Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial Plant Solution
Uploaded by
wanpudinCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Plant Solution
Uploaded by
wanpudinCopyright:
Available Formats
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
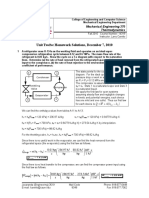
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Tutorial 1 Solution Steam Power Plant Winardi Sani
State 3 : p3 = 3 MPa. t3 = 350o C. Condenser pressure of p4 = 75 kPa. a) Sketch this cycle in p h diagram and read the value of each state variable:
boiler
q in
e
wp pump
q out condenser
h1 h2
h4
tur
wout
bin
h3
h1 = 350 kJ/kg; h3 = 3150 kJ/kg;
h2 = 390 kJ/kg; h4 = 2400 kJ/kg
(1) (2)
b) Determine the thermal efciency of this cycle. th = |wt | |wp | |qin | (3)
The 1. law of T/D applied on the pump 1 to 2 : h2 h1 = wp (isentropic, no kin. and pot. energy) (4)
The 1. law of T/D applied on the turbine 3 to 4 : h4 h3 = wt (isentropic, no kin. and pot. energy, work released)(5) (6)
| wt | = |wt | = |h4 h3 | = |h3 h4 | The 1. law of T/D applied on the boiler 2 to 3 : h3 h2 = qin (no work, no kin. and pot. energy)
(7)
The 1. law of T/D applied on the condenser 4 to 1 : h1 h4 = qout (no work, no kin. and pot. energy, heat is rejected) (8)
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Substitute equations (4) (7) into equation (3) yields: th = |h3 h4 | |h2 h1 | |h3 h2 | |3150 2400| |390 350| = |3150 390| 750 40 710 = = 2760 2760 = 0.257 = 25.7% (9)
(10) (11)
c) Compare your result with the thermal efciency of the Carnot cycle. Carnot cycle operates between two isothermal processes, TL (condenser temperature) and TH (boiler temperature) with efciency: . th = 1 TL TH 85 + 273.15 = 1 350 + 273.15 358.15 = 1 = 0.425 623.15 = 42.5% (12)
(13)
th,Carnot > th,Rankine You may compare the results using the data taken from the steam table (see thermodynamics book by Cengel). Hereby you must calculate the dryness factor x to determine the state properties (h4 for example) at point 4 with formula: x= s3 s4f s4f g (14)
p-h diagram is a convenient tool for energy analysis in Rankine cycle.
State 3 : p3 = 8 MPa, saturated vapor, = t3 = 300o C (read p-h diagram). Condenser pressure of p4 = 8 kPa, saturated liquid and turbine power delivered at t = 100 MW. W a) The thermal efciency th = |wt | |wp | |qin | (15)
The same procedures in the previous solution are applied here to obtain: th = |h4 h3 | |h2 h1 | |h3 h2 | |1750 2725| |200 180| = |2725 200| 975 20 955 = = 2525 2525 = 0.378 = 37.8% (16)
(17) (18)
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
boiler
3
q in
tur bin e
wp pump
wout
100 MW
condenser
1
q out
h1
h2
h4
h3
b) The back work ratio(bwr, pump work divided by turbine work) bwr = = = = |wp | |wt | |h2 h1 | |h4 h3 | |200 180| |1750 2725| 20 = 2% 975 (19) (20) (21) (22)
c) The mass ow rate of the steam in kg/hr t = m W wt = m (h3 h4 ) t W = m = h3 h4 100 MW 105 kJ/s = = = 102.6 kg/s 975 kJ/kg 975 kJ/kg 3600 s = 102.6 kg/s 1 hr 5 = m = 3.7 10 kg/hr (23) (24) (25)
(26)
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
into the working uid as it passes through the d) The rate of heat transfer, Q boiler in = m Q qin = m (h3 h2 ) = 3.7 105 kg/hr (2725 200) kJ/kg kJ 1 hr = 934, 250 kJ/hr = 934, 250 hr 3600 s = 259, 514 kW = 259.5 MW (27) (28)
(29)
e) The mass ow rate of the condenser cooling water in kg/hr if cooling water enters the condenser at 25 o C and exists at 40 o C.
out = m Q qout = m (h4 h1 ) = 3.7 10 kg/hr (1750 180) kJ/kg 1 hr kJ = 580, 900 kJ/hr = 580, 900 hr 3600 s = 161.4 MW
5
(30) (31)
(32)
m cooling water
25 oC in
Q out
Q cw 40 oC out
Energy balance (1. law of T/D) applied on the condenser system: E t = m cw (hcw,in hcw,out ) + m (h4 h1 )
system
0 = m cw (hcw,in hcw,out ) + m (h4 h1 ) m cw = = m (h4 h1 ) hcw,out hcw,in out Q hcw,out hcw,in
The enthalpy values of saturated liquid at 25 o C and 40 o C from the saturated water table: ht=25o C = 104.88 kJ/kg, and ht=40o C = 167.57 kJ/kg. 161.4 MW = 2, 575 kg/s (167.57 104.88)kJ/kg = 9.3 106 kg/hr
cooling water
(33) (34) (35) (36)
m cw = = m cw
(37) (38)
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
With t = p = 85%, determine for the modied cycle:
2s
boiler q in
ise ntr op ic
wp
100 MW
wt
isentropic pump
condenser
1
q out
h2s h2
4s
h1
h4s
h4
wp,s
wp
not scaled
wt wt,s
h3
a) The thermal efciency: th = Turbine t = = wt Pump p = = wp = = = = wp,s wp wp,s p 1 |h2s h1 | p 1 |200 180| kJ/kg 0.85 23.5 kJ/kg; greater than wp,s = 20 kJ/kg (42) (43) (44) (45) (46) wt wt,s = t wt,s (40) (41) |wt | |wp | |qin | (39)
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Substitute the equations (43) and (41) into the equation (39) yields: |t wt,s | | th = |qin | t |h4s h3 | qin
1 p
wp,s | p |h2s h1 |
(47)
(48)
From the previous question we have calculated: |h4s h3 | = |1750 2725| kJ/kg = 975 kJ/kg |h2s h1 | = |200 180| kJ/kg = 20 kJ/kg qin = h3 h2 (49) and
The value of h3 remains constant, but h2 changes!. h2 must be calculated using the the value of wp . h2 = wp + h1 = (23.5 + 180) kJ/kg = 203.5 kJ/kg = qin = (2725 203.5) kJ/kg = qin = 2, 521.5 kJ/kg (52) (51) (50)
All the data necessary has been prepared to solve the new efciency in equation (48): th = 0.85 975 0.1 85 20 2, 521.5 = 0.319 (53)
= 31.9%
The new efciency must be lower compared to the ideal, isentropic case (37.8%). b) The back work ratio (pump work divided by turbine work) bwr = = = = = |wp | |wt | wp,s 1 p t wt,s wp,s 1 wt,s t p 1 bwrs t p 20 1 = 2.8% 975 0.85 0.85
It means, more investment compared to the isentropic process.
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
c) The mass ow rate of the steam in kg/hr. Energy balance applied on the steam power plant. (E = energy in energy out) per unit time. 0 = qin qout + wp wt wt wp = qin qout m (wt wp ) = m (qin qout ) cycle = m W (h3 h2 ) (h4 h1 ) = m = cycle W (h3 h2 ) (h4 h1 ) (54)
State property value [kJ/kg] h1 180 h2 203.5 h3 2725 h4 ? To obtain the value of h4 , we can apply the 1. law of T/D on the turbine, from state 3 to 4 : h4 = h3 wt = h3 t wt,s = h3 t (h4,s h3 ) = (2725 0.85 975) kJ/kg h4 = 1896.5 kJ/kg (56) (55)
Because of irreversibilities inside the turbine, h4 > h4s = 1750 kJ/kg. With cycle = 100 MW, the mass ow rate is then: W m = = = = = m = 100 MW (2725 203.5) (1896.5 180) kJ/kg 100, 000 kW 2521.5 1716.5 kJ/kg 100, 000 J/s 805 J/kg kg 124.223 s 5 kg 4.47 10 hr
(57)
into the working uid as it passes through the d) The rate of heat transfer, Q boiler in = m Q qin = m (h3 h2 ) = 124.223 kg/s (2725 203.5) kJ/kg in = 313.2 MW = Q (60) (58) (59)
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
More heat addition must be provided to overcome losses compared to in,s in the previous isentropic case. Q e) The mass ow rate of the condenser cooling water in kg/hr if cooling water enters the condenser at 25 o C and exists at 40 o C.
out = m Q qout = m (h4 h1 ) kg = 124.223 (1896.5 180) kJ/kg s = 213.2 MW
out = Q
(61)
f) Discuss the effects on the steam power plant of the irreversibilities within the turbine and pump. The effects of irreversibilities within the turbine and the pump can be gauged by comparing the present values with their counterparts. The turbine work is less and the pump work greater than in the previous case. The thermal efciency of the power plant is also less than in the ideal case. The magnitude of the heat transfer to the cooling water is greater than in the ideal case, consequently, so greater mass ow rate of cooling water would be required. This conclusion is still valid eventhough the net power output in the last case is not 100 MW. It is true because the difference of the back work ratio in both the cases is very small.
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Steam is the working uid in an ideal Rankine cycle with superheat and reheat. Steam enters the rst-stage turbine at 8.00 MPa, 480 o C and expands to 0.8 MPa. It is then reheated to 440 o C before entering the second-stage turbine, where it expands to the condenser pressure of 10 kPa. The net power output is 100 MW. Determine: The cycle illustrated in p h diagram:
boiler q in,1
superheat
bin HP tur
4 reheat 6
wt,1
5
q in,2 wp pump
LP
1
condenser q out
tur b
ine
wt,2
h3 h1 h2 h6 h4 h5
a) The thermal efciency of the cycle = = Net work output Heat input woutput winput qinput |w34 | + |w56 | |w12 | |q23 | + |q45 | (62)
From the 1. law of T/D applied on a cyclic system: energy in = energy out (63)
q23 + q45 + w12 = w34 + w56 q61 w34 + w56 w12 = q23 + q45 q61 replacing eq. (64) into eq. (62), yields =1 |q61 | |q23 | + |q45 | (65) (64)
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
00 34
E=2500
E=2800 0
E=
E= 00 35
3 5
sv=
0.0
sv=
0.0
0 E=30
05
4 2 1 6
You can describe the Rankine cycle using p h, T s, or h s diagram, or you can combine them to obtain more accuracy. Interpolation is often necessary if the location point does not lay on a constant line. To calculate the thermal efciency of the steam power plant, you can use the previous
10
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
method with the data read directly on the diagrams illustrated above. An alternative solution is to use the data taken from the steam table. It will be shown following. State 3 4 5 6 1 2 sat. liquid liquid phase superheated given p3 = 8.00 MPa, t3 = 480 0 C p4 = 0.8 MPa t5 = 440 0 C, p5 = p4 p6 = 10 kPa p1 = p6 steam table interpolation
superheated
interpolation
vf = 0.001010 m3 /kg, hf = 191.81 kJ/kg, sf = 0.6492 kJ/kg K
State change 3-4 4-5 5-6 6-1 1-2 2-3
Process isentropic,work out isobar,heat addition isentropic,work out isobar,heat rejection isentropic, compression isobar,heat addition
Meaning s3 = s4 , wt = w34 p4 = p5 , qin = q45 s5 = s6 , wt = w56 p6 = p1 , qout = q61 s1 = s2 , wout = w12 p2 = p3 , qin = q23
Interpolation at state 3 , p3 = 8 MPa Number Temperature 1 450 2 480 3 500
Enthalpy 3273.3 hp3 3399.5
Entropy 6.5579 sp3 6.7266
Linear interpolation to determine both the value of h2 = hp3 and s2 = sp3 h3 h1 t3 t1 = h2 h2 h2 h1 t2 t1 t2 t1 = h1 + (h3 h1 ) t3 t1 480 450 = 3273.3 + (3399.5 3273.3) 500 450 = 3273.3 + 75.72 =
(66)
= hp3 = 3349.02 kJ/kg 480 450 s2 = 6.5579 + (6.7266 6.5579) 500 450 s2 = 6.5579 + 0.10122 = sp3 = 6.65912 kJ/kg K
(67)
(68)
11
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
State 4 , p4 = 0.8 MPa Since sp3 = 6.65912 kJ/kg < 6.6616 kJ/kg = sp4,v , so the state 4 is laid in the liquid+vapor region!. x = s4 sf sf g 6.65912 2.0457 = 4.6160 = 0.9994 (69)
(70)
h4 = hf + x hf g = 720.87 + 0.9994 2047.7 = 2, 767.3 kJ/kg Interpolation at state 5 , p5 = 0.8 MPa Number 1 2 3 Temperature 400 440 500 Enthalpy 3267.7 hp5 3481.3 Entropy 7.5735 sp5 7.8692
(71) (72)
Linear interpolation to determine both the value of h2 = hp3 and s2 = sp3 h3 h1 t3 t1 = h2 h2 h2 h1 t2 t1 t2 t1 = h1 + (h3 h1 ) t3 t1 440 400 (3481.3 3267.7) = 3267.7 + 500 400 = 3267.7 + 85.44 =
(73)
= hp5 = 3, 353.14 kJ/kg 440 400 s2 = 7.5735 + (7.8692 7.5735) 500 450 s2 = 7.5735 + 0.11828 = sp5 = 7.6918 kJ/kg K
(74)
(75)
At state 6 , p6 = 10 kPa, s6 = s5 = 7.6918 kJ/kg K. At pressure of 10 kPa, the entropy of the uid at saturated state is of s = 8.1488 kJ/kg K. So the state 6 must be must be in the liquid vapor region!.
sf [kJ/kg K] 0.6492
At p = 10 kPa. sf g [kJ/kg K] sg [kJ/kg K] 7.4996 8.1488
12
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
x =
s6 sf sf g 7.6918 0.6492 = 7.4996 = 0.9391
(76)
(77)
At p = 10 kPa. hf [kJ/kg K] hf g [kJ/kg K] hg [kJ/kg K] 191.81 2392.1 2583.9
h6 = hf + x hf g = 191.81 + 0.9391 2392.1 = h6 = 2, 438.2 kJ/kg At state 2 : s2 = s1 = 0.6492 kJ/kg K w12 = wp = vf (p2 p1 ) = 0.001010 m /kg (8000 10) kPa m3 N/m2 = 8.0699 kPa kg Pa = 8.0699 kJ/kg h2 = h1 + w12 = 191.81 kJ/kg + 8.0699 kJ/kg = h2 = 199.88 kJ/kg We have prepared all the values needed for efciency: =1 |q61 | |q23 | + |q45 |
3
(78) (79)
(80)
(81) (82) (83)
q61 = h1 h6 = (191.81 2, 438.2) kJ/kg = 2, 246.39 kJ/kg q23 = h3 h2 = (3, 349.02 199.88) kJ/kg = 3, 149.14 kJ/kg (minus sign means heat rejection)
(84) (85) (86) (87)
q45 = h5 h4 = (3, 353.14 2, 767.3) kJ/kg = 585.84 kJ/kg
(88) (89)
13
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia 2, 246.39 3, 149.14 + 585.84 (90)
=1
= 0.4 = 40%
b) The mass ow rate of the steam in kg/hr out from the condensing steam as is passes through c) The rate of heat transfer, Q the condenser, in MW. d) Discuss the effects of reheat on the steam power plant e) Repeat the analysis with including that the turbine and pump each have the isentropic efciency of 85%.
14
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Consider a regenerative steam power plant with one open feedwater heater. Steam enters the turbine at 8.0 MPa, 480 o C and expands to 0.8 MPa, where some of the steam is extracted and diverted to the open feedwater heater operating at 0.8 MPa. The remaining steam expands through the second-stage turbine to the condenser pressure of 10 kPa. This portion of the total ow is condensed to saturated liquid, then pumped to the extraction pressure and introduced into the feedwater heater at 0.8 MPa. The isentropic efciency of each turbine is 85% and each pump operates isentropically. If the net power output of the cycle is 100 MW, determine: a) The thermal efciency
Steam generator 3 HP 4 LP Turbines
(1 y)
5
Open feedwater heater
Pump 2
Pump 1
40
3 E=
E=2500
E=2800 0
sv= 0
2 1 4s 4
7 5s 6 5
15
sv=
0.0
0 E=30
.00
Condenser
E= 35 00
(1 y)
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
The thermal efciency of the cycle Net work output th = Heat input woutput winput = qinput th = |wt | |wp | |q23 | (91)
Fraction of the total ow at state 4 by y . y = m 4 /m with the total mass m =m 4+m 5. Total turbine work per unit of total mass is: t W wt = = (h4 h3 ) + (1 y )(h5 h4 ) (92) m The pump work per unit of total mass is: p W = (h2 h1 ) + (1 y )(h7 h6 ) wp = m y=
(93)
h1 h7 (94) h4 h7 Calculation of the properties at state 3 The specic enthalpy at state 3 is evaluated in the solution to the previous question. = h3 = 3349.02 kJ/kg = s3 = 6.65912 kJ/kg K Calculation of the properties at state 4 h4 = h3 wt |wt | = t |wt,s | = t |h4,s h3 | (97) At state 4s , p4s = p4 = 0.8 MPa s3 = s4s = 6.65912 kJ/kg < 6.6616 kJ/kg = s4s,v , so the state 4s is laid in the liquid+vapor region!. s4s sf x = (98) sf g 6.65912 2.0457 = 4.6160 = 0.9994 (99) h4s = hf + x hf g = 720.87 + 0.9994 2047.7 = 2, 767.3 kJ/kg |wt,s | = |2, 767.3 3349.02| kJ/kg = 581.72 kJ/kg (101) (100) (95) (96)
16
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia The value of h4 can be now calculated: h4 = 3, 349.02 0.85 581.72 = 2854.56 kJ/kg
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
With this enthalpy value at at the pressure of 0.8 MPa, the state 4 is superheated (h4 > 2768.3 kJ/kg), see steam table. p4 = 0.8 MPa Number 1 3 Temp. 200 ? 250 Enthalpy 2839.8 h4 2950.4 Entropy 6.8177 s4 7.0402
Linear interpolation is applied to determine s4 : h3 h1 s3 s1 = s4 h4 h1 s4 s1 h4 h1 = s1 + (s3 s1 ) (102) h3 h1 2854.56 2839.8 (7.0402 6.8177) = 6.8177 + 2950.4 2839.8 = 6.8474 kJ/kg K (103) =
= s4
Determination of the property at state 6 At this stage the uid is at saturated with the condenser pressure of p6 = 10 kPa. The state properties are read at steam table: vf [m]3 /kg 0.001010 hf [kJ/kg] 191.81 sf [kJ/kg K] 0.6492
Calculation of the properties at state 7 , p7 = 0.8 MPa. h7 = h6 + wp1 wp1 = vf (p7 p6 ) m3 (800 10) kPa kg m3 N/m2 = 0.7979 kPa kg Pa kNm = 0.7979 kg kJ = 0.7979 kg = 0.001010 = h7 = 191.81 + 0.7979 kJ = h7 = 192.61 kg
(104)
17
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Determination of the property at state 1 At this stage the uid is at saturated with the open heater pressure of p1 = 0.8 MPa. The state properties are read at steam table: vf [m]3 /kg 0.001115 hf [kJ/kg] 720.87 sf [kJ/kg K] 2.0457
The fraction of the total ow, y : h1 h7 h4 h7 720.87 192.61 = 2854.56 192.61 = y = 0.20 y =
(105)
To determine the efciency in eq. (91), we need rst to calculate both the pump and turbine works according to eq. (92) and (93). i. Calculation of the enthalpy at state 2 , p7 = 8 MPa.
h2 = h1 + wp2 wp2 = vf (p2 p1 ) m3 (8 0.8) MPa kg N/m2 m3 MPa = 0.00803 kg Pa kJ = 8.03 kg = 0.001115 = h2 = 720.87 + 8.03 kJ = h2 = 728.9 kg ii. Calculation of the properties at state 5 , p5 = 10 kPa. s5s = s4 . h5 = h4 wt = h4 t |wt,s | = h4 t (h4 h5,s ) (107)
(106)
The state 5s is at the liquid + vapor region! So, we have to calculate x at this pressure. x = s5s sf sf g 6.8474 0.6492 = 7.4996 = 0.8265
(108)
18
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia h5s = hf + x hf g = 191.81 + 0.8265 2392.1 = 2, 168.88 kJ/kg = h5 = h4 t (h4 wt )
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
(109)
= 2854.56 0.85 (2, 854.56 2, 168.88) = h5 = 2271.732 kJ/kg iii. Total turbine work per unit total mass ow rate, wt : t W = (h4 h3 ) + (1 y )(h5 h4 ) wt = m = (2854.56 3349.02) + (1 0.2) (2271.732 2854.56) = 960.72 kJ/kg (work done by the system) (111) (110)
iv. The pump work per unit of total mass is: p W = (h2 h1 ) + (1 y )(h7 h6 ) wp = m = 8.03 + (1 0.2) 0.7979 = 8.67 kJ/kg v. Heat supply, q23 . q23 = h3 h2 = 3349.02 728.9 = 2620.12 kJ/kg The efciency of the cycle is then: th = = |wt | |wp | |q23 | 960.72 8.67 2620.12 (114) (113) (112)
= th = 0.363 = 36.3% b) the mass ow rate of the steam entering the rst stage turbine. cycle = W Net power output
t | |W p| = |W = m (|wt | |wp |) cycle W m = | wt | | wp | 100 MW J = 960.72 8.67 kJ/kg Ws Mg 1000 k 3600 s = 0.1050 s M hr kg = m = 3.78 105 hr
(115)
19
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
A reheat regenerative steam power plant operates with two feedwater heaters, a closed feedwater heater, and an open feedwater heater. Steam enters the rst turbine at 8.0 MPa, 450 C and expands to 0.8 MPa. The steam is reheated to 450 C before entering the second turbine. It expands through the turbine to the condenser pressure of 10 kPa. Steam is extracted from the rst turbine at 2 MPa and fed to the closed feedwater heater. Feedwater leaves the closed heater at 200 C and 8 MPa, and condensate exits as saturated liquid at 2 MPa. The condensate is trapped into the open feedwater heater. Steam extracted from the second turbine at 0.3 MPa and also fed into the open feedwater heater, which operates at 0.3 MPa. The stream exiting the open feedwater heater is saturated liquid at 0.3 MPa. The net power output of the cycle is 100 MW. The working uid experiences no irreversibilities as it passes through the turbines, pumps, condenser, and steam generator. Determine:
a) The thermal efciency b) The mass ow rate of the steam entering the rst turbine.
4 Reheater m3 3 m 8 MPa o 450 C Steam generator 11 m
Second turbines (1 y )
1
First turbines
1 y
1
m2
m3
m6 y
2
(1 y y )
. 5 m5
0.3 MPa
6 Condenser 10 kPa 7
1 2
8 MPa o 200 C Closed feedwater heater 2 MPa sat. liquid
m 10 m2 12
Open feedwater heater m 9
8 0.3 MPa sat. liquid m6 Pump 1 m2
Pump 2
Trap
13
20
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Reheater
450 C . m3 3 m 8 MPa o 450 C
4 Second turbines First turbines 2 MPa 1 m2 0.8 MPa 0.3 MPa 10 kPa
m3
Steam generator 11 m
m6 m5 0.3 MPa
5 6 Condenser
8 MPa o 200 C Closed feedwater heater 2 MPa sat. liquid
m 10 m2 12
Open feedwater heater m 9
8 0.3 MPa sat. liquid m6 Pump 1
10 kPa
sat. liquid 7
Pump 2 m2 Trap 13
a) The thermal efciency is calculated as follows: th = = = Turbine power output: t = W t1 + W t2 W 12 + W 23 + W 45 + W 56 = W t W wt m Pump power input: p = W p1 + W p2 W = m 6 wp1 + mw p2 wp Heat ow input: in = Q steam gen. + Q reheater Q = mq steam gen. + m 3 qreheater qin in Q m = q11-1 + m 3 q34 m (118) p W m = m 6 w78 + w910 m = mw 12 + m 3 w23 + m 3 w45 + m 6 w56 m 3 m 3 m 6 = w12 + w23 + w45 + w56 m m m Net work output Net power output = Heat input Heat ow input input output W t | |W p| W |W = in | input |Q Q t /m p /m |W | |W | in /m |Q | (116)
(117)
The thermal efciency is then: = th = | wt | | wp | |qin | (119)
21
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Mass balance on turbines control volume (thick dashed lines):
m =m 2+m 3 =m 2+m 5+m 6 m 2 m 5 m 6 1= + + m m m fractions of the total ow are dened: y1 = m 6 = 1 y1 y2 m m 2 m 5 , and y2 = m m (121)
(120)
Energy balance on the control volume of the Closed feedwater heater: 2 H 12 + H 10 H 11 0 = H = m 2 h2 m 2 h12 + mh 10 mh 11 = m 2 (h2 h12 ) + m (h10 h11 ) m 2 (h2 h12 ) = m (h11 h10 )
h11 h10 m 2 y1 = m h2 h12
(122)
Energy balance on the control volume of the Open feedwater heater: 5 +H 8 +H 13 H 9 0 = H = m 5 h5 + m 6 h8 + m 2 h13 mh 9 m 6 m 2 m 5 h5 + h8 + h13 h9 = m m m = y2 h5 + (1 y1 y2 )h8 + y1 h13 h9 = y2 [h5 h8 ] + y1 [h13 h8 ] + [h8 h9 ] y2 [h5 h8 ] = y1 [h8 h13 ] + [h9 h8 ]
y2 =
h9 h8 + y1 (h8 h13 ) h5 h8
(123)
Calculation of the state properties at every location: State 1 . Reading at the steam table: p[bar] 80 t [C] 450 h[kJ/kg] 3273.3 s[kJ/kg K] 6.558 Phase superheated
State 2 . 1 2 is isentropic expansion. Reading at the steam table with p2 = 2 MPa = 20 bar:
22
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
No. 1 2 3
t [C] 250 ? 300
h[kJ/kg] 2903.2 h2 3024.2
s[kJ/kg K] 6.548 6.558 6.768
Linear interpolation to get the value of h4 : s2 s1 (h3 h1 ) s3 s1 6.558 6.548 = 2903.2 + (3024.2 2903.2) 6.768 6.548 = 2, 908.70 kJ/kg
h2 = h1 +
= h2
(124)
450
Temperatur
8 MPa
12 200 10 11
2 MPa
5 0.8 MPa 3 0.3 MPa
9 7
13 10 kPa 6
State 3 . 1 3 is isentropic expansion (s1 = s3 = 6.558 kJ/kg K). Reading at the steam table with p3 = 0.8 MPa = 8 bar: p[MPa] t [C] hf 0.8 170.41 720.9 Enthalpy[kJ/kg] hfg 2047.4 hg 2768.3 Entropy[kJ/kg K] sf 2.0457 sfg 4.6159 sg 6.6616
Steam quality, x at state 3: x = x = s3 sf sf g 6.558 2.0457 = 0.9776 4.6159
(125)
h3 = hf + x hf g = 720.9 + 0.9776 2047.4 = h3 = 2, 722.3478 kJ/kg (126)
23
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
State 4 . Reading at the steam table: p[bar] 8 t [C] 450 h[kJ/kg] 3373.9 s[kJ/kg K] 7.726 Phase superheated
State 5 . Reading at the pressure of p5 = 3 bar in the steam table: No. 1 5 3 t [C] 300 ? 350 h[kJ/kg] 3069.6 h5 3172.0 s[kJ/kg K] 7.704 7.726 7.875
Linear interpolation to get the value of h5 : h5 = h1 + s5 s1 (h3 h1 ) s3 s1 7.726 7.704 = 3069.6 + (3172.0 3069.6) 7.875 7.704 = 3, 082.77 kJ/kg
= h5
(127)
State 6 . 4 6 is isentropic expansion (s6 = s4 = 7.726 kJ/kg K). Reading at the steam table with p3 = 10 kPa = 0.1 bar: p[kPa] t [C] hf 10 45.81 191.8 Enthalpy[kJ/kg] hfg 2392.1 hg 2583.9 Entropy[kJ/kg K] sf 0.6492 sfg 7.4996 sg 8.1488
Steam quality, x at state 6: x = x = s6 sf sf g 7.726 0.6492 = 0.9436 7.4996
(128)
h6 = hf + x hf g = 191.8 + 0.9436 2392.1 = h6 = 2, 449.04 kJ/kg (129)
State 7 . Reading at the steam table with p7 = 10 kPa = 0.1 bar, see the values in the state 6 above. The state 7 is saturated liquid. vf = 0.00101 m3 /kg, h7 = 191.8 kJ/kg. State 8 . State change 7 8 is an isentropic compression in the liquid phase with the specic pump work: wp1 = vf (p8 p7 ) = 0.00101 wp 1 N/m2 m3 (300 10) kPa kg Pa = 0.2929 kJ/kg
(130)
24
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
The specic enthalpy at the state 8 can be then calculated: h8 = wp1 + h7 = h8 = 0.2929 + 191.8 = 192.09 kJ/kg State 9 . It is saturated liquid at pressure of p9 = 0.3 MPa = 3 bar. p[MPa] v[f ] hf 0.3 0.00107 561.4 Enthalpy[kJ/kg] hfg 2163.5 hg 2724.9 Entropy[kJ/kg K] sf 1.6717 sfg 5.3199 sg 6.9916 (131)
h9 = 561.4 kJ/kg State 10 . State change 9 10 is an isentropic compression in the liquid phase with the specic pump work: wp2 = vf (p10 p9 ) = 0.00107 wp 2 m3 N/m2 (8000 300) kPa kg Pa = 8.239 kJ/kg
(132)
The specic enthalpy at the state 8 can be then calculated: h10 = wp2 + h9 = h10 = 8.239 + 561.4 = 569.639 kJ/kg (133)
State 11 . It is a compressed liquid water at 8 MPa and 200 C. The enthalpy value at this state can be interpolated in the compressed liquid water table. p[MPa] 5 8 10 h[kJ/kg] 853.68 h11 855.80
h11 = h5 +
= h11
h10 h5 (p8 p5 ) p10 p5 855.80 853.68 = 853.68 + (8 5) 10 5 = 854.95 kJ/kg
(134)
State 12 . It is a saturated liquid state at 2 MPa. From the steam table, we read h12 = 908.47 kJ/kg. State 13 . 12 13 is a throttling process or isenthalpic process, so h13 = s12 = 908.47 kJ/kg.
25
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Calculation of the fraction of the total ow y1 in eq. (122) y1 = = h11 h10 h2 h12
854.95 569.639 2, 908.70 908.47 = 0.143 Calculation of the fraction of the total ow y2 in eq. (123) y2 = h9 h8 + y1 (h8 h13 ) h5 h8 = 0.092
(135)
(136)
Turbine power output: wt = w12 + m 3 m m 6 m m 3 m 3 m 6 w23 + w45 + w56 m m m
= 1 y1 = 0.857 = 1 y1 y2 = 0.765
wt = (h2 h1 ) + 0.857 [(h3 h2 ) + (h5 h4 )] + 0.765(h6 h5 ) = 364.6 + 0.857 (477.48) + 0.765 (633.73) wt = 1258.75 kJ/kg Pump power input: wp = m 6 w78 + w910 m = (1 y1 y2 ) (h8 h7 ) + (h10 h9 ) = 0.765 (192.09 191.80) + (569.64 561.4) = 8.46 kJ/kg Heat ow input: qin = q11-1 + m 3 q34 m = (h1 h11 ) + (1 y1 ) (h4 h3 ) (139) (138) (137)
= (3, 273.30 854.95) + 0.857 (3, 373.90 2, 722.35) = 2976.97 kJ/kg The thermal efciency of the cycle is then: th = | wt | | wp | |qin | 1258.75 8.46 1250.29 = = 2976.97 2976.97 = 0.42 (140)
= th = 42%
26
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia b) The mass ow rate of the steam entering the rst turbine.
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
cycle = m W (|wt | |wp |) cycle W m = |wt | |wp | 100 MW J = 1250.29 kJ/kg Ws Mg 1000k 3600 s = 0.08 s M hr 5 kg = m = 2.88 10 hr
(141)
(142)
8 MPa
5 2
12 11 10 9 13 2 MPa 0.8 MPa 0.3 MPa 3
8 7 10 kPa 6
27
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
The schematic of a single-ash geothermal power plant with state numbers is given in the gure. Geothermal resource exists as saturated liquid at 230 C. The geothermal liquid is withdrawn from the production well at rate of 230 kg/s, and is ashed to a pressure of 500 kPa by an essentially isenthalpic ashing process where resulting vapor is separated from the liquid in a separator and directed to the turbine. The steam leaves the turbine at 10 kPa with a moisture content of 10 percent and enters the condenser where it is condensed and routed to a reinjection well along with liquid coming off separator.
Turbine Separator
Flash chamber
Condenser
6 5
Production well
Reinjection well
230
2.797 MPa
flashing 6 0.5 MPa 2 3
Temperatur
10 kPa 4s 4
a) The mass ow rate of steam through the turbine From the saturated water table, we get the following state properties:
Temp [C] 230
psat [kPa] 2,797.1
Enthalpy [kJ/kg] hf 990.14 hfg 1812.8 hg 2802.9
28
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
State 1 is at saturated liquid. h1 = 990.14 kJ/kg Process 1 2 is isenthalpic process to pressure of 500 kPa. Enthalpy [kJ/kg] hf 640.09 hfg 2108.0 hg 2748.1 Entropy [kJ/kg K] sf 1.8604 sfg 4.9603 sg 6.8207
psat [kPa] 500
Temp [C] 151.83
h1 = h2 = hf + xhf g h2 hf x = hf g 990.14 640.09 = 2, 108.0 x = 0.1661 m 3 = xm 1 = 0.1661 230 kg/s = m 3 = 38.2 kg/s
(143)
(144) (145)
b) the isentropic efciency of the turbine Process 3 4 is isentropic expansion to pressure of 10 kPa. Enthalpy [kJ/kg] hf 191.81 hfg 2392.1 hg 2583.9 Entropy [kJ/kg K] sf 0.6492 sfg 7.4996 sg 8.1488
psat [kPa] 10
Temp [C] 45.81
s3 = s2,g = s4,s = 6.8207 kJ/kg K. Calculation of the steam quality at 10 kPa: s3 sf sf g 6.8207 0.6492 = 7.4996 x = 0.8229 x= The isentropic enthalpy of the steam leaving the turbine: h4s = hf + xhf g = 191.81 + 0.8229 2392.1 = 2160.27 kJ/kg (147)
(146)
29
Solution Tutorial 1/ ws BDA 3043
Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
The actual enthalpy, h4 , is calculated at the steam quality of x = 0.9 (Moisture content 10 % means the steam quality is 90 %). h4 = hf + xhf g = 191.81 + 0.9 2392.1 = 2344.7 kJ/kg The turbine efciency is calculated as follows: t = = |h4 h3 | |h4s h3 | |2344.7 2748.1| 403.4 = |2160.27 2748.1| 587.83 (148)
= t = 0.686 = 68.6% c) the power output of the turbine t = m W 3 wt = m (h4 h3 ) kg kJ = 38.2 (403.4) s kg = 15, 409.88 kW (minus sign means power output) t = 15.41 MW = W d) the thermal efciency of the plant th = t| |W in | |Q
Energy input comes from the production well: in = m Q 1 h1 = 230 kg/s 990.14 kJ/kg = 227.73 MW The thermal efciency is then: th = 15.41 = 0.068 227.73
= th = 6.8%
30
You might also like
- Tutorial Gasturbine SolutionDocument27 pagesTutorial Gasturbine SolutionwanpudinNo ratings yet
- Jabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn MalaysiaDocument9 pagesJabatan Kejuruteraan Loji dan Automotif Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Pembuatan Universiti Tun Hussein Onn MalaysiawanpudinNo ratings yet
- NAME: Vincent Rey Olario: Bsme - 5Document11 pagesNAME: Vincent Rey Olario: Bsme - 5Pryce YurongNo ratings yet
- OTECDocument6 pagesOTECibong tiriritNo ratings yet
- THERMODYNAMICS SOLUTIONSDocument62 pagesTHERMODYNAMICS SOLUTIONSanthonytichaona100% (1)
- Reheat-Regenerative CycleDocument8 pagesReheat-Regenerative CycleBenjamin MabuteNo ratings yet
- Scalding Unit-USePDocument12 pagesScalding Unit-USePJesús Alejandro SantillánNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Worked ExamplesDocument13 pagesThermodynamics Worked ExamplesSalah Salman100% (1)
- Combined Power Cycles TutorialDocument5 pagesCombined Power Cycles TutorialEhsan WardakNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - B 02/08/1999 Instructions:: Answer Any TwoDocument4 pagesMathematics - B 02/08/1999 Instructions:: Answer Any TwoKiran Gayakwad100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - Energy Analysis For Open Systems Compatibility ModeDocument35 pagesChapter 5 - Energy Analysis For Open Systems Compatibility ModekhameesmarwanNo ratings yet
- Chap5 4Document8 pagesChap5 4Christopher EvanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 The Second Law of Thermodynamics (PP 82-99)Document18 pagesChapter 04 The Second Law of Thermodynamics (PP 82-99)Muhammad Ashfaq Ahmed71% (7)
- THER103 NFEE ApplicationsDocument7 pagesTHER103 NFEE ApplicationsshanecarlNo ratings yet
- Second Law of Thermodynamics NotesDocument15 pagesSecond Law of Thermodynamics Noteshirenpatel_universalNo ratings yet
- Motor Bakar Minggu-11Document45 pagesMotor Bakar Minggu-11setoNo ratings yet
- Vapor and Gas Power SystemsDocument10 pagesVapor and Gas Power SystemsCm EtcmNo ratings yet
- Problems of the second law of thermodynamicsDocument6 pagesProblems of the second law of thermodynamicsFauzi RamadhanNo ratings yet
- ENGRD 221 - Thermodynamics (Prof. N. Zabaras) Prelim IDocument9 pagesENGRD 221 - Thermodynamics (Prof. N. Zabaras) Prelim IMurat TülekNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document30 pagesCH 12hirenpatel_universal0% (3)
- ch08 1 40Document55 pagesch08 1 40Hadi Sobian100% (2)
- THERMO PROJECT DR KhawarDocument14 pagesTHERMO PROJECT DR KhawarHamza AliNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.1ADocument53 pagesProblem 5.1ALuis PiscalNo ratings yet
- Brayton cycle analysis with compressor and turbine efficienciesThe title "TITLE Brayton cycle analysis with compressor and turbine efficienciesDocument52 pagesBrayton cycle analysis with compressor and turbine efficienciesThe title "TITLE Brayton cycle analysis with compressor and turbine efficienciesGiuseppe TestarossaNo ratings yet
- Ens140 Quiz2Document9 pagesEns140 Quiz2Cristy Mae U. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- AGRI ENGINEERING FINAL EXAM SPRING 2023 and SOLUTIONDocument7 pagesAGRI ENGINEERING FINAL EXAM SPRING 2023 and SOLUTIONfalmubaddelNo ratings yet
- Me6301 QBDocument46 pagesMe6301 QBNaveen Dhanuraj100% (1)
- Presentation - Class#7 Thermal EfficiencyDocument15 pagesPresentation - Class#7 Thermal EfficiencyDar QuetzalNo ratings yet
- NPTEL IIT Roorkee Steam Power Systems Assignment #1Document3 pagesNPTEL IIT Roorkee Steam Power Systems Assignment #1Suraj ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Tutorium Refrigeration SolutionDocument20 pagesTutorium Refrigeration SolutionwanpudinNo ratings yet
- Examples (Psychrometric Chart) Continues Sunum PDFDocument23 pagesExamples (Psychrometric Chart) Continues Sunum PDFAysu KirazNo ratings yet
- Chapter10 PDFDocument10 pagesChapter10 PDFSaadMunirNo ratings yet
- 10 Vapor and Combined Power CyclesDocument44 pages10 Vapor and Combined Power CyclesLexNo ratings yet
- HW 5 SolnDocument7 pagesHW 5 SolnNik Hafiy HafiziNo ratings yet
- Power Plant 20 Years Gate Ies Ias Q ADocument106 pagesPower Plant 20 Years Gate Ies Ias Q ASaajal Sharma100% (12)
- Thermo Assignment #6Document10 pagesThermo Assignment #6mohamedNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Cycle:: 1. Power Generation 2. Refrigeration 1. Power Cycles (Engines)Document16 pagesThermodynamics Cycle:: 1. Power Generation 2. Refrigeration 1. Power Cycles (Engines)saketbajaj123No ratings yet
- ME3122E - Tutorial Solution 4Document12 pagesME3122E - Tutorial Solution 4LinShaodun82% (11)
- Lab 1Document13 pagesLab 1Joseph Villariza LapidoNo ratings yet
- Me 201Document7 pagesMe 201Laurie BradleyNo ratings yet
- 4200:225 Equilibrium Thermodynamics: Unit I. Earth, Air, Fire, and WaterDocument11 pages4200:225 Equilibrium Thermodynamics: Unit I. Earth, Air, Fire, and WaterRiky IkhwanNo ratings yet
- CEE 345 Spring 2002 problem set solutions pump efficiency discharge headDocument10 pagesCEE 345 Spring 2002 problem set solutions pump efficiency discharge headAdrian Antonio TorresNo ratings yet
- An Exergetic Analysis of Cogeneration Plants Operation Koģenerācijas Staciju Darbības Ekserģētiskā AnalīzeDocument6 pagesAn Exergetic Analysis of Cogeneration Plants Operation Koģenerācijas Staciju Darbības Ekserģētiskā AnalīzeKamal ZafrullahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 ThermoDocument27 pagesTutorial 3 ThermoHaiqal AzizNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 02 Answers 2014Document24 pagesTutorial Sheet 02 Answers 2014checkmeout803100% (1)
- Thermo HWDocument6 pagesThermo HWMuhammad Fawwad ObaidaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics homework solutions for mechanical engineering courseDocument5 pagesThermodynamics homework solutions for mechanical engineering coursemuru0105No ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap10 P001Document29 pagesThermo 5th Chap10 P001welberTonetoMotaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Thermodynamics Cycles: Heat-Engine CycleDocument7 pagesIntermediate Thermodynamics Cycles: Heat-Engine Cycleabdul_rehman_124No ratings yet
- Soft Computing in the Design and Manufacturing of Composite Materials: Applications to Brake Friction and Thermoset Matrix CompositesFrom EverandSoft Computing in the Design and Manufacturing of Composite Materials: Applications to Brake Friction and Thermoset Matrix CompositesNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Carbon Capture Technologies for Gas-Turbine-Based Power PlantsFrom EverandCarbon Capture Technologies for Gas-Turbine-Based Power PlantsNo ratings yet
- Zn alloy element concentration analysisDocument1 pageZn alloy element concentration analysiswanpudinNo ratings yet
- Incoming Material docs-HKI2000863 (JD)Document8 pagesIncoming Material docs-HKI2000863 (JD)wanpudinNo ratings yet
- Incoming Material docs-HKI2001181Document10 pagesIncoming Material docs-HKI2001181wanpudinNo ratings yet
- Glue Marking 26 Pcs 4.75% Patches of Paint:5 Pcs 0.91%: QIS Section Have Been Found Defect On Part Surface Such AsDocument1 pageGlue Marking 26 Pcs 4.75% Patches of Paint:5 Pcs 0.91%: QIS Section Have Been Found Defect On Part Surface Such AswanpudinNo ratings yet
- Sampling Check (Doraemon)Document1 pageSampling Check (Doraemon)wanpudinNo ratings yet
- 3 03 2Document1 page3 03 2wanpudinNo ratings yet
- Curado Plating Thickness NGDocument1 pageCurado Plating Thickness NGwanpudinNo ratings yet
- Incoming Material docs-HKI2000784 (JD)Document9 pagesIncoming Material docs-HKI2000784 (JD)wanpudinNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document1 pageBook 1wanpudinNo ratings yet
- ASME Y14.5M Geometric Tolerancing SymbolsDocument34 pagesASME Y14.5M Geometric Tolerancing SymbolsVinaya Almane DattathreyaNo ratings yet
- Bearing Stage Doreamon: 1. The Bearing Hole Still Failed at The Go Gauge, The Gauge Can't Touch The End of The HoldDocument2 pagesBearing Stage Doreamon: 1. The Bearing Hole Still Failed at The Go Gauge, The Gauge Can't Touch The End of The HoldwanpudinNo ratings yet
- Issue SummaryDocument2 pagesIssue SummarywanpudinNo ratings yet
- Threaded Inserts: Types of InsertDocument2 pagesThreaded Inserts: Types of InsertwanpudinNo ratings yet
- Complaint Bracket EE35EEG - Step at CoverDocument1 pageComplaint Bracket EE35EEG - Step at CoverwanpudinNo ratings yet
- Chuhan - Lot No d8x 18Document1 pageChuhan - Lot No d8x 18wanpudinNo ratings yet
- Plat Badminton DesignDocument1 pagePlat Badminton DesignwanpudinNo ratings yet
- 1168 001Document1 page1168 001wanpudinNo ratings yet
- Nakazawa Die Casting Badminton Tournament 2016: Logo Logo DepanDocument1 pageNakazawa Die Casting Badminton Tournament 2016: Logo Logo DepanwanpudinNo ratings yet
- Medal Badminton DesignDocument1 pageMedal Badminton DesignwanpudinNo ratings yet
- Book 2Document1 pageBook 2wanpudinNo ratings yet
- Full Page PhotoDocument1 pageFull Page PhotowanpudinNo ratings yet
- 2) Root Cause and Action TakenDocument1 page2) Root Cause and Action TakenwanpudinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1wanpudinNo ratings yet
- No Cop OK From QA Barrel (After Air Blast)Document2 pagesNo Cop OK From QA Barrel (After Air Blast)wanpudinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 5Document5 pagesTutorial Chapter 5wanpudinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial+2 Belting+ (Additional)Document1 pageTutorial+2 Belting+ (Additional)wanpudinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Gearing)Document80 pagesChapter 1 (Gearing)wanpudinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial+2 Belting With+SolutionDocument5 pagesTutorial+2 Belting With+SolutionwanpudinNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Machine Sem 2 1112 (160412)Document2 pagesTest 1 Machine Sem 2 1112 (160412)wanpudinNo ratings yet
- Test+2 BalancingDocument1 pageTest+2 BalancingwanpudinNo ratings yet
- Composite Materials For Civil Engineering Structures US Army Corps of EngineersDocument66 pagesComposite Materials For Civil Engineering Structures US Army Corps of EngineersRicardo AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Past Papers CXC MathsDocument77 pagesPast Papers CXC MathsShanice Henry96% (27)
- KSH - Korn Shell TutorialDocument5 pagesKSH - Korn Shell Tutorialramaniqbal123No ratings yet
- Fall Detection With Three-Axis Accelerometer and Magnetometer in A SmartphoneDocument6 pagesFall Detection With Three-Axis Accelerometer and Magnetometer in A Smartphonesimun3332000No ratings yet
- IR LM100A Crawlair Drill PDFDocument8 pagesIR LM100A Crawlair Drill PDFAnonymous 8yIptglHhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C Programming: S.V.Jansi RaniDocument14 pagesIntroduction To C Programming: S.V.Jansi RanisudhanNo ratings yet
- NX2 To NX4 TransitionDocument536 pagesNX2 To NX4 TransitionBogdan SocolescuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document35 pagesChapter 1Isagani AlonzoNo ratings yet
- DBMS Lab ManualDocument199 pagesDBMS Lab ManualMoulika Chowdary100% (1)
- 1 - Logic GatesDocument7 pages1 - Logic GatesAlfred GaleaNo ratings yet
- SssDocument24 pagesSssSaFdaR QaZiNo ratings yet
- Functions Modeling Change: A Precalculus CourseDocument239 pagesFunctions Modeling Change: A Precalculus CourseDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Protect transformers from over excitation with relay coordinationDocument7 pagesProtect transformers from over excitation with relay coordinationAnonymous zxtBoTT100% (1)
- Id3 DimensionsDocument2 pagesId3 DimensionsKornelija PadleckyteNo ratings yet
- In-Sight 7600/7800 Series Vision System: ManualDocument92 pagesIn-Sight 7600/7800 Series Vision System: Manualjulio perezNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan - KindergartenDocument3 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan - KindergartenMae Escobin BetonggaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering - A. Mittle and V. N. Mittle PDFDocument212 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering - A. Mittle and V. N. Mittle PDFSajal Singh Patel0% (5)
- GIS Approach To Fire Station Location PDFDocument6 pagesGIS Approach To Fire Station Location PDFafiNo ratings yet
- Schlenk Line Techniques: Liquid NDocument15 pagesSchlenk Line Techniques: Liquid NMarinoChavarroCordobaNo ratings yet
- Opencv Python TutorialDocument88 pagesOpencv Python TutorialParéto BessanhNo ratings yet
- 577roof Bolt TypesDocument15 pages577roof Bolt TypesOmar HelalNo ratings yet
- Euphonix - An OverviewDocument5 pagesEuphonix - An OverviewNathan BreedloveNo ratings yet
- Board characteristics and risk in Tunisian banksDocument12 pagesBoard characteristics and risk in Tunisian banksdhahri nourhenNo ratings yet
- EBS e PDFDocument92 pagesEBS e PDFRowan Cornelius100% (2)
- General Description: 8-Bit Synchronous Binary Down CounterDocument25 pagesGeneral Description: 8-Bit Synchronous Binary Down CounterspotNo ratings yet
- Skybox Appliance 8050 Quick Start GuideDocument73 pagesSkybox Appliance 8050 Quick Start GuideNet RunnerNo ratings yet
- Astm C 113-14Document3 pagesAstm C 113-14Tâm NgôNo ratings yet
- 180.5Mbps-8Gbps DLL-based Clock and Data Recovery Circuit With Low Jitter PerformanceDocument4 pages180.5Mbps-8Gbps DLL-based Clock and Data Recovery Circuit With Low Jitter PerformanceMinh KhangNo ratings yet
- The Reactivity Series PDFDocument33 pagesThe Reactivity Series PDFSandipan Chakraborty100% (1)