Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EDI Cost Benefit Analysis
Uploaded by
Allison KirbyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EDI Cost Benefit Analysis
Uploaded by
Allison KirbyCopyright:
Available Formats
Financial EDI Cost/Benefit Analysis I. Costs of Receiving Paper Payments.
For Receivers
Section I assists in quantifying costs associated with receipt and processing of paper payments. A. Personnel Expense of Receiving Paper Payments: This section identified labour costs associated with processing receipt of paper cheques and remittance data. 1. Receipt and processing of remittance cheques and data (if don internally) $ 2. Reconciliation of payments to invoices 3. Key entry of remittance data into receivables systems 4. Filing and/or retrieval of paper documents including cheque photocopies, remittance documents etc. 5. Filing of paper remittances, cheque photocopies 6. Other A. Total Personnel Expense for Paper Payments $ $ $ $ $ $ (A)
B. Error/Problem Resolution Costs: This section identified labour and other costs due to errors or error consequences related to receiving paper payments. Financial EDI can substantially improve the accuracy of cash application. 1. Loss of business due to misapplication or problem with payment 2. Time spend resolving payment and payment application errors 3. Expenses associated with returned cheques including A/R adjustments 4. Other B. Total Error/Problem Resolution Costs $ $ $ $ $ (B)
C. Mail, Paper and Storage Costs: This section identifies costs of paper receipts. 1. Filing and storage of paper remittance documents and cheque photocopies 2. Other C. Total Mail, Paper and Storage Costs $ $ $ (C)
D. Bank Service Charges: This section identified bank service charges associated with the receipt of existing payment mechanisms. The companys bank analysis statements should be used as a tool to complete this section. Often, bank service charges can be reduced with the use of electronic payments. 1. Deposit items charges 2. Lockbox processing charges 3. Lockbox delivery, overnight charges 4. Lockbox data entry charges $ $ $ $
Financial EDI Cost/Benefit Analysis 5. Other lockbox processing charges 6. Wire receipt fees D. Total Bank Service Charges $ $ $
For Receivers
(D)
E. Other Costs: This section notes other costs that are related to receiving and processing paper payments. 1. Capital expense on remittance processing equipment 2. Other E. Total Other Costs $ $ $ (E)
I. Total Cost of Receiving Paper Payments (Add lines A, B, C, D, E)
(I)
Note: After costs have been identified, a reduction in costs should be estimated based on the number of electronic payments targeted. II. Financial Cost/Benefit Section II identifies financial savings or costs associated with the receipt of electronic payments versus paper cheques. A. Value of improved cash forecasting and accelerated fund availability B. Cost or savings due to re-negotiation of trade terms C. Receivables financing costs D. Changes in credit, collection functions E. Other II. Total Financial Cost/Benefit (Add lines A, B, C, D, E) $ $ $ $ $ $ (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (II)
III. Cost of Implementing a Financial EDI System for Receipt of Electronic Payments Section III identifies on-time start-up costs to develop or buy and install EDI Receipt capabilities. A. Hardware: This section identifies any hardware or equipment that may be required to receive EDI payments. 1. Computer systems (new, upgrade or machine time) 2. Communications hardware (modem, line) 3. Security and authentication hardware A. Total Hardware Costs $ $ $ $ (A)
Financial EDI Cost/Benefit Analysis
For Receivers
B. Software: This section identifies costs of software required to receive EDI payments. Note that some of these costs are optional depending on whether the company wants to perform the function internally or through a service provider. 1. Bridging modifications to A/R systems and programming 2. File conversion 3. Translation software purchase 4. Translation software in-house development 5. Communications 6. Security and authentication software B. Total Software Costs $ $ $ $ $ $ $ (B)
C. Training & Marketing Materials, Implementation Guides, Customer/Vendor Education: This section identifies one-time costs associated with preparing materials to encourage customers to pay electronically. 1. Internal users in the firm 2. External trading partners 3. Conversion efforts C. Total Training & Marketing Materials $ $ $ $ (C)
D. Van, Bank and Third Party Implementation Costs: This section details implementation costs associated with defining the companys program and setting it up with a VAN, bank and/or other service providers. 1. VAN or other third party processor setup costs 2. Bank setup charges D. Total Van, Bank and Third Party Implementation Costs $ $ $ (D)
III.Total Financial EDI Receipt Implementation Costs (Add lines A, B, C, D)
(III)
Financial EDI Cost/Benefit Analysis
For Receivers
IV. Ongoing Maintenance Costs for Financial EDI Receipt Section IV identifies ongoing costs of maintaining a financial EDI receipt program. A. Van, Bank, and Third Party Ongoing Costs: These costs are associated with the method selected to receive payments and /or associated remittance data from the bank or third party provider. 1. Monthly base fee 2. Transaction costs: Number of transactions, segments or characters received (transaction analysis required) 3. Connect time 4. Mailbox charges 5. Report charges 6. Additional transmission costs 7. Other A. Total Van, Bank and Third Party Ongoing Costs $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ (A)
B. Personnel: This section notes any additional staff costs required to support the companys financial EDI efforts such as an EDI co-ordinator and other personnel and benefits. $ (B)
C. Internal, Customer and Vendor Education: This section records the costs for internal staff training and vendor/trading partner solicitation and set-up. 1. Internal training 2. Vendor/trading partner solicitation and set-up C. Total Internal, Customer and Vendor Education Costs $ $ $ (C)
D. Maintenance Costs: This section itemizes any ongoing maintenance costs of new hardware/software purchased for financial EDI receipt operations. 1. Hardware or machine time 2. Translation software 3. Application software 4. Communication (line charge, data transmission) 5. Security and authentication hardware and software D. Total Maintenance Costs $ $ $ $ $ $ (D)
Financial EDI Cost/Benefit Analysis
For Receivers
E. Bank Service Charges: This section itemizes any new ongoing bank service charges to receive electronic payments. 1. Monthly base fees 2. ACH transaction fees 3. Bank translation fees 4. VAN links (by bank) 5. EDI reporting charges 6. Transmission charges E. Total Bank Service Charges $ $ $ $ $ $ $ (E)
IV. Total Estimated Ongoing Maintenance Costs (Add lines A, B, C, D, E) This completes the analysis for financial EDI receivers.
(IV)
Financial EDI Cost/Benefit Analysis Benefits: 1. Reduction in paper base costs from all sources 2. Financial benefits from re-negotiation of terms, improved cash forecasting, float reductions 3. Other benefits from re-engineering processes and procedures (based on companys estimates, expectations and experience) Total Benefits for Financial EDI Costs: 1. Implementation costs (can be amortized) 2. Ongoing costs Total Costs for Financial EDI Net Benefit (Costs) for Financial EDI (S1 S2) Five Year Work Sheet: $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $
Summary
(I) (II)
(s1)
(III) (IV) (s2) (s3)
Some transactions costs are sensitive to volume. Determination of costs and benefits should be done over a multiple year horizon. Present value techniques and after tax costs and interest rates should be considered. Yr. 1 Cumulative no. of Trading Partners: Cumulative Conversion % (s4): Total Financial EDI Benefits (s1x s4): Total Financial EDI Costs (s2 x s4): Net Savings (s3 x s4): Yr. 2 Yr. 3 Yr. 4 Yr. 5
Cost Trends Favouring Financial EDI Labour costs are rising faster than the Consumer Price Index (CPI) Electronic communications costs are decreasing. Computer hardware costs are decreasing. An increasing number of financial institutions provide reformatting and conversion services, eliminating the need for most internal A/P or A/R systems modifications.
You might also like
- Guide For DatawarehousingDocument24 pagesGuide For DatawarehousingjramkiNo ratings yet
- ADT DFT ORU: The Most Commonly Used HL7 Message Types IncludeDocument1 pageADT DFT ORU: The Most Commonly Used HL7 Message Types IncludeRafi Uddin ShaikNo ratings yet
- EDI AnalystDocument5 pagesEDI Analystapi-121653196No ratings yet
- Case Study - AirlineDocument2 pagesCase Study - AirlineKiky Audrya HardiantiNo ratings yet
- Warehouse CompleteDocument6 pagesWarehouse CompletegurugabruNo ratings yet
- Designing Successful Go To Market SrategiesDocument21 pagesDesigning Successful Go To Market Srategiessaurav_edu67% (3)
- Brand Awareness of AirtelDocument13 pagesBrand Awareness of AirtelShraddha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Xengine Transaction ValidationDocument12 pagesXengine Transaction ValidationMitchell JohnsonNo ratings yet
- EDI 824 Guide New For Edi TestingDocument8 pagesEDI 824 Guide New For Edi TestingRamesh BodukaniNo ratings yet
- HR Staffing ProposalDocument11 pagesHR Staffing ProposalPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Ready To Lead: Five Leading Indicators of Leadership EffectivenessDocument9 pagesReady To Lead: Five Leading Indicators of Leadership Effectivenessjawad_kaleem9337No ratings yet
- Data Warehousing (2002-05 IBM Ex)Document40 pagesData Warehousing (2002-05 IBM Ex)Abou Bahaj100% (1)
- Nhóm 4 - In-Class Exercise BOP - 2020Document36 pagesNhóm 4 - In-Class Exercise BOP - 2020Thảo Hoàng PhươngNo ratings yet
- Ensuring Data QualityDocument16 pagesEnsuring Data QualityAlsayed AlgergawyNo ratings yet
- Data Warehousing Case Studies .Compressed-1Document8 pagesData Warehousing Case Studies .Compressed-1Zihni ThoriqNo ratings yet
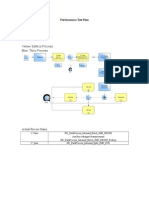
- Performance Test Plan: Yellow: Edifecs Process Blue: Tibco ProcessDocument2 pagesPerformance Test Plan: Yellow: Edifecs Process Blue: Tibco ProcessVaraprasada Rao ImandiNo ratings yet
- Of S A A AdjustmentsDocument12 pagesOf S A A AdjustmentssatyasainadhNo ratings yet
- International Standard: Second Edition 2002-07-01Document30 pagesInternational Standard: Second Edition 2002-07-01olol100% (1)
- Concepts of EDIDocument33 pagesConcepts of EDIJain_Mohit_111No ratings yet
- BA TecniquesDocument55 pagesBA Tecniquesloveykhurana5980100% (2)
- EDI GuidelinesDocument96 pagesEDI GuidelinesMirko100% (1)
- EDI Session 1Document33 pagesEDI Session 1Dileep Kumar Naidu RayalaNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse Architecture 032008Document3 pagesData Warehouse Architecture 032008Sumeet PalNo ratings yet
- Lecture - ERP BenefitsDocument23 pagesLecture - ERP BenefitsPurushottam Singh Meena100% (1)
- An EDI Implementation MethodologyDocument9 pagesAn EDI Implementation MethodologySatish Kumar BurraNo ratings yet
- Edi/Idoc: How Is An Edi Project Carried Out?: Note Number Released On ReleaseDocument3 pagesEdi/Idoc: How Is An Edi Project Carried Out?: Note Number Released On ReleaseCsaba OlahNo ratings yet
- The Integrated Logistics Management System CASE STUDYDocument19 pagesThe Integrated Logistics Management System CASE STUDYGejo Varkey100% (1)
- Electronic Data ExchangeDocument30 pagesElectronic Data ExchangeManuel ZaroNo ratings yet
- 13813-Case Study SolutionsDocument7 pages13813-Case Study SolutionsMaryam KhanNo ratings yet
- Sap Bussiness IntelligenceDocument200 pagesSap Bussiness IntelligenceJaguar100% (1)
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)Document15 pagesElectronic Data Interchange (EDI)Pallavi IngaleNo ratings yet
- HL7 Integration Analyst in Nashville TN Resume Éilís CreanDocument6 pagesHL7 Integration Analyst in Nashville TN Resume Éilís CreanEilisCreanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data InterchangeDocument20 pagesElectronic Data InterchangeMah D MohandesNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data InterchangeDocument16 pagesElectronic Data InterchangeGauravNo ratings yet
- EDI Manual PDFDocument119 pagesEDI Manual PDFLuis SousaNo ratings yet
- Case Study AcisDocument6 pagesCase Study AcisJunel MamarilNo ratings yet
- Oracle Business Intelligence Data Warehouse Administration ConsoleDocument342 pagesOracle Business Intelligence Data Warehouse Administration ConsoleKrishna Prasad KottiNo ratings yet
- MC Kinsey Investigación Impact of Internet On Economic GrowthDocument10 pagesMC Kinsey Investigación Impact of Internet On Economic GrowthfranjafearNo ratings yet
- Bi DatawDocument33 pagesBi DatawHenri IBOHNNo ratings yet
- Electronic Data InterchangeDocument21 pagesElectronic Data InterchangeJay Smith100% (1)
- Data WarehouseDocument3 pagesData WarehouseAlaa HamdanNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence DWDocument17 pagesBusiness Intelligence DWapi-3840617No ratings yet
- Case Study On IOSDocument3 pagesCase Study On IOSmsoneword0% (1)
- Assignment On EDIDocument58 pagesAssignment On EDIAaqueeb Pasha100% (1)
- Edi x12 Vs EdifactDocument3 pagesEdi x12 Vs EdifactabcNo ratings yet
- Sales/EDI Documents/X12 Transaction Descriptions AllDocument28 pagesSales/EDI Documents/X12 Transaction Descriptions Allmyrules45No ratings yet
- MIS EdiDocument50 pagesMIS Ediritesh85100% (1)
- A New Business ParadigmDocument31 pagesA New Business ParadigmChandrikaBajoriaNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence Business IntelligenceDocument32 pagesBusiness Intelligence Business IntelligenceSathish EppakayalaNo ratings yet
- Role of Business Intelligence in Business Performance Management.Document6 pagesRole of Business Intelligence in Business Performance Management.Ashar Sultan KayaniNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence in The Gaming IndustryDocument10 pagesBusiness Intelligence in The Gaming IndustryaadiljohnNo ratings yet
- Stock Exchange Listing and Firm Performance in GhanaDocument20 pagesStock Exchange Listing and Firm Performance in GhanaSaint Hilary Doe-Tamakloe100% (3)
- Document (3) QQQQDocument3 pagesDocument (3) QQQQAnupriya ChuriNo ratings yet
- Automotive RZ2 WebDocument20 pagesAutomotive RZ2 WebTimothy FieldsNo ratings yet
- Assessment BriefDocument6 pagesAssessment BriefAbeer PareekNo ratings yet
- Executive Information System: Miss Mima Razana Binti Mat GhaniDocument25 pagesExecutive Information System: Miss Mima Razana Binti Mat GhaniAdi Nur100% (1)
- Management Information System: Course Developed by K.K.NigamDocument271 pagesManagement Information System: Course Developed by K.K.NigamravirrkNo ratings yet
- Data Warehousing and Data Mining: Dr. Karunendra VermaDocument101 pagesData Warehousing and Data Mining: Dr. Karunendra VermaAbhishek SrivastavNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument240 pagesDBMShdabc123No ratings yet
- Dokumentation EDI Odette Kurs PDFDocument17 pagesDokumentation EDI Odette Kurs PDFrubenmun_No ratings yet
- Case Study 3Document2 pagesCase Study 3Divya NandiniNo ratings yet
- Prem's ResumeDocument1 pagePrem's ResumePrem KalevarNo ratings yet
- Inventory ERDDocument1 pageInventory ERDDock N DenNo ratings yet
- Presidential Decree No 442Document10 pagesPresidential Decree No 442Eduardo CatalanNo ratings yet
- A Primer On The Impact of The New Economic Stimulus Laws and IRC 409A On Executive Compensation in Mergers and AcquisitionsDocument48 pagesA Primer On The Impact of The New Economic Stimulus Laws and IRC 409A On Executive Compensation in Mergers and AcquisitionsArnstein & Lehr LLPNo ratings yet
- The Role of Non-Executive Directors in Corporate Governance: An EvaluationDocument34 pagesThe Role of Non-Executive Directors in Corporate Governance: An Evaluationsharonlow88No ratings yet
- Customer Journey MappingDocument1 pageCustomer Journey MappingPriyanka RaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment For First Sem CMDocument4 pagesAssignment For First Sem CMnishant khadkaNo ratings yet
- Affect of Branding On Consumer Purchase Decision: Research ProjectDocument7 pagesAffect of Branding On Consumer Purchase Decision: Research ProjectPooja RawatNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Prof. Parul Singh Fortune Institute 2010Document30 pagesHuman Resource Management: Prof. Parul Singh Fortune Institute 2010yogimeetNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 140115011613 Phpapp01Document12 pagesPresentation1 140115011613 Phpapp01wahid mohdNo ratings yet
- Is Enhanced Audit Quality Associated With Greater Real Earnings Management?Document22 pagesIs Enhanced Audit Quality Associated With Greater Real Earnings Management?Darvin AnanthanNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument52 pagesProject ReportAkanksha SinhaNo ratings yet
- Virtusa Pegasystems Engagement Success StoriesDocument20 pagesVirtusa Pegasystems Engagement Success StoriesEnugukonda UshasreeNo ratings yet
- Audit 2, PENSION-EQUITY-INVESTMENT-LONG-QUIZDocument3 pagesAudit 2, PENSION-EQUITY-INVESTMENT-LONG-QUIZShaz NagaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management Vansh Lamba GucciDocument10 pagesPrinciples of Management Vansh Lamba Guccivansh lambaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Banking: Basics, Savings, Current, CCOD, Remittance, CashDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Banking: Basics, Savings, Current, CCOD, Remittance, CashcutesunyNo ratings yet
- Venga Tu ReinoDocument2 pagesVenga Tu ReinoOmar camacho HernandezNo ratings yet
- Business Hub: National Case Study Challenge 2021Document13 pagesBusiness Hub: National Case Study Challenge 2021HimansuRathiNo ratings yet
- BUAD 807 SummaryDocument6 pagesBUAD 807 SummaryZainab Ibrahim100% (1)
- AS-Fill The Skill - 2Document2 pagesAS-Fill The Skill - 2Eema AminNo ratings yet
- Layout Plant PDFDocument1 pageLayout Plant PDFswarupNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle (PLC) StrategiesDocument31 pagesProduct Life Cycle (PLC) StrategiesPeggy ChengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Indian Financial System - IntroductionDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - Indian Financial System - IntroductionsejalNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesLiterature ReviewRohan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Report On Askari BankDocument64 pagesReport On Askari Bankzorish87% (15)