Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Multi-cylinder Engine Performance Tests
Uploaded by
manikandan0000000Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Multi-cylinder Engine Performance Tests
Uploaded by
manikandan0000000Copyright:
Available Formats
Experiment-1 Single Cylinder Four Stroke Diesel Engine Objectives 1. Studying a single cylinder four stroke diesel engine.
2. Measuring the performance of the engine at constant speed 3. Obtaining the bmep Vs bsfc, bmep Vs efficiency and bmep vs exhaust gas temperature curves for the engine 4. Drawing Willans line and obtaining friction power and mechanical efficiency Engine specifications Engine Type : Single cylinder Four stroke Diesel engine (Kirloskar), Bore : 0.0875m, Stroke : 0.11m Capacity : 661.5 cc, Power : 6 H.P. at 1500 rpm, Torque : 2.96 kg.m at 1500 rpm and Compression Ratio :17.5:1 Things to do 1. Study of the single cylinder diesel engine
a. Study the following components: Crank shaft, flywheel, piston and connecting rod; camshaft, push rods and valve system; diesel pump and injector; governing system; lubrication: oil sump and pump, oil paths; cooling system: water paths. b. Measure bore and stroke, and observe valve opening and closing when you rotate the crankshaft. c. How does the engine start? How does it stop? d. If you want to change engine speed, what would you do? e. Do you find any parts missing in the engine you studied? Are they there in the engine you did experiments on? What are the differences between these engines? 2. Measuring the performance at constant speed a. Study the instrumentation: Loading the engine: how is this done? How is the load measured? Speed: how is it measured? Exhaust temperature: how is it measured? Note: the question how is it measured should be answered in terms of what the measuring device is, what it measures, how it measures it, if there is any calibration constant, what it is, how you calibrate the device, etc. b. Start the engine. Run the engine at different loads from zero to maximum. At each load, measure the engine speed (this should be constant: how is this controlled?), fuel consumption rate, air consumption rate, exhaust gas temperature. c. From the data, compute the bmep, bsfc, thermal efficiency and plot curves ment\ioned in objective 3 above. d. Plot fuel flow rate Vs brake power and obtain the frictional power: Willans line method (what is this?). Using this calculate the indicated power and mechanical efficiency at the loads you measured engine data. Report Writing Your report should contain information pertaining to the items in things to do section above, with sections 1a, 1b, etc. Write your own reports, one for each subgroup, and be to the point. Reference / Textbook material Internal Combustion Engines by V. Ganesan.
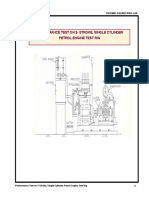
Experiment-2 Multi-cylinder Spark Ignited Engine Objectives
1. Study of a Maruti Zen engine components and test setup 2. Performing measurements of performance test at constant speed 3. Performing Morse test on the engine and obtaining frictional power and mechanical efficiency at that speed. Engine Specifications
Engine Type: Four cylinder Four stroke MPFI petrol engine (Maruti Zen), Bore: 0.072 m, Stroke: 0.061m Capacity: 993 cc, Power: 60 HP at 6000 rpm, Torque: 78.5 Nm at 4500 rpm and Compression Ratio: 9.4:1 Things to do 1. Study a multi-cylinder SI engine
a. Crank shaft, flywheel, connecting rods, pistons and their relative motions b. Camshaft(s) and valve mechanism c. Inlet and exhaust manifolds d. Fuel supply system e. Ignition system f. Cooling system and coolant passages g. Lubricating system and lubricant passages h. Other auxiliary systems: starter, alternator, ECU, etc. 2. Performance test at constant speed a. Study the instrumentation of the engine for measurement of fuel flow rate, airflow rate, load and speed. How do these instruments function? b. Start the engine and set the speed (how do you do this?). Measure fuel consumption rate, airflow rate, power and speed. Now vary the load, keeping the speed the same. (How is this done?) Measure the above quantities at each load. Plot the results in the form of bmep vs bsfc and bmep vs efficiency. Compute volumetric efficiency and air-fuel ratio at each data point. c. Now at the same speed perform Morse test on the engine (What is this test?) Using this test, obtain the frictional power and mechanical efficiency of the engine at various load conditions at the same speed. Report Writing Your report should contain information pertaining to the items in things to do section above, with sections 1a, 1b, etc. Write your own reports, one for each subgroup, and be to the point. Reference / Textbook material Internal Combustion Engines by V. Ganesan.
Experiment-3 Multi-cylinder Compression Ignited Engine Objectives
1. Study the Tata truck engine with the help of the chart (of Ashok Leyland Engine). 2. Measure the performance characteristics of the multi-cylinder diesel engine at constant speed 3. Drawing the Willans line for the engine to obtain its frictional power at this speed, and mechanical efficiency at different loads. Engine Specifications Engine Type: Four cylinder Four stroke Diesel engine, Bore: 0.073m, Stroke: 0.0889m, Capacity: 1489cc, Power: 36 H.P. at 4000 rpm, Torque: 8.5 kg.m at 2250 rpm and Compression Ratio :17.3:1 Things to do 1. Study a multi-cylinder CI engine a. Crank shaft, flywheel, connecting rods, pistons and their relative motions b. Camshaft(s), push rods and valve mechanism c. Inlet and exhaust manifolds d. Fuel supply system e. Cooling system and coolant passages f. Lubricating system and lubricant passages g. Other auxiliary systems: starter, alternator, etc. 2. Performance test at constant speed a. Study the instrumentation of the engine for measurement of fuel flow rate, airflow rate, load and speed. How do these instruments function? b. Start the engine and set the speed (how do you do this?). Measure fuel consumption rate, airflow rate, power and speed. Now vary the load, keeping the speed the same. (How is this done?) Measure the above quantities at each load. Plot the results in the form of bmep vs bsfc and bmep vs efficiency. Compute volumetric efficiency and air-fuel ratio at each data point. c. Plot the Willans line from your data (What is this line?), and obtain the frictional power and mechanical efficiency of the engine at various load conditions at this speed. Report Writing Your report should contain information pertaining to the items in things to do section above, with sections 1a, 1b, etc. Write your own reports, one for each subgroup, and be to the point. Reference / Textbook material Internal Combustion Engines by V. Ganesan.
Experiment-4 Intake and Exhaust Processes Objectives
1. Study the given engine and obtain the valve timing diagram and valve lift profile as a function of crank angles with reference to TDC. 2. Measure the discharge coefficient of the given valve at steady flow conditions for different valve lifts and plot Cd as a function of valve lift Things to do 1. Valve timing and Lift diagrams a. In the engine provided, mark the TDC position on the flywheel. b. Rotate the flywheel in the correct direction and figure out the processes of intake and exhaust, and hence identify intake and exhaust valves (how?) c. Using the dial guage, measure valve lift as a function of crank angle with reference to TDC for both intake and exhaust valves, and plot valve lift profile and valve timing diagrams (what are these?). 2. Discharge coefficient of valve system For a given engine cylinder head with valves, perform the following experiment: a. Start the blower and set the valve lift and flow rate (How?) b. Measure the pressure drop across the valve (how?) and flow rate through the valve using a venturi meter (how?). c. Change the flow rate and get these readings again for different flow rates for the same valve lift. d. Change the valve lift and repeat steps b and c for each valve lift. e. Compute discharge coefficients from the above data and examine how it varies with valve lift. Discuss the results. Report Writing Your report should contain information pertaining to the items in things to do section above, with sections 1a, 1b, etc. Write your own reports, one for each subgroup, and be to the point. Reference / Textbook material Internal Combustion Engines by John B. Heywood.
You might also like
- EC55B Service Training GuideDocument237 pagesEC55B Service Training GuideAimHigh100% (4)
- Structural EngineeringDocument168 pagesStructural Engineeringcjbalza100% (2)
- L3 Part1 Engine&TransmissionDocument391 pagesL3 Part1 Engine&TransmissionEdwin Torres100% (2)
- Specification S16R2 PTAWDocument4 pagesSpecification S16R2 PTAWMuhammad rizki100% (1)
- Ford Ranger Maintenance ScheduleDocument1 pageFord Ranger Maintenance ScheduleEdlir PeciNo ratings yet
- DifferentialsDocument48 pagesDifferentialsEngine Tuning UpNo ratings yet
- Types of Electric VehiclesDocument17 pagesTypes of Electric VehiclesjokerNo ratings yet
- Arctic Cat 2009 400 TRV 500 550 700 1000 Thundercat Service ManualDocument20 pagesArctic Cat 2009 400 TRV 500 550 700 1000 Thundercat Service Manualpaul98% (48)
- Cabin ModuleDocument76 pagesCabin ModuleESRANo ratings yet
- Engine Performance and Indicator CardsDocument27 pagesEngine Performance and Indicator CardsMeghanath AdkonkarNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall Design CalculationsDocument6 pagesRetaining Wall Design Calculationsdocument123456789100% (1)
- TRAINING HANDOUT T1+T2 42-400I500 and 72-212A (600 Variant)Document4 pagesTRAINING HANDOUT T1+T2 42-400I500 and 72-212A (600 Variant)Jesús Montalvo FernándezNo ratings yet
- 10M134 AIC Assignment 1 & 2 PDFDocument14 pages10M134 AIC Assignment 1 & 2 PDFChandannnn92No ratings yet
- Engine Performance Testing ParametersDocument39 pagesEngine Performance Testing ParametersashaNo ratings yet
- VW Polo Sedan 1.6 Manual Guide 2006Document2 pagesVW Polo Sedan 1.6 Manual Guide 2006avm4343No ratings yet
- Four-Stroke Diesel Engine Performance TestDocument2 pagesFour-Stroke Diesel Engine Performance Testعقيل حميد عنادNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 2 Objective: - Study and Performance Test On A Four-Stroke Single Cylinder Diesel Engine at Constant SpeedDocument2 pagesExperiment No 2 Objective: - Study and Performance Test On A Four-Stroke Single Cylinder Diesel Engine at Constant SpeedMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1 Objective: - Study and Performance Test On A Four-Stroke Multi Cylinder Diesel Engine at Constant SpeedDocument1 pageExperiment No 1 Objective: - Study and Performance Test On A Four-Stroke Multi Cylinder Diesel Engine at Constant SpeedMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - ExercisesDocument4 pagesChapter 2 - ExercisesMc AxNo ratings yet
- I.C. Engine Performance CalculationsDocument6 pagesI.C. Engine Performance Calculationsmailsk123No ratings yet
- ME6404 Thermal EngineeringDocument21 pagesME6404 Thermal EngineeringAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNo ratings yet
- Project Report TE LabDocument7 pagesProject Report TE LabRadhika GurjarNo ratings yet
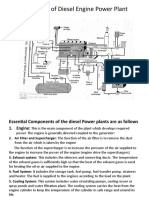
- General Layout of Diesel Engine Power PlantDocument34 pagesGeneral Layout of Diesel Engine Power PlantMahesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Expt No. 6Document8 pagesExpt No. 6Ariston D. TrazonaNo ratings yet
- 4 Stroke Petrol Lab 1Document3 pages4 Stroke Petrol Lab 1Eve GreenNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanical Engineering SessionalDocument18 pagesBasic Mechanical Engineering SessionalRahik WasifNo ratings yet
- Engine efficiency fundamentalsDocument18 pagesEngine efficiency fundamentalsKhushank MNo ratings yet
- AEN, ACD, TTW QB CT2Document5 pagesAEN, ACD, TTW QB CT2shlokkharat09No ratings yet
- Draw Engine Performance CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesDraw Engine Performance CharacteristicsnurhanakasimNo ratings yet
- Atd PaperDocument7 pagesAtd PaperWestNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Department of Mechanical Engineering Graphic Era Hill University, BhimtalDocument55 pagesLaboratory Manual: Department of Mechanical Engineering Graphic Era Hill University, BhimtalDigvijay RautelaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of 4 Stroke 4 Cylinder Petrol EngineDocument36 pagesAnalysis of 4 Stroke 4 Cylinder Petrol Enginesuri surendraNo ratings yet
- MAN B&W MC-C Engine DifferencesDocument67 pagesMAN B&W MC-C Engine DifferencesJack PotNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document12 pagesLab 3Hope LeeNo ratings yet
- DRMIIC4M4LO3Document38 pagesDRMIIC4M4LO3John Lester M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Memo Report 5BDocument2 pagesMemo Report 5BAnh NguyenNo ratings yet
- ME6404 Thermal EngineeringDocument12 pagesME6404 Thermal EngineeringprasanthprpNo ratings yet
- ThermalDocument40 pagesThermalvijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Paper 17Document9 pagesPaper 17Faitar CatalinNo ratings yet
- Dual fuel engine performance and emissions testingDocument1 pageDual fuel engine performance and emissions testingAMIT PRAJAPATINo ratings yet
- R7220303 Thermal Engineering-IDocument1 pageR7220303 Thermal Engineering-IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- ME6404 Thermal EngineeringDocument12 pagesME6404 Thermal EngineeringjohnpratheeshNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Gas Power CyclesDocument78 pagesUnit I: Gas Power CyclesBalaji DsNo ratings yet
- Basic GT EngineDocument22 pagesBasic GT EngineabuhurairamunirNo ratings yet
- Variable Compression Ratio ExperimentDocument7 pagesVariable Compression Ratio ExperimentMuruganNo ratings yet
- Fuel System Engine Control System Hydraulic sYSTEMDocument3 pagesFuel System Engine Control System Hydraulic sYSTEMlamborghini1991No ratings yet
- Bio Diesel JournalDocument10 pagesBio Diesel JournalMaheshNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - AEDDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank - AEDbhuvan raju t kNo ratings yet
- Ic Engines Laboratory ManualDocument35 pagesIc Engines Laboratory ManualYuvaraj Yuvi0% (1)
- 2015-SAE-Prediction of High Altitude Performance For UAV Engine PDFDocument6 pages2015-SAE-Prediction of High Altitude Performance For UAV Engine PDF128mansouriNo ratings yet
- Measure Engine Performance and Calculate Key ParametersDocument28 pagesMeasure Engine Performance and Calculate Key ParametersbroNo ratings yet
- Motor Solved Written Question AnswerDocument64 pagesMotor Solved Written Question Answerkum512No ratings yet
- Motors & Engines TransparencyDocument9 pagesMotors & Engines TransparencyLorenzo Niño BlasquezNo ratings yet
- Motors Engines TransparencyDocument9 pagesMotors Engines Transparencystephene larimNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power Plant Chapter: Measuring Brake and Indicated PowerDocument29 pagesDiesel Power Plant Chapter: Measuring Brake and Indicated PowerIvy Joy UbinaNo ratings yet
- Paper 17Document8 pagesPaper 17Faitar CatalinNo ratings yet
- Experiment Morse TestDocument3 pagesExperiment Morse TestSivi NallamothuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Overview of ICE: TR 2019 Internal Combustion EngineDocument62 pagesChapter 1: Overview of ICE: TR 2019 Internal Combustion EngineMinh Hồ BìnhNo ratings yet
- Ae LabDocument53 pagesAe LabAnkit DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Consultant Expert DR Mohamed Seif Al Den TahaDocument46 pagesConsultant Expert DR Mohamed Seif Al Den Tahaconsultant expert dr mohamed seif al den tahaNo ratings yet
- Performance of a Gasoline Engine at Partial LoadDocument5 pagesPerformance of a Gasoline Engine at Partial LoadGritz Kay Labucay MarforiNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT NO 3 Willan's LineDocument3 pagesEXPERIMENT NO 3 Willan's LineMohamad Ahmad100% (1)
- Evaluating Gasoline Engine PerformanceDocument10 pagesEvaluating Gasoline Engine PerformancePaul Ryan GeneralNo ratings yet
- I C ENGINES & COMPRESSORS QUESTION BANK UNIT ANALYSISDocument11 pagesI C ENGINES & COMPRESSORS QUESTION BANK UNIT ANALYSISYonatan NegusuNo ratings yet
- 09a52104 - Aerospace Propulsion-IDocument4 pages09a52104 - Aerospace Propulsion-IMoin KhanNo ratings yet
- Load Test On Single Cylinder 4s Diesel EngineDocument8 pagesLoad Test On Single Cylinder 4s Diesel EngineMathew JohnNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 IC PrintedDocument3 pagesExp 3 IC PrintedDipendra TiwariNo ratings yet
- EX.11 - Load Test-Single Cylinder, 2stroke - PetrolDocument6 pagesEX.11 - Load Test-Single Cylinder, 2stroke - Petrolmanojkhadka23No ratings yet
- MITE Energy Conversion Lab ManualDocument44 pagesMITE Energy Conversion Lab ManualSubuddhi DamodarNo ratings yet
- BT Promotion Panel Form For MathsDocument7 pagesBT Promotion Panel Form For Mathsmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Seismic Lateral Earth PressureDocument32 pagesSeismic Lateral Earth PressureKay CharlesNo ratings yet
- Spenser 2003Document25 pagesSpenser 2003manikandan0000000No ratings yet
- 10/11, 4 Cross, LIC Colony, Pammal, Chennai 600 075 PH.: 8939652038 Email: Engineersandconsultants"yahoo - Co MDocument2 pages10/11, 4 Cross, LIC Colony, Pammal, Chennai 600 075 PH.: 8939652038 Email: Engineersandconsultants"yahoo - Co Mmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Steel Structures: Amit H. Varma and Judy Liu CE697R Fall 2012 MWF 2:30 - 3:20 PM CIVL 2123Document2 pagesSeismic Design of Steel Structures: Amit H. Varma and Judy Liu CE697R Fall 2012 MWF 2:30 - 3:20 PM CIVL 2123manikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Some Important Aspects in Civil Works Design of A Mini Hydro Power ProjectDocument16 pagesSome Important Aspects in Civil Works Design of A Mini Hydro Power Projectmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Seismic Analysis of Retaining WallDocument8 pagesSeismic Analysis of Retaining Wallmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Ultra Low Cost HousingDocument12 pagesUltra Low Cost Housingmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Ultra Low Cost HousingDocument15 pagesUltra Low Cost Housingmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Cantilever Wall Sample ReportDocument8 pagesCantilever Wall Sample Reportmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Const of Pre FabDocument10 pagesConst of Pre Fabmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Seismic Lateral Earth PressureDocument32 pagesSeismic Lateral Earth PressureKay CharlesNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument6 pagesAbstractmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Cantilever Retaining Wall AnalysisDocument7 pagesCantilever Retaining Wall AnalysisnhulugallaNo ratings yet
- Payment Template ExcelDocument3 pagesPayment Template Excelmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Seismic Analysis of Retaining WallDocument8 pagesSeismic Analysis of Retaining Wallmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- AbstractDocument6 pagesAbstractmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Seismic Lateral Earth PressureDocument32 pagesSeismic Lateral Earth PressureKay CharlesNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument2 pagesExecutive Summarymanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- KSDesign PartThreeDocument14 pagesKSDesign PartThreeMohd HarizamNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument2 pagesExecutive Summarymanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- AbstractDocument6 pagesAbstractmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- AbstractDocument6 pagesAbstractmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument2 pagesExecutive Summarymanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Seismic Analysis of Retaining WallDocument8 pagesSeismic Analysis of Retaining Wallmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Payment Template ExcelDocument3 pagesPayment Template Excelmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Payment Template ExcelDocument3 pagesPayment Template Excelmanikandan0000000No ratings yet
- Price List for Shock Absorbers and StrutsDocument4 pagesPrice List for Shock Absorbers and StrutsMaracutaia GratisNo ratings yet
- Brake+system New ModelDocument30 pagesBrake+system New ModelTimkenNo ratings yet
- Engine Rebuild Spec - C SeriesDocument6 pagesEngine Rebuild Spec - C SeriesWoley Reagan RobertNo ratings yet
- 6x2 Midlift TractorDocument4 pages6x2 Midlift TractorfranciscobpNo ratings yet
- Modelling, Simulations, and Optimisation of Electric Vehicles For Analysis of Transmission Ratio SelectionDocument15 pagesModelling, Simulations, and Optimisation of Electric Vehicles For Analysis of Transmission Ratio SelectionKyla WindartaNo ratings yet
- TG 04Document35 pagesTG 04chrideer100% (1)
- Same Silver 100Document24 pagesSame Silver 100Γιάννης ΣειράςNo ratings yet
- Cobra Fi2000R Fuel Injection Module InstallationDocument3 pagesCobra Fi2000R Fuel Injection Module InstallationHelene MillerNo ratings yet
- Amsoil 100% Synthetic DCT Fluid (DCT)Document2 pagesAmsoil 100% Synthetic DCT Fluid (DCT)amsoildealerNo ratings yet
- P2 Forces and Braking Higher and IntermediateDocument13 pagesP2 Forces and Braking Higher and IntermediatedownendscienceNo ratings yet
- Conti TechDocument36 pagesConti Techmichaelquimica8623No ratings yet
- Report On Vacuum Braking SystemDocument16 pagesReport On Vacuum Braking SystemPramod Sharma P67% (3)
- 15-Suspension Systems and Components v2Document43 pages15-Suspension Systems and Components v2HanieyzMyNo ratings yet
- JAC Pick-Ups ManualDocument49 pagesJAC Pick-Ups ManualDavid CoboNo ratings yet
- Honda ListDocument8 pagesHonda Listmoderncorporation402No ratings yet
- Catalogo Tokico 2012Document316 pagesCatalogo Tokico 2012Андрей СилаевNo ratings yet
- Trial On Diesel EngineDocument4 pagesTrial On Diesel EngineAbhishek KhatavkarNo ratings yet
- Fh64t6a GBR EngDocument7 pagesFh64t6a GBR EngarfanilyasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Chassis & PowertrainDocument118 pagesChapter 11 Chassis & PowertrainDicky KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Nissan CLDocument18 pagesNissan CLmohhizbarNo ratings yet
- C Rukava Nizkogo DavleniaDocument12 pagesC Rukava Nizkogo DavleniaMichael AkhramovichNo ratings yet