Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tentamen ET4384 Design of Low-Power Power Supplies. 14 May 2013
Uploaded by
shihabnittOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tentamen ET4384 Design of Low-Power Power Supplies. 14 May 2013
Uploaded by
shihabnittCopyright:
Available Formats
Tentamen ET4384 Design of Low-power power supplies.
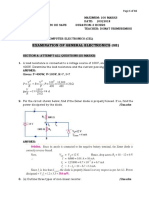
14 May 2013 Problem 1 Given is the foliowing waveform & circuit:
Herein: Crss=5pF, Coss=40pF, Rd=2 Ohm, Rg=5 Ohm, Cgs=lnF, Co=10pF, Lp=400uH, Vt=3V Vdrainmax=550V, Vvalley=250V. The capacitances are all assumed to be linear (voltage independent). Rd denotes the internal resistance of the driver when it discharges the gate. Cx is an external capacitor that might be useful, when connected it is parallel to Coss. Questions: In case Ipeak^at switch-off = 5A: 1. What is tine switch-off energy? 2. What are the total switching losses (energy)? 3. Could the addition of an additional Cx reduce switchoff losses, and, if yes, what is the value to reach zero switch-off losses? 4. In case of additional Cx, what value of Cx leads to the minimum of the total switching losses? 5. For what level of Ipeak are the switch-off losses just zero?
Problem 2. Write down at least 5 possible circuits to limit the/iia )dnTum voltage across the switch in a mains isolated flyback. Give of all the pro's and cons.
Problem 3 A transformer is to be designed, using a PQ32/20 core, material 3C95, See data attached. Lp=450uH, lpeak=3.95A. Turns ratio: Np/Nsec=6, switching frequency lOOkHz. BCM operation. For EMI reasons prim ary wound at inner side of coil former. Questions: 1. Calculate the number of turns Np, within safe margin from saturation. 2.Suppose the primary winding is wound first. Which type of wire to choose, and which number of layers? (assume massive wire can be used). What is the expected DC series resistance? When proximity effects are to be taken into account, what will be the AC resistance acc to Dowells graph? 3. What is the number of secondary windings? When massive wire is used, which type (when mains isolation is not required)? Calculate RDC and RAC. Would paralleling wires help? If so, what is your choice? RDC and RAC? 4. Which layers will have the most losses due to proximity effects? Could reverse order (first primary, than secondary) help? If so, why? 5. In case of mains isolation is needed, which TRISO wire (massive) could fit? RDC? RAC? 6. In case Litze wire will be used to reduce AC resistance, which size of the individual wire should be used? 7. Calculate the core losses 8. Calculate the thickness of the air gap. 9. Calculate the estimated leakage inductance
CORE SETS Effective core parameters SYMBOL E(l/A) Ve le Ae Afnin m PARAMETER core factor (Cl) effective volume effective lengtti effective area minimum area mass of set VALUE 0.331 9440 55.9 169 142 47 g UNIT nim"'' nlm^ mm mm^
-27.5
0.5-
Dimensions in mm.
Rg.1 PQ32/20 core set
-32.15 m a x - 26.7 max -
22.35 max 11.05 max -8.9-*|
j f
1S.9
cI
c }-
34.3 30
O 0.75
i(
2.8 min . 7.2 min Dimensions in mm.
()
) 1
Fig.2 PQ32/20 coii former; 12-pins. Winding data for 12-plns PQ32/20 coil former NUMBER OF SECTIONS 1 1 MINIMUM WINDING AREA (mm^) 44.8 44.8 NOMINAL WINDING WIDTH (mm) 8.9 8.9 AVERAGE LENGTH OF TURN (mm) 66.7 66.7
TYPE NUMBER CPV-PQ32/20-1S-12P CPV-PQ32/20-1S-12PD
You might also like
- Power Transformer DesignDocument4 pagesPower Transformer DesignMetalloyNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Colicraft Power Transformer DesignDocument4 pagesColicraft Power Transformer DesignPablo KuziwNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Delay Calculation:: Delays ModelsDocument9 pagesDelay Calculation:: Delays ModelsMUNAGALASAILOKESH RA1711004010401No ratings yet
- Interconnect Delay ModelsDocument16 pagesInterconnect Delay ModelsPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Chap9 SampleDocument51 pagesChap9 SampleAbhishek MatNo ratings yet
- Automated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAutomated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsNo ratings yet
- Chapter04 ExDocument6 pagesChapter04 ExKarthikeya VemparalaNo ratings yet
- Linear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandLinear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Matching (Part 2)Document9 pagesMatching (Part 2)adauNo ratings yet
- VLSI Interconnects: Credits: David HarrisDocument46 pagesVLSI Interconnects: Credits: David Harrisparty0703No ratings yet
- No 2 Power DissipationDocument28 pagesNo 2 Power DissipationHasanAlBannaBhuiyanNo ratings yet
- Ge S6 Cel OkDocument16 pagesGe S6 Cel Okves vegasNo ratings yet
- Sizing CircuitsDocument130 pagesSizing Circuitsinhenyeronerb100% (17)
- Bypass Capacitors IntersilDocument10 pagesBypass Capacitors IntersilBlykerNo ratings yet
- Circuit and Systems Assignment (1) .Doc EC Y1S2Document28 pagesCircuit and Systems Assignment (1) .Doc EC Y1S2sadyehclenNo ratings yet
- How To Determine Correct Number of Earthing Electrodes (Strips, Plates and Pipes) - Part 1 - EEPDocument8 pagesHow To Determine Correct Number of Earthing Electrodes (Strips, Plates and Pipes) - Part 1 - EEPsupermannonNo ratings yet
- Bypass Caps An1325Document10 pagesBypass Caps An1325Paolo RoccaratoNo ratings yet
- Choosing and Using Bypass CapacitorsDocument10 pagesChoosing and Using Bypass CapacitorsDimitris LyberisNo ratings yet
- Example To Calculate Short Circuit Current For Circuit BreakerDocument6 pagesExample To Calculate Short Circuit Current For Circuit BreakermarlonNo ratings yet
- DAC AnalysisDocument19 pagesDAC Analysisమురళీధర్ ఆది ఆంధ్రుడుNo ratings yet
- SCAA048 - Filtering TechniquesDocument7 pagesSCAA048 - Filtering TechniquesAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasNo ratings yet
- AND8241/D A 5.0 V/2.0 A Standby Power Supply For INTEL Compliant ATX ApplicationsDocument16 pagesAND8241/D A 5.0 V/2.0 A Standby Power Supply For INTEL Compliant ATX ApplicationsJonatan LunaNo ratings yet
- Wair Ya 2010Document6 pagesWair Ya 2010abhishek shuklaNo ratings yet
- Low Swing Signaling Using A Dynamic Diode-Connected DriverDocument4 pagesLow Swing Signaling Using A Dynamic Diode-Connected DriverAkash RaykarNo ratings yet
- An-791 A Simplified Approach To VHF Power Amplifier DesignDocument10 pagesAn-791 A Simplified Approach To VHF Power Amplifier DesignEdward YanezNo ratings yet
- Designing Loop AntennasDocument18 pagesDesigning Loop AntennasCesar AvilaNo ratings yet
- Cable Sizing & Voltage DropDocument10 pagesCable Sizing & Voltage DropJyothisrikanth75% (4)
- Grounding-Back To BasicsDocument5 pagesGrounding-Back To BasicsUsman TariqNo ratings yet
- Local Media5941271462837301265Document65 pagesLocal Media5941271462837301265jason mr.perfect11No ratings yet
- Cat5 Cable Modeling DVI HDMIDocument12 pagesCat5 Cable Modeling DVI HDMIrvshah4No ratings yet
- Cables Theory DesignDocument25 pagesCables Theory DesignA. HassanNo ratings yet
- Earth Fault Loop ImpedenceDocument3 pagesEarth Fault Loop Impedencemsn-silva100% (1)
- Application Guide: Designing RC Snubber NetworksDocument3 pagesApplication Guide: Designing RC Snubber NetworksThrawn Mitth'rawnuruodoNo ratings yet
- Class D RF Power AmplifierDocument12 pagesClass D RF Power AmplifierhaoyuqianNo ratings yet
- CMOS Interview QADocument14 pagesCMOS Interview QAarammartNo ratings yet
- Electrical Thumb Rules - (Part 1)Document4 pagesElectrical Thumb Rules - (Part 1)Electrical Radical100% (3)
- Vlsi 2-Marks With AnswerDocument23 pagesVlsi 2-Marks With Answerk poornimaNo ratings yet
- On-Chip Decoupling Capacitor Optimization For Noise and Leakage ReductionDocument5 pagesOn-Chip Decoupling Capacitor Optimization For Noise and Leakage Reductioneppramod3271No ratings yet
- Questions: Chapter 6 ChallengesDocument2 pagesQuestions: Chapter 6 Challengesapi-358354056No ratings yet
- Index: Matching Networks and QWTDocument20 pagesIndex: Matching Networks and QWTKavita KamerikarNo ratings yet
- Issues and Solutions in Setting A Quadrilateral Distance CharacteristicDocument16 pagesIssues and Solutions in Setting A Quadrilateral Distance CharacteristicAnonymous KTvCCMarbNo ratings yet
- Short Questions Power System For Competitive Exams Prepared by Venkatesh, Siddhartha Engineering CollegeDocument15 pagesShort Questions Power System For Competitive Exams Prepared by Venkatesh, Siddhartha Engineering Collegevenki249100% (11)
- Electrical Design Training Class: Line LossDocument54 pagesElectrical Design Training Class: Line Losssri_electricalNo ratings yet
- Cat1Document3 pagesCat1Manoharan KandasamyNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit Calculations Made EasyDocument18 pagesShort Circuit Calculations Made EasyBong Oliveros100% (1)
- Lab 4 Directional CouplerDocument10 pagesLab 4 Directional Couplernurin runNo ratings yet
- Contents Fefe F VDDocument13 pagesContents Fefe F VDevansparrowNo ratings yet
- Flyback Converter Without SnubberDocument2 pagesFlyback Converter Without SnubberReena ElangovanNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Electrically Small AntennasDocument3 pagesBasic Principles of Electrically Small AntennasA. Villa0% (1)
- 4 Practical Approaches To Minimize Voltage Drop ProblemsDocument2 pages4 Practical Approaches To Minimize Voltage Drop ProblemsArafat Lomangcolob BauntoNo ratings yet
- Compute RLC Parameters of Radial Copper Cables With Single Screen Based On Conductor and Insulator Characteristics - MATLABDocument8 pagesCompute RLC Parameters of Radial Copper Cables With Single Screen Based On Conductor and Insulator Characteristics - MATLABHai NguyenNo ratings yet
- EMDmod 2Document28 pagesEMDmod 2SuprithaNo ratings yet
- High Speed Layout AnalogDocument4 pagesHigh Speed Layout AnalogMahendra SakreNo ratings yet
- Protective Conductor Sizing CalculationsDocument18 pagesProtective Conductor Sizing CalculationsMohanchandra JyotishiNo ratings yet
- Electronics Workshop VivaDocument14 pagesElectronics Workshop VivaUsha ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- SMPS DesignDocument30 pagesSMPS Designshihabnitt100% (1)
- Links For GrapheneDocument1 pageLinks For GrapheneshihabnittNo ratings yet
- Time TableDocument1 pageTime TableshihabnittNo ratings yet
- PlotsDocument1 pagePlotsshihabnittNo ratings yet
- Course Information2009 2010Document4 pagesCourse Information2009 2010shihabnittNo ratings yet
- The Transaction Has Been Completed.: LejerDocument1 pageThe Transaction Has Been Completed.: LejershihabnittNo ratings yet
- Introduction Week: International@adm - Dtu.dkDocument1 pageIntroduction Week: International@adm - Dtu.dkshihabnittNo ratings yet
- Energinet Program 5november2013Document1 pageEnerginet Program 5november2013shihabnittNo ratings yet
- Chandanakkatte Kulir Kondu Vaa - Bheeshmacharya Lyric - Shabeer MTLDocument1 pageChandanakkatte Kulir Kondu Vaa - Bheeshmacharya Lyric - Shabeer MTLshihabnittNo ratings yet
- Time and Place: DTU Elektro 31730 Electric Power Engineering, Teaching Plan 2013Document4 pagesTime and Place: DTU Elektro 31730 Electric Power Engineering, Teaching Plan 2013shihabnittNo ratings yet
- Power Flow Oe O: Olga Lavrova Ivan Lopez PDocument9 pagesPower Flow Oe O: Olga Lavrova Ivan Lopez PshihabnittNo ratings yet
- Draft Report To The People On Environment and Forests 2010 11Document42 pagesDraft Report To The People On Environment and Forests 2010 11shihabnittNo ratings yet
- Power Flow Oe O: Olga Lavrova Ivan Lopez PDocument9 pagesPower Flow Oe O: Olga Lavrova Ivan Lopez PshihabnittNo ratings yet
- Study Methods Aug 13Document28 pagesStudy Methods Aug 13shihabnittNo ratings yet
- Load Flow AnalysisDocument4 pagesLoad Flow AnalysisshihabnittNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Lab 5a - Bus Admittance Matrix 200Document3 pagesMATLAB Lab 5a - Bus Admittance Matrix 200shihabnittNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TEMO Autumn 2013Document5 pagesIntroduction To TEMO Autumn 2013shihabnittNo ratings yet
- Wet Riser SpecificationDocument4 pagesWet Riser SpecificationshihabnittNo ratings yet
- Our Universe Class 8Document10 pagesOur Universe Class 8shihabnittNo ratings yet
- Albert Einstein - RelativityDocument86 pagesAlbert Einstein - Relativitysemiramiss22No ratings yet
- Linear Variable Differential TransformerDocument10 pagesLinear Variable Differential TransformerSoumik DasNo ratings yet
- 2n3903 2n3904 PDFDocument8 pages2n3903 2n3904 PDFOpik BiasaNo ratings yet
- Start: Training Pathway: E-011-1 Industrial Electronic Junior Technician - EquipmentDocument3 pagesStart: Training Pathway: E-011-1 Industrial Electronic Junior Technician - EquipmentzamriabdNo ratings yet
- SP3X DatasheetDocument4 pagesSP3X DatasheetJose BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Kbpc3504 Full Bridge RectifierDocument2 pagesKbpc3504 Full Bridge Rectifierrudey18No ratings yet
- 44 SuroundMixingDocument63 pages44 SuroundMixingDragan CvetkovicNo ratings yet
- qfx10002 Juniper Core Switch PDFDocument225 pagesqfx10002 Juniper Core Switch PDFMohd NazriNo ratings yet
- Ibm Infoprint 1570 DatasheetDocument3 pagesIbm Infoprint 1570 DatasheetxyzNo ratings yet
- Meraki Datasheet MR18Document4 pagesMeraki Datasheet MR18fiqur1No ratings yet
- M.tech Ece Vlsi System Design 1Document46 pagesM.tech Ece Vlsi System Design 1Mohan DasNo ratings yet
- Specification DNA-31734 Tracking Resistant ADSS CableDocument5 pagesSpecification DNA-31734 Tracking Resistant ADSS CableDerrick Kojo SenyoNo ratings yet
- Condor Cab SimDocument6 pagesCondor Cab SimWallas MouraNo ratings yet
- Relay and AVR Atmel Atmega 16Document12 pagesRelay and AVR Atmel Atmega 16Robo IndiaNo ratings yet
- s71500 CM PTP Function Manual en-US en-USDocument88 pagess71500 CM PTP Function Manual en-US en-USArunagiri MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Manual Carman Scan VGDocument138 pagesManual Carman Scan VGDeyvis Fernando Olivos MedinaNo ratings yet
- Nortel Voice FundamentalsDocument43 pagesNortel Voice FundamentalsQuoc NhaNo ratings yet
- 6300 055d Sentinel Installation Manual M SenzorDocument29 pages6300 055d Sentinel Installation Manual M SenzorBairon Alvira ManiosNo ratings yet
- Trip of A Zig Zag TransformerDocument22 pagesTrip of A Zig Zag TransformerPranesh PalNo ratings yet
- Economics (Internet Service Provider)Document20 pagesEconomics (Internet Service Provider)romelyn xygnetsNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) PDFDocument64 pagesSupplemental Restraint System (SRS) PDFruanm_1No ratings yet
- Ale Nokia 7368 Isam Ont Xs 250wx A Datasheet enDocument4 pagesAle Nokia 7368 Isam Ont Xs 250wx A Datasheet enNguyen AnhNo ratings yet
- Ruckus Zoneflex 7363 User GuideDocument108 pagesRuckus Zoneflex 7363 User GuideJorge PachecoNo ratings yet
- Erros Sonda AlpinaDocument2 pagesErros Sonda AlpinaraphaelpessNo ratings yet
- 2 Fiber Optic BasicsDocument11 pages2 Fiber Optic BasicsDheeraj Yadav100% (1)
- RRU5905/RRU5905w Description: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDDocument32 pagesRRU5905/RRU5905w Description: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDvasNo ratings yet
- PLZGDocument4 pagesPLZGgav oviNo ratings yet
- Iot Based Induction Motor Monitoring and Drive Based On SVPWMDocument19 pagesIot Based Induction Motor Monitoring and Drive Based On SVPWMMuhammad MoazzamNo ratings yet
- Xmax TechnologyDocument24 pagesXmax Technologyrajeev kumar sharmaNo ratings yet
- Multitester PartsDocument43 pagesMultitester PartsRamil TuasonNo ratings yet
- Lenze 9400 Software ManualDocument918 pagesLenze 9400 Software ManualAnuchit KamongiatpatNo ratings yet