Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modern Indian History Cronology of Events
Uploaded by
Ashish AnandCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modern Indian History Cronology of Events
Uploaded by
Ashish AnandCopyright:
Available Formats
Tags Act Institution Institution Annexation Battle Invasion Succesion Succesion Succesion Invasion Succesion Succesion Succesion Reform
Succesion Invasion Battle Succesion Succesion Succesion Succesion Battle Succesion Annexation Succesion Succesion Succesion Battle Succesion Succesion Battle Battle Succesion Succesion
Person British British British Portugese Mughal Mughal Maratha Bengal Mughal Mughal Maratha Mughal Mughal Deccan Bengal Mughal Bengal Awadh Maratha Maratha British Mughal Bengal Mughal Awadh Bengal British Mughal British Maratha Maratha
Year 1600 1623 1633 1658 1699 1713 1713 1717 1719 1719 1720 1722 1722 1724 1727 1738 1739 1739 1739 1740 1740 1742 1748 1751 1752 1754 1756 1757 1759 1760 1761 1761 1761 1763
Event British East India company was granted a royal charter and the exlusive privilege to trade in the East by Queen Elizabeth Had established factories at Surat, Broach, Ahmedabad, Agra and Musalipatnam First factory in East at Orissa Dutch conquered Sri Lanka from the Portugese This year onwards, Gurugobind Singh waged constant war against the armies of Aurangzed and the hill rajas Emperor Jahandar Shah was defeated at Agra by Farrukh Siyar Balaji Vishwanath was made Peshwa by Shahu Murshid Quli Khan was made Governor of Bengal Farrukh Siyar was killed by his estranged aid Saiyid Brothers. Muhammad Shah was made king Balaji Vishwanath helped Saiyid brothers in overthrowing Farrukh Siyar Balaji Vishwanath died and succeeded by his son Baji Rao I. He worked to contain Nzam-ul-Mulk's power and succeeded Nizam-ul-mulk became wazir in Muhammad Shah's court Saadat Khan Burhan-ul-Mulk was appointed Governor of Awadh Nizam-ul-mulk marched south to found the state of Hyderabad in Deccan Murshid Quli Khan died. His son-in-law Shuja-ud-Daula became ruler of Bengal Nadir Shah enterd Indian Territory Nadir Shah inflicted crushing defeat on the Mughal in the Battle of Karnal. Muhammad Shah taken prisoner Alivardi Khan killed Shuja-ud-din's son Sarfaraz Khan and made himself Nawab of Bengal Saadat Khan died and was succeeded by his nephew Safdar Jang Baji Rao died . The Maratha families of Gaekwad, Holkar, Sindhia and Bhonsle came into prominance Baji Rao's son, Balaji Baji Rao also known as Nana Shaheb (1740-1761) became peshwa War broke out in Europe between France and England Safdar Jang was appointed as wazir of Mughal Empire Bengal nawab had to cede Orissa to Marathas Maratha under Nana Shaheb helped Imad-ul-Mulk to become the wazir of Mughal Safdar Jang died Young and quick tempered Siraj-ud-Daula succeeded his grandfather Alivardi Khan Battle of Plassey. English defeated Siraj-ud-Daulah. Traitor Mir Jafar got throne Shah Alam II ascended Mughal Throne Mir Jafar was forced to abdicate in favour of his son-in-law, Mir Qasim Abdali defeated Marathas in the Third Battle of Panipat Haider Ali overthrew Nanjaraj and established his authority over Mysore state Balaji Baji Rao died and Madhav Rao became Peshwa After several defeats from British, Mir Qasim fled away and Mir Jafar was restored as Nawab
Battle Succesion Succesion Battle Act Governor General Battle
British British Bengal British British Warren Hastings Warren Hastings
1764 1765 1765 1766 1767 1772 1773
Act Battle Institution Battle Treaty Act Governor General Act Battle Institution Treaty Governor General Succesion Governor General Treaty Battle Succesion Treaty Institution Treaty Treaty Treaty
Warren Hastings Warren Hastings Warren Hastings Warren Hastings Warren Hastings Warren Hastings Lord Cornwallis Lord Cornwallis Lord Cornwallis Lord Cornwallis John Shore Lord Cornwallis Lord Wellesley Lord Wellesley Lord Wellesley Lord Wellesley Lord Wellesley Lord Wellesley Lord Wellesley Lord Wellesley Lord Wellesley
1773 1781 1781 1782 1782 1784 1786 1786 1789 1791 1792 1793 1793 1798 1798 1799 1799 1800 1800 1801 1801 1802
Shah Alam II joined hands with Mir Qasim and Shuja-ud -Daula in declaring war against East India Company at Battlefield of Buxar. British Army under Hector Munro defeated the allies Clive returned to Bengal as its Governor Mir Jafar died, His son Nizam-ud-Daulah was made Nawab and subordinated to British by Clive British joined Nizam of Hyderbad to wage war against Haider Ali Parliament passed an act obliging the company to pay to the British Treasury 400,000 pounds per year Warren Hastings became Governor General, remained till 1785 Raghunath Rao (younger brother of Balaji Baji Rao) and Narayan Rao (younger brother of Madahv Rao) got involved in struggle for succession. Narayan Rao was killed in 1773 but was succeeded by his son, Sawai Madhav Rao. Raghunath Rao sought british help which resulted in First Anglo- Maratha War. Nana Phadnis was supporter of Madhav Rao. Regulating Act, 1773; made changes in the constitution of the Court of Directors of Company and put them under supervision of British Gov. British army under Eyre Coot defeated Haidar Ali at Porto Novo and saved Madras Warren Hastings set up the Calcutta Madrasah for the study and teaching of Muslim law and related subjects Haider Ali died during the course of Second Anglo-Mysore war and was succeeded by Tipu Sultan First Anglo-Maratha war: Treaty of Salbai between British and Maratha to maintain status quo Pitt's India Act, 1784; British Gov got control over company's affairs and administration in India. This framework of governance continued till 1857 Cornwallis became Governor General, remained till 1793 the GG was given authority to overrule his council of 3 members War between Tipu and British began and ended in 1792 Jonathan Duncan started a Sanskrit College in Varanasi for study of Hindu law and Philosophy Treaty of Seringapatnam was signed between Tipu and British Sir John Shore was appointed Governor General. Till 1798 Permanent Settlement was introduced in Bengal and Bihar. It was planned by John Shore, the person who succeeded Cornwallis as GG Lord Wellesley became Governor General, remained till 1805 Nizam Ali of Deccan concluded Subsidiary Treaty with Wellesley Ruler Tipu Sultan died at the hands of British Ranjeet Singh established his own kingdom with its capital at Lahore Lord Wellesley signed subsidiary Treaty with Nizam Lord Wellesley established the College of Fort William at Calcutta for the education of young recruits to the Civil Service Nawab of Awadh Saadat Ali signed subsidiary treaty Wellesley compelled the Nawab of Carnatic to cede his kingdom through Treaty and Madras presidency was created Cowardly peshwa Bajirao II rushed into arms of British and signed the subsidiary treaty at Bassein
Annexation Battle Treaty Revolt Revolt Treaty Governor General Revolt Treaty Author Governor General Act Institution Invasion Battle Battle Institution Annexation Author Revolt Governor General Annexation Institution Treaty Institution Governor General Reform Reform revolt Author Act
Lord Wellesley British Lord Wellesley Lord Wellesley Lord Wellesley Lord Wellesley Lord Minto Lord Minto Lord Minto Rammohun Roy Lord Hastings Lord Hastings Rammohun Roy Lord Hastings Lord Hastings Maratha Rammohun Roy Lord Hastings Rammohun Roy Lord Hastings Lord Amherst Lord Amherst Rammohun Roy Lord Amherst Rammohun Roy Bentinck Bentinck Bentinck Bentinck Bentinck
1803 1803 1803 1804 1806 1806 1807 1808 1809 1809 1813 1813 1814 1814 1816 1817 1817 1818 1820 1822 1823 1824 1825 1826 1828 1828 1829 1831 1831 1832 1833
Delhi was occupied by British who ousted Mughals Second Anglo Maratha War; Holkar under Yeshwant Rao fought British Army till standstill British army led by Wellesley defeated combined armies of Sindhia and Bhonsle in Assaye and later in Argaon. Subsidiary alliance was signed Paik Rebellion in Orissa under Raja of Khurda Mutiny of Vellore Wellesley was called back from India and Company made peace with Holkar by the Treaty of Raighat Lord Minto succeeded Lord Wellesley Velu Thambi Revolt in Travancore Treaty of Amritsar with Ranjit Singh wrote in Persian his famous work Gift to Monotheists Lord Hastings became Governor General, remained till 1822 Charter Act of 1813; Except for trade in tea and with China, trade monopoly of company was ended and thrown open to all British subjects started Atmiya Sabha War with Nepal. Districts of Garhwal and Kumaon was ceded to India Third Anglo Maratha War. House of Peshwas extinguished Peshwas attacked the British residency at Poona David Hare founded Hindu College with assistance of Rammohun Roy Entire Indian subcontinent except Punjab and Sindh in British control published Percepts of Jesus Ramosis Revolt of Poona under Chittur Singh and Umaji Lord Amherst succeeded Lord Hastings; remained till 1828 War with Burma established Vedanta College Treaty of Yandabo; War with Burma that started in 1824 ended founded a new religious society, the Brahma Sabha, later known as Brahmo Samaj, based on vedas and Upanishads succeded Amherst in 1828; First Governor General of India by Government of India Act 1833, remained in power till 1835 Banned practice of Sati William Bentinck abolished the provincial court of appeal and circuit. Their work was assigned first to Commissions and later to District Judges and District Collectors Rebellion of Mysore, Titu Mir and koka took place Bal Shastri Jambedkar started a weekly, Darpan Charter Act of 1833; monopoly of tea trade and trade with China ended, conferred all law making power on GG in Council
Commission Reform Governor General Reform Governor General Treaty Institution Battle Institution Treaty Governor General Annexation Reform Governor General Battle Treaty Governor General Annexation Institution Institution Institution Institution Institution Institution Institution Author Annexation Reform Reform Act
Bentinck
1833 1835
Metcalfe Metcalfe Lord Auckland Lord Auckland Lord Auckland
1835 1835 1836 1839 1839 1839 1840
Lord Auckland Ellenborough Ellenborough Ellenborough Lord Hardinge Lord Hardinge Lord Hardinge Dalhousie Dalhousie
1841 1842 1843 1843 1844 1845 1846 1848 1848 1849 1849 1850 1851 1851 1851 1852 1852 1852 1853 1853 1853
Govt appointed a Law Commission headed by Lord Macaulay to codify Indian laws. It eventually resulted in Indian Penal Code Govt. decided to devote some resource to the teaching of Western Sciences and literature through the medium of English language alone Succeeded Bentinck and remained till 1836 Indian press was freed of restrictions by Charles Metcalfe Lord Auckland succeded Metcalfe; remained till 1842 Amirs of Sindh were made to sign Subsidiary Treaty Debendranath Tagore founded Tatvabodhini Sabha to propagate Rammohun Roy's idea First Afghan War:launched attack on Afghanistan and defeated it. Placed Shah Shuja on the throne. Religious reforms was become in Bombay by the Paramhans Mandali which aimed at fighting idolatory an the caste system Afghani tribes revolted. British were compelled to sign treaty in which they agreed to evacuate Afghanistan and restored Dost Muhammad on throne. Lord Ellenborough succeded Lord Auckland; remained till 1844 Sindh was annexed after brief campaign by Sir Charles Napier Abolished slavery Lord Hardinge replaced Ellenborough; remained till 1848 First Anglo-Sikh War : Punjab declared war on British when they heard that Lord Gough, the Commander-in-chief and Lord Hardinge the Governor General were marching towards Ferozepur Punjab Army was forced to concede defeat and to sign the humiliating, Treaty of Lahore Lord Dalhousie became Governor General by replacing Lord Hardinge, remained till 1856 Satara was annexed The Bethune School, founded in Calcutta was the first fruit of the powerful movement for women's education. It was an effort of Ishwarchand Vidyasagar Paramahansa Madali was founded; believed in one god and aganst caste rules Vishnu Shastri Pundit founded the Widow Remarriage Association For religious reforms of Parsis, the Rehnumai Mazdayasan Sabha or Religious Reform Association was started by Naoroji Furdonji, Dadabhai Naoroji, S.S. Bengalee and others. British India Association founded by Devendranath Tagore Jotiba Phule and his wife started a girl's school in Poona and soon many other schools came up Bombay Association founded by Jaganth Shanker Karsondas Mulji started the Satya Prakash in Gujarati Second Burmese War; mainly for commercial greed First rail between Bombay to Thana First telegraph line from Calcutta to Agra Charter Act, 1853: directed that all recruits to the Civil Service were to be selected through a competitive exam
Dalhousie Dalhousie Dalhousie
Institution Reform Annexation Reform Institution revolt Annexation Reform Governor General Battle Institution revolt Author Act Institution Governor General revolt Institution Governor General Reform Institution Institution reform Governor General Reform Institution Institution Institution
Dalhousie Dalhousie Dalhousie
1853 1854 1854 1854 1855 1855 1856 1856 1856 1857 1857 1859 1860 1861 1862 1862 1863 1863
Dalhousie Dalhousie Dalhousie Cannings Cannings Cannings Cannings Cannings Lord Elgin Lord Elgin
The first textile mill was started in Bombay by Cowasjee Nanabhoy Post Office Act was passed; Postage stamp introduced for the first time Nagpur and Jhansi was annexed The Wood's Dispatch (the document dispatched from the Court of Directors and named after Charles Wood, the President of Board of Control) kown as 'Magna Carta of English Education', was another step in development of education in India. It asked govt. to assume responsibility for education of masses. It thus repudiated the "downward filtration" theory The first Jute Mill started in Rishra Santhal uprising took place Nawab Wajid Ali Shah of Awadh was accused of misgovernment and was therefore annexed The first lawful Hindu widow remarriage among the upper castes in our country was celebrated in Calcutta under the inspiration and supervision of Vidyasagar Lord Cannings replaced Dalhousie; remained till 1862 Sepoy Mutiny or India's First Battle for Independence Departments of Education were instituted in all provinces and affiliating universitites were set up at Calcutta, Bombay and Madras Indigo revolt in Bengal in 1859-60 Dinabadhu Mitra wrote his play Neel Darpan on oppression of peasants in indigo cultivation Indian Council Act London India Committee founded by CP Mudaliar in London Lord Elgin replaced Cannings; remained till 1863 Wahabi movement was suppressed Muhammaden Literary Society was founded in Calcutta. This society promoted discussion of religious, social and political questions in the light of modern ideas and encouraged upper and middle class Muslims to take to western education Sir John Lawrence replaced Lord Elgin; remained till 1869 High Courts were established in Calcutta, Madras and Bombay to replace Sadar Court of Diwani and Nizamat Dadabhai Naoroji organised the East India Association in London to discuss the Indian question and to influence British public to promote Indian welfare. He was known as "Grand Old Man of India" National India Association founded by Mary Carpenter in London Rise of modern Japan Lord Mayo replaced John Lawrence, remained till 1872 First step in the direction of seperating central and provincial finances was taken by Lord Mayo Justice Ranade and others organised the Poona Sarvajanik Sabha Swami Dayanand Saraswati founded Arya Samaj for reforming Hindu religion in North India Sayyid Ahmad Khan founded at Aligarh the Muhammedan Anglo-Oriental College as a centre for spreading western sciences and culture. Later this college grew into Aligarh Muslim University
John Lawrence John Lawrence
1864 1865 1866 1867 1868 1869 1870 1870 1875 1875
Lord Mayo Lord Mayo
Governor General Author Institution Act Battle Treaty Treaty Institution Act Author Reform Reform Act Institution Reform Institution Institution Governor General Annexation Institution Institution Institution Institution
Lord Lytton Lord Lytton
1876 1876 1876
Lord Lytton Lord Lytton Lord Lytton Lord Lytton Lord Ripon Lord Ripon Lord Ripon Lord Ripon Lord Ripon
1878 1878 1879 1879 1880 1881 1881 1882 1882 1882 1883
Lord Lytton becamed GG and remained till 1880 Viceroy Lord Lytton openly declared that "the crown of England should henceforth be identified with the hopes, aspirations, sympathies and interests of a powerful native aristocracy" Led by Surendranath Benerjee and Anand Mohan Bose, the younger nationalists of Bengal founded the Indian Association . It was for creating strong public opinion on political questions Freedom of press was curbed by passing Vernacular Press Act Second Afghan War: due to Anglo-Russian rivalry. To force British terms on ruler Sher Ali, Afghanistan was attacked. Peace came with Treaty of Gandamak with Yakub Khan. Treaty of Gandamak with Sher Ali's son Yakub Khan in British favour British resident Major Cavagnari, and his millitary escorts were killed by Afghan rebells. British reversed their policy and made Abdur Rahman (grandson of Dost Muhammad) ruler Tilak helped in founding New English School, later came to be known as Fergusson College Indian Factory Act was passed Dadabhai Naoroji declared that the British rule was "an everlasting, increasing, and everyday increasing foreign invasion" that was "utterly, though gradually, destroying the country". Lord Ripon laid down policy of administering local affairs largely through rural and urban local bodies; Local self Government Act was passed in various provinces Appointment of an education commission under Sir William Hunter Vernacular Press Act was taken back, i.e. repealed. Till next 25 yrs Indian press enjoyed considerable freedom Indian National Society founded by Shishir Chandra Bose in Calcutta The Liberty Bill controversy, 1883-84 relating to passing of a bill framed by the law member of the viceroy's council Sir C.P. Liberty which abolished judicial disqualification based on race Indian National Conference founded by SN Banerjee in Calcutta M. Viraraghavachari, G Subramaniya Iyer, Ananda Charlu and others formed the Madras Mahajan Sabha Lord Duferin replaced Ripon; remained till 1888 Burma was invaded in 1885; King Thibaw surrendered and his dominions were annexed to Indian empire Pherozeshah Mehta, K.T.Telang, Badrudding Tyabji and others formed the Bombay Presidency Association A.O.Hume with the help of Indian leaders organised the first session of the Indian National Congress in Bombay in December 1885. Presided by W.C. Bonnerjee and attended by 72 delegates Syed Ahmad Khan with help of Raja Shiva Prasad formed a movement for loyality in opposition to Congress Theosophical society's headquarter was founded by Madam H. P. Blavatsky and Colonel H. S. Olcott at Adyar near Madras. This society was originally founded in US. It advocated the revival and strengthening of the ancient Hinduism, Zoroastrianism and Buddhism.
Lord Ripon
1883 1884 1884
Lord Duferin Lord Duferin
1884 1885 1885
Congress
1885 1885
Annie Besant
1886
Author Governor General Author Reform Author Act Act Governor General Reform Institution
Lord Duferin Lord Lansdowne Congress Congress Lord Lansdowne Lord Lansdowne Lord Elgin II
1887 1888 1889 1889 1890 1891 1892 1895 1896 1897 1897 1898
Duferin rediculed Congress as representing only "microscopic minority of the people" Lansdowne replaced Duferin; remained till 1894 Tilak started publication of Kesari in Marathi British Committee of Indian National Congress was founded. The idea was to make British authority aware about the ground situation of India British committee of Congress started a journal called India second Indian Factories Act was passed Agitation forced Govt. to pass Indian Councils Act of 1892: The no. of members of Imperial Legislative Council as well as Provincial Council was increased. Some indians could be elected indirectly while official's majority remained Lord Elgin II replaced Lansdowne; remained till 1898 Tilak started Shivaji Festival to spread nationalism among masses Vivekanand founded the Ramkrishna Mission to carry on humanitarian relief and social work Plague broke out in Poona, Tilak stayed and supported government against plague but strongly critisized them for the way govt. handled plague victim. This resulted in popular resentment against the official plague measures. Chapekar Brothers assassinated two unpopular British officials at Poona - Rand, the Chairman of Plague and Lt. Ayerst. Act was passed making 'feelings of disaffection' towards govt. an offense Curzon replaced Elgin II; remained till 1905 Lord Curzon announced to the Secaretary of States that "the Congress is tottering to its fall, and one of my great ambitions, while in India is to assist it to a peaceful demise". Swami Shradhananda started the Gurukul near Hardwar to propagate the more traditional ideals of education Indian Official Secret Act puts restriction on press Indian Universities Act; made to control and check the growth of higher education VD Savarkar had organised the Abhinava Bharat, a secret society of revolutionaries Defeat of Russia by Japan 7th Aug, Anti Partition movement started 16th Oct, Partition took affect; Rabindranath composed 'Amar Sonar Bangla' Servants of India Society founded by Gokhale in Bombay Minto II replaced Curzon; remained till 1910 15th Aug, National Council of Education was set up by nationalists National College was set up in Calcutta the All India Muslim League was founded by separatist and loyalists Indian Council Act popularty known as Morley-Minto reforms - an attempt to divide moderate and extremists provision for separate electorate, elections introduced first time officially, non-official majority in province, additional members in legislative council etc Punjab Hindu Sabha was founded in line of Muslim League
Tilak Revolt Act Governor General Author Institution Act Act Institution Battle revolt Author Institution Governor General Institution Institution Institution Act Institution Lord Curzon Lord Curzon Lord Elgin II Lord Curzon Lord Curzon
1898 1899 1900 1902 1904 1904 1904 1905 1905 1905 1905 1905 1906 1906 1906 1909 1909
Lord Curzon Lord Curzon Lord Minto II
Lord Minto II
Governor General Reform Battle Author Reform Institution Institution revolt Reform Institution Governor General Reform Revolt Revolt Act revolt revolt Battle Act Act Institution revolt Reform Reform revolt Institution Revolt Revolt
Lord Hardinge Lord Hardinge Lord Hardinge Lord Hardinge
1910 1911 1911 1912 1912 1913 1915
Lord Hardinge Lord Hardinge Lord Hardinge Lord Chelmsford Congress
1915 1916 1916 1916 1916 1917
Lord Hardinge replaced Minto II; remained till 1916 Annulment of partition and formation of separate Bihar and Orissa war started between Ottoman Empire of Turkey and Italy; British unsympatheic Abul Kalam Azad through his newspaper Al-Hilal spreaded nationalism Islington committee on civil services Ghadar Party founded in USA - Lala Har Dayal, Bhagwan Singh etc as its leaders April- First session of All India Hindu Mahasabha under presidentship of Maharaja of Kasim Bazar - Lajpat Rai, NC Kelkar etc its members Rebel planned in Punjab by Ghadar Party but was quenched Saddler Committee on universities was appointed Formation of two Homerule League one under Tilak and other under Annie Beasant and Subramanian Iyer Chelmsford replaced Hardinge; remained till 1921 Lucknow Session - presided by Ambika Charan Majmudar - unity came between moderates and extremists on one hand and Muslim League and Congress on the other on Nov 7th, Bolshevik party led by Lenin overthrew Czarist regime After return in 1915, Gandhi started Satyagraha in Champaran in 1917 for indigo planters - accompanied by Rajendra Prasad, Mazhar-ul-Haq, JB Kripalani, Narhari Parekh and Mahadev Desai. Montague-Chelmsford reforms were announced Gandhi intervened between worker and mill owners in Ahmedabad over salary hike Kheda Satyagrah - led by Gandhi after crop failure in Kheda, Gujarat Third Afghan War; Abdur Rahman (amir) assassinated. His son Amanullah declared open war on British India. Peace came in 1921 with independence of Afghanistan Montague-Chelmsford reform resulted in Govt. of India Act,1919: bicameral legislature, system of Dyrarchy, etc Rowlatt Act was passed in March which was very repressing Founded Satyagraha Sabha against Rowlatt Act and called for Hartal on 6th April 13th April, Jaliawalabagh Massacre by Dyre Hunter commission on Punjab Wrongs (Jaliawala Bagh) All India Khilafat Conference by Muslim Nationalists held in Delhi in Nov.- decided to withdraw all supports from Govt. Muslim League support to Congress- Gandhi soon became one of the leader of Khilafat Movement. Khilafat Committee under Gandhi launched Non-Cooperation Movement on 31 Aug 1920- mass boycott of Govt Communist Party of India founded by MN Roy in Tashkent The Sikh masses led by the Akalis started a powerful satyagraha against the mahants and the Government which aided them. Management of Gurudwaras was under corrupt and autocrat mahants. In July, All India Khilafat Committee passed resolution- no muslim should serve Army
Gandhi Lord Chelmsford Gandhi Gandhi Lord Chelmsford Lord Chelmsford Lord Chelmsford Gandhi Lord Chelmsford Lord Chelmsford Gandhi Gandhi
1917 1918 1918 1918 1919 1919 1919 1919 1919 1919 1919 1920 1920 1921 1921
Institution Revolt Governor General Reform Revolt Act Revolt Institution Revolt Institution Reform Reform Institution Reform Institution reform Governor General Revolt reform reform Institution Revolt Reform Revolt Revolt Revolt Institution Revolt Revolt
British British Lord Reading Lord Reading Gandhi Lord Reading Gandhi Congress Lord Reading Lord Reading Congress Congress Lord Reading Lord Reading Lord Reading Lord Irwin Congress Lord Irwin
1921 1921 1921 1921 1922 1922 1922 1922 1924 1924 1924 1925 1925 1925 1925 1926 1926 1927 1927 1927 1927
Chamber of Princes was created to enable the princes to meet under the British umbrella and discuss matters of common interest Huge demostration greeted Prince of Wales in India Reading replaced Chelmsford; remained till 1926 Railway Budget was separated from Central Budget Gandhi announced mass Civil Disobedience unless political prisoners are released. Akalis forced the Government to pass a new Gurudwara Act. This act was later ammended in 1925. Chauri Chaura incidence - all campaigns suspended by Gandhi Congress-Khilafat Swarajya Party by CR Das and Motilal Nehru - working within congress- decided to participate in elections - won Muzaffar Ahmed and S.A. Dange accused of spreading Communist ideas and tried alongwith others in Kanpur Conspiracy Case. Hindustan Republic Association (HRA) was founded to organise armed revolution Lee Committee on public services appointed Vithalbhai J. Patel, with support of Congress Khilafat Swarajya Party, became President of the Central Legislative Assembly Communist Party came into existance; remained integral part of national movement and Congress Skeen committee or Indian Sandhurst committee on Army reforms was appointed Foundation of Rashtriya Swayam Sevak Sangh by K. B. Hedgewar at Nagpur Hilton Young Committee on currency was appointed Irwin popularly known as Christian Viceroy replaced Reading; remained till 1931 Jawaharlal Nehru attended Congress of Oppressed Nationalities at Brussels Appointment of Indian States Commission under Harcourt Butler to recommend measures for the establishment of better relations between the Indian States and the Central Govt. Simon Commission appointed- all members Englishmen All India Women's Conference was founded for uplift of women Congress Annual Session- Madras- headed by Dr. Ansari - decided to boycott Simon Commission at every stage First All-Bengal Conference of Students; presided by Jawaharlal Nehru Bardoli Satyagraha under Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel led no tax campaogn among peasants Aug 1928, Nehru Report was prepared to evolve alternate scheme to challenge Simon Commission; Committee headed by Motilal Nhru consisted Sir Tej Bahadur Sapru, Sir Ali Iman, MS Aney, Magal Singh, Shuab Qureshi, GR Pradhan and SC Bose Strike in Bombay Textile Mills led by Communists Under the leadership of Chandrashekhar Azad HRA was renamed as Hindustan Socialist Republican Association (HSRA) Anti-Simon Committee demonstration on 30th Oct; Lala Lajpat Rai died of head injury Bhagat Singh, Azad and Rajguru assassinated Saunders who had led the lathi charge
Congress
1927 1928 1928
Congress
1928 1928 1928 1928 1928
Revolt Revolt reform Reform Reform Revolt Revolt Revolt Revolt Reform Revolt Governor General Revolt Revolt Revolt Institution Reform Reform Revolt Revolt Institution Reform Governor General Institution Reform Reform Reform Reform Institution Reform
Congress Lord Irwin Lord Irwin Lord Irwin Congress Gandhi Congress Gandhi Lord Wellington Gandhi Congress Lord Wellington Lord Wellington Lord Wellington Congress Congress Congress Lord Wellington Lord Linlithgow Congress Congress Congress Congress Gandhi Lord Linlithgow
1928 1929 1929 1929 1929 1929 1930 1930 1930 1931 1931 1931 1931 1931 1932 1932 1932 1933 1933 1934 1934 1935 1936 1936 1936 1937 1938 1939 1939 1940
Calcutta Session of Congress- headed by Motilal Nehru- Gandhiji returns to politics - Nehru Report failed to pass on communal grounds HSRA members, Bhagat Singh and B.K. Dutt threw a bomb in the Central Legislative Assembly Deepavali declaration that India would be granted dominion status in due course Royal Commission on Indian Labour was appointed Sarda Act was passed prohibiting marriage of girls below 14 and boys below 18 years Lahore Session of Congress- headed by Jawaharlal Nehru - Jawaharlal took charge from his father- declared Poorna Swaraj as congress objective backed by Congress, he launched Civil Disobedience Movement on 12th March 1930 large scale armed raid on Govt. armoury led by Surya Sen in Chittagong First Round Table Conference in London, Congress boycotted it Gandhi Irwin Pact: to release non violent prisoners, right to make salt, Civil Disobedience Movement suspended and agreed to take part in Second Round Table Conference Bhagat Singh, Sukhdev and Rajguru hanged on 23rd March Wellington replaced Irwin; remained till 1936; was determined to crush Congress -declared it illegal Second Round Table Conference: demand for immediate grant of dominion status rejected; Civil Disobedience Movement resumed after Gandhi's return Karachi Session of Congress headed by Vallabhbhai Patel- no rent,no tax campaign; resolution of Fundamental Rights and Economic Policy was passed on Nehru's request Communal Award to Lord Wellington Gandhiiji founded All India Harijan Sangh for abolition of untouchability Third Round Table Conference at London without congress; its result was Government of India Act 1935 White Paper on political reforms in India was published Civil Disobedience Movement suspended due to repression by Wellington Civil Disobedience Movement taken back by Congress; Gandhiji again withdrew from politics foundation of Congress Socialist Party under Acharya Narendra Dev and JP Narayan Government of India Act passed: All India Federation, provincial autonomy, responsible govt., Bicameral federal legislaturre, representatives of state to be appointed by ruler, defense and foreign relation in British control, GG retained special control Linlithgow replaced Wellington; remained till 1943 All India Kishan Sabha founded by Swami Sahajanand Saraswati Lucknow Session of Congress headed by Jawaharlal Nehru who urged members to include socialism as its goal Faizpur Session of Congress headed by Jawaharlal Nehru - socialist reforms promised Haripura Session headed by Subhash Chandra Bose - Congress committed itself to Economic Planning and set up a National Planning Committee under Jawaharlal Nehru Nehru became President of All India State People's Conference (originally founded in 1927) Subhash C Bose with his left wing followers founded Forward Bloc after leaving Congress on Aug 8th, British Govt declared August Offer
Revolt Revolt Revolt Revolt Revolt Revolt Revolt Governor General Reform Reform Revolt Revolt Reform Revolt Revolt Revolt Reform Reform Governor General Reform Reform Act
Gandhi
1940 1940 1942 1942 1942 1943 1943 1943 1945 1945 1946 1946 1946 1946 1946 1946 1946 1947 1947 1947 1947 1955
Lord Linlithgow Congress
in Oct, Gandhiji called for limited Satyagraha- Vinoba Bhave was first to respond Muslim League led by Jinnah passed resolution demanding partition of country and creation of Pak Japan Overran eastern and NE neighbours of India and Occupied Rangoon Crip's Mission headed by Cabinet Minister Sir Sanford Crips came India to secure Indian support in World War Crip's mission failed All India Congress Committee met at Bombay on 8th Aug and passed Quit India resolution - Quit India Movement started under leadership of Gandhiji - greatest revolt after 1857 - it was short lived since all leaders were arrested Femine in Bengal takes away 3 million lives SC Bose founded Azad Hind Fauz in Singapore with help of Ras Bihari Bose Wavell replaced Linlithgow; remained till 1947 Wavell Plan; memebers of Congress Working Committee let out of jail. Conference in Shimla on June 25th; failed due to Jinnah and Wavell Congress working committee adopted resolution recommending abolition of Landlordism Provincial elections, Congress and Muslim League won in their respective areas; in Feb, hartal and strike in Bombay factories in March, Govt. sent Cabinet Mission to negotiate on transfer of power in July, All India strike by Telegraph and postal workers Rin Mutiny in Aug, large scale communal violence errupted in Sept, Interim Cabinet headed by Nehru was formed by Congress on 20th Feb, British Premier Clement Attlee declared that British would quit India by June 1948 in March, Mountabatten replaced Wavell; remained during Independence till 1948 on 3rd June, Govt. announced separate India and Pakistan in Oct, Maharaja of Kashmir acceded to India Hindu Marriage Act
Lord Wavell Lord Wavell Congress Congress Lord Wavell Lord Wavell Lord Wavell Lord Wavell Lord Wavell Congress British Lord Mountbatten Lord Mountbatten Congress
You might also like
- 563Document17 pages563Subhasis PatraNo ratings yet
- ChronologyDocument14 pagesChronologyRajat XanderNo ratings yet
- New 1 Modern History - Basic LevelDocument38 pagesNew 1 Modern History - Basic LevelofferNo ratings yet
- Modern History EvernoteDocument18 pagesModern History EvernoteKuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Additional History Notes Modern IndiaDocument33 pagesAdditional History Notes Modern IndiaRajuNo ratings yet
- British in India 1825-1859: Organisation, Warfare, Dress and WeaponsFrom EverandBritish in India 1825-1859: Organisation, Warfare, Dress and WeaponsNo ratings yet
- History Facts + ChronolopgyDocument12 pagesHistory Facts + Chronolopgysaurabh.gahlot10100% (1)
- Important Wars and Battles in Indian HistoryDocument3 pagesImportant Wars and Battles in Indian HistoryRaj Vardhan TiwariNo ratings yet
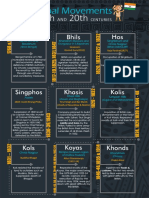
- Tribal Movements in 19th and 20th Centuries PDFDocument3 pagesTribal Movements in 19th and 20th Centuries PDFSingh NamanNo ratings yet
- History of Ancient India: Avks AcademyDocument21 pagesHistory of Ancient India: Avks AcademysayaliNo ratings yet
- Peasant-Movements 41307Document2 pagesPeasant-Movements 41307Joey saravanaNo ratings yet
- Modern Part 2Document18 pagesModern Part 2yasaswi yashNo ratings yet
- Governor Generals and ViceroysDocument14 pagesGovernor Generals and ViceroysGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Governor General/Viceroy Period Points To RememberDocument5 pagesGovernor General/Viceroy Period Points To Rememberkittu_sivaNo ratings yet
- Governors General Viceroys OfindiaDocument6 pagesGovernors General Viceroys Ofindiabrain boosterNo ratings yet
- Medeival History Capsule 2016Document12 pagesMedeival History Capsule 2016amoghvkiniNo ratings yet
- TABLESDocument22 pagesTABLESpranita kaleNo ratings yet
- Advent of EuropeansDocument26 pagesAdvent of EuropeansChandan TenduNo ratings yet
- List of Viceroy in IndiaDocument4 pagesList of Viceroy in Indiagopesh daga100% (1)
- Ancient Indian HistoryDocument7 pagesAncient Indian Historykomal komalNo ratings yet
- Modern History SpectrumDocument36 pagesModern History SpectrumSounak Biswas100% (1)
- List of GovernorsDocument2 pagesList of Governorsnewcontrol testNo ratings yet
- Congress SessionsDocument2 pagesCongress SessionsAzeem MaxNo ratings yet
- R S Sharma - Ancient Indian History Book Full Summary Useful For Ias Pcs SSCDocument52 pagesR S Sharma - Ancient Indian History Book Full Summary Useful For Ias Pcs SSCAkmal JalalNo ratings yet
- Satvahanas Political HistoryDocument16 pagesSatvahanas Political HistoryRavi RoshanNo ratings yet
- Advent of The EuropeansDocument22 pagesAdvent of The EuropeansAllieNo ratings yet
- Causes and Impact of Tebhaga MovementDocument2 pagesCauses and Impact of Tebhaga MovementRana SutradharNo ratings yet
- Complete List of Newspapers and Journals During British IndiaDocument4 pagesComplete List of Newspapers and Journals During British IndiaAnkit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Me Diva L India History by SNDocument71 pagesMe Diva L India History by SNprem kumarNo ratings yet
- Modern - History Unique Shiksha SampleDocument26 pagesModern - History Unique Shiksha SampleJoseph SmithNo ratings yet
- Modern History TimelineDocument5 pagesModern History Timelinepushkar kumar100% (1)
- Era of Mass Nationalism Begins (1919-1939)Document10 pagesEra of Mass Nationalism Begins (1919-1939)Samarth GargNo ratings yet
- About AP Full DetailsDocument45 pagesAbout AP Full DetailsPv ReachNo ratings yet
- List of Governor General and Viceroy in IndiaDocument17 pagesList of Governor General and Viceroy in IndiaRavi Kumar Agrahari100% (1)
- Tribal MovementsDocument30 pagesTribal MovementsNdnjsjsNo ratings yet
- Role of Tamilnadu in Freedom StruggleDocument13 pagesRole of Tamilnadu in Freedom Strugglegokul viratNo ratings yet
- Sher Shah SuriDocument12 pagesSher Shah SuriguriaNo ratings yet
- List of Indian MonumentsDocument7 pagesList of Indian Monumentsmebtahuljannat100% (1)
- Gupta EmpireDocument6 pagesGupta EmpireAshish Rockstar100% (1)
- Std12 Hist EM PDFDocument272 pagesStd12 Hist EM PDFAbhishek Krishna ChandraNo ratings yet
- Indian FeudalismDocument4 pagesIndian FeudalismShreya SinghNo ratings yet
- Indian Freedom Struggle (1857-1947) : Blogspot Blogspot Near Jaipur, 24 Searching For Blogspot?Document46 pagesIndian Freedom Struggle (1857-1947) : Blogspot Blogspot Near Jaipur, 24 Searching For Blogspot?Kishore PotnuruNo ratings yet
- A Forgotten EmpireDocument190 pagesA Forgotten EmpireATULNo ratings yet
- Battle of Plassey & BuxarDocument5 pagesBattle of Plassey & BuxarPrateek SinghNo ratings yet
- The Mauryan Empire (322bc To 188bc)Document2 pagesThe Mauryan Empire (322bc To 188bc)api-3737960100% (1)
- Meghalaya Police Service Commission SyllabusDocument165 pagesMeghalaya Police Service Commission SyllabusMangeshNo ratings yet
- Freedom Struggle Important DatesDocument2 pagesFreedom Struggle Important DatesLuvjoy Choker100% (1)
- Important Wars and Battles in Indian HistoryDocument3 pagesImportant Wars and Battles in Indian Historyvivek bhagat100% (1)
- Kharavela - WikipediaDocument11 pagesKharavela - WikipediaFlorosia StarshineNo ratings yet
- History I - Mughal Sikh ConflictDocument26 pagesHistory I - Mughal Sikh ConflictPrateek Mishra100% (2)
- Mughalempire PDFDocument20 pagesMughalempire PDFAngad KumarNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Indian National CongressDocument11 pagesFoundation of Indian National CongressShah12No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument122 pagesUntitledvarkalamohanNo ratings yet
- The Satavahanas: Pratishtana Dharanikota Amaravati Junnar PrathisthanDocument17 pagesThe Satavahanas: Pratishtana Dharanikota Amaravati Junnar PrathisthanVijay Bunga100% (1)
- History I - History of Law & Legal Institutions in Ancient V - D - Project TopicsDocument2 pagesHistory I - History of Law & Legal Institutions in Ancient V - D - Project TopicsHimanshiNo ratings yet
- Individual Satyagraha in Nagapattinam District - A StudyDocument4 pagesIndividual Satyagraha in Nagapattinam District - A StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 3 - B - A (History) - 108 23 - History of India (From 1707 To 1947 AD)Document276 pages3 - B - A (History) - 108 23 - History of India (From 1707 To 1947 AD)Muhammad Rashid ShahNo ratings yet
- The Tribes and Castes of the Central Provinces of India, Book IIFrom EverandThe Tribes and Castes of the Central Provinces of India, Book IINo ratings yet
- Arrival of European TradersDocument6 pagesArrival of European TradersTimothy EnglandNo ratings yet
- Modern India PDFDocument16 pagesModern India PDFAsrarNo ratings yet
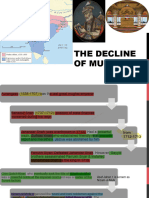
- 6746 0 Decline of Mughals PDFDocument9 pages6746 0 Decline of Mughals PDFDevendra DhruwNo ratings yet
- 3b - Nath - Madad-I MaashDocument14 pages3b - Nath - Madad-I Maashjha_abc6600No ratings yet
- Dalrymple 2012Document226 pagesDalrymple 2012Hizbullah RiazNo ratings yet
- Chronology of Events: Chapter - 2Document9 pagesChronology of Events: Chapter - 2Naman DadhichNo ratings yet
- PeshwasDocument57 pagesPeshwasKenneth KeymerNo ratings yet
- 5.mughul PeriodDocument31 pages5.mughul PeriodJames MarkNo ratings yet
- India in 18th CenturyDocument20 pagesIndia in 18th CenturyArvind Sanu Misra100% (3)
- Comprehensive Course On Modern Indian History: Presented by Pratik NayakDocument173 pagesComprehensive Course On Modern Indian History: Presented by Pratik Nayakpolu100% (1)
- Decline of Mughals - Marathas and Other StatesDocument73 pagesDecline of Mughals - Marathas and Other Statesankesh UPSCNo ratings yet
- Modern His Live Class 3Document58 pagesModern His Live Class 3AbrakaDabraNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 8 History Civics Sample Paper 1Document7 pagesICSE Class 8 History Civics Sample Paper 1Naman GuptaNo ratings yet
- List of Mughal EmperorsDocument8 pagesList of Mughal EmperorsAvaniJain100% (1)
- History Book L15Document18 pagesHistory Book L15deeksha vermaNo ratings yet
- IGP CSAT Paper 1 Indian History Modern Indian History Chronology of Events PDFDocument9 pagesIGP CSAT Paper 1 Indian History Modern Indian History Chronology of Events PDFniyorraj90No ratings yet
- Karen LeonardDocument18 pagesKaren LeonardUdayveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Modern History ChronologyDocument20 pagesModern History ChronologyANJALINo ratings yet
- Coins of India: Mughal Gold From The Skanda CollectionDocument15 pagesCoins of India: Mughal Gold From The Skanda CollectiontlananthuNo ratings yet
- Decline and Disintegration of The Mughal EmpireDocument24 pagesDecline and Disintegration of The Mughal EmpireLove SheoranNo ratings yet
- Mughal SealsDocument65 pagesMughal Sealssfaiz87No ratings yet
- Decline of Mughal Empire Lec 1Document9 pagesDecline of Mughal Empire Lec 1Varsha AhlawatNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Karkhanas, The Artisan and The Techniques of Production: Continuation and ChangeDocument38 pagesChapter-2 Karkhanas, The Artisan and The Techniques of Production: Continuation and ChangeArchana M Nair100% (1)
- Modern Indian History (Vajiram Ravi) (Z-Library)Document211 pagesModern Indian History (Vajiram Ravi) (Z-Library)tabishkhanaligNo ratings yet
- The Decline of The Mughal Empire 1707-1857Document14 pagesThe Decline of The Mughal Empire 1707-1857Rayyan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- 58 (B) Rise of The Regional PowersDocument11 pages58 (B) Rise of The Regional PowersIAS EXAM PORTAL100% (1)
- Building Jaipur: Vibhuti Sachdev Giles TillotsonDocument199 pagesBuilding Jaipur: Vibhuti Sachdev Giles Tillotsonsai420No ratings yet
- Later Mughals and Reasons For The Decline of The Mugha Lempire 150427083543 Conversion Gate01Document42 pagesLater Mughals and Reasons For The Decline of The Mugha Lempire 150427083543 Conversion Gate01haseebNo ratings yet
- Timeline of Mughal EmpireDocument4 pagesTimeline of Mughal EmpireHarsh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 2012 Mansfield T PHDDocument208 pages2012 Mansfield T PHDDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- History Lecture 1 Notes PDFDocument9 pagesHistory Lecture 1 Notes PDFSAHILNo ratings yet
- History 150 Questions With AnswersDocument20 pagesHistory 150 Questions With AnswerssenanimeshNo ratings yet