Professional Documents
Culture Documents
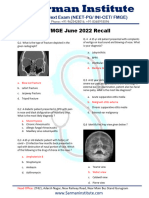
ENT & Ortho For Anglofibroma of Nasopharynx, The Most Appropriate
Uploaded by
drsayedacOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ENT & Ortho For Anglofibroma of Nasopharynx, The Most Appropriate
Uploaded by
drsayedacCopyright:
Available Formats
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.
1. For anglofibroma of a. Squamous tympanic
nasopharynx, the most fissure
appropriate investigation is b. Lateral margin of Tegmen
a. Plain x-ray tympani
b. MRI scan c. Petrosquamous suture
c. CT scan d. Petrosquamous fissure
d. Angiography 1. External auditory canal is
1. In positional vertigo, formed by groove
semicircular canal involved is a. First branchial
a. Posterior b. First visceral
b. Anterior c. Second branchial
c. Lateral d. Second visceral
d. Superior 1. Orontral fistula is common after
1. Rinne test will be negative if the the extraction of
loss of hearing is at --------dB a. 1st molar
a. 45-60 b. 2nd incisor
b. 0-15 c. 2nd premolar
c. 15-20 d. 1st premolar
d. 30-40 1. Not a contraindication for
1. In atrophic rhinitis nasal tonsillectomy
blockade is due to a. Past history of
a. Polyp Peritonsillar abscess
b. Turbinate hypertrophy b. Uncontrolled diabetes
c. Granuloma mellitus
d. Crusting c. URTI
1. Blood supply of nasal septum is d. Epidemic of poliomyelitis
a. Mainly internal carotid 1. Type IV thyroplasty is for
artery and partly external a. Vocal cord medialization
carotid artery b. Vocal cord lateralization
b. Mainly external carotid c. Vocal cord shortening
artery and partly internal d. Vocal cord lengthening
carotid artery 1. Carhart’s notch in audiogram is
c. Internal carotid artery deepost frequency of
d. External carotid artery a. 0.5KHz
1. Treatment of bilateral abductor b. 2KHz
vocal cord palsy is c. 4 KHz
a. Endotracheal intubation d. 8 KHz
b. Adrenaline 1. In coid caloric stimulation ten,
c. Tracheostomy which of the following is TRUE of
d. None of the above movements of the eye ball
1. Korner’s septum is formed by a. Towards the opposite
which of the following side
1 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
b. Towards the same side c. To maintain the
c. Upwards electronic milieu of
d. Downwards Endolymph
1. Which of the following is the d. None of the above
narrowest part of larynx is 1. Adenocarcinoma of ethmoid is
a. Supraglottis most common is
b. Saccule a. Dye industry worker
c. Rima glottidis b. Chimney worker
d. Vestibule of pharynx c. Wood workers
1. Abductors of vocal cord are d. Nickel workers
a. Thycarytenoid 1. In myringotomy, the incision is
b. Cricothyroid applied in the region of the
c. Posterior cricoarytenoid posteroinferior quadrant. This is
d. Lateral cincoarytenoid the preferred site for all the
1. Which of the following does not following reasons EXCEPT?
form nasal septum a. Easily accessible
a. Nasal crest of maxilla b. Less vascular region
b. Perpendicular plate of c. Less damage to ear
ethmoid ossicles
c. Concha of sphenoid d. Less change of injury to
d. Vomer the chorda tympani nerve
1. In which of the following 1. A chronic smoker with a history
conditions, cortical of hoarseness was found on
inastoidectomy is indicated examination to have keratosis
a. Malignant disease of of the larynx. All the following
middle ear are used for treatment except
b. CSOM without a. Partial laryngectomy
Cholesteatoma b. Stripping of the vocal cort
c. Acute coalescent c. CO2 laser vaporizer
mastoiditis d. Stop smoking
d. CSOM with 1. True regarding Reinke’s edema
Cholesteatoma is
1. Floor of middle ear is pierced by a. Cyst of ventricle of larynx
a. Vagus b. Edema of ventricular
b. Tympanic branch of 9th band
nerve c. Edema of free margin of
c. Caroticotympanic nerve vocal cord
d. Deep auricular artery d. Edema of uvula
1. The function of stria vascularis 1. In which of the following
is conditions negative Rinne test
a. To produce perilymph is seen
b. To absorb perilymph a. Meniere’s disease
2 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
b. Acoustic neuroma a. Right lateral basal
c. Tympanosclerosis segment
d. Sensorineural deafness b. Right medial basal
1. False regarding tympanic segment
membrane is c. Right posterior basal
a. It has sensory supply via segment
auriculotemporal nerve d. Right anterior basal
b. It is inclined at an angle segment
of 350 to the mealus 1. Which of the following sinuses is
c. Lined by stratified not present at birth
epithelium in continuity a. Ethmoidal
with external auditory b. Maxillary
canal c. Frontal
d. Tympanic membrane is d. Sphenoid
attached to annulus ring 1. In radical mastoidectomy all the
made of fibrous cartilage following are done EXCEPT
1. Cause of otitis externa a. Lowering of facial ridge
hemorrhagica is b. Mucosa and middle ear
a. Picornavirus muscles are removed
b. Influenza virus c. All the ossicles are
c. Adenovirus removed except the
d. Enterovirus stapes foot plate
1. In hypopharynx which of the d. Maintains patency of
following part is not included Eustachian tube
a. Posterior pharyngeal wall 1. Sensory supply of middle ear
b. Anterior pharyngeal wall cavity is by
c. Posterior cricoid region a. 5th nerve
d. Pyriform sinus b. 10th nerve
1. Gradenigo’s triad includes c. 9th nerve
which of the following d. Greater occipital nerve
a. Abducens nerve 1. Pulver Taft weave is a technique
b. Facial nerve of
c. Optic nerve a. Nerve repair
d. Trigeminal nerve b. Vein repair
1. Acoustic neuroma most c. Bone repair
commonly arises from d. Tendon repair
a. Superior vestibular nerve 1. The antibiotic of choice in acute
b. Interior vestibular nerve epiglottitis culture sensitivity
c. Cochlear nerve report is
d. Facial nerve a. Erythromycin
1. Foreign body in erect position b. Rolitetracycline
lies in c. Doxyclycline
3 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
d. Ampicillin d. Cortical mastoidectomy
1. In plummer Vinson syndorme, 1. CSF rhinorrhoea is commonest
the region involved is in fracture of the
a. Posterior pharyngeal wall a. Temporal bone
b. Valleculae b. Nasal bones
c. Postcricoid region c. Temporo sphenoid
d. Pyriform sinus d. Cribriform plate
1. Most common location of vocal 1. In cerebellopontine angle
nodules is tumor, the ‘earliest’
a. Anterior commissure manifestation is
b. Posterior 1/4th and a. Ipsilateral papillary
anterior 2/3rd junction dilatation
c. Anterior 1/3rd and b. Ipsilateral tongue
posterior 2/3rd junction paralysis
d. Posterior 2/3rd and c. Ipsilateral lateral squint
anterior 2/3rd junction d. Loss of corneal reflex
1. Stapedius is supplied by 1. Antrum of Highmore is also
a. V cranial nerve known as
b. VI cranial nerve a. Frontal
c. VII cranial nerve b. Maxillary
d. IX cranial nerve c. Ethmoidal
1. Which of the following is TRUE d. Mandibular
about Rhinosporidiosis 1. Cartilage which has signet ring
a. The most common sign is
organism is Klebsiella a. Arytenoid
rhinoscleromatis b. Cuneiform
b. Seen only in c. Thyroid
immunocompromised d. Cricoids
patient 1. A diabetic patient complains of
c. Presents as a nasal polyp discharge of blackish crusts.
d. Can be diagnosed by Most likely the cause of this is
isolation of the organism a. Candidiasis
1. A 7 year old child who presents b. Histoplasmosis
with acute otitis media does not c. Aspergillosis
respond to ampicillin. d. Mucormycosis
Examination reveals that the 1. 55 years old, Hema was
tympanic membrane is full and undergoing a face lift operation
bulging. The treatment of to reduce or eliminate facial
choice of rhytids, or wrinkles. While
a. Systemic steroids operation she suffered a nerve
b. Ciprofloxacin injury, which nerve is most
c. Myringotomy likely to be injured
4 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
a. Lesser occipital nerve c. Chondroma
b. Zygomatic branch of d. Ductal cyst
facial nerve 1. Which of the following virus is
c. Greater auricular nerve associated with Otosclerosis
d. Lesser petrosal nerve a. Mumps virus
1. Audiogram in early Meniere’s b. Measles virus
disease shows c. EBV
a. Notch at 2 kHz in bone d. RSV
conduction 1. Investigation of choice for Acute
b. Notch at 4 kHz in air sinusitis is
conduction a. X-ray (Water’s view)
c. A flat curve b. Computerized
d. A rising curve tomography (CT)
1. Cheval let fracture of nasal scanning
septum is c. MRI
a. Horizontal backwards d. Ultrasonography
b. Vertical backwards 1. The largest cartilage of larynx is
c. Transverse backwards a. Thyroid
d. Oblique backwards b. Cricoids
1. Trotter’s triad included all c. Arytenoids
except d. Corniculate
a. Conductive deafness 1. Most common complication of
b. Ipsilateral temporal tracheostomy is
neuralgia a. Tracheoesophageal
c. Palatal paralysis fistula
d. Contralateral temporal b. Tracheocutaneous fistula
neuralgia c. Surgical emphysema
1. The extent of glomus tumor is d. Tracheal stenosis
best shown by 1. Klippel- Feil syndrome results
a. CT scan from
b. MRI a. Congenital contracture of
c. Angiography the sternocleidomastoid
d. X-rays muscle
1. A 45yr male, trumpet player b. Failure of descent of the
presents with complain of scapula
cough, Dyspnea, hoarseness & c. Failure of closure of the
swelling in neck. Swellign is third branchial arch
reducible & increases in size d. Failure of segmentation
during Valsalva & coughing he’s of mesodermal somites
likely to be suffering from 1. CSF is similar to
a. Thyroglossal cyst a. Endolymph
b. Laryngocccle b. Perilymph
5 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
c. Cortilymph d. Thin odourless fluid
d. None 1. A 3-year old child present with
1. The “cone of light” is seen in fever and earaches on
which quadrant of tympanic examination there is congested
membrane? tympanic membrane with slight
a. Anterosuperior bulge. The treatment of choice
b. Anteroinferior is
c. Posterosuperior a. Myringotomy with
d. Posterorinferior penicillin
1. The most mobile part of b. Myringotomy with
tympanic membrane grommet
a. Central c. Only antibiotic
b. Peripheral d. Wait and watch
c. Both 1. Bezold’s abscess is situated at
d. None a. Diagstric triangle
1. What should be the loss of b. Tip of mastoid, deep to
hearing at least for weber’s test sternomastoid
to lateralize? c. Subtemporally
a. 5 db d. Parotid area
b. 10 db 1. Tobey Ayer test is useful for
c. 15 db diagnosing
d. 20 db a. Lateral sinus thrombosis
1. Which is the investigation of b. Medial sinus thrombosis
choice in assessing hearing loss c. Serous otitis media
in neonates? d. Eustachian tube defect
a. Impedance audiometry 1. Gelle’s test is done in
b. Brainstem evoked a. Senile deafness
response audiometry b. Traumatic deafness
(BERA) c. Otosclerosis
c. Free field audiometry d. Glue ear
d. Behavior audiometry 1. Phlep’s sign is seen in
1. Ear is sensitive to which a. Glomus jugulare
frequency of sound b. Vestibular neuroma
a. 500-3500 Hz c. Glomus tympanicum
b. 1000-3000 Hz d. Meniere’s disease
c. 3000-5000 Hz 1. Caloric test has
d. 5000-8000 HZ a. Slow component only
1. Tuberculous otitis media is b. Fast component only
characterized by all EXCEPT c. Slow and fast
a. Multiple perforation components
b. Pale granulations d. Fast component
c. Earache occasionally
6 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
1. A 30-year old woman with b. Behind the opening of
family history of hearing loss Eustachian tube
from her mother’s side c. In posterior pharyngeal
developed hearing problem wall
during pregnancy. Hearing loss d. Behind the opening of
is bilateral, slowly progressive, parotid duct
with audiometry shows 1. All of the following are true
conductive hearing loss with an about fungal sinusitis
apparent bone conduction a. Steroids spray may be
hearing loss at 2000 Hz. What is useful
the most likely diagnosis ? b. Heterogenous
a. Otosclerosis echogenicity
b. Acoustic neuroma c. Endoscopic surgery is
c. Otitis media with effusion TOC
d. Sigmoid sinus thrombosis d. Tissue invasive is seen
1. Nasolacrimal duct opens into 1. Opening in Caldwell Luc
a. Superior meatus operation is made in which of
b. Middle meatus the following
c. Inferior meatus a. Middle meatus
d. Sphenoethmoidal recess b. Inferior meatus
1. Abel’s bacillus auses c. Canine fossa
a. Rhinoscleroma d. Dental sulcus
b. Rhinosporodiosis 1. Dacrocystorhinostomy (DCR) is
c. Atrophic rhinitis contraindicated in all the
d. Rhinolith following EXCEPT
1. Mylasis is a. Atrophic rhinitis
a. Maggots seen in nose b. Deviated nasal septum
b. Maggots in the anus c. Carcinoma lacrimal gland
c. Inflammatory disease of d. Chronic dacrocystitis
nose 1. View for superior orbital fissure
d. Necrotic inflammation is
with maggots in ear a. Basal view
1. The most important cause b. Occipitomental view
unilateral nasal obstruction is c. Towne’s view
a. Atrophic rhinitis d. Basal skull view
b. Allergic rhinitis 1. The most common malignancy
c. Nasal polyp of the oropharynx
d. Deviated nasal septum a. Tonsil
1. Fossa of Rosenmuller is situated b. Soft palate
at c. Tongue base
a. Base of skull d. Valleculae
1. Killiance dehiscence is seen in
7 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
a. Oropharynx d. Obstruction by foreign
b. Nasopharynx body
c. Cricopharynx 1. Vocal cord is linked by
d. Vocal cords a. Stratified columnar
1. Which of the following epithelium
statements is true for Ludwig’s b. Pseudostratified
angina? columnar epithelium
a. It is an ischemic, painful c. Stratified Squamous
condition of pectoralis epithelium
minor muscle d. Cuboidal epithelium
b. It is diffuse cellulitis 1. Recurrent laryngeal nerve is
affecting the floor of the closely related to
mouth a. Superior laryngeal artery
c. Glycerin nitrate, local b. Superior thyroid artery
application is quite c. Inferior thyroid artery
helpful d. Middle thyroid vein
d. None of the above 1. Most common cause of stridor
1. All muscles of tongue are after birth is
supplied by hypoglossal nerve a. Laryngeal web
EXCEPT b. Laryngeal stenosis
a. Myoglossus c. Laryngomalacia
b. Palatoglossus d. Vocal cord palsy
c. Genioglossus 1. “Mouse nibbled” appearance of
d. Hyoglossus vocal cord is seen in
1. Lower esophageal sphincter a. Carcinoma larynx
a. Has no tonic activity b. Papilloma
b. Has a tone which is c. Syphilis
provided by the d. TB
sympathetic system 1. “kiss ulcer” of larynx is due to
c. Relaxes on increasing a. Vocal abuse
abdominal pressure b. Papilloma
d. Relaxes ahead of the c. Vocal nodule
peristaltic wave d. Tuberculosis
1. Dysphagia lusoria is commonly 1. Commonest cause of unilateral
due to vocal cord palsy is
a. Abnormal origin of left a. Idiopathic
subclavian artery b. Thyroid surgery
b. Abnormal origin of right c. Trauma
subclavian artery d. Epiglottic tumor
c. Compression by aortic 1. A 10-year old body developed
arch hoarseness of voice following an
attack of diphthera. On
8 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
examination his right vocal cord b. Bilateral incomplete
was paralysed. The treatment of paralysis
choice for paralysed vocal cord c. Unilateral complete
will be paralysis
a. Gel foam injection of right d. Bilateral complete
vocal cord paralysis
b. Fat injection of right vocal 1. In bilateral abductor palsy of
cord vocal cords, the voice described
c. Thyroplasty –type1 is
d. Wait for spontaneous a. Mogiophonia
recovery of vocal cord b. Phonasthenia
1. Sideropenic Dysphagia is seen c. Goor or normal
in d. Woody voice
a. Iron deficiency anaemia 1. For androphonia in females,
b. Vitamin B12 deficiency which thyroplastry is useful?
anaemia a. Type I
c. Folic acid deficiency b. Type II
anaemia c. type III
d. Any of the above d. type IV
1. The laryngeal mask airways 1. hoarseness of voice with little or
(LAM) used for securing the no affection of respiration is the
airway of a patient in all of the feature of
following conditions except a. bilateral recurrent
a. In a difficult intubation laryngeal nerve palsy
b. In cardiopulmonary b. unilateral recurrent
resuscitation laryngeal nerve palsy
c. In a child undergoing an c. carcinoma of pyriform
elective/ routine eye fossa
surgery d. retropharyngeal abscess
d. In a patient with a large 1. partial recurrent laryngeal
tumor in the oral caviry nerve palsy produces vocal cord
1. Reinke’s oedema is in which positon?
a. Oedema of the uvula a. Cadaveric
b. Oedema of the free b. Adducted (median)
margin of the vocal cord c. Abducted
c. Oedema of the d. Paramedian
ventricular band 1. The commonest cause of
d. Cyst of the ventricle of pathological fracture is
the larynx generalized affection is
1. Maximum stridor is seen in a. Carcinoma
a. Unilateral complete b. Osteoporosis
paralysis of cord c. Cyst
9 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
d. All of the above c. Fracture neck of femur
1. The treatment of choice in d. Anterior dislocation of
pathological fracture is shoulder
a. Internal fixation 1. Following anterior dislocation of
b. Plaster of paris casts the shoulder, a pt develops
c. Skin traction weakness of flexion at elbow
d. External skeletal fixation and lack of sensation over the
1. What is March fracture? lateral aspect forearm; nerve
a. Fracture of 2nd metatarsal injured is
b. Fracture of 4th metatarsal a. Radial nerve
c. Fracture of cuboids b. Musculocutaneous nerve
d. Fracture of cuboids c. Axillary nerve
1. Marker for bone formation is d. Ulnar nerve
a. Tartrate resistance acid 1. A 6 year old boy has a history of
phosphate recurrent dislocation of the right
b. Osteocalcin shoulder. On examination, the
c. Urinary calcium orthopedician puts the patient
d. Serum nucleotidase in the supine position and
1. Non “union is a complication of abducts his arm to 90 degrees
a. Scaphoid # with the bed as the fulcrum and
b. Colle’s # then externely rotates it but the
c. Inter – trochanteric # of boy does not allow the test to
hip be perfomed. The test done by
d. Supra condylor # of the the opthopedician is
humerus a. Apprehension test
1. Hill sachs lesion in recurrent b. Sulcus test
shoulder dislocation is c. Dugas test
a. Injury to humeral head d. MC Murray’s test
b. Rupture of tendon of 1. “figure of eight” bandage used
supraspinatus muscle commonly in the fracture of
c. Avulsion of glenoid a. Scapula
labrum b. Humerus
d. None of the above c. Clavicle
1. Which nerve is damaged in ant d. Metacarpals
dislocation of shoulder 1. All are true regarding clavicular
a. Axillary fracture except
b. Median a. May be caused by a fall
c. Radial on to the outstretched
d. Musculocutaneous arm
1. Duga’s test is helpful in b. Commonly occurs
a. Dislocation of hip between the insertions of
b. Scaphoid fracture caraco-clavicular and the
10 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
costo Clavicular c. Hammate
ligaments d. Pisciform
c. May jeopardize blood 1. In classical Scaphoid cast
supply to the overlying position of wrist is
skin a. Dorsal & ulnar flexion
d. Usually requires careful b. Dorsal & radial flexion
reduction c. Ventral & ulnar flexion
1. In fracture surgical neck of d. Ventral & radial flexion
humeus, the following nerve 1. Which carpal bone fracture
injury is common causes median nerve
a. Axillary involvement?
b. Radial a. Scaphoid
c. Ulnar b. Lunate
d. Median c. Trapezium
1. Treatment of choice in 65 year d. Trapezoid
of old female with impacted # 1. Commonest dislocation of the
neck of humerus is hip is
a. Triangular sling a. Posterior
b. Arm chest strapping b. Anterior
c. Arthroplasty c. Central
d. Observation d. None
1. Hanging cast is used in 1. Traumatic dislocation of hip is
a. # femur characterized by
b. # Radius a. Adduction internal
c. # Tibia rotation deformity
d. # humerus b. Abduction external
1. The best radiological view for rotation deformity
fracture Scaphoid c. Adduction external
a. AP rotation deformity
b. PA d. Abduction internal
c. Lateral rotation deformity
d. Oblique 1. Vascular sign of Narath is
1. Avascular necrosis of bone is noticed is
most common in a. Fracture neck of femur
a. Scapula b. Perthes disease
b. Scaphoid c. Posterior dislocation of
c. Calcaneus hip
d. Cervical spine d. All of the above
1. Carpal bone which fracture 1. Kumar, a 31 yrs old motorcyclist
commonly sustained injury over his right
a. Scaphoid hip joint. X-ray revealed a
b. Lunate posterior dislocation of the
11 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
Right hip joint. The clinical 1. True regarding Hangman’s
attitude of the affected lower fracture is
limb will be a. Odotoid process fracture
a. External rotation, of C2
extendion & abduction b. Spondylolisthesis of C2
b. Internal rotation, flexion over C3
& adduction c. Whiplash injury
c. Internal rotation, d. Fracture of hyoid bone
extension & abduction 1. The compression fracture is
d. External rotation, flexion commonest in
& abduction a. Cervical spine
1. In anterior dislocation of hip, the b. Upper thoracic spine
positive of lower limb will be c. Lower thoracic spine
a. Abduction, externally d. Lumbosacral region
rotated and extension 1. A paralysed bladder following
b. Abduction, externally spinal injury is best manged by
rotated and flexion a. Gibbon’s catheter
c. Abducted externally b. Malicot catheter
rotated and flexion c. Foley’s catheter
d. Adducted, internally d. Metallic catheter
rotated and flexion 1. “Tinel ‘s sign “ indicates
1. In per rectal examination, a. Neurofibroma
femora head is palpable in b. Injury to peripheral
a. Anterior dislocation of hip nerves
b. Posterior dislocation of c. Atrophy of nerves
hip d. Regeneration of nerves
c. Central dislocation of hip 1. In seddon’s classification,
d. Lateral dislocation of hip complete division of nerve is
1. ‘Whip-lash’ injury is caused due a. Neuropraxia
to b. Axonotmesis
a. A fall from a height c. Neurotmesis
b. Acute hyperextension of d. None of the above
the spine 1. Most common cause of
c. A blow on top to head neurological deficit in upper
d. Acute hyper flexion of the limb is
spine a. Polio
1. Jefferson’s # is b. Erb’s palsy
a. C1 c. C1-C2 dislocation
b. C2 d. Fracture dislocation of
c. C2 C1 cervical spine
d. C2 C3
12 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
1. All of the following are features 1. X-ray showing decreased
of musculocutaneous nerve intervertebral space and
injury at axilla except presence of para vertebral
a. Loss of flexion of shadow. What could be the
shoulder diagnosis?
b. Loss of flexion of elbow a. Tuberculosis of spine
c. Loss of supination of b. Ankylosing spondylitis
forearm c. Eosinophilic granuloma
d. Loss of sensation on d. Multiple myeloma
radial side of forearm 1. The ideal surgical treatment for
1. The following is the commonest pott’s paraplegia is
cause of loose body in joint a. Laminectomy and
a. Osteoarthritis decompression
b. Osteochondral fracture b. Anterior decompression
c. Synovial chondromatosis and bone grafting
d. Osteochondritis dissecans c. Anterolateral
1. Disease where distal decompression
interphalangeal joint is d. Costotransversectomy
characteri-stically involved 1. Short long bones of hand and
a. Psoriatic arthritis foot are commonly infected by
b. Rheumatoid the following organism
c. SLE a. Pyogenic
d. Gout b. Tuberculosis
1. Biamboo spine is seen in c. Fungal
a. Tuberculosis d. All of the above
b. Rheumatoid arthritis 1. All are feature of joint
c. Ochronosis tuberculosis except
d. Ankylosing spondylosis a. Synovium is involved
1. MC joint involved in Gout b. Synovial fluid has < 20%
a. Knee blood sugar
b. Hip c. Kissing arthritis –
c. MP joint of the big toe subchondral bone is
d. MP joint of thumb involved
1. Earliest radiological sign of d. Pain is a common feature
spinal tuberculosis is 1. Simple bone cyst is seen most
a. Wedging of vertebra commonly in
b. Syndesmophyte a. Tibia
formation b. Radius
c. Formation of c. Femur
paravertebral abscess d. Humerus
d. Decreased joint space
13 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
1. Soap bubble appearance at
lower end of radius, the
treatment of choice is
a. Local excision
b. Excision and bone
grafting
c. Amputation
d. Radiotherapy
1. Most common site of origin of
adamantinoma is
a. Mandible near molar
tooth
b. Middle alveolar margins
c. Hard palate
d. Mandible near symphisis
menti
1. Most common benign tumor of
the bone is
a. Giant cell tumor
b. Simple bone cyst
c. Osteochondroma
d. Enchondroma
1. A 60 yrs old male has bone
pain, vertebral collapse,
fracuture pelvis, the probable
diagnosis is
a. Multiple myeloma
b. Secondaries
c. TB
d. Hemangioma of bone
1. Metastases least common in
a. Skull
b. Pelvis
c. Proximal part of long
bones of the upper limb
d. Small bones of the hand
14 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
1. C 46.D 91 13
2. A 47.D . A 6. D
3. C 48.B 92 13
4. D 49.D . C 7. A
5. B 50.B 93 13
6. C 51.B . A 8. D
7. C 52.B 94 13
8. A 53.B . C 9. C
9. A 54.A 95 14
10.A 55.D . B 0. D
11.D 56.D 96 14
12.B 57.A . B 1. A
13.A 58.B 97 14
14.C 59.A . C 2. B
15.C 60.B 98 14
16.C 61.B . C 3. B
17.C 62.A 99 14
18.B 63.C . B 4. B
19.D 64.A 10 14
20.C 65.B 0. B 5. D
21.D 66.A 10 14
22.A 67.C 1. B 6. B
23.C 68.C 10 14
24.C 69.C 2. A 7. A
25.B 70.A 10 14
26.B 71.C 3. A 8. C
27.B 72.C 10 14
28.A 73.A 4. B 9. A
29.A 74.D 10 15
30.C 75.B 5. A 0. D
Answer 31.C 76.A 10
32.D 77.C 6. A
33.C 78.D 10
34.D 79.D 7. A
35.D 80.A 10
36.C 81.C 8. D
37.C 82.B 10
38.C 83.B 9. B
39.C 84.D 11
40.C 85.A 0. A
41.D 86.A 11
42.D 87.C 1. C
15 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
43.B 88.C 11 13
44.D 89.D 2. D 3. C
45.D 90.A 11 13
3. A 4. B
11 13
4. A 5. A
11
5. D
11
6. D
11
7. B
11
8. A
11
9. B
12
0. B
12
1. A
12
2. A
12
3. C
12
4. B
12
5. B
12
6. C
12
7. B
12
8. A
12
9. B
13
0. C
13
1. C
13
2. D
16 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
KIMS ENT & Ortho I.S
17 KAROL INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
24HRS
HELPLINE:9884329457,9962850383,9895666065,WEBSITE:www.kimsindi
a.com
You might also like
- Parasitic Protozoa: Toxoplasma, Cryptosporidia, Pneumocystis, And MicrosporidiaFrom EverandParasitic Protozoa: Toxoplasma, Cryptosporidia, Pneumocystis, And MicrosporidiaNo ratings yet
- EntDocument26 pagesEntNuriaNo ratings yet
- OTORHINO Ixtlilton Finals ReviewerDocument18 pagesOTORHINO Ixtlilton Finals ReviewerMika SaldanaNo ratings yet
- A Handbook on Biotelemetry and Radio Tracking: Proceedings of an International Conference on Telemetry and Radio Tracking in Biology and Medicine, Oxford, 20-22 March 1979From EverandA Handbook on Biotelemetry and Radio Tracking: Proceedings of an International Conference on Telemetry and Radio Tracking in Biology and Medicine, Oxford, 20-22 March 1979Charles J. AmlanerNo ratings yet
- ENT Paper 2Document13 pagesENT Paper 2John M. Hemsworth100% (1)
- Advances in Oral Biology: Volume 3From EverandAdvances in Oral Biology: Volume 3Peter H. StapleNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document3 pagesQuiz 1daniel amparadoNo ratings yet
- The Biology of Stentor: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyFrom EverandThe Biology of Stentor: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment QuestionsDocument35 pagesSelf Assessment QuestionsAli QuwarahNo ratings yet
- Board Revision2014 2Document8 pagesBoard Revision2014 2Adham Sharaf AldeenNo ratings yet
- Antarctic Fish Biology: Evolution in a Unique EnvironmentFrom EverandAntarctic Fish Biology: Evolution in a Unique EnvironmentNo ratings yet
- Four Alternatives Are Given For Each Question. You Are Required To Fill The Most Appropriate Numbered Circle Completely in Section "A" of The Given OMR. Return This Question Paper Along With OMRDocument6 pagesFour Alternatives Are Given For Each Question. You Are Required To Fill The Most Appropriate Numbered Circle Completely in Section "A" of The Given OMR. Return This Question Paper Along With OMRMahesh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1+10Document3 pagesQuiz 1+10daniel amparadoNo ratings yet
- Common Facial Vein: Superior Hiatus SemilunarisDocument5 pagesCommon Facial Vein: Superior Hiatus SemilunarissuntiNo ratings yet
- Jipmer 2010 Rapid Review: Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education & ResearchDocument15 pagesJipmer 2010 Rapid Review: Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education & ResearchgokunambiarNo ratings yet
- ظ Untitled20Document4 pagesظ Untitled20adham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Endodontics (Review Center)Document10 pagesEndodontics (Review Center)LangNo ratings yet
- ENT Paper Mcqs (1) - 2Document9 pagesENT Paper Mcqs (1) - 2Muhammad Sheraz75% (4)
- ENT Nose Block II ScenariosDocument23 pagesENT Nose Block II Scenariosrumman tariqNo ratings yet
- 2011 - MCQ It Blok 19Document12 pages2011 - MCQ It Blok 19Mohamad Fiqih ArrachmanNo ratings yet
- Cluster IXDocument12 pagesCluster IXTJ OberioNo ratings yet
- Otology: Anatomy and Physiology of The EarDocument2 pagesOtology: Anatomy and Physiology of The EarKenneth MiguelNo ratings yet
- Answendo PerioDocument5 pagesAnswendo Periof9fhzxszqcNo ratings yet
- Radiology (Yw)Document9 pagesRadiology (Yw)Abhay Singh100% (1)
- Aim4aiims - In: The EarDocument39 pagesAim4aiims - In: The EardorjeesengeNo ratings yet
- Dr. Laxman FileDocument55 pagesDr. Laxman FileAbdul Rahman50% (2)
- ENT Paper 3Document13 pagesENT Paper 3John M. HemsworthNo ratings yet
- Revision Test Series ENTDocument8 pagesRevision Test Series ENTSuga PriyaNo ratings yet
- FMG JUNE 2022 All QusDocument41 pagesFMG JUNE 2022 All QusRohan RathoreNo ratings yet
- Ent Prelims Ears PDFDocument3 pagesEnt Prelims Ears PDFKenneth MiguelNo ratings yet
- CBT B4 Inter 2016: AscloxacillinDocument8 pagesCBT B4 Inter 2016: AscloxacillinAndre LuthfiNo ratings yet
- McqssDocument6 pagesMcqssfatimaawan8989No ratings yet
- Wa0000Document16 pagesWa0000hassan qureshi100% (1)
- Final SET 2 Formated by PSB in HomeDocument28 pagesFinal SET 2 Formated by PSB in HomeBikram KarkiNo ratings yet
- OtologiDocument13 pagesOtologimr_curiousityNo ratings yet
- Drkamalkv's CHOICE: Please NoteDocument17 pagesDrkamalkv's CHOICE: Please NoteAnonymous AvbmJ5JTNo ratings yet
- Manipal PG 2003Document11 pagesManipal PG 2003prasun_vNo ratings yet
- Mfds April 2016Document26 pagesMfds April 2016Joyce LimNo ratings yet
- MCQ KhaldounDocument9 pagesMCQ Khaldounadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Exit Exam MayDocument2 pagesExit Exam Maydaniel amparadoNo ratings yet
- Endo Set 3 QuestionsDocument3 pagesEndo Set 3 QuestionsBinayak Upadhyaya100% (1)
- Oral Pathology (Review Center)Document12 pagesOral Pathology (Review Center)yellow rangerNo ratings yet
- Omsb Part I - 2010Document10 pagesOmsb Part I - 2010Firyal Balushi100% (1)
- Ent Mcqcfor Ug CH-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesEnt Mcqcfor Ug CH-WPS OfficeJayahar AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Neet TestDocument26 pagesNeet Testanurag sharmaNo ratings yet
- ENDO 2023-07-05 at 7.51.17 AMDocument112 pagesENDO 2023-07-05 at 7.51.17 AMshekinah echavezNo ratings yet
- Larynx MCQSDocument114 pagesLarynx MCQSsidsudp100% (2)
- Ent - MCQ ExamDocument41 pagesEnt - MCQ ExamAhmed Noori100% (1)
- Soal Unas UGMDocument8 pagesSoal Unas UGMMonik AlamandaNo ratings yet
- HPSC Dental Surgeon Model Question PaperDocument10 pagesHPSC Dental Surgeon Model Question PapergauravkokraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Lecture RespiratoryDocument13 pagesNursing Lecture RespiratoryAedge010100% (1)
- Name: Year Level: Date: Score: /20 Exam Number 2 Answer KeyDocument3 pagesName: Year Level: Date: Score: /20 Exam Number 2 Answer KeyMoritz SolivenNo ratings yet
- MCQ Old-Textbook-Qs-SearchableDocument45 pagesMCQ Old-Textbook-Qs-Searchableareej alblowiNo ratings yet
- MCQ 2010Document4 pagesMCQ 2010adham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis PDFDocument2 pagesHepatitis PDFazlanNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Orl CourseDocument46 pagesMCQ in Orl CoursesulnaikNo ratings yet
- Ent MCQ (All Team) PDFDocument40 pagesEnt MCQ (All Team) PDFHaitham Haytham90% (30)
- Msds Jotafloor Topcoat Comp ADocument6 pagesMsds Jotafloor Topcoat Comp AzayzanNo ratings yet
- Biology of Humans Concepts Applications and Issues 4th Edition Goodenough Solutions ManualDocument37 pagesBiology of Humans Concepts Applications and Issues 4th Edition Goodenough Solutions Manualveramurray6qr7u100% (12)
- Understanding Triage: Three Sorts and Cases: Frank BraioDocument23 pagesUnderstanding Triage: Three Sorts and Cases: Frank BraioAdelina RotaruNo ratings yet
- How Does Radiation Therapy Work?Document5 pagesHow Does Radiation Therapy Work?mikeadrianNo ratings yet
- Suffixes and PrefixesDocument2 pagesSuffixes and PrefixesBeckyNo ratings yet
- Enterobacteriaceae in Food PDFDocument2 pagesEnterobacteriaceae in Food PDFsivabioteckNo ratings yet
- Rodney L. Fernan MD, FPCR, FUSP Section Chief Ultrasound Imaging Cardinal Santos Medical Center Manila, PhilippinesDocument71 pagesRodney L. Fernan MD, FPCR, FUSP Section Chief Ultrasound Imaging Cardinal Santos Medical Center Manila, PhilippinesReviza Adhya PutriNo ratings yet
- Puberty: Arshiya Sultana Lecturer, Dept. of Obstetrics & Gynaecology NIUM, Bangalore, KarnatakaDocument63 pagesPuberty: Arshiya Sultana Lecturer, Dept. of Obstetrics & Gynaecology NIUM, Bangalore, KarnatakamickageliNo ratings yet
- Bruxism and Prostho TreatmentDocument10 pagesBruxism and Prostho Treatmentdorasani99No ratings yet
- Infrastructure Requirement For B.Pharma & D. PharmaDocument2 pagesInfrastructure Requirement For B.Pharma & D. Pharmaanon_968573480No ratings yet
- Refkas CondylomaAccuminataDocument18 pagesRefkas CondylomaAccuminatamichelle1945No ratings yet
- Prescription - 139643 - 27 06 2020 - Dr. Vimee Bindra Basu - Apollo 2471642923981512Document2 pagesPrescription - 139643 - 27 06 2020 - Dr. Vimee Bindra Basu - Apollo 2471642923981512Mohan PvdvrNo ratings yet
- 5 Proven Home Remedies For Seborrheic Dermatitis On The Scalp - Skin DroneDocument7 pages5 Proven Home Remedies For Seborrheic Dermatitis On The Scalp - Skin DroneIliasNo ratings yet
- DR Bhagwat PDFDocument50 pagesDR Bhagwat PDFAishita MahendruNo ratings yet
- Raheem Khan - WikipediaDocument10 pagesRaheem Khan - WikipediaRaheem MahirNo ratings yet
- Pulse Oximeters Working PrincipleDocument2 pagesPulse Oximeters Working PrinciplealbertpatelusaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Rescue and Transfer HardDocument5 pagesEmergency Rescue and Transfer HardJorhally B Edzraphil100% (1)
- Deleuze - Critical and ClinicalDocument139 pagesDeleuze - Critical and Clinicalbornon8thofjulyNo ratings yet
- PMLS PRESENTATION (Lesson 3&4) (10.5 × 9 CM)Document4 pagesPMLS PRESENTATION (Lesson 3&4) (10.5 × 9 CM)Rhygn SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Softsoap Antibacterial Liquid Hand Soap Light MoisturizersDocument12 pagesSoftsoap Antibacterial Liquid Hand Soap Light MoisturizersTim WillformNo ratings yet
- 4 671945747968557164Document67 pages4 671945747968557164McMillanNo ratings yet
- Septic Shock PathophysiologyDocument33 pagesSeptic Shock Pathophysiologytummalapalli venkateswara rao67% (3)
- Journal Reading - Impact of PreRamadan Intervention Program On Diabetic PatientsDocument13 pagesJournal Reading - Impact of PreRamadan Intervention Program On Diabetic PatientsQurrota Ayun RumayshahNo ratings yet
- TgaDocument33 pagesTgavarun rajNo ratings yet
- OB PACU Severe PreeclampsiaDocument65 pagesOB PACU Severe Preeclampsiasurbakti_christineNo ratings yet
- The Demise of Bloodletting: PaperDocument6 pagesThe Demise of Bloodletting: PaperjjNo ratings yet
- BONUS - 7 Day Ab Targeted Cardio and Intervals PDFDocument42 pagesBONUS - 7 Day Ab Targeted Cardio and Intervals PDFScott Levine100% (6)
- Ayuspray ResearchDocument9 pagesAyuspray ResearchJay AherkarNo ratings yet
- Leave and Joining Time Rules: National Seeds Corporation Limited (A Government of India Undertaking)Document26 pagesLeave and Joining Time Rules: National Seeds Corporation Limited (A Government of India Undertaking)Rojan MathewNo ratings yet
- Kundalini YogaDocument3 pagesKundalini YogaHoutan Afkhami100% (4)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (80)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingFrom EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1138)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)