Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Insurance Sheet
Uploaded by
api-252377967Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Insurance Sheet
Uploaded by
api-252377967Copyright:
Available Formats
7.10.1.
L1 Note taking guide
Types of Insurance Essentials Note-Taking Guide
Alexis McNees Name__________________
39 Total Points Earned Total Points Possible Percentage
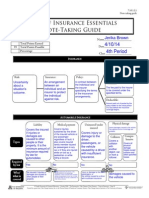
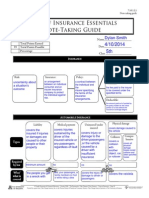
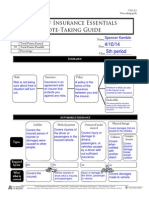
INSURANCE Policyholder:
4/10/2014 Date__________________
2nd Class _________________
Risk:
Insurance:
Insurance is an arrangement between an individual and an insurer to protect the individual against risk.
Policy:
A contract between the individual and the insurer specifying the terms of the insurance arrangements.
Consumer who purchased the policy.
Premium:
Fee paid to the insurer to be covered under the specified terms.
Risk is uncertainty about a situations outcome. Risk can be unpredictable events which lead to loss or damage.
Deductible:
Amount paid out of pocket by the policy holder for the initial portion of a loss before the insurance coverage begins.
AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE Liability
Covers the insured if injuries or damages are caused to other people or their property. It is the minimum amount of insurance required by law for automobiles.
Health
Provides protection against financial losses resulting from injury, illness, and disability.
Medical payment
Covers injuries sustained by the driver of the insured vehicle or any passenger regardless of fault. It also covers insured family members injured as passengers in any car or if they are injured while on foot as a pedestrian or while riding a bicycle.
Uninsured/under insured
Physical damage
Covers damages caused to the vehicle. Two optional forms of coverage are available
Types
Covers injury or damage to the driver, passengers, or the vehicle caused by a driver with insufficient insurance.
Disability
Replaces a portion of ones income if they become unable to work due to illness or injury.
Collision
Covers a collision with another object, car, or from a rollover
Comprehensive
Covers all physical damage losses except collision and other specified losses.
Required by law Who/ what is covered
Life
A contract between an insurer and policyholder specifying a sum to be paid to a beneficiary upon the insureds death
Homeowners/Renter's
Combines property and liability insurance into one policy to protect a home from damage costs due to perils. protects the insured from loss to the contents of the dwelling rather than the dwelling itself.
Family Economics & Financial Education October 2010 The Essentials to Take Charge of Your Finances Types of Insurance Page 10 Funded by a grant from Take Charge America, Inc. to the Norton School of Family and Consumer Sciences Take Charge America Institute at The University of Arizona
7.10.1.L1 Note taking guide
HEALTH INSURANCE Why is it important to purchase health insurance?
Health care costs are extremely high and it can be hard for the average person to afford health care. Large medical expenses could wipe out an individuals savings. To protect individuals from this risk, health insurance can be purchased.
Provides protection against:
May cover:
How may health insurance be purchased?
Health insurance may be purchased by an individual or through their employer.
financial losses resulting from injury, illness, and disability.
may cover hospital, surgical, dental, vision, long-term care, prescription, and other major expenditures.
Children may stay on their parents health insurance until:
They are 19 or while they are in college.
LIFE INSURANCE Life insurance:
Life insurance is a contract between an insurer and policyholder specifying a sum to be paid to a beneficiary upon the insureds death.
Beneficiary:
Dependent:
recipient of any policy proceeds if the insured person dies.
a person who relies on someone else financially.
Who should purchase life insurance?
Life insurance is necessary for people who have a dependent spouse, dependent children, an aging or disabled dependent relative, or are business owners.
DISABILITY INSURANCE Disability insurance:
Disability insurance replaces a portion of ones income if they become unable to work due to illness or injury.
If needed, how much does disability insurance pay an individual?
The insurance typically pays between 60% 70% of ones full time wage.
HOMEOWNERS AND R ENTERS INSURANCE Peril:
event which can cause a financial loss like fire, falling trees, lightning, and others.
Renters insurance:
protects the insured from loss to the contents of the dwelling rather than the dwelling itself.
Homeowners insurance:
combines property and liability insurance into one policy to protect a home from damage costs due to perils.
Property insurance:
protects the insured from financial losses due to destruction or damage to property or possessions.
Why is it important for a renter to purchase renters insurance?
because the landlords insurance policy on the dwelling does not cover the renters personal possessions.
Liability insurance:
protects the insured party from being held liable for others financial losses.
Covers:
It covers major perils, provides liability protection, and provides for additional living expenses if the dwelling is rendered uninhabitable by one of the covered perils.
Family Economics & Financial Education October 2010 The Essentials to Take Charge of Your Finances Types of Insurance Page 11 Funded by a grant from Take Charge America, Inc. to the Norton School of Family and Consumer Sciences Take Charge America Institute at The University of Arizona
You might also like
- Property, Liability and Auto Insurance: A Handbook and Guide for Insurance Concepts and Coverage!From EverandProperty, Liability and Auto Insurance: A Handbook and Guide for Insurance Concepts and Coverage!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDocument2 pagesInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252384953No ratings yet
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDocument2 pagesInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252392987No ratings yet
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDocument2 pagesInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252460708No ratings yet
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDocument2 pagesInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252384641No ratings yet
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDocument2 pagesInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-2523918430% (1)
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDocument2 pagesInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252390333100% (1)
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDocument2 pagesInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252377919No ratings yet
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDocument2 pagesInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252988764No ratings yet
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDocument2 pagesInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252387344100% (1)
- InsuranceDocument2 pagesInsuranceapi-252391740No ratings yet
- Law of Insurance AnswersheetDocument55 pagesLaw of Insurance Answersheetkhatriparas71No ratings yet
- Insurance BasicsDocument24 pagesInsurance BasicsKomal LalwaniNo ratings yet
- Understanding InsuranceDocument64 pagesUnderstanding InsuranceMikant Fernando63% (8)
- Insurance – Definition and Meaning 2Document4 pagesInsurance – Definition and Meaning 2ЕкатеринаNo ratings yet
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDocument2 pagesInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252391503No ratings yet
- Introduction of Mediclaim InsuranceDocument17 pagesIntroduction of Mediclaim InsuranceKunal KaduNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document3 pagesLesson 7shadowlord468No ratings yet
- Definition of InsuranceDocument11 pagesDefinition of InsurancePuru SharmaNo ratings yet
- Insurance BasicsDocument23 pagesInsurance BasicsChamandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- InsuranceDocument6 pagesInsuranceHarsh SadavartiaNo ratings yet
- Insurance MGT NotesDocument36 pagesInsurance MGT NotesHONEY AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Unit FourDocument35 pagesUnit FourBI SH ALNo ratings yet
- The key types of insurance contractsDocument7 pagesThe key types of insurance contractsAnupriya HiranwalNo ratings yet
- Insurance Fraud DetectionDocument74 pagesInsurance Fraud DetectionJai GaneshNo ratings yet
- Daniel AyoolaDocument10 pagesDaniel AyoolaSalim SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Insurance and Risk ManagementDocument10 pagesInsurance and Risk Managementhitesh gargNo ratings yet
- RMIN 4000 Exam Study Guide Ch 2 & 9Document13 pagesRMIN 4000 Exam Study Guide Ch 2 & 9Brittany Danielle ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofDocument74 pagesSummer Training Report: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Award of The Degree ofrahul19myNo ratings yet
- Family Risk ManagementDocument12 pagesFamily Risk ManagementAakash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Frauds in Insurance SectorDocument74 pagesFrauds in Insurance Sectoranilmourya5100% (1)
- Insuranc 1Document10 pagesInsuranc 1zunaira sarfrazNo ratings yet
- Types of Insurance Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesTypes of Insurance Lesson PlanpcsgdnwuNo ratings yet
- Law Economics Risk Management Hedge Risk Uncertain: Types of InsuranceDocument3 pagesLaw Economics Risk Management Hedge Risk Uncertain: Types of InsuranceEdvergMae VergaraNo ratings yet
- INSURANCE MANAGEMENT GUIDEDocument25 pagesINSURANCE MANAGEMENT GUIDEDeepak ParidaNo ratings yet
- 5-Insurance Planning (Insurance Planning)Document35 pages5-Insurance Planning (Insurance Planning)Farahliza RosediNo ratings yet
- Apollo MunichDocument52 pagesApollo MunichSumit ManglaniNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument20 pagesINTRODUCTIONLEARN WITH AGALYANo ratings yet
- Finance ReportDocument4 pagesFinance ReportKatrina FregillanaNo ratings yet
- Insurance and Risk Management Unit IDocument9 pagesInsurance and Risk Management Unit Ipooranim1976No ratings yet
- Chapter 1-What Is Insurance?Document20 pagesChapter 1-What Is Insurance?Akshada Chitnis100% (2)
- What Is Insurance by VISHALDocument6 pagesWhat Is Insurance by VISHALVishalNo ratings yet
- Insurance Is The Granted To An Individual, Institution or Indeed The TradersDocument109 pagesInsurance Is The Granted To An Individual, Institution or Indeed The TradersMahesh KempegowdaNo ratings yet
- Insurance and Risk ManagementDocument6 pagesInsurance and Risk Managementbhupendra mehraNo ratings yet
- InsurancesDocument7 pagesInsuranceskidvictor16No ratings yet
- Insurance Company ProfileDocument12 pagesInsurance Company ProfileKai MK4No ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 ModuleDocument7 pagesChapter - 5 ModuleAllyjen SampangNo ratings yet
- Iom Concept of InsuranceDocument4 pagesIom Concept of Insuranceowuor PeterNo ratings yet
- Insurance & Risk Management JUNE 2022Document11 pagesInsurance & Risk Management JUNE 2022Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Banking and Insurance ElementsDocument11 pagesBanking and Insurance ElementsNisarg ShahNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 InsuranceDocument9 pagesUNIT 1 InsuranceHarleenNo ratings yet
- Insurance ManagementDocument27 pagesInsurance Managementzaks69No ratings yet
- 7 InsuranceDocument10 pages7 InsuranceLynner Anne DeytaNo ratings yet
- 18BCO32C-U1Document14 pages18BCO32C-U1Vipul TyagiNo ratings yet
- Insurance Concepts ExplainedDocument6 pagesInsurance Concepts ExplainedSHAURYA MAHAJANNo ratings yet
- COMM 229 Notes Chapter 6Document5 pagesCOMM 229 Notes Chapter 6Cody ClinkardNo ratings yet
- 5-RISK MANAGEMENT AND LIFE INSURANCE (Insurance Planning)Document45 pages5-RISK MANAGEMENT AND LIFE INSURANCE (Insurance Planning)Haliyana HamidNo ratings yet
- Insurance ProvisionDocument8 pagesInsurance ProvisionJake GuataNo ratings yet
- Institution That Offers A Person, Company, or Other Entity Reimbursement or Financial Protection Against Possible Future Losses or DamagesDocument16 pagesInstitution That Offers A Person, Company, or Other Entity Reimbursement or Financial Protection Against Possible Future Losses or DamagesHrishikesh DharNo ratings yet
- Lecture Plan FormatDocument33 pagesLecture Plan FormatSahil KhanNo ratings yet
- Ayeesha - Principles of Management AccountingDocument5 pagesAyeesha - Principles of Management AccountingMahesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Io73moh25 - ACTIVITY - CHAPTER 4 - TYPES OF MAJOR ACCOUNTS.Document4 pagesIo73moh25 - ACTIVITY - CHAPTER 4 - TYPES OF MAJOR ACCOUNTS.James CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Part I - Introduction To AISDocument46 pagesPart I - Introduction To AISAgatNo ratings yet
- 04 Victorias Milling Co. Inc. vs. Municipality of VictoriasDocument2 pages04 Victorias Milling Co. Inc. vs. Municipality of VictoriasJamaica Cabildo ManaligodNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: The Costs of ProductionDocument8 pagesMicroeconomics: The Costs of ProductiondewiNo ratings yet
- Full Download Corporate Finance Canadian 3rd Edition Berk Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Corporate Finance Canadian 3rd Edition Berk Solutions Manualkisslingcicelypro100% (32)
- F3 and FFA Full Specimen Exam Answers PDFDocument5 pagesF3 and FFA Full Specimen Exam Answers PDFFarhanHaiderNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance - Mock ExamDocument5 pagesCorporate Finance - Mock ExamMinh Hạnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- RM Dynamic Pricing Demand ForecastingDocument41 pagesRM Dynamic Pricing Demand ForecastingSankha BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- MTN Group Business Report Highlights Cellular Growth Across AfricaDocument170 pagesMTN Group Business Report Highlights Cellular Growth Across AfricaMercy OfuyaNo ratings yet
- Solved Ashley Company Uses A Perpetual Inventory System From The Following PDFDocument1 pageSolved Ashley Company Uses A Perpetual Inventory System From The Following PDFAnbu jaromiaNo ratings yet
- The Impacts of Unemployment in Zimbabwe From The 2009-2019Document12 pagesThe Impacts of Unemployment in Zimbabwe From The 2009-2019Tracy AlpsNo ratings yet
- Report Arutmin Indonesia September 2011Document56 pagesReport Arutmin Indonesia September 2011Fredy Milson SimbolonNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting International Student 7th Edition Kimmel Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesFinancial Accounting International Student 7th Edition Kimmel Solutions ManualDannyJohnsonobtk100% (58)
- SLIP GAJI DANDI Des Jan FebDocument3 pagesSLIP GAJI DANDI Des Jan Febharun chandraNo ratings yet
- Ms - MuffDocument17 pagesMs - MuffDayuman LagasiNo ratings yet
- Research Grant GuidelinesDocument12 pagesResearch Grant GuidelinessckamoteNo ratings yet
- Ifrs Edition: Prepared by Coby Harmon University of California, Santa Barbara Westmont CollegeDocument75 pagesIfrs Edition: Prepared by Coby Harmon University of California, Santa Barbara Westmont CollegeKaram AlhajNo ratings yet
- Ed SyllaDocument82 pagesEd SyllaDr.V.Bastin JeromeNo ratings yet
- Taxation IIDocument5 pagesTaxation IIAnandNo ratings yet
- GratuityDocument8 pagesGratuityManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Uy Law Office Balance SheetDocument2 pagesUy Law Office Balance SheetA c100% (1)
- Expense report templateDocument1 pageExpense report templateTom CatNo ratings yet
- Principles of AccountingDocument13 pagesPrinciples of AccountingRoe BelleNo ratings yet
- Partnership Fundamentals 2Document6 pagesPartnership Fundamentals 2sainimanish170gmailcNo ratings yet
- NLG - Annual Report 2016Document48 pagesNLG - Annual Report 2016Kiva DangNo ratings yet
- Marks and Spencer Marketing MixDocument27 pagesMarks and Spencer Marketing MixTushar Sharma50% (4)
- Glencore 2018Document240 pagesGlencore 2018Eduardo AzorsaNo ratings yet
- Palepu 3e ch4Document21 pagesPalepu 3e ch4Nadine SantosNo ratings yet