Professional Documents
Culture Documents
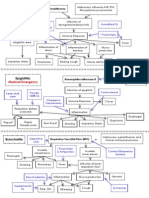
Classification and Pathophysiology of Respiratory Diseases
Uploaded by
TONY GO AWAYOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Classification and Pathophysiology of Respiratory Diseases
Uploaded by
TONY GO AWAYCopyright:
Available Formats
27/11/2013
CLASSIFICATION PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF RESPIRATORY DISEASE
Dr Bridget Ellul According to anatomical site
Upper / lower respiratory tract
According to aetiology / pathogenesis
enetic !ardio"ascular #n$ections %ypersensiti"ity reactions &eoplasia
2
RESPIRATORY DISEASES: Classification according to Anatom
!""#r RT: Nos#$ lar n%$ &trac'#a(
Cong#nital Disord#rs &trac'#a( Inf#ctions &nos#$ lar n%( All#rgi#s &nasal "ol "s( T)mo)rs &lar n%$ naso"'ar n%(
RESPIRATORY DISEASES: Classification according to A#tiolog
AIR1AYS and L!NG Cong#nital Disord#rs H "o"lasia$ S#2)#stration /asc)lar Dis#as#s D/T $ ")lmonar #m,olism P)lmonar O#d#ma ARDS 0 Ad)lt R#s"irator Distr#ss S ndrom# Tra)ma Pn#)mot'ora% O,str)cti-# P)lmonar Dis#as#
COPD: C'ronic +ronc'itis . Em"' s#ma +ronc'ial Ast'ma
Lo*#r RT: +ronc'i$ l)ngs$ "l#)ra
Cong#nital Disord#rs
Inf#ctions '(ronchi) lung*
Pn#)monia$ T+ OPD: C'ronic +ronc'itis . Em"' s#ma '(ronchi and lung* +ronc'ial Ast'ma '(ronchi*
O,str)cti-# P)lmonar Dis#as#
R#stricti-# P)lmonar Dis#as#
Int#rstitial &infiltrati-#( l)ng dis#as#
Pn#)moconiosis H "#rs#nsiti-it Dr)gs$ to%ins$ radiation Idio"at'ic fi,rosis
R#stricti-# P)lmonar Dis#as# 'al"eoli*
Int#rstitial &infiltrati-#( l)ng dis#as#
Pn#)moconiosis H "#rs#nsiti-it Dr)gs$ to%ins$ radiation Idio"at'ic fi,rosis
T)mo)rs
+#nign 3alignant
/asc)lar Dis#as#s D/T $ ")lmonar #m,olism P)lmonar O#d#ma ARDS 0 Ad)lt R#s"irator Distr#ss S ndrom#
PLE!RA
T)mo)rs Pl#)ral #ff)sion
3 +
T)mo)rs '(ronchi) lung) pleura*
SY3PTO3S
-unny nose E.cess sputum production Dyspnoea !ough /hee0ing !hest pain
,
SY3PTO3S
R)nn nos#
Allergy !ommon cold &asal (loc2age
E%c#ss m)c)s
3mo2ing 4 clear #n$ection 4 yellow/green Asthma 4 yellow 'eosinophils* Bronchial carcinoma) 5B) pneumonia 4 (lood 6 haemoptysis
1
27/11/2013
SY3PTO3S
1'##4ing
Air$low limitation $rom any cause 4 not necessarily asthma
S m"toms
D s"no#a 'di$$iculty in (reathing* 7ulmonary disease !ardio"ascular disease 8eta(olic disease :thers
C'#st "ain
7leuritic 4 sharp) worse on (reathing -i( pain -etrosternal soreness 4 tracheitis !onstant dull chest wall pain 4 in"asion (y lung carcinoma !entral chest pain with radiation to nec2) arms 4 cardiac 3houlder pain 4 diaphragmatic pleura / 8#
7
Co)g'
Ca)s#s of c'ronic co)g' !:7D Asthma astro6oesophageal re$lu. 6 heart(urn 7ost6nasal drip 7ost chest in$ection 8edications
9
IN/ESTIGATION OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTE3 ;ung <unction 5ests Blood as Analysis -adiology Histolog C tolog 8icro(iology :thers
10
IN/ESTIGATION OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTE3
HISTOLOGY CYTOLOGY
IN/ESTIGATION OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTE3
+ronc'ial ,io"s at ,ronc'osco" L)ng ,io"s
trans(ronchial transthoracic open wedge Lo,#ctom 5 *'ol# l)ng Pl#)ral ,io"s 3#diastinal ,io"s L m"' nod# ,io"s $ n#c6
S")t)m
+ronc'ial as"irat#s 5 *as'ings 5 ,r)s'ings +ronc'oal-#olar la-ag# 0 +AL
Fin# n##dl# as"iration 7 FNA
trans,ronc'ial transt'oracic
L m"' nod#$ n#c6$ as"irat#
Pl#)ral fl)id
11 12
27/11/2013
/asc)lar Dis#as#s
Deep =ein 5hrom(osis
and pulmonary em(olism
/irc'o*8s triad:
P!L3ONARY E3+OL!S
?,@ arise $rom throm(i in large "eins) lower legs usually deep "eins o$ cal$ muscles) D=5) or pel"ic "eins em(oli tra"el to right side o$ heart and pulmonary trun2 and i$ total (loc2age cause death i$ small no symptoms till late pulmonary hypertension pulmonary in$arction i$ increase in "enous pressure in lungs
endothelial in>ury alterations in (lood $low hypercoagula(ility
13
1+
R#s"irator Inf#ctions
Inflammations
R#s"irator Inf#ctions
more $reAuent than in$ections o$ any other organ largest num(er o$ wor2days lost in general population ma>ority in"ol"e only the upper respiratory tract and are caused (y "iruses 6 tri"ial or mild diseases
!""#r R#s"irator Tract Inf#ction /iral5,act#rial inf#ction Lo*#r R#s"irator Tract Inf#ction Pn#)monia 7 +act#rial Pn#)monia 7 /iral
P)lmonar T),#rc)losis
H "#rs#nsiti-it r#actions
1, 11
Im"air#d D#f#nc#s of R#s"irator Tract
cough re$le.
coma) anaesthesia) drugs 6 aspiration possi(le
T'# R#s"irator S st#m
#n$ection may (eB primary 6 "iral) (acterial) mycoplasmal) $ungal secondary (acterial 6 $ollowing a "iral in$ection secondary to irritants
$iltering $unction o$ nasopharyn. ciliary apparatus 6 action towards mouth
cigarette smo2e) hot gasses) corrosi"es) "iruses
secretion o$ #gA anti(odies phagocytic acti"ity (y al"eolar macrophages
alcohol) to(acco) smo2e) e.cess o.ygen
accumulation o$ secretions
cystic $i(rosis) (ronchial o(struction
al"eolar $luid 6 sur$actant) #gs) complement cell mediated immunity
chronic disease / cancer patients /treatment with chemotherapy immune diseases / %#= in$ection
"irulent in$ections
17
19
27/11/2013
!""#r R#s"irator Tract S#"sis
/iral common cold 0 commonest 6 di$$erent serotypes o$ rhino"irus Infl)#n4a 6 in$luen0a "irus +act#rial
healthy indi"iduals 6 uncommon in de"eloped countries
Lo*#r R#s"irator Tract S#"sis
Pn#)monia in$ection o$ al"eolar spaces host reaction 6 al"eolar e.udates polymorphs) $i(rin) oedema $luid resulting in consolidation
Str#"tococc)s in nose and throat
Ac)t# lar ngitis 5 #"iglottitis
Classification 3or"'olog
Bronchopneumonia) ;o(ar 7neumonia
many organisms present with either pattern C con$luent (ronchopneumonia / lo(ar radiologically
Ha#mo"'il)s infl)#n4a# t "# + or str#"tococc)s " og#n#s
swelling and mechanical ina(ility in (reathing irritation (y pollutants including smo2e and corrosi"es and no.ious gases
1?
A#tiolog Clinical S#tting
20
+ronc'o"n#)monia
in$lammation starts in (ronchi 6 polymorphs) $i(rin spreads to ad>acent al"eoli patchy $oci coalesce consolidation
3treptococcus pneumoniae %aemophilus in$luen0ae 3taphylococcus pneumonia Dle(siella 7seudomonas aeruginosa !oli$orm (acteria
Lo,ar Pn#)monia
"irulent organism host "ulnera(ility ?06?,@ 3treptococcus
pneumoniae
in$lammation starts
in al"eoli
21
22
Pn#)monia
Pn#)monia : Clinical S#tting
!ommunity AcAuired Acute 7neumonia
Str#"9 Pn#)monia#$ H9 infl)#n4a#$ 3ora%#lla catarr'alis$ Sta"'9 a)r#)s$ L#gion#lla$ :l#,si#lla$ Ps#)domonas
!ommunity AcAuired Atypical 7neumonia
m co"lasma$ c'lam dia$ co%i#lla$ -ir)s#s
&osocomial 7neumonia
Gram n#gati-# rods &:l#,si#lla$ E9 coli$ Ps#)domonas($ sta"' lococc)s a)r#)s &)s)all 3RSA(
Aspiration 7neumonia 7neumonia in #munocompromised %ost
C3/$ Pn#)moc stis carinii$ m co,act#ri)m a-i)m0 intrac#ll)lar#$ as"#rgillosis$ candidiasis$ ;)s)al< organisms 2+
<or in$o
23
27/11/2013
Com"lications
complete resolution i$ correct anti(iotic uncommon complications
pleural adhesions (eing the most common complications commoner with lo(ar pneumonia
(ut E10@ now die
/iral Pn#)monia
interstitial pneumonia misnomer as interstitial in$iltrate
histiocytes) lymphocytes
lung a(scess septicaemia uncommon i$ se"ere pneumonia is not treated death may occur
no al"eolar e.udate in$luen0a "irus / -3= / adeno"iruses / rhino"iruses
2,
21
Pn#)monia 7 Ot'#r Organisms
Atypical Bacteria 4 atypical pneumonia
8ycoplasma !hlamydia ;egionella
P!L3ONARY T!+ERC!LOSIS
8yco(acterium tu(erculosis
droplet in$ection $rom acti"e 5B 7rimary 5u(erculosis in childhood 6 rare now primary lesion 6 hon $ocus (elow pleura) mid lung tu(ercles 6 epithelioid granulomas with caseation (acteria spread to hilar lymph nodes hon $ocus F nodes heal with $i(rosis / calci$ication 5B sur"i"es in $oci and (ecomes source o$ later in$ection cell mediated immunity to antigens o$ tu(ercle (acillus 6 positi"e tu(erculin s2in test 6 increased resistance to su(seAuent in$ection
<ungi
27
29
P!L3ONARY T!+ERC!LOSIS
3econdary 5u(erculosis people pre"iously sensitised (y a primary lesion a new in$ection or (y reacti"ation o$ micro(e in chronic disease) steroid therapy) %#= ape. o$ the upper and lower lo(es $oci heal with $i(rosis and calci$ication haemoptysis with erosion o$ a "essel in the lung coughing up o$ caseous material 'ca"ities in the lung* pro"ides a source o$ in$ection to the other lung spread "ia lymph and (lood spreads tu(erculosis throughout the (ody 'military 5B*
2?
R#s"irator Dis#as#s
O,str)cti-# P)lmonar Dis#as# 0 Air*a s
COPD: C'ronic +ronc'itis . Em"' s#ma +ronc'ial Ast'ma
R#stricti-# P)lmonar Dis#as# 0 Al-#oli
Int#rstitial &infiltrati-#( l)ng dis#as#
Pn#)moconiosis H "#rs#nsiti-it Dr)gs$ to%ins$ radiation Idio"at'ic fi,rosis
30
27/11/2013
R#s"irator Dis#as#s
O,str)cti-# P)lmonar Dis#as# 7 Air*a s
airflo* limitation$ not f)ll r#-#rsi,l# "rogr#ssi-# in most a,normal inflammator r#s"ons# e.piratory $low rate <=! & or <E=1 <E=1 B <=! is low
CHRONIC +RONCHITIS
clinical term persistent cough with sputum production $or at least three months in at least two consecuti"e years middle6aged men especially smo2ers smo2e predisposes to in$ection (y inter$ering with ciliary action and causing direct damage to epithelium 1062,@ o$ ur(an population due to irritation (y inhaled pollutants
32
R#stricti-# P)lmonar Dis#as# 7 Al-#oli
restriction o$ air $low due to reduced e.pansion o$ the lung parenchyma total lung capacity) "ital capacity) residual "olume) lung compliance <=! <E=1 & or <E=1 B <=! is & or high
31
CHRONIC +RONCHITIS
Em"' s#ma
pathological term condition o$ the lung characterised (y a(normal permanent enlargement o$ the air spaces distal to the terminal (ronchiole) with destruction o$ their walls
elastases destroy elastin $ree radicals $rom smo2e
pathhsw,m,+Gucs$Gedu/o"er"iew/te.tGhtml
commoner in men) ,0690years associated with hea"y smo2ing
3+
33
Em"' s#ma
proteases 'elastase* or antiproteases 'antielastase) alpha616 antitrypsin* elastin destruction in al"eolar walls
Em"' s#ma: Pat'og#n#sis
3,
de"elopment o$ emphysema in smo2ers there is lung in$ection with neutrophils and macrophages) which produce elastase lung damage stimulated neutrophils release o.ygen $ree radicals 6 cause damage
31
27/11/2013
Em"' s#ma 7rognosis with se"ere emphysema) cor pulmonale 'heart disease secondary to lung disease* and congesti"e heart $ailure de"elop death due to right heart $ailure and respiratory $ailure
37
Ast'ma
increased responsi"eness o$ (ronchial tree to "arious stimuli) resulting in paro.ysmal constriction o$ the (ronchial airways triggered (y e.posure to an allergen (ronchospasm triggers se"ere dyspnoea and whee0ing (etween attac2s asymptomatic an unremitting attac2) status asthmaticus) may pro"e $atal
39
Ast'ma
lungs are o"er distended (ronchi occluded (y thic2 mucous plugs eosinophils F oedema in (ronchial walls hypertrophy o$ (ronchial smooth muscle
Ast'ma
5ypes o$ Asthma 7recipitating <actors
3peci$ic allergens !hemicals Antigens'spores*
8echanism #mmune -eaction
5ype # '#gE* 5ype # 5ype # and 5ype ###
EH5-#&3#!
Atopic 'allergic* :ccupational Allergic aspergillosis
#&5-#&3#!
&onatopic 7harmacologic -espiratory 5ract #n$ection Aspirin Un2nownI hyper reacti"e airways prostaglandins leu2otrines
%yper reacti"e airways) which respond to non6speci$ic irritants 6 cold) e.ercise and stress
+0
3?
Ast'ma
Atopic or Allergic Asthma commonest type triggered (y en"ironmental antigens 6 dusts) pollen) $oods) house dust mite $amily history common 6 allergic rhinitis) urticaria or ec0ema genetic predisposition positi"e s2in tests classic 5ype # #gE hypersensiti"ity reaction
RESTRICTI/E P!L3ONARY DISEASE
Disorders o$ chest wall or pleural space
polio and 2yphoscoliosis
#nterstitial or in$iltrati"e diseases
J 1,0 di$$erent disease processes al"eolar wall and capillary endothelium damage results in $i(rosis 8ain !auses #diopathic $i(rosis 7neumoconiosis 6 inhalation o$ inorganic atmospheric
pollutants eGgG as(estos
%ypersensiti"ity 6 organic material is inhaled) eGgG pigeon
+1
$ancierKs lung due to protein $rom (ird droppings
+2
Drugs) to.ins) radiation
27/11/2013
St)d G)id# 5 O,=#cti-#s
1G 2G 3G +G ,G 1G 7G 9G ?G 10G 11G 12G
!lassi$y the common respiratory diseases ;ist the methods o$ in"estigation o$ the respiratory system Discuss the de$ence mechanisms o$ the respiratory system Discuss the importance o$ U-5 in$ections Discuss the pathogenesis and morphology o$ (ronchopneumonia and lo(ar pneumonia Di$$erentiate (etween "iral and (acterial pneumonia /rite a short note on pulmonary tu(erculosis Distinguish (etween o(structi"e and restricti"e lung diseases) in terms o$ lung $unction and morphological a(normalities De$ine chronic (ronchitis and emphysema Brie$ly discuss the pathogenesis o$ chronic (ronchitis and emphysema :utline the pathogenesis o$ asthma Descri(e the morphological changes that occur in asthma
+3
You might also like
- Respiratory Therapy: 66 Test Questions Student Respiratory Therapists Get Wrong Every Time: (Volume 2 of 2): Now You Don't Have Too!: Respiratory Therapy Board Exam Preparation, #2From EverandRespiratory Therapy: 66 Test Questions Student Respiratory Therapists Get Wrong Every Time: (Volume 2 of 2): Now You Don't Have Too!: Respiratory Therapy Board Exam Preparation, #2No ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory Study SheetDocument13 pagesLower Respiratory Study SheetJune Rhoades100% (2)
- Respiratory Care Review: An Intense Look at Respiratory Care Through Case StudiesFrom EverandRespiratory Care Review: An Intense Look at Respiratory Care Through Case StudiesNo ratings yet
- TMCQuestions AllocationDocument2 pagesTMCQuestions AllocationMyra BuellaNo ratings yet
- RT!: Reflections on a Career in Respiratory TherapyFrom EverandRT!: Reflections on a Career in Respiratory TherapyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- 500 CRT Practice QuestionsDocument138 pages500 CRT Practice QuestionsCPD MAS0% (1)
- RRT PT AssessmentDocument39 pagesRRT PT AssessmentRam NasaluddinNo ratings yet
- Breath Sounds Study GuideDocument28 pagesBreath Sounds Study GuideGustavo OlguinNo ratings yet
- EXAM RRTCheatSheetBookDocument22 pagesEXAM RRTCheatSheetBookGustavo Olguin100% (2)
- Respiratory PharmacologyDocument12 pagesRespiratory PharmacologywahyudhanapermanaNo ratings yet
- John PFTDocument231 pagesJohn PFTAlexander Santiago ParelNo ratings yet
- Adjusting Ventilator SettingsDocument7 pagesAdjusting Ventilator SettingsSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Therapy PresentationDocument11 pagesRespiratory Therapy Presentation003cbty9No ratings yet
- Respi MVDocument25 pagesRespi MVtimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PathophysDocument1 pageRespiratory PathophysTori IkeharaNo ratings yet
- RT Student CRT Entry Exam Review QuestionsDocument71 pagesRT Student CRT Entry Exam Review QuestionsRenita Washington100% (4)
- CRT Test BanksDocument257 pagesCRT Test BanksRain Catan Gagarra Saquin100% (2)
- Board Exam Prep: Essential Tips for SuccessDocument108 pagesBoard Exam Prep: Essential Tips for SuccessAnonymous FvUBZa100% (1)
- Respiratory AgentsDocument67 pagesRespiratory AgentsJune Dumdumaya100% (2)
- Pulmonary Function Test, JARA CSUDocument73 pagesPulmonary Function Test, JARA CSUJohn NicoleNo ratings yet
- RRT Practice Set 2Document26 pagesRRT Practice Set 2Ram NasaluddinNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Study GuideDocument37 pagesFundamentals Study GuideGustavo OlguinNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Diseases of NewbornDocument93 pagesRespiratory Diseases of NewbornTheva Thy100% (1)
- Mechanical Ventilation FinalDocument46 pagesMechanical Ventilation FinalNaven ScorpNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Therapists 09-2021 ROOM ASSIGNMENTDocument9 pagesRespiratory Therapists 09-2021 ROOM ASSIGNMENTPRC BaguioNo ratings yet
- Test Banks Gary PersingDocument35 pagesTest Banks Gary PersingAlexander Santiago ParelNo ratings yet
- NBRC Nps Test Content AreasDocument19 pagesNBRC Nps Test Content AreasMarla Karina Urbach0% (1)
- Pharmacology of Respiratory SystemDocument67 pagesPharmacology of Respiratory Systemmanish086100% (2)
- Registered Respiratory TherapistDocument3 pagesRegistered Respiratory Therapistapi-76909521No ratings yet
- My Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesMy Cheat SheetTenzin KyizomNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument18 pagesRespiratoryReneé Camille50% (2)
- Respiratory Therapy Cave - Ventilator Graphics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesRespiratory Therapy Cave - Ventilator Graphics Cheat SheetMarwa El-DegwiNo ratings yet
- Ventilator Modes Study GuideDocument34 pagesVentilator Modes Study GuideRyn ShadowNo ratings yet
- Formulas and Calculations (Study Guide)Document86 pagesFormulas and Calculations (Study Guide)Ravneet singh100% (2)
- Adult Invasive Mechanical VentilationDocument73 pagesAdult Invasive Mechanical Ventilationmed2004100% (1)
- 33 Airway ManagementDocument19 pages33 Airway ManagementTiffany Helmes100% (2)
- EXAM RRTPracticeQuestionsDocument30 pagesEXAM RRTPracticeQuestionsGustavo OlguinNo ratings yet
- Trachs, Vents, and Passy-MuirDocument30 pagesTrachs, Vents, and Passy-MuirCharles S. Williams RRT, AE-C100% (4)
- Respiratory Therapy FormulasDocument3 pagesRespiratory Therapy Formulasrtman50% (2)
- 99 TMCPractice QuestionsDocument31 pages99 TMCPractice QuestionsGustavo OlguinNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Respiratory Disease A Case Study Approach To Patient Care 3rd Edition by WilkinsDocument10 pagesTest Bank For Respiratory Disease A Case Study Approach To Patient Care 3rd Edition by Wilkinsa498226706No ratings yet
- Cheat Sheets For Ventilation 5Document19 pagesCheat Sheets For Ventilation 5Syed Shahrul Naz Syed100% (1)
- Pediatric Mechanical VentilationDocument36 pagesPediatric Mechanical VentilationrizalNo ratings yet
- Inotropes and Vasoconstictor PackageDocument25 pagesInotropes and Vasoconstictor PackageYoussef MokdadNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument9 pagesPulmonary Function TestsRick Frea0% (1)
- PerfusionDocument9 pagesPerfusionAmanda Brittain100% (2)
- 161111163114Document31 pages161111163114lejizixNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Care ModalitiesDocument5 pagesRespiratory Care ModalitiesWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- COPD Acute Management ABCDEDocument11 pagesCOPD Acute Management ABCDESSNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Therapist, NICU/ICUDocument5 pagesRespiratory Therapist, NICU/ICUapi-77517256No ratings yet
- Chapter (10) : Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesChapter (10) : Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemSandra GabasNo ratings yet
- Stages of ShockDocument13 pagesStages of ShockA. P.No ratings yet
- Ventilation For DummiesDocument39 pagesVentilation For Dummiessuyalamit100% (6)
- 5 Patient Assessment Skills To Crush The TMC-RRT ExamDocument4 pages5 Patient Assessment Skills To Crush The TMC-RRT ExamNaser Abdulfatah Al Hazmi100% (1)
- Vent Modes ChartDocument1 pageVent Modes Chartladyhavocinc100% (1)
- Respiratory Notes Sample ChapterDocument10 pagesRespiratory Notes Sample ChapterHitesh Deora75% (4)
- Acid Base Who Is Your DaddyDocument66 pagesAcid Base Who Is Your Daddyjenn1722100% (14)
- Cardiac GlycosidesDocument8 pagesCardiac GlycosidesShan Sicat100% (1)
- ABGs Respiratory/MetabolicDocument3 pagesABGs Respiratory/MetabolicJoe B100% (1)
- Inhaler LexiconDocument4 pagesInhaler LexiconRick Frea100% (2)
- Neurofibromatosis - Pediatrics - MSD Manual Professional EditionDocument6 pagesNeurofibromatosis - Pediatrics - MSD Manual Professional EditionTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus - Pediatrics - MSD Manual Professional EditionDocument4 pagesHydrocephalus - Pediatrics - MSD Manual Professional EditionTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Medical and Dental Student Application FormDocument4 pagesMedical and Dental Student Application FormTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Rheum FeverDocument1 pageRheum FeverTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- MRCPCH Theory Examination Syllabi v2 0Document32 pagesMRCPCH Theory Examination Syllabi v2 0hebaNo ratings yet
- Junior Doctors GuidelinesDocument8 pagesJunior Doctors GuidelinesTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Developmental Assessment in One PageDocument1 pageDevelopmental Assessment in One PageTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- 8.4 Management of Bacterial Meningitis in InfantsDocument1 page8.4 Management of Bacterial Meningitis in InfantsHendik RiawanNo ratings yet
- Spina Bifida - Pediatrics - MSD Manual Professional EditionDocument4 pagesSpina Bifida - Pediatrics - MSD Manual Professional EditionTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Guyana Travel InformationDocument4 pagesGuyana Travel InformationTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Adult Bradycardia AlgoritmaDocument1 pageAdult Bradycardia AlgoritmaTogu MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Resuscitation Council (UK)Document18 pagesResuscitation Council (UK)Abdelfattah RashwanNo ratings yet
- Bongo Nyah Food Menu PDFDocument6 pagesBongo Nyah Food Menu PDFTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Editing Reference TypesDocument56 pagesEditing Reference TypesTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- MCQ Sample Questions on COPD and Glucocorticoid ReceptorsDocument1 pageMCQ Sample Questions on COPD and Glucocorticoid ReceptorsTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Comp TineDocument3 pagesComp TineTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions by PVCDocument3 pagesSample Questions by PVCTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- CSJ Guide Santiago To Finisterre, 2009: UpdateDocument2 pagesCSJ Guide Santiago To Finisterre, 2009: UpdateTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- II Yr MD June 2015 TT Provisional Version 1Document1 pageII Yr MD June 2015 TT Provisional Version 1TONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Passive ImmunizationDocument3 pagesPassive ImmunizationTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Prophylaxis GuideDocument13 pagesProphylaxis GuideTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Medically Assisted Procreation History in MaltaDocument3 pagesMedically Assisted Procreation History in MaltaTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress in Children AimsDocument2 pagesRespiratory Distress in Children AimsTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Head Injury Admission To Bservation NIT: Xclusion RiteriaDocument3 pagesHead Injury Admission To Bservation NIT: Xclusion RiteriaTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Situational JudgementDocument6 pagesSituational JudgementTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- PassmedicineDocument12 pagesPassmedicineTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Health Professionals Role in Tobacco ControlDocument30 pagesHealth Professionals Role in Tobacco ControlTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Care of The Critically Ill Surgical PatientDocument1 pageCare of The Critically Ill Surgical PatientTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Some Hints About Infections in Surgery - Arthur FeliceDocument2 pagesSome Hints About Infections in Surgery - Arthur FeliceTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Motor Neurone Disease PDFDocument4 pagesMotor Neurone Disease PDFTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Chlorhexidine's Effect on Fibroblast AttachmentDocument5 pagesChlorhexidine's Effect on Fibroblast AttachmentAna Maria Montoya GomezNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Shaikh Rukshana SalimDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Shaikh Rukshana SalimMithlesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Knee Joint Aspiration and InjectionDocument4 pagesKnee Joint Aspiration and InjectionaimanshalpyNo ratings yet
- FINALS ReviewerDocument14 pagesFINALS ReviewerJustine Simeon lagunzadNo ratings yet
- Case Study SLDocument5 pagesCase Study SLCharmie Mei Paredes-RoqueNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Unconciousness: Subject:-Advanced Nursing PracticeDocument15 pagesAssignment On Unconciousness: Subject:-Advanced Nursing PracticeShaells JoshiNo ratings yet
- NCP FormDocument3 pagesNCP FormJasmine diokNo ratings yet
- Principles of OncologyDocument26 pagesPrinciples of OncologyDr Shahzad Alam ShahNo ratings yet
- Workplace Site Audit Checklist PharmacyDocument3 pagesWorkplace Site Audit Checklist PharmacyWaqar LatifNo ratings yet
- ENDOCHAT 162 Uriel JOE 2016 PDFDocument9 pagesENDOCHAT 162 Uriel JOE 2016 PDFMaria Camila Sarmiento100% (1)
- Barangay Klinan6 Bhs - Continuous Monitoring and Surveillance For Covid-19 Symptoms On All PuroksDocument3 pagesBarangay Klinan6 Bhs - Continuous Monitoring and Surveillance For Covid-19 Symptoms On All PuroksInchic MirandaNo ratings yet
- Castration of Calves: Castration: Gettings The Best Results For Farm and Calf What Techniques Are Available?Document5 pagesCastration of Calves: Castration: Gettings The Best Results For Farm and Calf What Techniques Are Available?WAQAS SHAHIDNo ratings yet
- DMSCO Log Book Vol.25 1947Document49 pagesDMSCO Log Book Vol.25 1947Des Moines University Archives and Rare Book RoomNo ratings yet
- Administration of Medication in SchoolsDocument8 pagesAdministration of Medication in SchoolsDavid KefferNo ratings yet
- PHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jan2020 PDFDocument2 pagesPHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jan2020 PDFJyotirmaya RajaNo ratings yet
- Willis Commission 2012Document56 pagesWillis Commission 2012Jean Duckworth100% (1)
- Nursing Concept Map TemplateDocument4 pagesNursing Concept Map TemplateAris Kendell BungabongNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesRosalie Navales LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Study This Question Med Surg FinalDocument14 pagesStudy This Question Med Surg FinalAna Gonzalez83% (6)
- PENGARUH PENDIDIKAN KESEHATAN TERHADAP PENGETAHUAN KANKER OVARIUMDocument7 pagesPENGARUH PENDIDIKAN KESEHATAN TERHADAP PENGETAHUAN KANKER OVARIUMSalsabila DindaNo ratings yet
- NCP Cva Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageNCP Cva Ineffective Tissue PerfusionNina Glaiza Goto100% (1)
- Or ExamDocument21 pagesOr Examlouie roderosNo ratings yet
- S. No. City Name Full Address With Contact No.: List of Our ProductsDocument3 pagesS. No. City Name Full Address With Contact No.: List of Our Productsprakashrat1962No ratings yet
- Blank 1 Panel Landscape Comic StripDocument2 pagesBlank 1 Panel Landscape Comic StripPatervel Ceasar CutamoraNo ratings yet
- CCG Elderholme Responses To Final ReportDocument24 pagesCCG Elderholme Responses To Final ReportLeonard BeddowsNo ratings yet
- CandidiasisDocument27 pagesCandidiasisWr Newgate50% (2)
- Kode DiagnosaDocument1 pageKode Diagnosapuskesmas sukahening100% (1)
- What Is Autism?: Characteristics of Children With AutismDocument7 pagesWhat Is Autism?: Characteristics of Children With AutismAnandNarayananNo ratings yet
- Student Response Sheet: PurposeDocument4 pagesStudent Response Sheet: PurposeYoshi NNo ratings yet
- Tube+Aftercare+Tear Off+Sheets+PDFDocument8 pagesTube+Aftercare+Tear Off+Sheets+PDFNikola StojsicNo ratings yet