Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Network Topologies Are Similar Regardless of The Areas of Their Application
Uploaded by
Essays Are EasyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Network Topologies Are Similar Regardless of The Areas of Their Application
Uploaded by
Essays Are EasyCopyright:
Available Formats
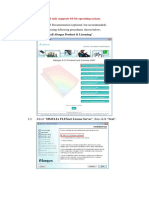
COURSEWORK
Coursework
COURSEWORK Coursework Network topologies are similar regardless of the areas of their application. Simple topologies such as star, bus, ring, etc. were invented at the dawn of the networking technology emergence. These topologies provided network users with the opportunity to communicate, share files, and perform other tasks within one network. However, each topology has its peculiarities that can be considered as disadvantages for a particular situation. Therefore, hybrid topologies became the resolution of the emerging need in a more sophisticated but yet reliable network topology. Hybrid topology is the combination of bus, ring, and star topologies in order to provide the necessary redundancy, reliability, etc. or solve any other particular issues. The most common examples of hybrid networks are: star ring and star bus network
(Wikipedia.org, 2012a). Thus, according to Wikipedia.org (2012a), first type consists of two or more star topologies connected using a multistation access unit (MAU) as a centralized hub; the second type is the two or more star topologies connected using a bus trunk (the bus trunk serves as the network's backbone). Considering hybrid topologies, it is possible to apply old names of the simple topologies, such as tree or snowflake, in order to describe the existing hybrid ones. Thus, tree hybrid topology can be described as follows: it is the set of various topologies, connected sequentially with each other. Snowflake topology is different: it is the set of various topologies, connected to the one centralized hub (or through it). The Internet has its own conceptual models or topologies. They are jellyfish model and bow tie model (Wikipedia.org, 2012a). Jellyfish model is the one where pages are strongly connected to one core while bow tie model represents the situation when there are two cores with In and Out links (Siganos, Tauro, & Faloutsos, 2010). It is the development of the jellyfish model.
COURSEWORK References Siganos, G., Tauro, S. L., & Faloutsos, M. (2010). Jellyfish: A Conceptual Model for the AS Internet Topology. Retrieved from:
http://www.google.com.ua/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=3&ved=0C GcQFjAC&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.cs.ucr.edu%2F~michalis%2FPAPERS%2FJe llyfishJCN.pdf&ei=IHAVUPvIIMjOmAX1xYHADA&usg=AFQjCNGMUJq28cJTgjLpBM 8WjBiVDg3c3w Wikipedia.org (2012a). Network topology. Retrieved from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network_Topology#Hybrid Wikipedia.org (2012b). Internet topology. Retrieved from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_topology
You might also like
- The Ethical Issues Inherent in Any Engineering DesignDocument4 pagesThe Ethical Issues Inherent in Any Engineering DesignEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- What Should Ms. Rollison Know About Behavior in Order To Help JosephDocument8 pagesWhat Should Ms. Rollison Know About Behavior in Order To Help JosephEssays Are Easy100% (1)
- The Jaguar Project CaseDocument5 pagesThe Jaguar Project CaseEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management ExamDocument4 pagesSupply Chain Management ExamEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- Role of Literature Review in The Research ProcessDocument5 pagesRole of Literature Review in The Research ProcessEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- Selective Abortion Based On Prenatal Diagnosis of DisabilityDocument8 pagesSelective Abortion Based On Prenatal Diagnosis of DisabilityEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- IT Governance For SMEsDocument32 pagesIT Governance For SMEsEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- Network DesignDocument4 pagesNetwork DesignEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- Passwords Are Everywhere These DaysDocument4 pagesPasswords Are Everywhere These DaysEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- Information Systems EngineeringDocument15 pagesInformation Systems EngineeringEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- M AmriDocument2 pagesM AmriEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument6 pagesBiologyEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Trends in Luxury Product Category GloballyDocument5 pagesDiscuss The Trends in Luxury Product Category GloballyEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- Illustrate The Importance of Selfish GenesDocument7 pagesIllustrate The Importance of Selfish GenesEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- Bridging The Gap Between Accounting Education andDocument8 pagesBridging The Gap Between Accounting Education andEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- Computer RAM CourseworkDocument3 pagesComputer RAM CourseworkEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- CourseworkDocument4 pagesCourseworkEssays Are EasyNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Kourtney Kardashian Invites Sportsheets To Be Included in Her Celebrity Poosh VIP BoxDocument2 pagesKourtney Kardashian Invites Sportsheets To Be Included in Her Celebrity Poosh VIP BoxPR.comNo ratings yet
- KCL Dissertation Title PageDocument6 pagesKCL Dissertation Title PageWriteMyPaperCollegeCanada100% (1)
- Information Retrieval in Folksonomies: Search and RankingDocument15 pagesInformation Retrieval in Folksonomies: Search and RankingtempNo ratings yet
- Exercises For Week 5Document9 pagesExercises For Week 5Mayang Sari100% (1)
- 71 To 51 My Journey From FailureDocument139 pages71 To 51 My Journey From FailurePunam SinghNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Promoting To Server StatusDocument16 pagesLab 3 Promoting To Server StatusNagavelli Aravind reddyNo ratings yet
- Lis6711 Research Paper by Crystal StephensonDocument8 pagesLis6711 Research Paper by Crystal Stephensonapi-470886892No ratings yet
- Process PaperDocument2 pagesProcess Paperjoemass2No ratings yet
- NII Sample PT Report PDFDocument23 pagesNII Sample PT Report PDFnieltalkxNo ratings yet
- Blond Queens, Red Spiders, and Neurotic Old Maids - Gender and Espionage in The Early Cold War - Intelligence and National Security - Volume 19, Issue 1Document6 pagesBlond Queens, Red Spiders, and Neurotic Old Maids - Gender and Espionage in The Early Cold War - Intelligence and National Security - Volume 19, Issue 1malicusNo ratings yet
- TRAKTOR DJ Studio 3 Manual - 3rd RevisionDocument219 pagesTRAKTOR DJ Studio 3 Manual - 3rd RevisionwillevoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document29 pagesLesson 1AshleyNo ratings yet
- Vsphere Distributed Switch Best PracticesDocument30 pagesVsphere Distributed Switch Best PracticesnewbeoneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Foundational Concepts in SecurityDocument18 pagesChapter 1 - Foundational Concepts in SecurityRandom EmailNo ratings yet
- Abaqus 6.13-1 Installation GuideDocument4 pagesAbaqus 6.13-1 Installation GuideAPSNo ratings yet
- Genex Cloud ACP GuidelineDocument10 pagesGenex Cloud ACP GuidelineMohammad RidwanNo ratings yet
- Got ItDocument106 pagesGot ItArvan SiagianNo ratings yet
- Upkar PrakashanDocument1 pageUpkar PrakashanPrabhu Charan TejaNo ratings yet
- Soca BetDocument51 pagesSoca Betanthonio200078% (9)
- Form 4Document1 pageForm 4s5b7drq8f5No ratings yet
- 64) Mailchimp Project Certificate PDFDocument1 page64) Mailchimp Project Certificate PDFDr Alla SrivaniNo ratings yet
- NCC Group Annual Report For Year Ended 31 May 2015Document154 pagesNCC Group Annual Report For Year Ended 31 May 2015rayimasterNo ratings yet
- LG 42LS4600 User GuideDocument83 pagesLG 42LS4600 User GuideMahfooz AliNo ratings yet
- Wu2018 JournalDocument27 pagesWu2018 JournalSyafrie MuhammadNo ratings yet
- User Guide: AC1200 Wireless Dual Band RouterDocument111 pagesUser Guide: AC1200 Wireless Dual Band Routerkyrie eleisonNo ratings yet
- Mobile NDocument15 pagesMobile NckmmrhNo ratings yet
- Online Hybrid Course DefinitionsDocument1 pageOnline Hybrid Course DefinitionsAmanda BrunerNo ratings yet
- Mac Interval TreeDocument723 pagesMac Interval TreeVishal jadhavNo ratings yet
- The Visibooks Guide To Access 2003 (2006) PDFDocument242 pagesThe Visibooks Guide To Access 2003 (2006) PDFMEHEDINTEANUNo ratings yet
- Javascript Notes: Background and OverviewDocument41 pagesJavascript Notes: Background and OverviewSamudra guptaNo ratings yet