Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 2 - ReviewPackage Multiple ChoiceSolution
Uploaded by
Thuran NathanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 2 - ReviewPackage Multiple ChoiceSolution
Uploaded by
Thuran NathanCopyright:
Available Formats
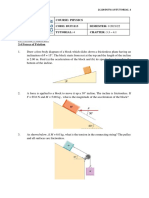
2.
00 kg
rope
ground
3.00 m
What is the tension in the rope during the acceleration?
A. 5.33 N
B. 14.3 N
C. 23.6 N
D. 24.9 N
4. A 4.00 kg block is accelerated along a level surface at 3.00 m/s
2
. The applied force is 20.0 N.
3.00 m/s
2
20.0 N
4.00 kg
What is the coefficient of friction between the block and the surface?
A. 0.20
B. 0.31
C. 0.51
D. 0.67
5. A 3.00 kg object is being accelerated vertically upwards at 2.80 m/s
2
, as shown.
3.00 kg
cord
ground
2.80 m/s
2
What is the tension in the cord?
A. 8.40 N
B. 21.0 N
C. 29.4 N
D. 37.8 N
6. What minimum horizontal force F will just prevent the 5.0 kg block from sliding if the coefficient
of friction between the wall and the block is 0.65?
F
A. 6.4 N
B. 32 N
C. 49 N
D. 75 N
7. An object is sliding down a smooth incline. If friction is negligible, the object has
A. constant velocity.
B. constant momentum.
C. constant acceleration.
D. constant displacement.
- 2 -
8. A pendulum is swinging freely between points R and S as shown in the diagram below.
R S
Which of the following diagrams best represents the forces acting on the pendulum bob at point R?
A. B.
C. D.
9. A constant force is applied to an object on a frictionless surface, as shown in the diagram below.
Force
The resulting motion has
A. constant velocity.
B. constant momentum.
C. constant acceleration.
D. constant kinetic energy.
10. What is the frictional force due to air resistance on a 0.50 kg object falling vertically with an
acceleration of 8.5 m/s
2
?
A. 0.65 N
B. 4.3 N
C. 4.9 N
D. 9.2 N
- 3 -
Which of the following best represents the free body diagram for the cart?
A. B.
C. D.
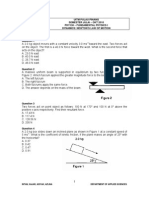
12. A massless, frictionless pulley is suspended by a rope. When the masses are allowed to accelerate,
the tension in the string joining them is 28 N at X . What will the tension be at Y and at Z?
Y X F
T
=28 N
5. 0 kg
Z
2.0 kg
TENSION AT Y TENSION AT Z
A. 20 N 48 N
B. 20 N 69 N
C. 28 N 56 N
D. 28 N 69 N
2.00 kg
m
Find the tension in the string while the system is accelerating.
A. 3.20 N
B. 16.4 N
C. 19.6 N
D. 22.8 N
14. Force F gives mass m
1
an acceleration of 4.0 m/s
2
. The same force F gives mass m
2
an
acceleration of 2.0 m/s
2
. What acceleration would force F give to the two masses m
1
and m
2
if
they were glued together?
A. 1.0 m/s
2
B. 1.3 m/s
2
C. 3.0 m/s
2
D. 6.0 m/s
2
15. A 4.0 kg block has a speed of 9.0 m/s at X.
35
What is the maximum distance, d, travelled by the block? Ignore friction.
A. 0.92 m
B. 1.6 m
C. 4.1 m
D. 7.2 m
16. The tension in the string shown is 12 N. Find the acceleration of mass m
1
.
m
1
=4.0 kg
m
2
A. 3.0 m/s
2
B. 6.4 m/s
2
C. 6.8 m/s
2
D. 13 m/s
2
17. A 75 kg man stands on a scale while accelerating upwards in an elevator. If the scale reads
850 N, what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the elevator?
A. 1.2ms
2
B. 1.5ms
2
C. 9.8ms
2
D. 11ms
2
18. A 45 kg toboggan and rider decelerate on level snow at 0.53 m/s
2
. What is the coefficient of
friction between the toboggan and the snow?
A. 0.012
B. 0.054
C. 0.22
D. 0.53
19. The 2.0 kg head of an axe strikes a tree horizontally at 40 m/s. The blade penetrates 0.040 m
into the tree. What is the average force exerted by the blade on this tree?
A. 2.010
1
N
B. 2.010
3
N
C. 2.010
4
N
D. 4.010
4
N
- 6 -
20. Two forces act on an object as shown in the diagram.
F
1
F
2
Which of the following best shows the resultant R of these forces?
A.
C.
R
F
1
F
2
F
2
F
1
R
B.
D.
R
F
1
F
2
F
2
F
1
R
21. The 4.0 kg block shown accelerates across a frictionless horizontal table at 1.5ms
2
.
m
1
a =1.5 m
2
=4.0 kg m s
2
Find the mass of object m
1
.
A. 0.61 kg
B. 0.72 kg
C. 6.0 kg
D. 26 kg
- 7 -
22. Which of the following is not a statement of one of Newton's laws of motion?
A. For every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force.
B. If no net force acts on an object, the object will remain at rest, or continue to move at a
constant velocity.
C. The acceleration of freely falling objects is proportional to their mass.
D. If a net force does act on an object, the object will accelerate in the direction of the net force.
23. Three blocks have masses 1.0 kg, 7.0 kg and 5.0 kg as shown. The horizontal surface is
frictionless.
7.0 kg
1.0 kg 5.0 kg
What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the system?
A. 3.0ms
2
B. 3.8ms
2
C. 6.5ms
2
D. 7.8ms
2
24. A 2.0 kg block is sliding down a 15 incline. The coefficient of friction is 0.62. At some
position the block has a speed of 7.0ms.
What distance d will this block move before coming to rest?
A. 2.5 m
B. 4.0 m
C. 4.2 m
D. 7.4 m
- 8 -
25. A student exerts a 120N horizontal force on a 25 kg carton of apples, causing it to
accelerate over level ground at 1.8ms
2
.
120 N
a =1.8ms
2
Find the coefficient of friction between the carton and the ground.
A. 0.31
B. 0.38
C. 0.49
D. 0.67
26. A net force F acts on an object of mass m, causing it to accelerate at 4.0ms
2
. If the same
net force F acts on an object of mass 2m, its acceleration will be
A. 1.0ms
2
B. 2.0ms
2
C. 4.0ms
2
D. 8.0ms
2
- 9 -
27. A 5.0 kg concrete block accelerates down a 34 slope at 4.2ms
2
. Find the coefficient of
friction between the block and the slope.
34
A. 0.13
B. 0.16
C. 0.43
D. 0.67
28. The free body diagram shown below represents a crate being dragged towards the left over a
rough surface.
F
1
F
2
F
3
F
4
Which of the vectors represent the normal force and the friction force acting on the crate?
NORMAL FORCE FRICTION FORCE
A.
F
1
F
2
B.
F
2
F
3
C.
F
3
F
4
D.
F
4
F
1
29. A girl applies a 140 N force to a 35 kg bale of hay at an angle of 28 above horizontal.
The friction force acting on the bale is 55 N. What will be the horizontal acceleration of the
bale?
28
F =140 N
A. 0.31ms
2
B. 2.0ms
2
C. 2.4ms
2
D. 2.6ms
2
-10 -
- 11 -
30. A block is on a frictionless incline.
Which of the following is a correct free body diagram for the block?
A. B. C. D.
31. A cart on a frictionless surface is attached to a hanging mass of 8.2kg.
3.5ms
2
8.2 kg
m
If this system accelerates at 3.5ms
2
, what is the mass m of the cart?
A. 6.0kg
B. 15kg
C. 23kg
D. 31kg
32. A 15 kg block on a horizontal surface has a 100 N force acting on it as shown.
m=15.0kg
F =100 N
What is the normal force?
A. 47 N
B. 100 N
C. 147 N
D. 247 N
- 12 -
33. Which of the following graphs shows the relationship between acceleration and net force?
A.
C.
a
net F
a
net F
B.
D.
a
net F
a
net F
34. A 12 kg cart on a 23 frictionless incline is connected to a wall as shown.
Wall
What is the tension T in the cord?
A. 46 N
B. 50 N
C. 110 N
D. 120 N
- 13 -
35. A 5500 kg helicopter is travelling at constant speed in level flight.
5 500 kg
F
25
Rotor
v
What is the force F provided by the rotor?
A. 4.910
4
N
B. 5.410
4
N
C. 5.910
4
N
D. 1.210
5
N
36. A 15 kg block has a constant acceleration of 2.2ms
2
down a 30 incline.
m=15kg
30
What is the magnitude of the friction force on the block?
A. 33 N
B. 41 N
C. 74 N
D. 130 N
37. A curling rock is travelling to the right across the ice as shown in the diagram.
Which of the following best represents the forces acting on the curling rock?
A. B. C. D.
38. The system of blocks on a frictionless surface in the diagram below is accelerating at 2.0ms
2
.
3.0 kg
1.0 kg
4.0 kg X
a =2.0ms
2
What is the tension in the cord at X?
A. 2.0N
B. 6.0N
C. 8.0N
D. 16N
39 A 15 kg block is pushed up a 35 incline. A friction force of 110 N exists between the block
and the incline.
35
v
F
What minimum force F, would be necessary to move the block up the incline at a constant
speed?
A. 26 N
B. 84 N
C. 150 N
D. 190 N
40. Two forces act at a single point as shown.
31 25
12 N
18 N
What is the magnitude of the resulting force?
A. 15 N
B. 22 N
C. 27 N
D. 30 N
- 14 -
41. Two masses are connected together by a rope and pulley on a frictionless inclined plane
as shown.
When the system is released, what is the initial acceleration of the 21 kg mass?
MAGNITUDE OF THE ACCELERATION DIRECTION THE MASS WILL TRAVEL
A. 0.26ms
2
up the incline
B. 0.26ms
2
down the incline
C. 0.48ms
2
up the incline
D. 0.48ms
2
down the incline
42. A 5.0 kg block is being pulled to the right by a 75 N force.
20
m= 5.0kg
What is the normal force on this block?
A. 23 N
B. 26 N
C. 49 N
D. 75 N
- 15 -
43. The system of blocks shown in the diagram below is being accelerated to the right at 4.4ms
2
.
=0. 35
0.20 kg
0.10 kg
a= 4.4 ms
2
What pulling force is applied by the hand?
A. 0.3 N
B. 1.0 N
C. 1.3 N
D. 2.3 N
- 16 -
44. A 0.055kg bullet was fired at 250ms into a block of wood as shown in the diagram below.
d
Assuming an average force of 9500 N brings the bullet to rest in the wood, what distanced did
the bullet penetrate the block?
A. 1.410
-3
m
B. 1.410
-2
m
C. 1.810
-1
m
D. 3.610
-1
m
I9
q Sok
F
MjSxliSeggipivexmsrSmwS8?Sqw
0SlexSmwSxliSq ekrmxyhiSsjSJCC
E?S S44SR
F?S S89SR
G?S S,4SR
H?S 4,SR
SAS4?S9
I8I D irufh FSlv dssolhg dw dq dqjoh ri 8 Sderyh wkh krulrqwdo wr sxoo d S4 nj fudwh dfurvv d
vsyklSiorru dv vkrzq ehorzIS
You might also like
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Laws of Motion: Multiple ChoiceDocument8 pagesThe Laws of Motion: Multiple Choicealiya mNo ratings yet
- Extra Problems Chap. 5Document11 pagesExtra Problems Chap. 5Roaa HamadaNo ratings yet
- Practice # 8Document9 pagesPractice # 8AfifaFarooqNo ratings yet
- Ce2 Sample2Document5 pagesCe2 Sample2ParZiValNo ratings yet
- USTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part3 SolutionDocument10 pagesUSTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part3 Solutionabcvn67No ratings yet
- Chap2 Q USTH Exercise B1 QuestionOnlyDocument7 pagesChap2 Q USTH Exercise B1 QuestionOnlyTrần Hoàng Việt100% (1)
- Static Equilibrium Ex.Document15 pagesStatic Equilibrium Ex.Marc Harold ChuaNo ratings yet
- The tension in each string will be the sameDocument7 pagesThe tension in each string will be the sameRomou AlsaaqNo ratings yet
- 081 CH 5Document5 pages081 CH 5Andrew James ReadNo ratings yet
- JR Iit StarDocument18 pagesJR Iit Star2pwxanqt8aNo ratings yet
- USTH B1 Exercise Part3 QuestionDocument7 pagesUSTH B1 Exercise Part3 Questionbình minh trầnNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium TorquesDocument14 pagesEquilibrium TorquesmartinNo ratings yet
- 2b-Dynamics FR Practice ProblemsDocument24 pages2b-Dynamics FR Practice ProblemsTiff VoNo ratings yet
- (A) What Is The Magnitude of The ResultantDocument4 pages(A) What Is The Magnitude of The ResultantAadar NNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 - Test 05 - Force and Motion Score:: A B C D EDocument6 pagesAP Physics 1 - Test 05 - Force and Motion Score:: A B C D ESTNo ratings yet
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocument14 pagesRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBá Phong LêNo ratings yet
- NLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Document19 pagesNLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Mohit GargNo ratings yet
- g3 Physics 2Document15 pagesg3 Physics 2Carlina FerreraNo ratings yet
- Newton's 2nd Law of Motion ExplainedDocument14 pagesNewton's 2nd Law of Motion ExplainedGarrey BrionesNo ratings yet
- 3.1 ForceDocument80 pages3.1 ForceMuhd AfifNo ratings yet
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocument17 pagesRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBaoduy NguyenNo ratings yet
- FORCES AND MOTION TUTORIALDocument5 pagesFORCES AND MOTION TUTORIALlove sunwooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7—Energy of a System Multiple ChoiceDocument25 pagesChapter 7—Energy of a System Multiple ChoiceLeo Fuentes100% (1)
- Linear DynamicsDocument11 pagesLinear DynamicsInfrion MatiqueonNo ratings yet
- C4-Dynamics Newton's Law of MotionDocument13 pagesC4-Dynamics Newton's Law of MotionHisyammudin RoslanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Newton's Law of MotionDocument12 pagesTutorial - Newton's Law of MotionNURUL NAJIHAH KHAIRUDDINNo ratings yet
- BB 2.0 - NLMDocument142 pagesBB 2.0 - NLMParthMaluNo ratings yet
- Physics Problems and SolutionsDocument7 pagesPhysics Problems and Solutionsnailia eliasNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument8 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion ExplainedMohammed Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Fizik PAT 2016Document15 pagesPaper 1 Fizik PAT 2016Junaidah Mohamad RamliNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document4 pagesTutorial 4Farah HananiNo ratings yet
- AP Physics - Chapter 8 Practice Test: Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesAP Physics - Chapter 8 Practice Test: Multiple Choicedipankar65No ratings yet
- 100 Laws of Motion Practice QuestionsDocument33 pages100 Laws of Motion Practice QuestionsLyn RegaladoNo ratings yet
- Test 2 (August) Physics Form 4Document5 pagesTest 2 (August) Physics Form 4Macita KaoruNo ratings yet
- 2.4 2.6 Newtons Laws and Momentum PDFDocument10 pages2.4 2.6 Newtons Laws and Momentum PDFAZTonseNo ratings yet
- PHYCS101 - Test2 RevisionDocument8 pagesPHYCS101 - Test2 RevisionAli MaarajNo ratings yet
- ODocument11 pagesO2pwxanqt8aNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Physics For Scientists and Engineers With Modern Physics 9th Edition Raymond A Serway John W JewettDocument20 pagesTest Bank For Physics For Scientists and Engineers With Modern Physics 9th Edition Raymond A Serway John W Jewettguyzunigaiadzrbpfes100% (10)
- Test Bank 7Document20 pagesTest Bank 7LukeLi100% (1)
- Chapter 5-The Laws of Motion: Multiple ChoiceDocument31 pagesChapter 5-The Laws of Motion: Multiple ChoiceHasan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Moments 1Document5 pagesUnit 11 Moments 1Kesha DilworthNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 Force and MotionDocument4 pagesTutorial 5 Force and MotionNadhirah Kaspol AnuarNo ratings yet
- 2a-Dynamics MC Practice ProblemsDocument26 pages2a-Dynamics MC Practice Problemsruuki25No ratings yet
- Int Mech Practice Exam 2Document9 pagesInt Mech Practice Exam 2Kevin ApodacaNo ratings yet
- Measure Moments with MomentsDocument10 pagesMeasure Moments with MomentsVarshLok100% (2)
- TB Chapter7 PDFDocument24 pagesTB Chapter7 PDFAsmaa AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1d Forces Concepts Practice TestDocument9 pages1d Forces Concepts Practice TestNütella VallejosNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers 9th Edition Serway Test BankDocument23 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers 9th Edition Serway Test Bankninhletitiaqt3100% (29)
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers 9Th Edition Serway Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument44 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers 9Th Edition Serway Test Bank Full Chapter PDFwadeperlid9d98k100% (8)
- TB Chapter5Document18 pagesTB Chapter5Jerry HuntNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam Covering Newtons Laws (Chapter 5 & 6 in Serway)Document9 pagesPractice Exam Covering Newtons Laws (Chapter 5 & 6 in Serway)Hasan AlomariNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers 9th Edition Serway TB 1Document31 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers 9th Edition Serway TB 1edith100% (43)
- 07 NLM-Exercise PDFDocument32 pages07 NLM-Exercise PDFDeepak LakharaNo ratings yet
- Forces on masses connected by rope over pulleyDocument28 pagesForces on masses connected by rope over pulleydebasijNo ratings yet
- 3b-Torque FR Practice ProblemsDocument4 pages3b-Torque FR Practice ProblemsSnowy JiangNo ratings yet
- Latihan UTSDocument13 pagesLatihan UTSAyu Patresia NababanNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers Foundations and Connections 1st Edition Katz Test Bank 1Document35 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers Foundations and Connections 1st Edition Katz Test Bank 1nell100% (43)
- New Economic Model For Malaysia: WWW - Neac.gov - MyDocument209 pagesNew Economic Model For Malaysia: WWW - Neac.gov - MyThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry 2012 PDFDocument2 pagesSPM Chemistry 2012 PDFThuran Nathan100% (1)
- Latihan Masa Cuti f4Document1 pageLatihan Masa Cuti f4Amalina KamarudinNo ratings yet
- Notes Form 4 KSSM Bio BM 28 Sept 2021Document54 pagesNotes Form 4 KSSM Bio BM 28 Sept 2021Thuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Physics Chapter 5 - StudentDocument15 pagesForm 5 Physics Chapter 5 - StudentPavithiranNo ratings yet
- NLP StatsDocument5 pagesNLP StatsThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- A Math Formula ListDocument8 pagesA Math Formula Listacsbr4science1100% (1)
- Heymanya Nathan: Cempaka International School Persiaran Awana Taman Cheras Permata Dua 43200 Cheras SelangorDocument1 pageHeymanya Nathan: Cempaka International School Persiaran Awana Taman Cheras Permata Dua 43200 Cheras SelangorThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Module 10 Graf FunctionDocument10 pagesModule 10 Graf FunctionHelen PappuNo ratings yet
- Registration Information: Managing Projects Today (MPT) Date: 5 To7 April 2010Document1 pageRegistration Information: Managing Projects Today (MPT) Date: 5 To7 April 2010Thuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: Saturated Each Carbon Atom Is Bonded To Four Other Atoms by Single Covalent BondsDocument10 pagesAlkanes: Saturated Each Carbon Atom Is Bonded To Four Other Atoms by Single Covalent BondsThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Repeated Bright Minds contact informationDocument22 pagesRepeated Bright Minds contact informationThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Page Cover BRIGHTmINDSDocument1 pagePage Cover BRIGHTmINDSThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Awards Won by Multimedia University ITEX Malaysia 2013 Awards Won by Multimedia UniversityDocument7 pagesAwards Won by Multimedia University ITEX Malaysia 2013 Awards Won by Multimedia UniversityThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- June 2013 Intake: Programmes OfferedDocument2 pagesJune 2013 Intake: Programmes OfferedThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Shiva Mahimna Stotram - English Lyrics (Text)Document6 pagesShiva Mahimna Stotram - English Lyrics (Text)Thuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Add Maths FormulaeDocument9 pagesAdd Maths FormulaeThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Nota Ekpress PMR SainsDocument10 pagesNota Ekpress PMR SainsThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- NLPDocument1 pageNLPThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document17 pagesChapter 7Thuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document7 pagesChapter 6Thuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Rental FlyersDocument1 pageRental FlyersThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- IHT SC No 2014Document1 pageIHT SC No 2014Thuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Sukatan Pelajaran Maths T STPMDocument23 pagesSukatan Pelajaran Maths T STPMKar Wai NgNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Checkpoint Maths P1 Specimen 2012Document12 pagesCambridge Checkpoint Maths P1 Specimen 2012Maryam Rai80% (10)
- Biodiversity: Hierarchy in The Classification of OrganismsDocument2 pagesBiodiversity: Hierarchy in The Classification of OrganismsKesha623No ratings yet
- Order Science and Maths SoftwareDocument1 pageOrder Science and Maths SoftwareThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- SPM ENGLISH Form 5 Step by Wicked StepDocument113 pagesSPM ENGLISH Form 5 Step by Wicked StepThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Bright Minds Dad Ads A As PM 2014Document1,472 pagesBright Minds Dad Ads A As PM 2014Thuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Migration (LIN 19/051: Specification of Occupations and Assessing Authorities) Instrument 2019Document28 pagesMigration (LIN 19/051: Specification of Occupations and Assessing Authorities) Instrument 2019Ajay palNo ratings yet
- 01 Design of Flexible Pavement Using Coir GeotextilesDocument126 pages01 Design of Flexible Pavement Using Coir GeotextilesSreeja Sadanandan100% (1)
- AIATS 2021 (OYMCF) Test 01 Offline - Code A - SolutionsDocument34 pagesAIATS 2021 (OYMCF) Test 01 Offline - Code A - Solutionsbhavyakavya mehta100% (1)
- Indian Institute OF Management, BangaloreDocument20 pagesIndian Institute OF Management, BangaloreGagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Trimble Oem Gnss Bro Usl 0422Document3 pagesTrimble Oem Gnss Bro Usl 0422rafaelNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Ee3311.002.07f Taught by Gil Lee (Gslee)Document3 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Ee3311.002.07f Taught by Gil Lee (Gslee)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Revised Man As A Biological BeingDocument8 pagesRevised Man As A Biological Beingapi-3832208No ratings yet
- Av1 OnDocument7 pagesAv1 OnLê Hà Thanh TrúcNo ratings yet
- Tugas B InggrisDocument6 pagesTugas B Inggrisiqbal baleNo ratings yet
- Crash Cart - General Checklist For Medical Supplies On Crash CartsDocument3 pagesCrash Cart - General Checklist For Medical Supplies On Crash CartsYassen ManiriNo ratings yet
- (App Note) How To Design A Programmable Gain Instrumentation AmplifierDocument7 pages(App Note) How To Design A Programmable Gain Instrumentation AmplifierIoan TudosaNo ratings yet
- France: French HistoryDocument16 pagesFrance: French HistoryMyroslava MaksymtsivNo ratings yet
- Denodo Job RoleDocument2 pagesDenodo Job Role059 Monisha BaskarNo ratings yet
- Executive Education Portfolio Soft Copy-INSEADDocument58 pagesExecutive Education Portfolio Soft Copy-INSEADОля КусраеваNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Questions & AnswersDocument161 pagesMechanical Questions & AnswersTobaNo ratings yet
- Practical LPM-122Document31 pagesPractical LPM-122anon_251667476No ratings yet
- DNT Audit Cash CountDocument2 pagesDNT Audit Cash CountAnonymous Pu7TnbCFC0No ratings yet
- Linguistics: Chapter 1 - 10Document41 pagesLinguistics: Chapter 1 - 10Ahmad A. JawadNo ratings yet
- No.6 Role-Of-Child-Health-NurseDocument8 pagesNo.6 Role-Of-Child-Health-NursePawan BatthNo ratings yet
- StsDocument10 pagesStsSamonte, KimNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Managerial Accounting Concepts 9th Edition Edmonds Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFundamental Managerial Accounting Concepts 9th Edition Edmonds Solutions ManualDrMichelleHutchinsonegniq100% (15)
- LLoyd's Register Marine - Global Marine Safety TrendsDocument23 pagesLLoyd's Register Marine - Global Marine Safety Trendssuvabrata_das01100% (1)
- CV Abdalla Ali Hashish-Nursing Specialist.Document3 pagesCV Abdalla Ali Hashish-Nursing Specialist.Abdalla Ali HashishNo ratings yet
- Osora Nzeribe ResumeDocument5 pagesOsora Nzeribe ResumeHARSHANo ratings yet
- 3.2 Probability DistributionDocument38 pages3.2 Probability Distributionyouservezeropurpose113No ratings yet
- T23 Field Weld Guidelines Rev 01Document4 pagesT23 Field Weld Guidelines Rev 01tek_surinderNo ratings yet
- Euro4 vehicle diesel engines 199 - 397 kW (270 - 540 hpDocument6 pagesEuro4 vehicle diesel engines 199 - 397 kW (270 - 540 hpBranislava Savic63% (16)
- Write 10 Lines On My Favourite Subject EnglishDocument1 pageWrite 10 Lines On My Favourite Subject EnglishIrene ThebestNo ratings yet
- VNC Function Operation InstructionDocument11 pagesVNC Function Operation InstructionArnaldo OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Genre Worksheet 03 PDFDocument2 pagesGenre Worksheet 03 PDFmelissaNo ratings yet