Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TTT
Uploaded by
Carol CrosbyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TTT
Uploaded by
Carol CrosbyCopyright:
Available Formats
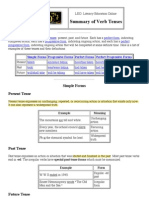
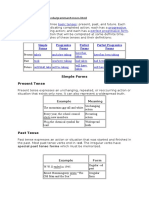
In English, there are three basic tenses: present, past, and future.
Each has a perfect form, indicating completed action; each has a progressive form, indicating ongoing action; and each has a perfect progressive form, indicating ongoing action that will be completed at some definite time. Here is a list of examples of these tenses and their definitions: Simple Forms Present take/s Past took Progressive Forms am/is/are taking was/were taking will be taking Perfect Forms have/has taken had taken will have taken Perfect Progressive Forms have/has been taking had been taking will have been taking
Future will/shall take
Simple Forms Present Tense Present tense expresses an unchanging, repeated, or reoccurring action or situation that exists only now. It can also represent a widespread truth. Example The mountains are tall and white. Meaning Unchanging action
Every year, the school council elects new members. Recurring action Pb is the chemical symbol for lead. Past Tense Past tense expresses an action or situation that was started and finished in the past. Most past tense verbs end in -ed. The irregular verbs have special past tense forms which must be memorized. Example W.W.II ended in 1945. Ernest Hemmingway wrote "The Old Man and the Sea." Future Tense Future tense expresses an action or situation that will occur in the future. This tense is formed by using will/shall with the simple form of the verb. The speaker of the House will finish her term in May of 1998. The future tense can also be expressed by using am, is, or are with going to. The surgeon is going to perform the first bypass in Minnesota. We can also use the present tense form with an adverb or adverbial phrase to show future time. The president speaks tomorrow. (Tomorrow is a future time adverb.) Form Regular -ed past Irregular form Widespread truth
Progressive Forms Present Progressive Tense Present progressive tense describes an ongoing action that is happening at the same time the statement is written. This tense is formed by using am/is/are with the verb form ending in -ing. The sociologist is examining the effects that racial discrimination has on society. Past Progressive Tense Past progressive tense describes a past action which was happening when another action occurred. This tense is formed by using was/were with the verb form ending in -ing. The explorer was explaining the lastest discovery in Egypt when protests began on the streets. Future Progressive Tense Future progressive tense describes an ongoing or continuous action that will take place in the future. This tense is formed by using will be or shall be with the verb form ending in -ing. Dr. Jones will be presenting ongoing research on sexist language next week.
Perfect Forms Present Perfect Tense Present perfect tense describes an action that happened at an indefinite time in the past or that began in the past and continues in the present.This tense is formed by using has/have with the past participle of the verb. Most past participles end in -ed. Irregular verbs have special past participles that must be memorized. Example The researchers have traveled to many countries in order to collect more significant data. Women have voted in presidential elections since 1921. Meaning At an indefinite time Continues in the present
Past Perfect Tense Past perfect tense describes an action that took place in the past before another past action. This tense is formed by using had with the past participle of the verb. By the time the troops arrived, the war had ended. Future Perfect Tense Future perfect tense describes an action that will occur in the future before some other action. This tense is formed by using will have with the past participle of the verb. By the time the troops arrive, the combat group will have spent several weeks waiting.
You might also like
- Simple Forms Progressive Forms Perfect Forms Perfect Progressive FormsDocument4 pagesSimple Forms Progressive Forms Perfect Forms Perfect Progressive FormsYolanda RuizNo ratings yet
- Summary of Verb TensesDocument3 pagesSummary of Verb TensesWan Hazlina A TajudinNo ratings yet
- 1 Overview of Verb TensesDocument5 pages1 Overview of Verb TensesedithNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument4 pagesVerb TenseshendyahmarNo ratings yet
- Summary of Verb Tenses: CCCCC CCCCC CCC CC C CCCC CC C CC CCC CC C CCCC CC CCCCCCC CC CCCCCDocument5 pagesSummary of Verb Tenses: CCCCC CCCCC CCC CC C CCCC CC C CC CCC CC C CCCC CC CCCCCCC CC CCCCCMark Christian BagsicNo ratings yet
- Summary of Verb TensesDocument4 pagesSummary of Verb TensesTrinh100% (1)
- Progressive Form Basic Tenses Perfect Form Perfect Progressive FormDocument10 pagesProgressive Form Basic Tenses Perfect Form Perfect Progressive FormLilibeth Magbanua PasicaranNo ratings yet
- Summary of Verb TensesDocument4 pagesSummary of Verb TensesRamir Y. LiamusNo ratings yet
- Simple Forms Present Tense: Example MeaningDocument16 pagesSimple Forms Present Tense: Example MeaningyanieggNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses and AspectDocument17 pagesVerb Tenses and AspectJosh BhonNo ratings yet
- Summary of Verb TensesDocument4 pagesSummary of Verb TensesMayur RawoolNo ratings yet
- Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument10 pagesClick To Edit Master Subtitle StylekyuziziNo ratings yet
- Basic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormDocument4 pagesBasic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormsumitNo ratings yet
- Simple Forms Present Tense: Simple Forms Progressive Forms Perfect Forms Perfect Progressive FormsDocument8 pagesSimple Forms Present Tense: Simple Forms Progressive Forms Perfect Forms Perfect Progressive FormsJp Karl Gonzales UliganNo ratings yet
- Simple Forms Progressive Forms Perfect Forms Perfect Progressive FormsDocument4 pagesSimple Forms Progressive Forms Perfect Forms Perfect Progressive Formshardy annawayNo ratings yet
- Basic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormDocument29 pagesBasic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormRadheShyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument29 pagesEnglish TensesRadheShyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormDocument29 pagesBasic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormRadheShyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormDocument29 pagesBasic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormRadheShyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument30 pagesEnglish TensesMohamed Tayeb SELT100% (65)
- Verb Tenses (Condensed Notes)Document3 pagesVerb Tenses (Condensed Notes)zarimNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 2 Verbs PDFDocument8 pagesPertemuan 2 Verbs PDFriko cmenoxNo ratings yet
- Shiela's Verb TensesDocument30 pagesShiela's Verb TensesShiela Aringo100% (1)
- CJC Lesson9 Verb TensesDocument9 pagesCJC Lesson9 Verb TensesJohn Carl AparicioNo ratings yet
- CSC GrammarDocument5 pagesCSC Grammarsandra seguienteNo ratings yet
- ELCS PG 65-70Document6 pagesELCS PG 65-70roughNo ratings yet
- Review On GrammarDocument14 pagesReview On GrammarattyalanNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument9 pagesParts of SpeechJose BrabanteNo ratings yet
- VerbTensesJuly08 000Document6 pagesVerbTensesJuly08 000Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- The Twelve Tenses of EnglishDocument10 pagesThe Twelve Tenses of EnglishMary Marsheey Jamero ManipisNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument4 pagesTensesGaurav bansalNo ratings yet
- Overview of Verb Tenses-3Document4 pagesOverview of Verb Tenses-3Afrim TonuziNo ratings yet
- Tense Nagkalan AmritsarDocument17 pagesTense Nagkalan Amritsarapi-3731257100% (1)
- 12 Basic Tenses and Verb TensesDocument9 pages12 Basic Tenses and Verb TensesniensjvrNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument4 pagesTensesCharisel Jeanne CasalaNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument16 pagesTensesMisham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Tenses: Course: Functional English 1 Course Code: 103Document66 pagesTenses: Course: Functional English 1 Course Code: 103Nimra AslamNo ratings yet
- Aspects of TensesDocument4 pagesAspects of TenseszoroNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument1 pageEnglishiamchristinebooNo ratings yet
- Grammar Coorect UsageDocument4 pagesGrammar Coorect UsagePaul EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Verbs: Reported By: Angelita A. JocsonDocument36 pagesVerbs: Reported By: Angelita A. JocsonANGELITA A JOCSONNo ratings yet
- How To Add and Subtract PolynomialsDocument13 pagesHow To Add and Subtract PolynomialsGeremyJustineBonifacioNo ratings yet
- A Past TenseDocument26 pagesA Past TenseCitra CuteeNo ratings yet
- Verbs in English: Verb) - Auxiliary Verbs Can Add Detail To The Action or Help The Principal Verb (They Are AlsoDocument33 pagesVerbs in English: Verb) - Auxiliary Verbs Can Add Detail To The Action or Help The Principal Verb (They Are AlsoSou SouNo ratings yet
- What Are Tenses in EnglishDocument3 pagesWhat Are Tenses in EnglishEmmanuel Bahena AvelinoNo ratings yet
- Future Tense and Its Aspect (English-I)Document13 pagesFuture Tense and Its Aspect (English-I)Subhankar AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- VERB Tenses 2Document31 pagesVERB Tenses 2BagasWicaksana100% (1)
- Present Perfect Simple Tense in EnglishDocument6 pagesPresent Perfect Simple Tense in EnglishAntoaneta StancuNo ratings yet
- Have SatDocument4 pagesHave SatLim SenglyNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR Past Tenses in English LanguageDocument10 pagesSEMINAR Past Tenses in English LanguageSulejman BeširovićNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument9 pagesEnglishqwertyphonesNo ratings yet
- What Is A Verb TenseDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Verb TenseDavie Jane PascuaNo ratings yet
- Assignment GrammarDocument54 pagesAssignment GrammarRameshLoganathanNo ratings yet
- TenseDocument17 pagesTenseDashbayar EmmyNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument6 pagesVerb TensesnornNo ratings yet
- Sentence Correction For GmatDocument92 pagesSentence Correction For GmatSuraj BhaduNo ratings yet
- The Present ContinuousDocument3 pagesThe Present ContinuousAtall Nedita João PauloNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument49 pagesVerb TensesHazel GaylanNo ratings yet
- 6-2kipper and Giant Work Book2Document2 pages6-2kipper and Giant Work Book2Carol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- 6-1in The Garden WorkbookDocument7 pages6-1in The Garden WorkbookCarol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- 6-11the Shiny Key Work BookDocument8 pages6-11the Shiny Key Work BookCarol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- 6 Robin Hood Work BookDocument4 pages6 Robin Hood Work BookCarol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- 6-2kipper and Giant Work Book1Document5 pages6-2kipper and Giant Work Book1Carol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- 6-2kipper and Giant Work Book2Document2 pages6-2kipper and Giant Work Book2Carol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- 6-3the Outing Work BookDocument7 pages6-3the Outing Work BookCarol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- 6-2kipper and Giant Work Book1Document5 pages6-2kipper and Giant Work Book1Carol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- 6 Robin Hood Work BookDocument4 pages6 Robin Hood Work BookCarol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- Making DecisionsDocument2 pagesMaking DecisionsCarol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- 6-1in The Garden WorkbookDocument7 pages6-1in The Garden WorkbookCarol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- ESL Questions: COVID 19Document1 pageESL Questions: COVID 19Carol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- Newcomer's Guide To The Canadian Job MarketDocument47 pagesNewcomer's Guide To The Canadian Job MarketEstefanía Cáceres AcostaNo ratings yet
- Gram ExDocument1 pageGram ExCarol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- Rain and YouDocument2 pagesRain and YouCarol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- Adjectives Describing PersonalityDocument3 pagesAdjectives Describing PersonalityCarol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- Qualifiers YDocument1 pageQualifiers YCarol CrosbyNo ratings yet
- 4 MS - 2nd Generation Sequence 2 Me, My Personality and Experiences - All Lessons by Khelil Moudjib Arrahmane 2018-2019-ConvertiDocument64 pages4 MS - 2nd Generation Sequence 2 Me, My Personality and Experiences - All Lessons by Khelil Moudjib Arrahmane 2018-2019-ConvertiZellagui SaidNo ratings yet
- The Comparison Between The Tenses of English and Those of Arabic PDFDocument14 pagesThe Comparison Between The Tenses of English and Those of Arabic PDFNda MiraNo ratings yet
- Complete First For Schools 2nd Edition Word ListDocument36 pagesComplete First For Schools 2nd Edition Word ListTaniaNo ratings yet
- Sat Practice Test 1 Writing and Language Assistive TechnologyDocument102 pagesSat Practice Test 1 Writing and Language Assistive TechnologyImmaNo ratings yet
- Spell Bee Word List-Class - 7 (2021-22)Document3 pagesSpell Bee Word List-Class - 7 (2021-22)Shreyansh KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Speech and Language Processing. Daniel Jurafsky James H. MartinDocument25 pagesSpeech and Language Processing. Daniel Jurafsky James H. MartinSheilaNo ratings yet
- Frequency Adverbs HKDocument2 pagesFrequency Adverbs HKHERNANDEZ VARGAS JOSE MANUELNo ratings yet
- Lexical SyllabusDocument142 pagesLexical Syllabussomething100% (2)
- Bài Giảng Dạng Văn Bản (Script) : Môn học: Đọc hiểu 4 Unit 8 - Part 2Document6 pagesBài Giảng Dạng Văn Bản (Script) : Môn học: Đọc hiểu 4 Unit 8 - Part 2trongnhan1479No ratings yet
- ABA Unit 1Document4 pagesABA Unit 1Paulo SantosNo ratings yet
- 7 24 2012 6 36 27 PMFinal Syllabus 2014 fINAL-1Document121 pages7 24 2012 6 36 27 PMFinal Syllabus 2014 fINAL-1Jitu PradhanNo ratings yet
- A Pedagogic Grammar For Cebuano Visayan LectureDocument9 pagesA Pedagogic Grammar For Cebuano Visayan LectureCyrel jay Bautista MoronNo ratings yet
- Position of Adverbs TableDocument1 pagePosition of Adverbs TableJulaNo ratings yet
- #2 First Impressions: Lesson TranscriptDocument10 pages#2 First Impressions: Lesson TranscriptBella LuchianNo ratings yet
- Pau Inglés-10Document2 pagesPau Inglés-10AlfodNo ratings yet
- Grammar For English Language Teachers - ParrottDocument477 pagesGrammar For English Language Teachers - ParrottDhara Zatapathique0% (1)
- Aktiv I Pasiv'Document3 pagesAktiv I Pasiv'Dusko SladojevicNo ratings yet
- CheltonDocument17 pagesCheltonGersonn TaueliaNo ratings yet
- Types of Parts of Speech NounDocument20 pagesTypes of Parts of Speech NounNurul Aida NionsiNo ratings yet
- English Guide Propedeutico 2 ActDocument18 pagesEnglish Guide Propedeutico 2 ActMayte OlveraNo ratings yet
- Rules of PrepositionsDocument3 pagesRules of PrepositionsSM TANVIR AHAMMADNo ratings yet
- The Same Meaning Sentence TestDocument9 pagesThe Same Meaning Sentence TestAnggun DiahNo ratings yet
- Who Vs Whom HandoutDocument5 pagesWho Vs Whom HandoutSeanNo ratings yet
- Grammar Exercises: Verb Patterns (2) 1 0Document3 pagesGrammar Exercises: Verb Patterns (2) 1 0Lucia LopezNo ratings yet
- Let's Prepare TogetherDocument130 pagesLet's Prepare TogetherEnglish with SAYARNo ratings yet
- SentenceDocument12 pagesSentenceSumera BokhariNo ratings yet
- Back Alive: Name: Class: TeacherDocument4 pagesBack Alive: Name: Class: TeacherYashvi JangraNo ratings yet
- Right On! 3 Teachers BookDocument441 pagesRight On! 3 Teachers BookLevan Medoshvili74% (27)
- Unit 1 Can Be Able To and CouldDocument45 pagesUnit 1 Can Be Able To and CouldSamuel MtzNo ratings yet
- Bahnwärter Thiel Chapter 3Document19 pagesBahnwärter Thiel Chapter 3ramonsb1No ratings yet