Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Notes
Uploaded by
Suraj ReddyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Notes
Uploaded by
Suraj ReddyCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Notes
Chapter1
Proteins
A. Proteins are vital for growth and repair.
B. For sending signal from one cell to another
C. Catalyzing chemical reactions
D. Regulating hormones
E. Moving muscles
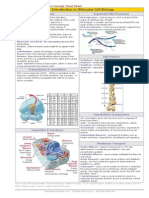
Proteins are polymers- ammino acids joined together by polypeptide chains.
- Made up of S, P, C, O, H, N.
- Ammino acids are made up of a carboxyl, anime group and a variable
attached to a carbon atom.
- Only 20 ammino acids are there
- 4 types of proteins: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary.
Types i n Depth:
Primary: linear sequencing of ammino acids. Slight changes in the chain can cause
huge problems.
Secondary: Proteins created through hydrogen bonding in a polypeptide chain.
Folds either into alpha helix or a beta pleated sheat. These are refered to fiborous
proteins ( wool, reptile scales, human hair outer appearences.
Tertiary:
tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with
one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. The
tertiary structure is determined by a variety of bonding interactions
between amino acid side chains.( Multiple secondary proteins if hydrogen
bonding)
Quaternary:
More than one polypeptide chain. Hemoglobin for example.
Portein Folding:
- Denaturation is when weak intramolecular forces cause proteins to lose their
shape.
- Chaperoin porteins assist in folding other porteins which determine protein
functions.
- Prions are proteins that result in misfolded protentins.
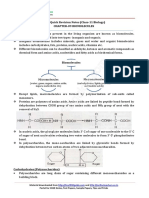
Nucleic Acids:
- RNA and DNA encode hereditary information. RNA send info to the DNA,
which is used to manufacture ammino acids for proteins. Nuclecid acids
consist of nucleotides.
- Nucleotides are made up of a phosphate, a 5-carbon sugar and a nitrogen
base.
Functional groups:
Organic chemicals replace hydrogen atoms that would have been present in
hydrocarbons.
Gibbs free energy:
If energy is released it is exothermic, and if energy is absorbed it is endothermic.
Metabolism is the total number of chemical reactions that are taking place in a cell.
Catblolism reactions break down molecules and anabolism builds up molecules in
the cell. The Metabolic reactions happen in pathways that are sped up by enzymes.
Enzyems reduce the amount of the activation energy needed to speed up reactions.
The transition state is the unstable state after energy has been absorbed to initate
the reaction.
Enzymes:
Enzymes are global
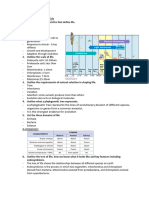
The Cell
- Theory of endosymbiosis states that prokaryotic cells such as mitochondria
and chloroplasts merged into larger cells.
- Modern theory states that all living organism are made up of cells and all
cells arrived from previous cells.
- All cells have permeable membranes, Cytosol, and Ribosomes to create DNA
- Prokaryotic cells have a nucleoid that isnt bound by plasma membrane that
contains chromosomes there, and doesnt have internal memebranes.
Eukaryotic cells have nucleus with plasma double membrane and internal
membranes for organelles ( in order to specialize the chemical reactions).
- The function of a cell dictates its form ( the shape that it takes).
- Cells are determined by their volumes and surface area. Because the cells
volume determines metabolic activity, millions of cells are made in large
organisms to undertake a lot of metabolic activity. Surface are controls what
comes in and out of a cell.
- Nucleolus: Place where Ribosomal RNA is synthesized according to
instructions from the DNA. Also where some ribosome units are assembled.
Nucleolus takes proteins from cytosol and combines it with rRNA made in
the nucleolus.
-
You might also like
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Cell Biology IntroductionDocument1 pageCell Biology IntroductionChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Seduction As A Manipulation TacticDocument6 pagesSeduction As A Manipulation TacticByrlyne Van DykeDowersNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Life Strategy 101: How To Live Live by Vision, Work With Purpose, and Achieve More SuccessDocument31 pagesLife Strategy 101: How To Live Live by Vision, Work With Purpose, and Achieve More SuccessMichelle Casto100% (2)
- The Cells: Structure and FunctionsDocument121 pagesThe Cells: Structure and FunctionsJoan Ano CaneteNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and EnzymesDocument5 pagesBiomolecules and Enzymesprashanth100% (1)
- Vodafone - Market Research ProposalDocument4 pagesVodafone - Market Research ProposalNikita Sanghvi100% (2)
- Optimizing RMAN RecoveryDocument61 pagesOptimizing RMAN RecoveryVijay ParuchuriNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria: The Power Generators of CellsDocument30 pagesMitochondria: The Power Generators of CellsMah Noor100% (1)
- November 2008Document14 pagesNovember 2008Aldrin ThomasNo ratings yet
- José Rizal: The Life of The National HeroDocument9 pagesJosé Rizal: The Life of The National HeroMark Harry Olivier P. VanguardiaNo ratings yet
- Assessment - The Bridge Between Teaching and Learning (VFTM 2013)Document6 pagesAssessment - The Bridge Between Teaching and Learning (VFTM 2013)Luis CYNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesDocument5 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesSIDHARTH SBNo ratings yet
- Bimolecules G10Document15 pagesBimolecules G10hmoncatar.bulNo ratings yet
- Ch1 2 4 2012 PDFDocument23 pagesCh1 2 4 2012 PDFA Hyun SonNo ratings yet
- Cell and MacromoleculesDocument3 pagesCell and Macromoleculespubg662299No ratings yet
- Proteins and Peptides 20msc01029Document10 pagesProteins and Peptides 20msc01029Ritu ParmarNo ratings yet
- Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary Structures of A ProteinDocument21 pagesPrimary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary Structures of A ProteinDALITSO CHIKOYA100% (1)
- AP Biology Exam GuideDocument13 pagesAP Biology Exam GuideChristine NguyenNo ratings yet
- 87314094-83be-428d-9d4d-a459e43691a9Document21 pages87314094-83be-428d-9d4d-a459e43691a9SAMPATH SPNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-01-07 at 1.34.05 PMDocument25 pagesScreenshot 2022-01-07 at 1.34.05 PMPaolaNo ratings yet
- Sinh Hóa HọcDocument375 pagesSinh Hóa HọcCẩm TúNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology NotesDocument147 pagesClass 11 Biology NotesreilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lecture NotesDocument52 pagesCell Biology Lecture NotesSheh ZadNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Scientific Study of LifeDocument27 pagesEvolution and Scientific Study of LifeZackNo ratings yet
- MITOCHONDRIADocument3 pagesMITOCHONDRIACris PachecoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document4 pagesGeneral Biology 2Wee-Weh HamjaNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 &2 Biology IUDocument5 pagesHomework 1 &2 Biology IUVanessa NguyenNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria, Endoplasmic Reticulum, RibosomesDocument39 pagesMitochondria, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Ribosomesanos2002No ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY Cells OrganellesDocument6 pagesHISTOLOGY Cells OrganellesAhsan KamalNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Quarter 3 Week 4Document5 pagesGrade 10 Quarter 3 Week 4James GalvezNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements of Life: TB-BA-2: 18-4-2022Document5 pagesEssential Elements of Life: TB-BA-2: 18-4-2022Khánh NhiNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES Lesson 2Document3 pagesBIOMOLECULES Lesson 2Mekka Mae Taday JunasaNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch09 Biomolecules PDFDocument5 pages11 Biology Notes ch09 Biomolecules PDFprashanth100% (1)
- Biohem NotesDocument118 pagesBiohem Notesdalweravikumar69No ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument2 pagesProteinsPrasanna SankheNo ratings yet
- Proteins Structure, Classification and Biological Functions: DR - AchyuthaDocument33 pagesProteins Structure, Classification and Biological Functions: DR - AchyuthaMohammad AadilNo ratings yet
- Bio Long NoteDocument12 pagesBio Long Notejacob guerreroNo ratings yet
- Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDocument5 pagesProteins and Nucleic AcidsSexbomb Adela KirstenNo ratings yet
- 04b AP Bio The Structure and Function of Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDocument51 pages04b AP Bio The Structure and Function of Proteins and Nucleic Acidsrahul singhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-ProteinsDocument9 pagesLecture 3-ProteinsOminousCroakNo ratings yet
- Name-Saikat Layek ROLL NO-20H80020 Subject-Biology Sub - Code-Btc01Document13 pagesName-Saikat Layek ROLL NO-20H80020 Subject-Biology Sub - Code-Btc01Saikat LayekNo ratings yet
- 420-510chapter 1 (3) An Introduction To CellsDocument6 pages420-510chapter 1 (3) An Introduction To Cellstomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology (Zeb 361)Document7 pagesMolecular Biology (Zeb 361)Jacob WalterNo ratings yet
- 1 - Cell Structure and DiversityDocument13 pages1 - Cell Structure and Diversityarahunt253No ratings yet
- L8 2023 Protein Structure 1Document22 pagesL8 2023 Protein Structure 1maddie.jngNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument59 pagesProteinsCraig MitchellNo ratings yet
- Bio 102 Assign 3Document3 pagesBio 102 Assign 3arica foxNo ratings yet
- He Cell 1Document34 pagesHe Cell 1Le Phuong LyNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument38 pagesProteinseugieniogienioNo ratings yet
- Living OrganizationDocument10 pagesLiving OrganizationAbbas TalibNo ratings yet
- Cellbiologyreview AnswersDocument8 pagesCellbiologyreview AnswersCARLISABEL GALLARDONo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biochemistry A Short Course 3Rd Edition by Tymoczko Test Bank Isbn 1464126135 9781464126130 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Biochemistry A Short Course 3Rd Edition by Tymoczko Test Bank Isbn 1464126135 9781464126130 Full Chapter PDFcindy.bishop135100% (12)
- Proteins Structure Functions Cell WorkDocument45 pagesProteins Structure Functions Cell WorkEdith BelenNo ratings yet
- Macromolecule - ProteinDocument50 pagesMacromolecule - Proteinadinda tyasprabandariNo ratings yet
- The importance of proteins in living organismsDocument4 pagesThe importance of proteins in living organismsLeah Loren BrazilNo ratings yet
- Body PhysiologyDocument88 pagesBody PhysiologyThe KittyNo ratings yet
- Class Notes - Biology SAC 1Document24 pagesClass Notes - Biology SAC 1carmelynnnamoresNo ratings yet
- Human BodyDocument10 pagesHuman BodyTurky TurkyNo ratings yet
- Proteins Are Good For HealthDocument30 pagesProteins Are Good For HealthMohsin SheikhNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument14 pagesBioenergeticsmunozayshiaNo ratings yet
- 8 MitochondriaDocument13 pages8 Mitochondriawhether913No ratings yet
- Biochemical Composition of CellDocument84 pagesBiochemical Composition of Cellmuskaankhan27No ratings yet
- Unit 2 (1) 2Document11 pagesUnit 2 (1) 2Johnieer Bassem MoferdNo ratings yet
- Cells and Genomes MacromoleculesDocument10 pagesCells and Genomes MacromoleculesAkmad SugodNo ratings yet
- Gauge Invariance in Classical ElectrodynamicsDocument22 pagesGauge Invariance in Classical ElectrodynamicsArindam RoyNo ratings yet
- Urology Case Reports: Shakhawan Hama Amin Said, Rezhin Yaseen Abdalla, Ismaeel Aghaways, Ari Mohammed AbdullahDocument3 pagesUrology Case Reports: Shakhawan Hama Amin Said, Rezhin Yaseen Abdalla, Ismaeel Aghaways, Ari Mohammed AbdullahHardiTariqHammaNo ratings yet
- Critical AnalysisDocument4 pagesCritical AnalysisAyet PNo ratings yet
- Mugunthan ResumeDocument4 pagesMugunthan Resumeapi-20007381No ratings yet
- R209292y@students Msu Ac ZWDocument7 pagesR209292y@students Msu Ac ZWColias DubeNo ratings yet
- Holliday - 2006 - Native-Speakerism - ELT JournalDocument3 pagesHolliday - 2006 - Native-Speakerism - ELT JournalBob HowesNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Sociological PerspectivesDocument39 pagesModule 1 Sociological PerspectivesCristine BalocaNo ratings yet
- Thank You LetterDocument2 pagesThank You LetterFathina57% (7)
- Learning Disabilities in The ClassroomDocument5 pagesLearning Disabilities in The ClassroomekielaszekNo ratings yet
- Writing Statement of PurposeDocument1 pageWriting Statement of PurposeArunmani Arunachalam100% (1)
- NIH Strategic Plan For Data ScienceDocument26 pagesNIH Strategic Plan For Data ScienceAristide AhonzoNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 Who Is A Contributor PDFDocument28 pagesUnit 01 Who Is A Contributor PDFKumpavatJayarajsinhNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Course Alagappa UniversityDocument10 pagesMathematics Course Alagappa UniversityTirthajit SinhaNo ratings yet
- 9851 BCG Vaccine Professional HCWDocument4 pages9851 BCG Vaccine Professional HCWIuliana PanaitNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper 2019-20Document33 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper 2019-20omvrat singhNo ratings yet
- Disirders of Synaptic Plasticity and Schizophrenia - J.smythiesDocument559 pagesDisirders of Synaptic Plasticity and Schizophrenia - J.smythiesBrett CromptonNo ratings yet
- Transportasi Kelembagaan PengantarDocument26 pagesTransportasi Kelembagaan Pengantarade wiraNo ratings yet
- Climate and Urban FormDocument10 pagesClimate and Urban FormYunita RatihNo ratings yet
- Semaphore Twinsoft Manual PDFDocument101 pagesSemaphore Twinsoft Manual PDFReza AnantoNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Dose Is DR PDFDocument4 pagesMinimizing Dose Is DR PDFYamuna GovindarajNo ratings yet
- ARIMA Models in Python Chapter3Document52 pagesARIMA Models in Python Chapter3FgpeqwNo ratings yet
- 7 Basic Control ActionsDocument27 pages7 Basic Control ActionsAhmad ElsheemyNo ratings yet
- A Multivocal Literature Review of Decentralized Finance: Current Knowledge and Future Research AvenuesDocument37 pagesA Multivocal Literature Review of Decentralized Finance: Current Knowledge and Future Research Avenuesnofeh84660No ratings yet