Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Two Peg Test
Uploaded by
Tidus FarronCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Two Peg Test
Uploaded by
Tidus FarronCopyright:
Available Formats
Two Peg Test: The test that we undertake in order to determine the amount of error and then eliminate
it from our measurement is known as the Two Peg Test.
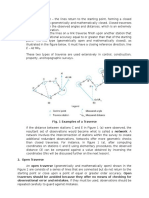
FIGURE 1.0: Two Peg Test
Procedure: 1) Two Pegs A and B are hammered firmly into the ground by 50 meters apart. 2) A level is set up exactly between the pegs at a point C and read a staff held on each peg in turn.
Reading on peg A= m Reading on peg B = m True difference in level A and B = m This is the true difference in level between the pegs irrespective of whether the line of collimation in inclined or not. If there were a collimation error it would be equal in both directions CA and CB since the distances are equal. 3) The level to a point D is removed some distance beyond peg B. The best distance is 1/10th of distance AB,which is 5 meters. A second set of reading on pegs A and B is taken.
Reading on peg A = m Reading on peg B = m Apparent difference in level A to B = m
4) Since the true difference in level does not equal the apparent different, there is a collimation error in the line of sight of the instrument. Because the apparent difference is greater than the true difference, the line of collimation error points upwards in the case. 5) The correct staff reading required to adjust the level are now required. They are calculated by one of the following methods. Calculation of Adjustment:
You might also like
- Surveying Note Curve Ranging Chapter 6Document9 pagesSurveying Note Curve Ranging Chapter 6Michael Noi0% (2)
- The Triangle AdjustmentDocument29 pagesThe Triangle AdjustmentWassan IdreesNo ratings yet
- The+Six+Pillars+of+Self Esteem+by+Nathaniel+BrandenDocument1 pageThe+Six+Pillars+of+Self Esteem+by+Nathaniel+Branden› PHXNTOM; ‹No ratings yet
- Levelling and Profile Ploting PDFDocument5 pagesLevelling and Profile Ploting PDFShamsUlislam100% (3)
- Formula For Launching of SatelliteDocument3 pagesFormula For Launching of SatelliteTidus FarronNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersFrom EverandHandbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 7 - Distance Measurement - PacingDocument4 pagesWorksheet 7 - Distance Measurement - PacingTOt's Vin100% (1)
- Curve RangingDocument10 pagesCurve RangingAqilah Taufik100% (1)
- Liquid Waste ManagementDocument12 pagesLiquid Waste ManagementTidus FarronNo ratings yet
- Linear Survey ReportDocument15 pagesLinear Survey ReportSyahmi Fadzi100% (1)
- Ebook PDF Consumer Behaviour Buying Having Being 4th Edition PDFDocument42 pagesEbook PDF Consumer Behaviour Buying Having Being 4th Edition PDFmarvin.tappen82697% (38)
- Report Traverse PDFDocument7 pagesReport Traverse PDFliyana203050% (2)
- Report Traverse Group 22Document12 pagesReport Traverse Group 22ewanz89100% (1)
- Traverse ReportDocument8 pagesTraverse Reporthibby_tomey100% (1)
- Report Two Peg TestDocument5 pagesReport Two Peg TestRizal Roger100% (1)
- Levelling ReportDocument13 pagesLevelling Reportwanyy100% (4)
- Tachoemetry ReportDocument12 pagesTachoemetry ReportAin Sherin0% (1)
- Two Peg TestDocument24 pagesTwo Peg TestjatteNo ratings yet
- CONCLUSION Survey TheodoliteDocument6 pagesCONCLUSION Survey Theodolitemaizansofia50% (6)
- Traverse Report COMPLETEDocument17 pagesTraverse Report COMPLETEAidaFarzanaNana50% (2)
- Sieve AnalysisDocument14 pagesSieve Analysisneutron_8797% (38)
- CurveDocument30 pagesCurvelegendz12380% (15)
- Softening Point of BitumenDocument8 pagesSoftening Point of BitumenVanithaa Ponnaiah100% (3)
- Lecture 1b Precise LevellingDocument30 pagesLecture 1b Precise LevellingNur Fatin Are Tien58% (12)
- Errors in Tacheometric Surveying: This Study Resource Was Shared ViaDocument6 pagesErrors in Tacheometric Surveying: This Study Resource Was Shared ViaBindeshwar YadavNo ratings yet
- Levelling ContouringDocument58 pagesLevelling ContouringWan Abdul WafiNo ratings yet
- Elementary Surveying Field Manual Field Work No.2 Taping On Level and On Uneven GroundDocument16 pagesElementary Surveying Field Manual Field Work No.2 Taping On Level and On Uneven GroundSid LimNo ratings yet
- TraverseDocument20 pagesTraverseTumis Budu88% (8)
- Theodolite Traverse SurveyDocument6 pagesTheodolite Traverse SurveySiti Aishah Sahul Hamid57% (7)
- Survey Camp ReportDocument32 pagesSurvey Camp Reportfatin nursyafiqah bt zudi86% (7)
- Formwork PDFDocument27 pagesFormwork PDFKandarp Rajyaguru100% (1)
- Surveying BEC102 4 - Longitudinal and Cross SectionsDocument31 pagesSurveying BEC102 4 - Longitudinal and Cross Sectionsjfejfe0% (1)
- Complete Traverse ReportDocument5 pagesComplete Traverse ReportBobari Bilong Nelson41% (17)
- Activity 3 - LevellingDocument2 pagesActivity 3 - LevellingMateo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Report Levelling UthmDocument10 pagesReport Levelling Uthmأمير صفوان100% (9)
- TraversingDocument8 pagesTraversingMarc Dared CagaoanNo ratings yet
- Stadia Survey Lab ReportDocument6 pagesStadia Survey Lab ReportLorelie de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Geomatic Engineering: Lab ReportDocument8 pagesGeomatic Engineering: Lab ReportHati Saya50% (2)
- Two Peg TestDocument8 pagesTwo Peg Testnicholas100% (1)
- Open Channel Module1Document24 pagesOpen Channel Module1pankaj_mbmNo ratings yet
- Report Standart TraverseDocument25 pagesReport Standart TraverseAmirul Yaakub57% (7)
- Traverse SurveyDocument9 pagesTraverse SurveyIkhwan JoniNo ratings yet
- Introduction LevellingDocument5 pagesIntroduction Levellingfattihafatt100% (1)
- Lab Sheet-LevellingDocument12 pagesLab Sheet-LevellingMuhammadBinHanifNo ratings yet
- Levelling 1Document22 pagesLevelling 1opulithe100% (1)
- Run Two-Peg TestDocument6 pagesRun Two-Peg Testhazheer183% (6)
- 06 - Two Peg TestDocument23 pages06 - Two Peg TestHibaZreikFarhat100% (1)
- Traversing DiscussionDocument1 pageTraversing DiscussionFelicia LingNo ratings yet
- Chain SurveyingDocument3 pagesChain SurveyingUlfathbary AB100% (3)
- Precautions For TraverseDocument1 pagePrecautions For Traverseaoi_chiep0% (1)
- RACHO - Discussion and ConclusionDocument3 pagesRACHO - Discussion and ConclusionWei Shen56% (9)
- Total Station LabDocument3 pagesTotal Station Labnickie_harvey4046998100% (1)
- Horizontal Curve Ranging.r1 StudentDocument44 pagesHorizontal Curve Ranging.r1 StudentDennis Lai Zhan WenNo ratings yet
- Traverse Report - Group 3 - Red ZoneDocument41 pagesTraverse Report - Group 3 - Red ZonenajmiNo ratings yet
- Background of Electronic Distance Measurement (EDM)Document8 pagesBackground of Electronic Distance Measurement (EDM)Siti ZulaikhaNo ratings yet
- Open and Closed TraverseDocument5 pagesOpen and Closed TraverseMercy Lacno100% (1)
- Geomatic Levelling ReportDocument9 pagesGeomatic Levelling Reportlzero93No ratings yet
- REPORT ContourDocument7 pagesREPORT ContourFariduddin Rosman100% (1)
- Report Lab#4Document8 pagesReport Lab#4ibrahim100% (2)
- Lab Report On SurveyingDocument7 pagesLab Report On SurveyingJoycelyn UyNo ratings yet
- Dcc20063 - Engineering Survey Lab Report 4: CurveDocument17 pagesDcc20063 - Engineering Survey Lab Report 4: CurvewawaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Measurement of Vertical Distances Leveling MethodDocument12 pagesModule 3 Measurement of Vertical Distances Leveling MethodLance De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Al Mustansiriyah University Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument16 pagesAl Mustansiriyah University Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Departmentt8ktwrcvj4No ratings yet
- Lecturer: Assoc. Prof. Dr. M. Zeki COŞKUN: Department of Geomatics Engineering E-Mail: Coskun@itu - Edu.trDocument19 pagesLecturer: Assoc. Prof. Dr. M. Zeki COŞKUN: Department of Geomatics Engineering E-Mail: Coskun@itu - Edu.trmuhammadrz1No ratings yet
- 5 Two-Peg TestDocument19 pages5 Two-Peg TestInter GalacticNo ratings yet
- Ranging in Surveying - Types of RangingDocument6 pagesRanging in Surveying - Types of RangingSunil ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Two Peg Test: Stage 1Document3 pagesTwo Peg Test: Stage 1Israel PopeNo ratings yet
- 2nd Mastery QuestsDocument7 pages2nd Mastery QuestsTidus FarronNo ratings yet
- WasteWater Engineering 1516 Sem 1Document7 pagesWasteWater Engineering 1516 Sem 1Tidus FarronNo ratings yet
- Method of ErectingDocument3 pagesMethod of ErectingTidus FarronNo ratings yet
- EC03-702 Precision Agriculture - Applications of Remote Sensing inDocument7 pagesEC03-702 Precision Agriculture - Applications of Remote Sensing inTidus FarronNo ratings yet
- Sieve AnalysisDocument9 pagesSieve AnalysisTidus FarronNo ratings yet
- Image PixelsDocument1 pageImage PixelsTidus FarronNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument1 pageSummaryTidus FarronNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - Levelling DetailDocument17 pagesCHAPTER 4 - Levelling DetailNurisz IskandarNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroductionTidus FarronNo ratings yet
- Sieve AnalysisDocument9 pagesSieve AnalysisTidus FarronNo ratings yet
- 1) Multitemporal: Remote Sensing Is The Acquisition of Information About An Object or Phenomenon WithoutDocument1 page1) Multitemporal: Remote Sensing Is The Acquisition of Information About An Object or Phenomenon WithoutTidus FarronNo ratings yet
- Surveying Lab ManualDocument26 pagesSurveying Lab Manualandy_tatte32No ratings yet
- CC103 Engineering Survey Civll Levelling Ukur ArasDocument9 pagesCC103 Engineering Survey Civll Levelling Ukur ArasAdron LimNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument1 pageSummaryTidus FarronNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Effective StressDocument18 pagesLecture 4 Effective StressAdi Fikri Sidi83% (6)
- Unified Soil Classification SystemDocument8 pagesUnified Soil Classification SystemTidus Farron100% (1)
- TimberDocument1 pageTimberTidus FarronNo ratings yet
- What Is DatumDocument1 pageWhat Is DatumTidus FarronNo ratings yet
- Determining The Location of The Sustainable Fishing Industry With Center of Gravity Method, Case Study Northeast Coast of JavaDocument6 pagesDetermining The Location of The Sustainable Fishing Industry With Center of Gravity Method, Case Study Northeast Coast of JavaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Aqa 8300 RS Nov23Document12 pagesAqa 8300 RS Nov23leomaunganidze8No ratings yet
- Electroplating Know How II Know HowDocument5 pagesElectroplating Know How II Know HowrankeenNo ratings yet
- 13.2 Biotic & Abiotic FactorsDocument3 pages13.2 Biotic & Abiotic FactorsOmar AlwaerNo ratings yet
- Preservation of Indigenous Culture of Bataan Through An Ayta Magbukon School of Living Tradition (SLT) ProgramDocument11 pagesPreservation of Indigenous Culture of Bataan Through An Ayta Magbukon School of Living Tradition (SLT) ProgramEuniz ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Nano Macro BuehlerDocument66 pagesLecture 1 Nano Macro BuehlerVarun RavikumarNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE MELCsDocument18 pagesSCIENCE MELCsAntoneaNo ratings yet
- Institute For Career Research Editors - Careers in Medical Research-Institute For Career Research (2007)Document32 pagesInstitute For Career Research Editors - Careers in Medical Research-Institute For Career Research (2007)Cynthia CNo ratings yet
- The Mandalorian S02E08 WEBRip x264-ION10Document27 pagesThe Mandalorian S02E08 WEBRip x264-ION10AlexJKDCQCNo ratings yet
- Writer's Block and Procrastination in CIPD Level 5 AssignmentsDocument1 pageWriter's Block and Procrastination in CIPD Level 5 AssignmentsCIPD Assignment HelpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Non-Linear Equations: Nguyen Thi Minh TamDocument26 pagesChapter 2: Non-Linear Equations: Nguyen Thi Minh TamPhương Anh Nguyễn0% (1)
- A Hybrid Approach For Face Recognition Using A Convolutional Neural Network Combined With Feature Extraction TechniquesDocument14 pagesA Hybrid Approach For Face Recognition Using A Convolutional Neural Network Combined With Feature Extraction TechniquesIAES IJAINo ratings yet
- Hydrograph Analysis: Streamflow MeasurementDocument17 pagesHydrograph Analysis: Streamflow MeasurementUmange RanasingheNo ratings yet
- Say It With Charts - McKinsey-32Document4 pagesSay It With Charts - McKinsey-32YONGXING CHENNo ratings yet
- Micro-Climate ReportDocument10 pagesMicro-Climate Reportaadya agrawalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhonologyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To PhonologyJunjet FamorcanNo ratings yet
- Equipment List For Resection and IntersectionDocument6 pagesEquipment List For Resection and IntersectionDiegoNo ratings yet
- Pressure Answer SchemeDocument4 pagesPressure Answer SchemetrisyiajottNo ratings yet
- Assessment in Special EdDocument27 pagesAssessment in Special EdAlfred IntongNo ratings yet
- Lit21st 1 Semester (1 Quarter) Social Innovation Fundamental: Global Issues I. The Universe Some Terminologies & Points To PonderDocument13 pagesLit21st 1 Semester (1 Quarter) Social Innovation Fundamental: Global Issues I. The Universe Some Terminologies & Points To PonderRoie Andrae ArayonNo ratings yet
- Celso Gen Chem m1 ActivitiesDocument7 pagesCelso Gen Chem m1 ActivitiesRaine Gabrielle CelsoNo ratings yet
- TextbookList2021-2022 ST Paul CoventDocument17 pagesTextbookList2021-2022 ST Paul Coventkww3007No ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Introduction To Environmental Geology 5th Edition Keller Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Introduction To Environmental Geology 5th Edition Keller Test Bank PDFgilmadelaurentis100% (12)
- 01 Plant Design and Economics IntroductionDocument32 pages01 Plant Design and Economics Introductionهادی طاهریNo ratings yet
- MOSFET - Working, Types, Operation, Advantages & ApplicationsDocument28 pagesMOSFET - Working, Types, Operation, Advantages & ApplicationsgezahegnNo ratings yet
- Factoring Using Common Monomial FactorDocument26 pagesFactoring Using Common Monomial FactorHappyNo ratings yet
- PTD25 Series Pressure Transmitters: Features ApplicationsDocument3 pagesPTD25 Series Pressure Transmitters: Features Applicationsjim bobNo ratings yet
- Intllbe Calondi) R For DSSBB Elani - Durlnfl Yai (MZZDocument4 pagesIntllbe Calondi) R For DSSBB Elani - Durlnfl Yai (MZZanirudh yadavNo ratings yet