 pagesQuadrilateral Properties Quiz: I Am A TrapeziumSasam KcNo ratings yet
- Y9 Spring Block 5 ANSDocument21 pagesY9 Spring Block 5 ANScf4b2sp6p4No ratings yet
- Always Sometimes Never QuadrilateralsDocument3 pagesAlways Sometimes Never QuadrilateralsAnthea ClarkeNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Grade 4 Summative Test in MATHEMATICSDocument8 pagesQuarter 3 Grade 4 Summative Test in MATHEMATICSCharles Carl Garcia100% (4)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics IV 2020Document17 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics IV 2020FloryVicBarranco100% (9)
- 2020 MMC JSDocument11 pages2020 MMC JSJomar EjedioNo ratings yet
- Engineering Visualization: Question BankDocument10 pagesEngineering Visualization: Question Bankloda lassanNo ratings yet
- Group 6: Submitted To: Ma'Am Karen PaduaDocument11 pagesGroup 6: Submitted To: Ma'Am Karen PaduaRolly Fallorina SenangeloNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document6 pagesActivity 2Richelle MallillinNo ratings yet
- Coordinate SystemDocument4 pagesCoordinate SystemCue PiaNo ratings yet
- Volume NotesDocument15 pagesVolume Notesapi-310102170No ratings yet
- PolygonsDocument8 pagesPolygonsDaisuke InoueNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Quadrilaterals in PDFDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Quadrilaterals in PDFprince tiwariNo ratings yet
- Angles and Lines QuestionsDocument16 pagesAngles and Lines QuestionsWayne OnSaxNo ratings yet
- Yr7 AreaPerimeterExercisesDocument10 pagesYr7 AreaPerimeterExercisesfanjiexi200No ratings yet