Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Effect of dilution factor on BOD
Uploaded by
Faeez ZainOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Effect of dilution factor on BOD
Uploaded by
Faeez ZainCopyright:
Available Formats
Discussion
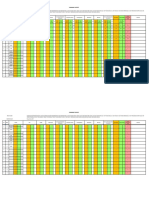
The experiment result we obtained is consistent with the theory given in which the Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) is getting higher if there are a lot of microorganism in the water sample. From the result, we can see that the lower the dilution factor would increase the amount of BOD. In the presence of free oxygen, aerobic bacteria use the organic matter found in wastewater as food. The BOD test is an estimate of the food available in the sample. The more food present in the waste, the more Dissolved Oxygen (DO) will be required. The BOD test is used to measure waste loads to treatment plants, determine plant efficiency (in terms of BOD removal), and control plant processes. It is also used to determine the effects of discharges on receiving waters.
However, there are still some considerations that we must take into account in order to get a good result. Firstly, organic matter in the water sample is continually oxidised by the microorganism. Therefore, the sample should be preserved by cooling process in order to slower the rate of oxidation. Secondly, we should also avoid extreme pH value and provide a neutral pH environment for the microorganisms. This is because the microorganisms could be killed in an extreme pH values environment. Moreover, toxic substances in the water sample must be removed by certain chemical reaction or provide acclimated seed. The presence of algae in the water sample will also affect the BOD result. So, we must store the samples in the incubators in order to prevent sunlight. Finally, good sampling is necessary if laboratory testing is to be accurate. The sample must be representative, collected properly, handled carefully and preserved correctly. No matter how accurate the actual testing is, if the sample is not representative, the results of the test will be misleading and can lead to poor plant performance.
You might also like
- BOD Lab ReportDocument17 pagesBOD Lab ReportAmirulizwan Azamri69% (13)
- The Handbook of Histopathological Practices in Aquatic Environments: Guide to Histology for Environmental ToxicologyFrom EverandThe Handbook of Histopathological Practices in Aquatic Environments: Guide to Histology for Environmental ToxicologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- BOD Lab ReportDocument11 pagesBOD Lab ReportShauQi Lutfi100% (3)
- Lab 4 BODtestDocument7 pagesLab 4 BODtestcindyn_46100% (2)
- COD Measurement Technique ComparisonDocument3 pagesCOD Measurement Technique ComparisonFaeez Zain100% (2)
- Report BODDocument16 pagesReport BODMuhammad Aimi100% (1)
- Bod ReportDocument6 pagesBod ReportdiyanaNo ratings yet
- BOD Full ReportDocument11 pagesBOD Full ReportAhmad Farid75% (4)
- Cod Lab ReportDocument6 pagesCod Lab ReportNizam AmirNo ratings yet
- COD Lab ReportDocument13 pagesCOD Lab ReportAmirulizwan Azamri83% (12)
- Experiment 4 CODDocument3 pagesExperiment 4 CODNurul Noorfazleen78% (9)
- VSS Analysis Determines Organic Contamination LevelsDocument7 pagesVSS Analysis Determines Organic Contamination LevelsSamuelNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 Total Suspended SolidsDocument3 pagesExp 2 Total Suspended Solidssaras8788% (8)
- Bod ConclusionDocument1 pageBod ConclusionShu Aruys100% (2)
- COD Test Measures Organic Pollutants in WaterDocument2 pagesCOD Test Measures Organic Pollutants in WaterNire Ro Iaz67% (9)
- Lab Report Structure Expriment 3Document8 pagesLab Report Structure Expriment 3Akame Takashita100% (3)
- Exp 1-TS, TSS, VSSDocument8 pagesExp 1-TS, TSS, VSSsabbysamura50% (2)
- What Is The Purpose of Using Blank Sample in The ExperimentDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Purpose of Using Blank Sample in The Experimentmohamad syafiq100% (3)
- Total Solid ReportDocument16 pagesTotal Solid ReportNurul Izzati Raihan RamziNo ratings yet
- Full Lab Report 5Document12 pagesFull Lab Report 5Siti SyuhadahNo ratings yet
- COD Test Report Latest 2012Document10 pagesCOD Test Report Latest 2012emmafatimah0% (1)
- Exp.3 Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand CODDocument24 pagesExp.3 Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand CODSYaz WAni100% (2)
- Experiment 2 Total SolidDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 Total SolidMuhd FadzrilNo ratings yet
- Softening N Penetration Test (Bitumen)Document11 pagesSoftening N Penetration Test (Bitumen)Thamilaarasan SonOf Nathan29% (7)
- TBC 3013 Information and Communication Technology in Biology Data Logging Report "Biochemical Oxygen Demand"Document12 pagesTBC 3013 Information and Communication Technology in Biology Data Logging Report "Biochemical Oxygen Demand"fara erma100% (6)
- Experiment On Total Solid and Total Suspended SolidDocument3 pagesExperiment On Total Solid and Total Suspended SolidRosa Chelley77% (26)
- Determining Softening Point of BitumenDocument2 pagesDetermining Softening Point of BitumenmaizansofiaNo ratings yet
- Full Report Bacterial CountDocument10 pagesFull Report Bacterial CountSuzeanni Jalil100% (1)
- Water Quality Assessment of Sediment PondDocument34 pagesWater Quality Assessment of Sediment PondMudin DinNo ratings yet
- COD Lab Report FullDocument9 pagesCOD Lab Report FullLutfi Amin67% (3)
- Suspended Solid Lab TestDocument13 pagesSuspended Solid Lab TestAzzam Kaka84% (19)
- Jar Test Lab ReportDocument14 pagesJar Test Lab Reportilasensei97% (176)
- COD Lab ReportDocument4 pagesCOD Lab ReportFarah KharuddinNo ratings yet
- Jar Test OptimizationDocument12 pagesJar Test OptimizationAmirulizwan Azamri33% (6)
- Water Lab Report - E.coli (FINAL)Document6 pagesWater Lab Report - E.coli (FINAL)SP Aslam SyznNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Part B Bod FullDocument12 pagesLab Report Part B Bod Fullnor atiqah82% (22)
- Jar Test Lab ReportDocument6 pagesJar Test Lab Reportaqilah suleiman100% (6)
- Penetration test grades bitumen for constructionDocument2 pagesPenetration test grades bitumen for constructionMohd Zamzuri100% (4)
- Results N Discussion TDS TSD TSSDocument5 pagesResults N Discussion TDS TSD TSSsyafiq zulkefli64% (11)
- Exp.4-Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) PDFDocument10 pagesExp.4-Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) PDFaoi_chiepNo ratings yet
- PH Test Lab SheetDocument4 pagesPH Test Lab Sheetnor5903No ratings yet
- Jar Test Lab Report Environmental EngineeringDocument7 pagesJar Test Lab Report Environmental EngineeringNur Hazimah100% (1)
- Contoh Report Jar TestDocument12 pagesContoh Report Jar TestIzzat75% (4)
- 3.2 Spot Speed Study Results, Calculation, Discussion, ConclusionDocument11 pages3.2 Spot Speed Study Results, Calculation, Discussion, Conclusionwho_haris96No ratings yet
- BOD and DO Levels of Water SamplesDocument1 pageBOD and DO Levels of Water SamplesKhairul FitryNo ratings yet
- Total Solid Group 4Document26 pagesTotal Solid Group 4Tiesya Ciut100% (4)
- Lab Report Bod Exp 4Document5 pagesLab Report Bod Exp 4ridzuwan rahimi88% (8)
- COD by Reactor Digestion MethodDocument6 pagesCOD by Reactor Digestion MethodYulNo ratings yet
- Env LabDocument19 pagesEnv LabEJ KooNo ratings yet
- DCC30122 QUESTION PALT Set ADocument6 pagesDCC30122 QUESTION PALT Set ANazrul IzdhamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biochemical Oxygen DemandDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Biochemical Oxygen Demandlollol91No ratings yet
- Biological Oxygen DemandDocument7 pagesBiological Oxygen DemandRahul RajNo ratings yet
- EVT577 Wastewater Exp3 BODDocument6 pagesEVT577 Wastewater Exp3 BODFadzrilNo ratings yet
- DBO IntroducciónDocument22 pagesDBO IntroducciónLiliana De AlbaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Oxygen Demand: by DR Utpal Sharma Assist. Professor Department of Community Medicine, SMIMSDocument24 pagesBiochemical Oxygen Demand: by DR Utpal Sharma Assist. Professor Department of Community Medicine, SMIMSZaman RaiNo ratings yet
- BOD Measurement for Water Quality AnalysisDocument12 pagesBOD Measurement for Water Quality AnalysisIera AliasNo ratings yet
- B Biological Oxygen Demand: Water Quality Field GuideDocument6 pagesB Biological Oxygen Demand: Water Quality Field Guiderisma jamilatulNo ratings yet
- Experiment BODDocument6 pagesExperiment BODMuhd Fadzril100% (1)
- Introduction BODDocument4 pagesIntroduction BODShaoline LungaoNo ratings yet
- Concrete Continuous Footing Quantity Take-Off WorksheetDocument17 pagesConcrete Continuous Footing Quantity Take-Off WorksheetFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Method of Statement Pda TestDocument9 pagesMethod of Statement Pda TestFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Kire Pelantar PDFDocument3 pagesKire Pelantar PDFFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- SikaTopSeal107 UsDocument6 pagesSikaTopSeal107 UsFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For PilingDocument13 pagesMethod Statement For Pilingfree4bruce100% (1)
- Method of Statement Piling WorksDocument4 pagesMethod of Statement Piling WorksFaeez Zain0% (1)
- STP 2 Cube Test Update Until 6.2.2018Document1 pageSTP 2 Cube Test Update Until 6.2.2018Faeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Ceiling WorksDocument3 pagesCeiling WorksFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Muhamad Ariff Bin Zainuddin: Site Supervisor (1 Year)Document3 pagesMuhamad Ariff Bin Zainuddin: Site Supervisor (1 Year)Faeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Appendix B Piling Record FormDocument1 pageAppendix B Piling Record FormFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Piling Work (Edited)Document18 pagesMethod Statement For Piling Work (Edited)Faeez Zain100% (6)
- Method Statement For Piling Work (Edited)Document18 pagesMethod Statement For Piling Work (Edited)Faeez Zain100% (6)
- Soil Investigation Method Statements for Vietnam King-Whale ProjectDocument17 pagesSoil Investigation Method Statements for Vietnam King-Whale ProjectbprimusNo ratings yet
- Method of Statement Pda Test PDFDocument9 pagesMethod of Statement Pda Test PDFFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Method of Statement Piling WorksDocument4 pagesMethod of Statement Piling WorksFaeez Zain0% (1)
- Upsi - Method Statements Piling WorksDocument129 pagesUpsi - Method Statements Piling WorksFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Nisbah Konkrit g40Document3 pagesNisbah Konkrit g40Faeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For PilingDocument13 pagesMethod Statement For Pilingfree4bruce100% (1)
- Pda Method StatementDocument12 pagesPda Method StatementFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Abs TrakDocument2 pagesAbs TrakFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- T.off ReinforcementDocument20 pagesT.off ReinforcementFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Internal and External FinishesDocument7 pagesInternal and External FinishesFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- How to Build a 115mm Brick Wall with Less Than 40 CharactersDocument1 pageHow to Build a 115mm Brick Wall with Less Than 40 CharactersFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Summary Defect List 28.7.2017Document2 pagesSummary Defect List 28.7.2017Faeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Teknikal ReportDocument6 pagesTeknikal ReportFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Method 0f Statement of Earthworks NCRDocument2 pagesMethod 0f Statement of Earthworks NCRFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument6 pagesProjectFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- SteelDocument10 pagesSteelFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Steel DesignDocument24 pagesSteel DesignFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- SteelDocument10 pagesSteelFaeez ZainNo ratings yet
- YESAB's 2018 Decision Regarding Placer Project in Indian River WatershedDocument50 pagesYESAB's 2018 Decision Regarding Placer Project in Indian River WatershedThe NarwhalNo ratings yet
- Everpure+Pentek+Sterilight - Water Filter & UV SystemDocument12 pagesEverpure+Pentek+Sterilight - Water Filter & UV SystemongNo ratings yet
- Naked Forex Highprobability Techniques For Trading Without IndicatorsDocument6 pagesNaked Forex Highprobability Techniques For Trading Without IndicatorsHashim0% (1)
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/12 October/November 2019Document19 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/12 October/November 2019Miguel Oubiña SánchezNo ratings yet
- CEDA's Industrial Cleaning & Environmental ServicesDocument6 pagesCEDA's Industrial Cleaning & Environmental ServicesHendi RustandiNo ratings yet
- PAM - ValvesDocument100 pagesPAM - Valvesabdul jackilNo ratings yet
- Abiotic and Biotic Factors DFDocument2 pagesAbiotic and Biotic Factors DFAnonymousNo ratings yet
- BESWMCDocument2 pagesBESWMCOmar DizonNo ratings yet
- Centre For Sustainbility PPT 1Document12 pagesCentre For Sustainbility PPT 1Mithilesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint 101Document9 pagesPowerpoint 101Shyra Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Kfri RR351Document40 pagesKfri RR351Rajib DasNo ratings yet
- Pemodelan Keruntuhan Bendungan Menggunakan HEC-RAS 2D Studi Kasus Bendungan Gondang, Kabupaten KaranganyarDocument7 pagesPemodelan Keruntuhan Bendungan Menggunakan HEC-RAS 2D Studi Kasus Bendungan Gondang, Kabupaten KaranganyarjavanimeNo ratings yet
- Thealgaedist 32Document20 pagesThealgaedist 32Kathleen SaldonNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Coral Reefs 1 - Abiotic FactorsDocument13 pagesStudent Exploration: Coral Reefs 1 - Abiotic FactorsangieNo ratings yet
- Gigquit Earth and Life Science 1st Quarter ExamDocument7 pagesGigquit Earth and Life Science 1st Quarter ExamMaryjul Ramos Ranay100% (4)
- Weather and Climate FactorsDocument24 pagesWeather and Climate Factorsdefinite ChibvongodzeNo ratings yet
- Reading Reflection: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesReading Reflection: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesMao TuazonNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Ecosystems & BiomesDocument4 pagesAquatic Ecosystems & BiomesMaria Gabriela Cabrera Trelles33% (3)
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Product and CompanyDocument7 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Product and CompanyKharisul IhsanNo ratings yet
- Review Exam1-S23Document43 pagesReview Exam1-S23et268No ratings yet
- Hydrograph, Stream Gauging and Peak Flood Estimation: Unit 2Document93 pagesHydrograph, Stream Gauging and Peak Flood Estimation: Unit 2amitpatilnitkNo ratings yet
- I7 Erosion Control Mat Takino FilterDocument4 pagesI7 Erosion Control Mat Takino FilterBrendita CortezNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEM - Components, Energy Flow and Matter CyclingDocument91 pagesECOSYSTEM - Components, Energy Flow and Matter CyclingAngelica Mae PazNo ratings yet
- Ecology Term Paper ExampleDocument6 pagesEcology Term Paper Examplec5e4jfpn100% (1)
- Ten Strategies ReportDocument50 pagesTen Strategies ReportThe Salt Lake Tribune100% (2)
- Ari Catalogo de ProductosDocument260 pagesAri Catalogo de ProductosYGWHNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Arpit PorwalDocument14 pagesPresented By: Arpit PorwalSaddaqatNo ratings yet
- SECTION 9.10 Mining: W. D. HaentjensDocument4 pagesSECTION 9.10 Mining: W. D. HaentjensAbhijeet KeerNo ratings yet
- Potable & Fire Water Tanks Cleaning Method StatementDocument18 pagesPotable & Fire Water Tanks Cleaning Method StatementSachin DharneNo ratings yet
- Geography NotesDocument4 pagesGeography NotesPassw0rdNo ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsFrom EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (722)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (41)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonFrom EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (103)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceFrom EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (51)
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldFrom EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterFrom EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNo ratings yet
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- Brain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolFrom EverandBrain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (702)