Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English Block 1 Learning Materials 13-14-15
Uploaded by
Diana LozPratCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
English Block 1 Learning Materials 13-14-15
Uploaded by
Diana LozPratCopyright:
Available Formats
about sobre, acerca de
action accin
afternoon tarde
any algn, alguna, algunos / as
(ningn, ninguna, ningunos / as)
article artculo
boring aburrido / a, os / as (cosas)
cinema cine
clock reloj
comedy comedia
computer ordenador
day da
desk escritorio
eleven once
e-mail correo electrnico (electronic mail)
evening tarde, noche
family familia
film pelcula
first primer, primera, primeros / as
Good afternoon buenas tardes
Good evening buenas tardes (buenas noches)
Good morning buenos das
her su (de ella)
his su (de l)
hour hora
information informacin
its su (de ello referido a cosa / animal)
long largo
mayor alcalde
mobile phone telfono mvil
morning maana
office oficina
on sobre
our nuestro (a) / nuestros (as)
plant planta
programme programa
romance novela de amor
slow lento
telephone telfono
their su (de ellos, ellas)
time tiempo (hora)
today hoy
twelve doce
until hasta
Copyright (c) Computer Aided Education SA
VOCABULARY
Megans job. Her first day
Part 1, 2, 3
week semana
well bien
Whose? De quin?
Monday lunes
Tuesday martes
Wednesday mircoles
Thursday jueves
Friday viernes
Saturday sbado
Sunday domingo
(Good) Morning Buenos das
(Good) Afternoon Buenas tardes
(Good) Evening Buenas tardes (noches)
Thats alright Est bien, no pasa nada
Anything else? Algo ms?
until hasta
any algo, algn, ninguno / a
three hours long dura tres horas
How is he? Cmo est l?
How are you? Cmo ests, est ud., estais,
estn uds.?
also tambin
What is ... like? Cmo es ...?
There is - There are
There is y there are se usan para decir hay. Si estamos hablando
en singular usamos there is y si estamos hablando en plural
usamos there are. Se pueden utilizar tanto en afirmativa como en
negativa como en interrogativa.
Afirmativa:
There is a book Hay un libro
There are some books Hay libros
PHRASES
GRAMMAR
Interrogativa:
Is there a book? Hay un libro?
Are there any books? Hay libros?
Negativa:
There is not a book No hay un libro
There are not any books No hay libros
There isnt a book No hay un libro
There arent any books No hay libros
Para responder se suele utilizar la forma corta, es decir, la forma
there seguida de is / are en afirmativa o negativa, en singular o
plural segn convenga. Esta forma de responder es mucho ms
usual en ingls.
Eg.:
Are there any books?
Yes, there are. / No, there arent.
Is there a book?
Yes, there is. / No, there isnt.
Con estas expresiones usamos normalmente los determinantes
some y any.
Some y Any
Son determinantes que se usan con palabras incontables y con
nombres en plural (tienen ms o menos el mismo significado que
el artculo indefinido a / an). Significan una cierta cantidad de.
Some se puede generalizar como la forma plural de a / an y one.
Eg.:
There are some biscuits Hay algunas galletas
Some: Se usa en oraciones afirmativas.
Eg.:
There is some milk in the fridge
You have some friends
Copyright (c) Computer Aided Education SA
Any: Se usa en oraciones negativas e interrogativas.
Eg.:
There isnt any sugar in the cupboard
Are there any oranges on the table?
I dont have any brothers
Demostrativos
This (singular) este, esta, esto
These (plural) estos, estas
That (singular) ese, esa, eso, aquel, aquella, aquello
Those (plural) esos, esas, aquellos, aquellas
Adjetivos posesivos
my book / my books mi libro / mis libros
your book / your books tu, su (de usted, ustedes),
vuestro libro / tus libros
his book / his books su libro (de l) / sus libros
her book / her books su libro (de ella) / sus libros
its book / its books su libro (de ello referido a cosa /
animal) / sus libros
our book / our books nuestro libro / nuestros libros
their book / their books su libro (de ellos / as) / sus libros
Genitivo sajn
En ingls, cuando hablamos de posesin con personas, es decir,
cuando algo pertenece a alguien, utilizamos lo que se llama
genitivo sajn, que consiste en colocar primero la persona que
posee algo seguido de la forma s, y despus la cosa poseda.
Poseedor + s + cosa poseda
Si decimos, por ejemplo, La casa de Mara, en este caso la
persona que posee es Mara y el objeto posedo es la casa, luego
la forma correcta sera: Maras house.
Tenemos que prestar atencin al hecho de que en espaol se usa
un artculo que en ingls se omite como hemos visto en el ejemplo
anterior.
Cuando el poseedor es singular o no acaba en s, el genitivo se
forma con s, pero si el poseedor est en plural o acaba en s, el
genitivo se forma solamente con .
Eg.: my fathers wife my parents car
la mujer de mi padre el coche de mis padres
Por otra parte, cuando el poseedor es una cosa, expresamos
posesin con la preposicin of como en espaol.
Eg.: The capital of France La capital de Francia
Also y Too
Also significa tambin y se usa despus del verbo To be o
cualquier otro verbo usado como auxiliar. En estos casos, el
sujeto no se puede separar del verbo.
Sujeto + verbo To be + also + ...
Eg.: I am also a doctor Yo tambin soy (un) mdico
Sin embargo, cuando usamos cualquier otro verbo, also se coloca
entre el sujeto y el verbo. En este caso si podemos separar el
sujeto del verbo.
Sujeto + also + verbo + ...
Eg.: I also study Yo tambin estudio
Too significa tambin, pero siempre va colocado al final de
la frase, cualquiera que sea el verbo.
Eg.: I am a doctor, too Yo tambin soy (un) mdico
I study, too Yo tambin estudio
Plurales irregulares
foot - feet woman - women child - children
goose - geese tooth - teeth
man - men mouse - mice
Copyright (c) Computer Aided Education SA
Vocabulary. Which word doesnt fit? (Vocabulario. Qu
palabra no tiene relacin con el resto?)
1) Monday Wednesday Friday Holiday Thursday
2) Comedy Romance Mayor Action Film
3) Eleven Computer Desk Fax Telephone
4) Time Minute Cinema Clock Hour
5) Parents Dog Child Father Mother
6) Morning Evening Week Afternoon
Make sentences comparing John and Karens lives.
When you want to say their situations are similar, write
two sentences, one with too and another with also.
(Haz frases comparando las vidas de Karen y Tom. Cundo
quieras indicar que sus situaciones son similares habrs de
hacer frases con too o con also como en el ejemplo.
Mejor haz dos frases, una con cada)
ADDITIONAL EXERCISES
This is John. He is a tall man.
He is an American doctor from
Washington. His mother is a
doctor, too. His house is new
and beautiful. He is twenty-nine
years old and married.
This is Karen. She isnt married.
She is young, she is twenty-nine
years old. She is a short woman.
Her mother is a doctor. She is a
police officer. Her house is old
but beautiful.
John is a doctor. Karen is a police officer.
Karen is American. John is American, too.
John is also American.
1. Karens house is old. ________________________
2. Johns mother is a doctor. ________________________
3. Johns house is beautiful. ________________________
4. Karen is short. ________________________
5. John is married. ________________________
6. John is twenty-nine years old. ________________________
True or false? Correct the wrong sentences. (Verdadero
o falso? Corrige las frases que sean falsas)
1. There is one telephone in the office. False: There are two
telephones in the office.
2. There are three desks in the office. True
3. There is a plant.
4. There are two computers.
5. There is a book.
6. There is a camera.
7. There are two newspapers.
8. There is a fax.
9. There is a poster on the wall.
Copyright (c) Computer Aided Education SA
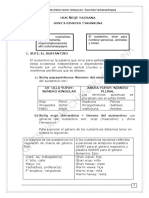
Complete the chart with the possessive adjectives.
(Completa la tabla con los adjetivos posesivos)
Complete these sentences with the possessives.
Whats your name? __________ name is Bob.
Whats __________ name? Shes Helene.
Whats __________ name? Hes Jimmy.
This is my car and your car, too. Its __________ car.
Is this __________ pen? No, that isnt my pen.
Change two sentences into one. (Cambia las dos frases en una)
- This is Tom and that is his telephone.
That is Toms telephone.
- This is Sue and those are her books.
Those are ___________ ___________.
- This is Brenda and that is her family.
___________ is ___________ ___________.
- That is Edward and that is his car.
___________ ______ ___________ ___________.
- Those are Terry and Debbie and this is their family.
_________ _____ _________ _____ _________ _________.
PERSONAL
POSSESSIVE
PRONOUNS
ADJECTIVES
I
YOU
HE
SHE
IT
WE
YOU
THEY
You might also like
- English Block 6 Learning Materials 01-02-03Document7 pagesEnglish Block 6 Learning Materials 01-02-03Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- Potencial Teórico de Las RSDocument5 pagesPotencial Teórico de Las RSDiana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 6 Learning Materials 01-02-03Document7 pagesEnglish Block 6 Learning Materials 01-02-03Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 4 Learning Materials 04-05-06Document8 pagesEnglish Block 4 Learning Materials 04-05-06Diana LozPrat100% (1)
- English Block 4 Learning Materials 01-02-03Document17 pagesEnglish Block 4 Learning Materials 01-02-03Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 4 Learning Materials 01-02-03Document17 pagesEnglish Block 4 Learning Materials 01-02-03Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 3 Learning Materials 07-08-09Document8 pagesEnglish Block 3 Learning Materials 07-08-09Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 3 Learning Materials 04-05-06Document8 pagesEnglish Block 3 Learning Materials 04-05-06Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 1 Learning Materials 25-26-27Document1 pageEnglish Block 1 Learning Materials 25-26-27Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 3 Learning Materials 04-05-06Document8 pagesEnglish Block 3 Learning Materials 04-05-06Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 3 Learning Materials 10-11-12Document7 pagesEnglish Block 3 Learning Materials 10-11-12Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 3 Learning Materials 07-08-09Document8 pagesEnglish Block 3 Learning Materials 07-08-09Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 3 Learning Materials 13-14-15Document8 pagesEnglish Block 3 Learning Materials 13-14-15Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 3 Learning Materials 01-02-03Document9 pagesEnglish Block 3 Learning Materials 01-02-03Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 3 Learning Materials 07-08-09Document8 pagesEnglish Block 3 Learning Materials 07-08-09Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 2 Learning Materials 16-17-18Document1 pageEnglish Block 2 Learning Materials 16-17-18Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 3 Learning Materials 01-02-03Document9 pagesEnglish Block 3 Learning Materials 01-02-03Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 2 Learning Materials 01-02-03Document8 pagesEnglish Block 2 Learning Materials 01-02-03Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 2 Learning Materials 07-08-09Document8 pagesEnglish Block 2 Learning Materials 07-08-09Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 1 Learning Materials 19-20-21Document9 pagesEnglish Block 1 Learning Materials 19-20-21Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 1 Learning Materials 25-26-27Document1 pageEnglish Block 1 Learning Materials 25-26-27Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 2 Learning Materials 04-05-06Document8 pagesEnglish Block 2 Learning Materials 04-05-06Diana LozPrat0% (1)
- English Block 1 Learning Materials 22-23-24Document8 pagesEnglish Block 1 Learning Materials 22-23-24Diana LozPrat100% (1)
- English Block 1 Learning Materials 10-11-12Document8 pagesEnglish Block 1 Learning Materials 10-11-12Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 1 Learning Materials 04-05-06Document6 pagesEnglish Block 1 Learning Materials 04-05-06Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 1 Learning Materials 19-20-21Document9 pagesEnglish Block 1 Learning Materials 19-20-21Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 1 Learning Materials 16-17-18Document6 pagesEnglish Block 1 Learning Materials 16-17-18Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 1 Learning Materials 16-17-18Document6 pagesEnglish Block 1 Learning Materials 16-17-18Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- English Block 1 Learning Materials 07-08-09Document6 pagesEnglish Block 1 Learning Materials 07-08-09Diana LozPratNo ratings yet
- 5g - Lenguaje - Unidad 3Document71 pages5g - Lenguaje - Unidad 3Mercy de RamírezNo ratings yet
- Formas Verbales y Conjugación Del Verbo InglésDocument16 pagesFormas Verbales y Conjugación Del Verbo InglésTc CTNo ratings yet
- EL ADJETIVO - EJERCICIOS - InformaValenciaDocument2 pagesEL ADJETIVO - EJERCICIOS - InformaValenciaPEDRO ESTUARDO HERNANDEZ100% (1)
- Tecnicismos - Prefijos y SufijosDocument8 pagesTecnicismos - Prefijos y SufijosVANESSA BARRERA MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Taller 1 Partes de La OracionDocument11 pagesTaller 1 Partes de La OracionVictor Ramos (TIALONG)No ratings yet
- El Sistema BlissDocument9 pagesEl Sistema BlissEncarniNo ratings yet
- Sapo Tiene MiedoDocument2 pagesSapo Tiene MiedoNohemi CamachoNo ratings yet
- Evaluación Quechua 01Document1 pageEvaluación Quechua 01marcialNo ratings yet
- Las Conjunciones y Su Clasificacion.Document3 pagesLas Conjunciones y Su Clasificacion.Mario LaínezNo ratings yet
- Guía.1 UndécimoDocument11 pagesGuía.1 UndécimoF'ernando R'ojas100% (1)
- Uso de La C, S y ZDocument10 pagesUso de La C, S y ZGuillermo Ahumada LeónNo ratings yet
- Acentuacion y TildacionDocument6 pagesAcentuacion y TildacionDulio AlberthNo ratings yet
- Ingles 3Document6 pagesIngles 3Angelik LópezNo ratings yet
- José Juan TabladaDocument3 pagesJosé Juan TabladaDaniel Marín VázquezNo ratings yet
- LENGUAJEJEDocument4 pagesLENGUAJEJEMarkos Antonio HerediaNo ratings yet
- Categorías Gramaticales y Funciones Sintácticas Del Idioma Español PDFDocument3 pagesCategorías Gramaticales y Funciones Sintácticas Del Idioma Español PDFJv BanegNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument18 pagesAdverbsjuanjosewongNo ratings yet
- Oraciones FinalesDocument1 pageOraciones FinalesDiegoNo ratings yet
- Cepunt II 2018Document4 pagesCepunt II 2018Oscar De La Cruz CalvoNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument3 pagesAdverbsJosse LazzoNo ratings yet
- 50 Ejemplos de Oraciones Con Sujeto y PRDocument5 pages50 Ejemplos de Oraciones Con Sujeto y PREddy HansenNo ratings yet
- Las Categorias Gramaticales para Segundo de SeundariaDocument5 pagesLas Categorias Gramaticales para Segundo de SeundariaSebastian BohorquezNo ratings yet
- Sintaxis IDocument63 pagesSintaxis IAna Meiriño MorenoNo ratings yet
- Abreviaturas, Acronimos, Signos y SiglasDocument2 pagesAbreviaturas, Acronimos, Signos y SiglasDiego M. LópezNo ratings yet
- Análisis MorfológicoDocument6 pagesAnálisis MorfológicoAbigail CorderoNo ratings yet
- Español y Habilidad Verbal Examen Guia de EspañolDocument24 pagesEspañol y Habilidad Verbal Examen Guia de EspañolWalter CarranzaNo ratings yet
- Examen de Conocimientos 6° PrimariaDocument6 pagesExamen de Conocimientos 6° PrimariaDiana HernandezNo ratings yet
- Tema 2Document18 pagesTema 2Bryan Rafael Carrion ManotupaNo ratings yet
- Cuarta y Quinta PracticaDocument10 pagesCuarta y Quinta PracticaCristobalina Rosario BurgosNo ratings yet
- Oración Simple y CompuestaDocument14 pagesOración Simple y CompuestaPatricia Avila Luna100% (2)