Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laminar Complex
Uploaded by
almengarunCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laminar Complex
Uploaded by
almengarunCopyright:
Available Formats
1
TK5102
Ad d T t Ph Advanced Transport Phenomena
Transports in Laminar Regimes:
Complex Problems
I Dewa Gede Arsa Putrawan
Chemical Engineering ITB
28-Sep-09 DGA/1
TK5102
Outcomes
Students can simplify equations of change to derive Students can simplify equations of change to derive
mathematical models of complex problems in transport
phenomena.
Students can estimate property profiles for complex
problems in transport phenomena.
28-Sep-09 DGA/2 TK5102
2
The Equation of Change
for Isothermal System
28-Sep-09 DGA/3
TK5102
Equation of Continuity
28-Sep-09
TK5102
DGA/4
3
Mass balance
over a volume element Ax, Ay, Az
Ax, Ay, Az
Rate of mass accumulation
z
AxAyAz c/ct
Rate of mass in
( v
x
AyAz)
x
+ ( v
y
AxAz)
y
+ ( v
z
AxAy)
z
x, y, z
x
y
Rate of mass out
( v
x
AyAz)
x+Ax
+ ( v
y
AxAz)
y+Ay
+ ( v
z
AxAy)
z+Az
28-Sep-09 DGA/5 TK5102
Mass Balance
over a volume element Ax, Ay, Az
( ) ( )
y z v v
x y z
c
(
A A
A A A =
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
x x
x x x
y y
y y y
z z
z z z
y z v v
x y z
t
x z v v
x y v v
+A
+A
+A
(
A A
A A A =
c
(
+ A A
(
(
+ A A
( )
( ) ( )
0
y
x z
v
v v
t x y z
c
c c c
+ + + =
c c c c
28-Sep-09 DGA/6 TK5102
4
Mass Balance
over a volume element Ax, Ay, Az
D c
( ) ( )
0 0
D
v or v
t Dt
c
+ V = + V =
c
G G
(Rate of increase of mass per unit volume = Net rate
of mass addition per unit volume by convection)
Incompressible fluid
0 v V =
G
28-Sep-09 DGA/7 TK5102
The equation of continuity
28-Sep-09 DGA/8 TK5102
5
The Equation of Motion
28-Sep-09
TK5102
DGA/9
Momentum concentration
Three components of momentum (x y z Three components of momentum (x, y, z
components)
Concentration of x-component of
momentum : v
x
Accumulation rate of x component of Accumulation rate of x-component of
momentum
( )
x
v
x y z
t
c
A A A
c
28-Sep-09 DGA/10 TK5102
6
Flow of momentum
by molecular diffusion
y
y z
xx
yx
zx
x
y z
xx yx zx
y z x z x y t t t A A + A A + A A
28-Sep-09 DGA/11 TK5102
Flow of momentum in by molecular
xx yx
x x
y y
y z x z t t
=
=
A A + A A
Flow of momentum out by molecular
zx
z z
x yt
=
+ A A
xx yx
y z x z t t
A
A A + A A
xx yx
x x x
y y y
zx
z z z
y
x yt
= + A
= + A
= + A
+ A A
28-Sep-09 DGA/12 TK5102
7
Flow of momentum
by convective mechanism
x
v y z A A
x
y
z
volumetric flow rate v
v
x
y
v x z
x y
A A
A A
x
( v )( )
x
y z v A A
Q
Q
z
AxAy
y
z
( v )( )
( v )( )
x
x
x z v
x y v
+ A A
+ A A
Q
x
Q
y
28-Sep-09 DGA/13 TK5102
Flow of momentum in by convective
x y
( v )( ) ( v )( )
x x
x x
y y
y z v x z v
=
=
A A + A A
z
( v )( )
x
z z
x y v
=
+ A A
Flow of momentum out by convective
x y
( v )( ) ( v )( )
x x
y z v x z v
A
A A + A A
x y
z
( )( ) ( )( )
( v )( )
x x
x x x
y y y
x
z z z
y
x y v
= +A
= +A
= +A
+ A A
28-Sep-09 DGA/14 TK5102
8
Forces acting on fluid
Gravity Gravity
Pressure
( )( )
x
x y z g A A A
( )( ) y z p p
A
A A ( )( )
x x x x x
y p p
= = +A
28-Sep-09 DGA/15 TK5102
The equation of motion in terms of
28-Sep-09 DGA/16 TK5102
9
The equation of motion in terms of
28-Sep-09 DGA/17 TK5102
The equation of motion in terms of
28-Sep-09 DGA/18 TK5102
10
Equation of motion for a newtonian
fluid with constant and
28-Sep-09 DGA/19 TK5102
Equation of motion for a newtonian
fluid with constant and
28-Sep-09 DGA/20 TK5102
11
Equation of motion for a newtonian
fluid with constant and
28-Sep-09 DGA/21 TK5102
Tangential annular flow of a
Newtonian fluid
Outer cylinder rotates at Outer cylinder rotates at
angular velocity of
o
Incompressible and
Newtonian fluid with constant
transport properties
Laminar flow in direction
only at steady state condition
28-Sep-09 DGA/22 TK5102
y y
1D momentum transfer in
radial direction
Pressure varies in radial and
axial directions
12
Continuity equation
( ) ( ) ( ) 1 1
0
r z
v rv v
t r r r z
u
u
c c c c
+ + + =
c c c c
v c
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/23
0
v
u
u
c
=
c
Equation of motion for r-component
| |
2
r r r r
r z
v v v v v v p
v v
t r r r z r
u u
u
| | c c c c c
+ + + =
|
c c c c c
\ .
2 2
( ) 1 1 2 v rv v v
(
| | c c c c c
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/24
2 2 2 2
( ) 1 1 2
r r r
r
v rv v v
g
r r r r r z
u
u u
(
| | c c c c c
+ + + +
( |
c c c c c
\ .
13
Equation of motion for -component
1
r
r z
v v v v v v v p
v v
t r r r z r
u u u u u u
u u
c c c c c
| |
+ + + =
|
c c c c c
\ .
2 2
( ) 1 1 2 rv v v v
(
| | c c c c c
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/25
2 2 2 2
( ) 1 1 2
r
rv v v v
g
r r r r r z
u u u
u
u u
(
| | c c c c c
+ + + + +
( |
c c c c c
\ .
Equation of motion for z-component
| |
2
z z z z
r z
v v v v v v p
v v
t r r r z z
u u
u
| |
c c c c c
+ + + =
|
c c c c c
\ .
2 2
1 1 v v v
(
| | c c c c
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/26
2 2 2
1 1
z z z
z
v v v
g
r r r r z
u
(
| | c c c c
+ + + +
( |
c c c c
\ .
14
Simplified equations of motion
2
v p
u
c
(Effect of centrifugal
Eq. B.6.4
v p
r r
u
c
=
c
(Effect of centrifugal
force on pressure)
Eq. B.6.5
1
( ) 0
d d
rv
dr r dr
u
| |
=
|
\ .
(Velocity
distribution)
27
Eq. B.6.6
p
g
z
c
=
c
(Effect of gravity
force on pressure)
Distribution of angular velocity
1
( ) 0
d d
| |
|
Eq. B.6.5
1
( ) 0
d d
rv
dr r dr
u
| |
=
|
\ .
BC: v
= 0 at r = R and v
=
o
R at r = R
Velocity profile
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/28
( )
( )
/( ) /
1/
o
r R R r
v R
u
k k
k k
= O
15
Momentum flux and torque
v d
| |
Momentum flux
2 2 2
2 ( / ) ( /(1 ))
r
o
v d
r
dr r
R r
u
u
t
k k
| |
=
|
\ .
= O
Torque
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/29
Torque
2 2 2
2
4 /(1 )
z r
r R
o
T RL R
R L
u
k
t tk k
t k k
=
=
= O
Concentric cylinder viscometer
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/30
16
Flow near a slowly rotating sphere
| |
2
2
1
v
r
r r r
|
c
| | c
+
|
c c
\ .
2
1 1
( sin ) 0
sin
v
r
|
u
u u u
c c
| |
=
|
c c
\ .
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/31
\ .
BC 1 : v
= R sin at r = R
BC 2 : v
= 0 at r =
Cone and Cup Viscometer
28-Sep-09 DGA/32 TK5102
17
Cone and Cup Viscometer
2
( / ) sin v R R r
Velocity distribution
Torque
28-Sep-09 DGA/33 TK5102
3
8
z
T R
Equations of Change
for non isothermal system
28-Sep-09 DGA/34
TK5102
18
Energy Equation
2 2
(0, 5 ) { (0, 5 )} v U v U q
c
+ = V + V (0, 5 ) { (0, 5 )} v U v U q
t
+ V + V
c
( ) ( [ ]) ( ) pv v v g t V V +
Accumulation
of energy
Convective
mechanism
Conduction
( ) ( [ ]) ( ) pv v v g t V V +
28-Sep-09 DGA/35 TK5102
Pressure
forces
Gravitational
forces
Viscous
forces
Special Forms of Energy Equation
( ) ( ) U U
c
V V V V ( ) ( : ) U Uv q p v v
t
t =V V V V
c
( ) ( : )
DU
q p v v t =V V V
28-Sep-09 DGA/36 TK5102
( ) ( : ) q p v v
Dt
t = V V V
(the equation of thermal energy)
19
Special Forms of Energy Equation
Incompressible fluid (constant )
( : )
DU
q v
Dt
t = V V
U = H p/
( : )
DH Dp
q v
Dt Dt
t = V V +
28-Sep-09 DGA/37 TK5102
Energy equation
in terms of fluid temperature
DT p c
| |
( : ) ( )
v
V
DT p
C q v T v
Dt T
t
c
| |
= V V V
|
c
\ .
(1/ )
( : )
p
p
DT Dp
C q v T
Dt T Dt
t
c
| |
= V V
|
c
\ .
For incompressible fluid : C
v
= C
p
( : )
p
DT
C q v
Dt
t = V V
28-Sep-09 DGA/38 TK5102
20
Energy equations
for incompressible fluids
28-Sep-09 DGA/39 TK5102
28-Sep-09 DGA/40 TK5102
21
28-Sep-09 DGA/41
TK5102
28-Sep-09 DGA/42
TK5102
22
28-Sep-09 DGA/43
TK5102
28-Sep-09 DGA/44
TK5102
23
28-Sep-09 DGA/45
TK5102
28-Sep-09 DGA/46
TK5102
24
Forced Convection
of Laminar Flow in Pipe
Fluid in at T
1
z
r
f
l
u
k
s
q
o
Steady state momentum and heat
transfer
1D momentum transfer (v
z
= v
(r)
)
T = T
(r,z)
Constant physical properties
H
e
a
t
Constant physical properties
28-Sep-09 DGA/47 TK5102
Continuity equation
( ) ( ) ( ) 1 1
0
r z
v rv v
t r r r z
u
u
c c c c
+ + + =
c c c c
v c
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/48
0
z
v
z
c
=
c
25
Equation of motion for z-component
| |
2
z z z z
r z
v v v v v v p
v v
t r r r z z
u u
u
| |
c c c c c
+ + + =
|
c c c c c
\ .
2 2
1 1 v v v
(
| | c c c c
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/49
2 2 2
1 1
z z z
z
v v v
g
r r r r z
u
(
| | c c c c
+ + + +
( |
c c c c
\ .
Energy Equation
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/50
26
Forced Convection
of Laminar Flow in Pipe
Fluid in at T
1
Continuity equation
z
r
f
l
u
k
s
q
o
y q
dv
z
/dz = 0
Equation of motion
1
0
z
dv dP d
r g
dz r dr dr
| |
= + +
|
\ .
Energy equation
viscous
dissipation
H
e
a
t
2
2
2
1
z
p
dv dT dT T
C k r
dz r r dr z dr
( c c | | | |
= + +
| | (
c c
\ . \ .
28-Sep-09 DGA/51 TK5102
heat conduction
in z direction
Tangential flow in an annulus with
viscous heat generation
Incompressible and Newtonian
fl id i h fluid with constant transport
properties
Outer cylinder rotates
Laminar flow in direction
Steady state condition
1D momentum and heat transfers
in radial direction
28 September 2009 DGA/52
in radial direction
Pressure varies in radial and axial
directions
27
Energy Equation
T T T T c c c c
| |
r z
v T T T T
Cp v v
t r r z
u
u
c c c c
| |
+ + + =
|
c c c c
\ .
2 2
1 1 T T T
k
( c c c c
| |
u
| (
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/53
2 2 2
v
k r
r r r r z u
| |
+ + + u
| (
c c c c
\ .
Dissipation Function
2
2 2
1
2
r z
v v v
u
c ( c c | | | | | |
u
`
| | | (
2 2
2
1
r z
v r
z z r
v
r r z
v v v v
z r r z
u
u
u
(
| | | | | |
u = + + + +
`
| | | (
c c c
\ . \ . \ .
)
c c c c | | | |
+ + + +
| |
c c c c
\ . \ .
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/54
2
1
r
v v
r
r r r
u
u
( c c | |
+
`
| (
c c
\ .
)
28
Energy Equation
2
1 v T ( c c c
| | | |
1 v T
k r r
r r r r r
u
( c c c
| | | |
+
| | (
c c c
\ . \ .
From momentum balance:
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/55
( )
( )
/( ) /
1/
o
r R R r
v R
u
k k
k k
= O
Energy Equation
2 4 4
4 1 1 R T k O c c
| |
2 2 4
4 1 1
0
(1 )
o
R T
k r
r r r r
k
k
O c c
| |
+ =
|
c c
\ .
Boundary conditions :
T = T at r = R
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/56
T = T
b
at r = R
T = T
o
at r = R
29
Energy Equation
(dimensionless form)
1 1
4
d d
N
| | O
|
2 4 4
2 2
( )(1 )
o o
b o b o
T T R r
N
R T T k T T
k
k
O
= O = =
4
4N
d d
=
|
\ .
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/57
( )( )
b o b o
k
Boundary conditions :
= 1 at = 1
= 0 at = 0
Temperature Profiles
Annulus
2 2
ln 1 1 ln
1 1 1
ln ln
N
k k k
(
| |
| | | |
O = +
( | | |
\ . \ .
\ .
1 (1 )( )
Br
k k (
| |
O = +
| (
Annulus
Treating annulus as parallel plates
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/58
2
1 2 (1 )
Br
k k
O = +
| (
\ .
Note : N = Br
4
/ (1
2
)
2
30
Tangential flow in an annulus with
viscous heat generation
= 92 3 cP = 92.3 cP
= 1.22 g/ml
k = 0.0055 cal/(s cm C)
Tb = 100 C
To = 70 C
R = 5.060 cm
= 0.99
= 7980 rpm
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/59
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/60
31
Tangential flow in an annulus with
viscous heat generation
= 92 3 cP = 92.3 cP
= 1.22 g/ml
k = 0.0055 cal/(s cm C)
Tb = 100 C
To = 70 C
R = 5.060 cm
= 0.50
= 7980 rpm
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/61
28-Sep-09 TK5102 DGA/62
32
Continuity Equation for Component
28-Sep-09 DGA/63
TK5102
Mass Balance of A
over volume element Ax, Ay, Az
Ax, Ay, Az
z
Rate of accumulation
y
z
AxAyAz c
A
/ct
Rate of Ain
Rate of production
AxAyAz r
A
x, y, z
x
Rate of A in
n
Ax
x
AyAz + n
Ay
y
AxAz
+ n
Az
z
AxAy Rate of A out
n
Ax
x+Ax
AyAz + n
Ay
y+Ay
AxAz + n
Az
z+Az
AxAy
28-Sep-09 DGA/64 TK5102
33
Equations of Continuity
for a Binary System
Component A Component A
A A
A
A
Az
Ay
Ax A
r n
t
atau r
z
n
y
n
x
n
t
= V +
c
c
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
c
c
+
c
c
+
c
c
+
c
c
Component B
B B
B
B
Bz
By
Bx A
r n atau r
n
n
n
= V +
c
=
|
|
|
| c
+
c
+
c
+
c
B B B
t z y x t c
|
|
.
\
c c c c
Mixer
0 ) ( ) ( = V +
c
c
+ = + V +
c
c
v
t
atau r r n n
t
B A B A
28-Sep-09 DGA/65 TK5102
Equations of Continuity
for a Binary System
Component A Component A
A A
A
A
Az
Ay
Ax A
R N
t
C
atau R
z
N
y
N
x
N
t
c
= V +
c
c
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
c
c
+
c
c
+
c
c
+
c
c
Component B
B B
B
B
Bz
By
Bx A
R N
c
atau R
N
N
N c
= V +
c
=
|
|
|
| c
+
c
+
c
+
c
B B B
t z y x t c
|
|
.
\
c c c c
Mixer
B A B A B A
R R cv
t
c
atau R R N N
t
c
+ = V +
c
c
+ = + V +
c
c
) ( ) (
*
28-Sep-09 DGA/66 TK5102
34
Equations of Continuity
for a Binary System
Component A Average velocity Component A
A A
A
r n
t
= V +
c
c
Ficks law
A AB B A A A
w D n n w n V + + = ) (
Average velocity
v n n
B A
= +
Component A
A A AB A
A
r w D v
t
+ V V = V +
c
c
) ( ) (
28-Sep-09 DGA/67 TK5102
Equations of Continuity
for a Binary System
Component A Average velocity Component A
A A
A
R N
t
c
= V +
c
c
Ficks law
A AB B A A A
x cD N N x N V + + = ) (
Average velocity
*
cv N N
B A
= +
Component A
A A AB A
A
R x cD v c
t
c
+ V V = V +
c
c
) ( ) (
*
28-Sep-09 DGA/68 TK5102
35
Equations of Continuity
for a Binary System (dilute component)
Component Awith constant and D
AB
(weight base) Component A with constant and D
AB
(weight base)
A A AB A A
A
r D v v
t
+ V = V + V +
c
c
2
A A AB A
A
r D v
t
+ V = V +
c
c
2
Component Awith constant and D
AB
(molar base) Component A with constant and D
AB
(molar base)
A A AB A A
A
R c D c v v c
t
c
+ V = V + V +
c
c
2 * *
) (
2 *
B A A A A AB A
A
R R x R c D c v
t
c
+ + V = V +
c
c
28-Sep-09 DGA/69 TK5102
28-Sep-09 DGA/70 TK5102
36
28-Sep-09 DGA/71
TK5102
Reaction in Pipe Reactor
Fast reaction A B at cylinder wall
z
r
L
2R
Dilute solution
Concentration c
A
B in solution can be neglected
Steady state, isothermal, and laminar flow
Constant transport properties
28-Sep-09 DGA/72 TK5102
37
Reaction in Pipe Reactor
Equation of motion Equation of motion
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
dr
dv
r
dr
d
r dz
dP
z
1
0
Continuity equation of A
( c
|
|
| c c c
2
1 c c
D
c
A A A
Boundary conditions:
Boundary conditions:
v
z
= 0 at r = R
dv
z
/dr = 0 at r = 0
(
c
c
+ |
.
|
\
|
c
c
c
c
=
c
c
2
1
z
c
r
c
r
r r
D
z
c
v
A A
AS
A
z
y
c
A
= c
A0
at z = 0
c
A
= 0 at r = R
dc
A
/dr = 0 at r = 0
neglected
28-Sep-09 DGA/73 TK5102
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Physics in Focus Year 12Document476 pagesPhysics in Focus Year 12mariam h100% (2)
- Engineering Mechanics Course Description and ContentsDocument2 pagesEngineering Mechanics Course Description and ContentsSarah LeonenNo ratings yet
- Thermo Compressor CalculatorDocument6 pagesThermo Compressor CalculatorVilas m ChinkeNo ratings yet
- Api 610 PDFDocument10 pagesApi 610 PDFAlvaro Torres BozzoNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual HydraulicsDocument14 pagesSolution Manual HydraulicsVivekka Olivia John75% (4)
- (David Crolla - Behrooz Mashadi) Vehicle Powertrain Systems-Integration and Optimization - Solution ManualDocument256 pages(David Crolla - Behrooz Mashadi) Vehicle Powertrain Systems-Integration and Optimization - Solution Manualsadegh_199067% (3)
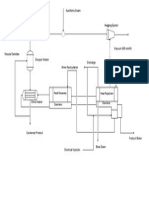
- Ethanol P&IDDocument1 pageEthanol P&IDalmengarun100% (1)
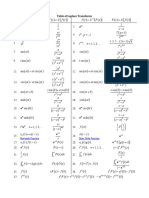
- FormulasDocument31 pagesFormulasJL PerezNo ratings yet
- Homwork - 1Document15 pagesHomwork - 1TimoNo ratings yet
- Steam EjectorDocument2 pagesSteam EjectoralmengarunNo ratings yet
- Lampiran CDocument413 pagesLampiran CalmengarunNo ratings yet
- Lembar Pengesahan TA AntoDocument1 pageLembar Pengesahan TA AntoalmengarunNo ratings yet
- HOW CELL GROW&Batch Growth KineticsDocument46 pagesHOW CELL GROW&Batch Growth KineticsalmengarunNo ratings yet
- Daily Progres - CTA - 2016Document4 pagesDaily Progres - CTA - 2016almengarun100% (1)
- HE, PompaDocument285 pagesHE, PompaalmengarunNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument1 pageDaftar PustakaalmengarunNo ratings yet
- PFD Acetic AcidDocument2 pagesPFD Acetic AcidalmengarunNo ratings yet
- EksporDocument31 pagesEksporalmengarunNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Basis MolDocument384 pagesPerhitungan Basis MolalmengarunNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Basis MolDocument384 pagesPerhitungan Basis MolalmengarunNo ratings yet
- CBE 461L 2 TripleEffect EvaporatorDocument6 pagesCBE 461L 2 TripleEffect EvaporatorRendy Bayu AjiNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan GPMDocument3 pagesPerhitungan GPMalmengarunNo ratings yet
- Preparing Equipment For MaintenanceDocument4 pagesPreparing Equipment For MaintenancealmengarunNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakaalmengarunNo ratings yet
- PVD Indonesia Power DesalinasiDocument1 pagePVD Indonesia Power DesalinasialmengarunNo ratings yet
- Drawing Prespective Plant IndustriesDocument13 pagesDrawing Prespective Plant IndustriesalmengarunNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan DistilasiDocument46 pagesPerhitungan DistilasialmengarunNo ratings yet
- Lampiran Pembhasan MixingDocument8 pagesLampiran Pembhasan MixingalmengarunNo ratings yet
- The Origin of The City of BanyuwangiDocument2 pagesThe Origin of The City of BanyuwangialmengarunNo ratings yet
- Latihan PDB IIDocument12 pagesLatihan PDB IIalmengarunNo ratings yet
- Preparing Equipment For MaintenanceDocument4 pagesPreparing Equipment For MaintenancealmengarunNo ratings yet
- Aspirin and SoapDocument4 pagesAspirin and SoapyeeeyyyNo ratings yet
- Sample Question 2Document6 pagesSample Question 2charleswcoleNo ratings yet
- Rectifire and Voltage ControleDocument27 pagesRectifire and Voltage ControleWoldemariam WorkuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Salt, Acid, Base and Metal: ChemicalDocument6 pagesChemistry of Salt, Acid, Base and Metal: ChemicalrezadNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Section 16-7Document25 pagesLecture Notes For Section 16-7Joshua D'CruzNo ratings yet
- Pre Requisite: BE 100 Engineering MechanicsDocument3 pagesPre Requisite: BE 100 Engineering MechanicsBalagopal VNo ratings yet
- Random WalkDocument8 pagesRandom WalkMeral OcakNo ratings yet
- InterferenceDocument1 pageInterferenceJumar CadondonNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Honors PacketDocument8 pagesUnit 1 Honors Packetapi-259040408No ratings yet
- Doron Barnea 1993 Three Layer Model For Solid Liquid FlowDocument15 pagesDoron Barnea 1993 Three Layer Model For Solid Liquid FlowrestdeepakNo ratings yet
- Problems (Relativity of Time)Document13 pagesProblems (Relativity of Time)Jumar CadondonNo ratings yet
- Heat Conduction Term ProjectDocument7 pagesHeat Conduction Term ProjectRashed KaiserNo ratings yet
- Mutual Coupling in Antenna ArraysDocument48 pagesMutual Coupling in Antenna ArrayshomeiraNo ratings yet
- Laplace TableDocument2 pagesLaplace TableosmanfıratNo ratings yet
- Cufsm Advanced IdeasDocument23 pagesCufsm Advanced Ideaschristos032No ratings yet
- Radioactivity Revision Question For Edexcel IgcseDocument11 pagesRadioactivity Revision Question For Edexcel IgcseLatona Oladipupo Olawale83% (6)
- Lie Groups For 2D and 3D Transformations: Ethan EadeDocument24 pagesLie Groups For 2D and 3D Transformations: Ethan EadeLe Dinh PhongNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1A Bicycle Brake Lever Loading AnalysisDocument4 pagesCase Study 1A Bicycle Brake Lever Loading AnalysisKORATASAINo ratings yet
- Wave Optics (MCQS)Document21 pagesWave Optics (MCQS)Ronda StewartNo ratings yet
- CH 04Document20 pagesCH 04msy83635No ratings yet
- Two Small Spheres in MotionDocument12 pagesTwo Small Spheres in MotionharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Multivector Calculus: Journal of Mathematical Analysis AND ApplicationsDocument13 pagesMultivector Calculus: Journal of Mathematical Analysis AND ApplicationsCloue Contad DeriadaNo ratings yet