Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PPCE 2 Marks QA
Uploaded by
Manoj BallaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PPCE 2 Marks QA
Uploaded by
Manoj BallaCopyright:
Available Formats
1
UNIT-I
(WORKSTUDY AND ERGONOMICS)
Part-A (2 Marks)
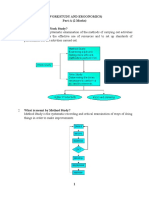
1. What is meant by Work Study?
Work Study is the systematic examination of the methods of carrying out activities
such as to improve the effective use of resources and to set up standards of
performance for the activities carried out.
2 What is meant by Method Study?
Method Study is the systematic recording and critical examination of ways of doing
things in order to make improvements.
2
3 What is Process Charts?
Graphical representation of the sequence of steps or tasks (workflow) constituting a
process, from raw materials through to the finished product. It serves as a tool for
examining the process in detail to identify areas of possible improvements. Also
called process map.
4 What is SIMO Charts?
A basic motion-time chart used to show the simultaneous nature of motions;
commonly a therblig chart for two-hand work with motion symbols plotted
vertically with respect to time, showing the therblig abbreviation and a brief
description for each activity, and individual times values and body-member detail.
Also known as simultaneous motion-cycle chart.
5 What is multiple activity charts?
Multiple Activity Charts (or Multi-Activity Charts) are a very useful tool for
understanding the flow of work in a cyclical process and as a consequence
understanding which resource is controlling the overall progress of the work. The
tool can be used to model different scenarios to determine the optimum mix of
resources for the work. The example below is based on using a tower crane to lift
concrete from the street to a high floor for placing. Each resource is represented by
a column; time is on the vertical axis.
6 What are therbligs?
The therblig is used in the study of motion economy in the workplace. A workplace
task is analyzed by recording each of the therblig units for a process, with the
results used for optimization of manual labor by eliminating unneeded movements.
The word therblig was the creation of Frank Bunker Gilbreth and Lillian Moller
Gilbreth, American industrial psychologists who invented the field of time and
motion study. It is a reversal of the word Gilbreth, with 'th' treated as one letter.
7 What is travel chart?
A Travel Chart is a simple table that is useful where there are multiple (and
possibly irregular) movement between places. It is a variation on the Check Sheet,
indicating movements from and to any combination of a given set of locations.
8 What is meant by work measurement?
Application of time and motion study and activity sampling techniques to determine
the time for a qualified worker to complete a specific job at a defined level of
performance. Work measurement is used in budgeting, manpower planning,
scheduling, standard costing, and in designing worker incentive schemes. See also
therblig.
9 What is allowance?
1. A sum set aside for an occurrence that may or may not come to pass. For
example, funds earmarked for expenses associated with potential bad weather.
2. Funds allocated periodically for a stated purpose, such as a per diem.
3. A discount, especially one offered as a result of specific circumstances.
3
10 What is meant by ergonomics?
Definition: Ergonomics is the science of work. Ergonomics derives from two Greek
words: ergon, meaning work, and nomoi, meaning natural laws. Combined they
create a word that means the science of work and a persons relationship to that
work.
UNIT-II
(PROCESS PLANNING)
Part-A (2 Marks)
1 What is meant by process planning?
A process is something in which the forms of material undergo some changes by
doing some manual or mechanical work. Lots of steps are involved under a
process. Process planning can be defined as a planning of facts of a process before
starting that process.
2
What are the factors affect process planning?
The three classic factors that affect the planning process in business are inputs,
processes and outcomes. Inputs are raw materials, resources, knowledge and
anything else brought to the planning process. Processes are what you do to the
inputs to create outcomes. Outcomes are partly profits, but also jobs created for
employees, and the use and pleasure that consumers receive from finished
products or services.
3 What are the reasons for process documentation?
A process consists of inputs and outputs that are created and used to produce
significant outcomes. Companies rely on processes because they bring value and
cohesiveness. You will find different types of processes in the marketplace,
including management, support, and operations. One of the methods you want to
apply when it comes to documenting a process is identifying and interviewing the
right individuals or groups.
4 State the general approaches to process planning?
Process planning is a key element in project management that focuses on selecting
resources for use in the execution and completion of a project. In a manufacturing
setting, this aspect of planning also includes establishing the general sequence of
steps that begin with the acquisition of materials and end with the creation of a
finished product. Process planning is often closely associated with project
planning, although the specific functions of each tool are used differently in the
overall strategic planning.
5 What is CAPP?
Computer-aided process planning (CAPP) is the use of computer technology to
aid in the process planning of a part or product, in manufacturing. CAPP is the link
between CAD and CAM in that it provides for the planning of the process to be
used in producing a designed part.
4
6 What are the advantages of CAPP?
Investment in hardware and software is not much.
The system offers a shorter development time and lower manpower
consumption to develop process plan.
The system is very reliable and reasonable in real production
environments for small and medium size companies.
Quality of process plan depends on knowledge and background of process
planner.
7 What is Flow Chart?
A flowchart is a type of diagram that represents an algorithm or process, showing
the steps as boxes of various kinds, and their order by connecting these with
arrows. This diagrammatic representation can give a step-by-step solution to a
given problem. Process operations are represented in these boxes, and arrows
connecting them represent flow of control. Data flows are not typically represented
in a flowchart, in contrast with data flow diagrams; rather, they are implied by the
sequencing of operations. Flowcharts are used in analyzing, designing,
documenting or managing a process or program in various fields.
8 What are the disadvantages of flow charts?
Complex logic: Sometimes, the program logic is quite complicated. In that
case, flowchart becomes complex and clumsy.
Alterations and Modifications: If alterations are required the flowchart may
require re-drawing completely.
Reproduction: As the flowchart symbols cannot be typed, reproduction of
flowchart becomes a problem.
The essentials of what is done can easily be lost in the technical details of how
it is done.
9 What is decision table?
A decision table is a table composed of rows and columns, separated into four
separate quadrants.
Conditions Condition Alternatives
Actions Action Entries
The upper left quadrant contains the conditions. The upper right quadrant contains
the condition rules ofr alternatives. The lower left quadrant contains the actions to
be taken and the lower right quadrant contains the action rules.
10 State the benefits of decision table?
Easy to understand
Map nicely to a set of business rules
Applied to real problems
Make no prior assumptions about the data
Able to process both numerical and categorical data
5
UNIT-III
(INTRODUCTION TO COST ESTIMATION)
Part-A (2 Marks)
1 Define Cost Estimation
An approximation of the probable cost of a product, program, or project,
computed on the basis of available information. Four common types of cost
estimates are: (1) Planning estimate: a rough approximation of cost within a
reasonable range of values, prepared for information purposes only. Also called
ball park estimate. (2) Budget estimate: an approximation based on well-defined
(but preliminary) cost data and established ground rules. (3) Firm estimate: a
figure based on cost data sound enough for entering into a binding contract. (4)
Not-to-exceed /Not-less-than estimate: the maximum or minimum amount
required to accomplish a given task, based on a firm cost estimate.
2 What are the types of Estimation?
Order of Magnitude Estimate
Square Foot and Cubic Foot Estimates
Assemblies (or Systems) Estimate
Unit Price Estimate
3 What are the methods of Estimation?
Estimation methods broadly follow evaluation designs, with the determination of
the counterfactual being the core of the evaluation design. Different ways to
establish controls under different evaluation designs determine the methods to be
used to measure the counterfactual:
4 State the importance of realistic estimates.
Effective project managers cultivate the courage and competency to push back
against arbitrary budgets and deadlines to negotiate realistic win-win cost and
schedule estimates for their projects. This article explores how to negotiate
realistic estimates to set realistic expectations.
5 What is design cost?
Design-to-cost is a strategic management commitment to invest in the present for
a significantly greater reward in the future. Design-to-cost is one of the strongest
levers in the cost improvement toolbox.
Design-to-cost simply means designing a product from scratch to meet the target
cost or the market price which customers are willing to pay, for a particular (or
specified) level of functionality and quality, while returning a profit to the
enterprise.
6 What is labour cost?
The cost of wages paid to workers during an accounting period on daily, weekly,
monthly, or job basis, plus payroll and related taxes and benefits.
6
7 What do you mean by overhead cost?
The ongoing administrative expenses of a business which cannot be attributed to
any specific business activity, but are still necessary for the business to function.
Examples include rent, utilities, and insurance.
8 Define costing.
System of computing cost of production or of running a business, by allocating
expenditure to various stages of production or to different operations of a firm.
9 What are the methods of costing?
As per the nature and peculiarities of the business, different Industries follow
different methods to find out the cost of their product. There are different
principles and procedure for doing the costing. However the basic principle and
procedure of costing remain the same. Some of the methods are mentioned below:
1. Unit Costing
2. Job Costing
3. Contract Costing
4. Batch Costing
5. Operating Costing
6. Process Costing.
7. Multiple Costing
8. Uniform Costing.
UNIT-IV
(COST ESTIMATION)
Part-A (2 Marks)
1 What are the elements of cost?
There are broadly three elements of cost - (1) material, (2) labour and (3)
expenses.:
The substance from which the product is made is known as material. It may
be in a raw state-raw material, e.g., timber for furniture and leather for shoe,
etc. It may j also be in manufactured state-components, e.g., battery for car,
speaker for radio, etc, Materials can be direct and indirect.
2 What are the types of cost?
The different types of costs:
opportunity cost
accounting cost or historical costs
transaction cost
sunk cost
marginal cost
3 What is meant by direct material?
All items such as raw materials, standard and specialized parts, and sub-
assemblies required to assemble or manufacture a complete product. Direct
material costs are assignable to a specific product, cost center, or work
order.
7
4 What are the types of direct material?
Manufacturing a product needs input of raw materials. Raw materials are
main component of the product. There are two types of materials.
1. Direct Materials
The materials required for producing a product are called direct materials.
Direct materials are also known as raw materials or input materials. Direct
raw materials constitute the main component or part of a finished product. It
is identified in terms of cost per unit of output. Wood for furniture industry,
sugarcane for sugar mills. textile for garment industry are some of the
examples of direct materials.
2. I ndirect Materials
The materials that can not be form as the main part of a finished product are
called indirect materials. Therefore, such materials can not be easily
identified with the product. Nails used in furniture industry and threads used
in garment industry are some example of indirect materials.
5 State some examples for direct material.
From the perspective of a manufacturer, Direct Material is any object that
will become part of the product that is sold to the end customer. Indirect
Material is considered and object that is used in the creation of your end
product but does not become part of the end product. For example an "air
tool" used to assemble a car is indirect material. A "bearing" used to
maintain a conveyor system is considered an indirect material. While a "gas
pedal" that leaves the dealership with a car, for example, is direct material.
6 What is meant by indirect material?
Consumables (such as cleaning chemicals, disposable tools, protective
devices) not used as raw materials, but which make the production of a
good or service possible, more efficient, or safer. Indirect material costs are
not readily identifiable with a specific product or job. They are termed
indirect costs and are charged to overhead accounts.
7 Who are called direct labour?
Workers such as those who operate machines, who are directly involved in
the production of goods or services, rather than those involved in organizing
or managing the cost of employing workers to make a particular product or
provide a particular service. This does not include other costs such as the
amount spent on materials etc in Britain, workers who are employed
directly by an organization such as a local government authority, rather than
being employed through a separate company.
8 State some examples for direct labour?
"Direct labor" refers to the work done by those employees who actually
make the product on the production line. ("Indirect labor" is work done by
employees who work in the production area, but do not work on the
production line. Examples include employees who set up or maintain the
equipment.)
8
Unlike direct materials (which are obtained prior to being used) direct labor
is obtained and used at the same time. This means that for any given good
output, we can compute the direct labor rate variance, the direct labor
efficiency variance, and the standard direct labor cost at the same time.
9 Who are called indirect labour?
Wages paid to the indirect laborer is called indirect labor cost, or indirect
wages, or unproductive wages. These laborers are not directly engaged in
manufacturing of goods or services. They are engaged generally in office &
maintenance activities, selling & distribution of goods & services. Example
of indirect labor are wages or salary paid to the office peon, clerk, watch
man, store keeper etc.
10 What is meant by factory on cost?
Total cost of making a product at the production location, and comprising of
raw material, labor, and overhead costs.
UNIT-V
(PRODUCTION COST ESTIMATION)
Part-A (2 Marks)
1
Define forging.
A process of working metal to a finished shape by hammering or pressing and
is primarily a "hot" operation. It is applied to the production of shapes either
impossible or too costly to make by other methods or needing properties not
obtainable by casting. Categories of forgings include Hammer, Press, Drop or
Stamping.
2
Differentiate hot forging and cold forging.
Hot forging is defined as working a metal above its recrystallization
temperature. The main advantage of hot forging is that as the metal is deformed
the strain-hardening effects are negated by the recrystallization process.
Cold forging is defined as working a metal below its recrystallization
temperature, but usually around room temperature. If the temperature is above
0.3 times the melting temperature (on an absolute scale) then it qualifies as
warm forging.
3 Contrast smith forging and drop forging.
Forging worked between flat or simple contour dies by repeated strokes and
manipulation of the workpiece. Also known as "hand" or "flat die "
forging.Heavy workpieces could be processed using a smith-forging hammer,
and smaller forgings are die formed in drop hammers. Smith forging hammers
are typically steam or air-operated, consisting of a power actuated ram
supported by a heavy cast iron frame. The final product is a result of the ram
being powered into the dies containing the workpiece.
9
An operation in which a metal shape is formed by forcing hot metal into
impressions formed in solid blocks of hardened alloy steel, the forging dies.
The dies are made in halves, one attached to the rising and falling block of the
drop forge and the other to the stationary anvil. Drop forgings are widely used
in the automotive industry for crankshafts, stub-axles, gears, etc.
4 In what ways, press forging and upset forging are different?
Press forging works by slowly applying a continuous pressure or force, which
differs from the near-instantaneous impact of drop-hammer forging. The
amount of time the dies are in contact with the workpiece is measured in
seconds (as compared to the milliseconds of drop-hammer forges). The press
forging operation can be done either cold or hot.
Upset forging increases the diameter of the workpiece by compressing its
length. Based on number of pieces produced this is the most widely used
forging process. A few examples of common parts produced using the upset
forging process are engine valves, couplings, bolts, screws, and other fasteners.
5 Define man hour and machine hour rate.
As the name indicates, this method is simply a combination of man-hour rate
and machine-hourrate methods. The man-hour rate method is suitable only where work is
done by hand, for example,in fitting and assembly shops etc. Similarly, machine hour rate
method is suitable where almost allthe work is done by machines. Thus, in this way, both the
methods can be applied in one factory.This method is combination of man-hour and
machine-hour rate method of allocation.
6 What is unit rate?
A rate is a ratio that is used to compare different kinds of quantities. A
unit rate describes how many units of the first type of quantity
corresponds to one unit of the second type of quantity. Some common
unit rates are miles (or kilometers) per hour, cost per item, earnings per
week, etc. In each case the first quantity is related to 1 unit of the
second quantity.
7 What is scale loss?
Scale loss is not normal for goldfish. They do not molt. Most often scale loss is
the result of physical injury banging against hard objects in the tank
(especially during breeding season) or rough handling. It may also result from
skin infections, but in this latter instance clear signs of skin deterioration,
bleeding and so on are obvious.
8 What are the types of welding?
1. Tig welding
2. Shielded metal arc welding also known as just plain arc welding or stick
welding
3 Mig welding
10
9 What is the pattern?
A pattern, from the French patron, is a type of theme of recurring events or
objects, sometimes referred to as elements of a set of objects. The elements of a
pattern repeat in a predictable manner. Patterns can be based on a template or
model which generates pattern elements, especially if the elements have
enough in common for the underlying pattern to be inferred, in which case the
things are said to exhibit the unique pattern.
10 What is shrinkage allowance?
A shrinkage allowance for metal casting is something that must be figured into
a design from the very beginning. As the molten metal cools and solidifies it
will begin to contract. This means that although the molten metal completely
filled up a mold, by the time the casting was cold, the casting is smaller than
the mold.
You might also like
- Cost Estimation in Agile Software Development: Utilizing Functional Size Measurement MethodsFrom EverandCost Estimation in Agile Software Development: Utilizing Functional Size Measurement MethodsNo ratings yet
- WORKSTUDY AND ERGONOMICSDocument8 pagesWORKSTUDY AND ERGONOMICSSirajAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Qfd-Quality Function DeploymentDocument11 pagesQfd-Quality Function DeploymentOral RobertzNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Name: P. VaishnaviDocument16 pagesAssignment: Name: P. Vaishnavivaishnavi_mscmbaNo ratings yet
- Questions - Task 2Document5 pagesQuestions - Task 2Alessandro FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 PMDocument61 pagesAssignment 2 PMInfant RajNo ratings yet
- Work DesignDocument47 pagesWork DesignDeepali Singhai JainNo ratings yet
- Planning Techniques and Tools and Their Application.Document30 pagesPlanning Techniques and Tools and Their Application.Charles Benedict Capayan50% (2)
- MCS-044 Solved AssignmentDocument5 pagesMCS-044 Solved AssignmentkavithakiranNo ratings yet
- ACCN 301 PresentationDocument41 pagesACCN 301 PresentationMcdonald MutsvangaNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS IT3 Group 4 2Document15 pagesBUSINESS IT3 Group 4 2Naja MadineNo ratings yet
- Unit I Operation Research Introduction: Characteristics of Operations ResearchDocument90 pagesUnit I Operation Research Introduction: Characteristics of Operations ResearchhariroopganeshNo ratings yet
- By Dr. Ali SajidDocument61 pagesBy Dr. Ali SajidSyed Abdul Mussaver ShahNo ratings yet
- 100 Project Management Terms ExplainedDocument19 pages100 Project Management Terms Explainedranjitkumar1977No ratings yet
- Computers and Operations Research Simulation: Computers Have Had A Dramatic Impact On The Management of IndustrialDocument4 pagesComputers and Operations Research Simulation: Computers Have Had A Dramatic Impact On The Management of IndustrialJesus Armando Araujo MeloNo ratings yet
- What Is Project ManagementDocument14 pagesWhat Is Project Managementआदित्य त्रिपाठी100% (1)
- New Developments in Project SchedulingDocument3 pagesNew Developments in Project SchedulingالمهندسالمدنيNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 3Document4 pagesAssignment # 3Natasha SaleemNo ratings yet
- Agile Estimating and PlanningDocument6 pagesAgile Estimating and PlanningElNo ratings yet
- What Is Project ManagementDocument19 pagesWhat Is Project Managementgill27888No ratings yet
- Application of Network Scheduling Techniques in The Project ManagementDocument14 pagesApplication of Network Scheduling Techniques in The Project Managementgcc_5083708No ratings yet
- Method StudyDocument23 pagesMethod Studypravin nirmaleNo ratings yet
- Group9 IT4520QDocument6 pagesGroup9 IT4520QVũ Đức AnhNo ratings yet
- Specific Answers Are Given To The Questions, Students Need To Modify Their Answers As Per The Questions or Case Given in The Paper.Document14 pagesSpecific Answers Are Given To The Questions, Students Need To Modify Their Answers As Per The Questions or Case Given in The Paper.Lokesh BhattaNo ratings yet
- Lec#03Document23 pagesLec#03Muhammad MoizNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 110Document5 pages02 Handout 110Eliza ColomaNo ratings yet
- Course Mba - 2 Semester Subject Assignment MB0044 - Set 2: Production and Operations ManagementDocument12 pagesCourse Mba - 2 Semester Subject Assignment MB0044 - Set 2: Production and Operations Managementkct_thomasNo ratings yet
- Distinguish Between Aggregate Production Planning and Material Requirement PanningDocument10 pagesDistinguish Between Aggregate Production Planning and Material Requirement PanningDesu mekonnenNo ratings yet
- UK Space Agency: International Partnerships Programme: Monitoring & Evaluation (M&E) Tools and TechniquesDocument13 pagesUK Space Agency: International Partnerships Programme: Monitoring & Evaluation (M&E) Tools and TechniquesJimmy DagupanNo ratings yet
- StraMa Report WPS OfficeDocument54 pagesStraMa Report WPS OfficeDAVERICK DE LEONNo ratings yet
- BSBPMG522 - Task 1Document5 pagesBSBPMG522 - Task 1sharingdaastradingNo ratings yet
- IE Lab Manual Expt 1Document5 pagesIE Lab Manual Expt 1Rajat DubeyNo ratings yet
- Quality Management in ProjectsDocument10 pagesQuality Management in Projectsselinasimpson2601No ratings yet
- Economics 102221Document7 pagesEconomics 102221Hossam Mohamed Ahmed ahmedNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Construction Operations - A 1.1Document11 pages1.0 Construction Operations - A 1.1Anfield FaithfulNo ratings yet
- PM Terms Concepts Tasks RisksDocument21 pagesPM Terms Concepts Tasks RisksViraja GuruNo ratings yet
- Operation Supply Chain ManagementDocument17 pagesOperation Supply Chain ManagementMeet VermaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Budget: Break Even Point AnalysisDocument6 pagesCorporate Budget: Break Even Point AnalysisMayurRawoolNo ratings yet
- Heizer SummaryDocument27 pagesHeizer Summarychandra kiranNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Project ManagementDocument11 pagesGlossary of Project ManagementJ SM100% (1)
- Final Project of Project MagtDocument29 pagesFinal Project of Project Magttempcad100% (1)
- Master of Business Administration-MBA Semester 4: Project Management - PM0015Document8 pagesMaster of Business Administration-MBA Semester 4: Project Management - PM0015Harsha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Important Aspects of HR: Assignment-6Document4 pagesImportant Aspects of HR: Assignment-6JAISHINI SIVARAM 2023259No ratings yet
- Chapter-3-Methods Engineering and Operations AnalysisDocument30 pagesChapter-3-Methods Engineering and Operations AnalysismtdestaNo ratings yet
- Section A-2Document7 pagesSection A-2Karo100% (1)
- Chapter 5. Project Management: What Is A Project Plan?Document10 pagesChapter 5. Project Management: What Is A Project Plan?Mominul MominNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem Facility Planning NotesDocument126 pages6th Sem Facility Planning NotesManikant SAh75% (57)
- SMU MBA 3rd Sem Assignments - Operation ManagementDocument8 pagesSMU MBA 3rd Sem Assignments - Operation ManagementRahul Thekkiniakath100% (1)
- 2.purchasing Tools and Techniques PPT NotesDocument82 pages2.purchasing Tools and Techniques PPT NotesFauzanNo ratings yet
- Sigmato Operations Club Guide to Operations ManagementDocument40 pagesSigmato Operations Club Guide to Operations ManagementshakeDNo ratings yet
- Statistical tools for project analysisDocument2 pagesStatistical tools for project analysisanugraha vasanNo ratings yet
- AI in CAPPDocument6 pagesAI in CAPPDhanabal Palanisamy PNo ratings yet
- Project Management Portal: Title of The ProjectDocument24 pagesProject Management Portal: Title of The ProjectPraful SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Project Management-Aspublished PDFDocument13 pagesProject Management-Aspublished PDFPrince McGershon100% (1)
- Project Management BasicsDocument18 pagesProject Management BasicsBehlool BharmalNo ratings yet
- Ppce Essay Two MarksDocument29 pagesPpce Essay Two Markskarthiksubramanian94No ratings yet
- The Management Spectrum: People, Product, Process and Project in Software EngineeringDocument9 pagesThe Management Spectrum: People, Product, Process and Project in Software EngineeringPoonam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1Nasr AlabdaliNo ratings yet
- Rail Track Material Catalogue Nov17Document44 pagesRail Track Material Catalogue Nov17Manoj BallaNo ratings yet
- CSWIP Welding Inspection Notes and QuestionsDocument133 pagesCSWIP Welding Inspection Notes and Questionslram70100% (20)
- Papers-1: Telegram To JoinDocument1 pagePapers-1: Telegram To JoinManoj BallaNo ratings yet
- International StandardDocument10 pagesInternational StandardManoj BallaNo ratings yet
- API 510 Exam - 5C - Answer - KeyDocument1 pageAPI 510 Exam - 5C - Answer - KeyManoj BallaNo ratings yet
- Welding Inspector Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesWelding Inspector Interview QuestionsValli Raju91% (23)
- Combined ChecklistDocument9 pagesCombined ChecklistKrishnaBanjareNo ratings yet
- Fabrication Guide PDFDocument96 pagesFabrication Guide PDFbookpp100% (2)
- Combined ChecklistDocument9 pagesCombined ChecklistKrishnaBanjareNo ratings yet
- WELDER TRAINING: CURRICULUM FOR WELDING APPRENTICESDocument34 pagesWELDER TRAINING: CURRICULUM FOR WELDING APPRENTICESManoj BallaNo ratings yet
- Welded Steel PenstockDocument63 pagesWelded Steel PenstockIfnu Setyadi100% (1)
- API 510 Sample QuestionsDocument10 pagesAPI 510 Sample Questionsbichibtech1No ratings yet
- Pressure Shaft Installation Methodology PDFDocument8 pagesPressure Shaft Installation Methodology PDFRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument18 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationRatnakumarChittoorNo ratings yet
- NEB Submission for Enbridge Line 3 Replacement Program AppendixDocument14 pagesNEB Submission for Enbridge Line 3 Replacement Program AppendixVelpandian ManiNo ratings yet
- AsmeDocument11 pagesAsmeManoj BallaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Party-NDT-CCS-Post Weld Heat Treatement Procedure For SAPID Approval PDFDocument11 pages3rd Party-NDT-CCS-Post Weld Heat Treatement Procedure For SAPID Approval PDFManoj Balla100% (1)
- Weld Cracking PDFDocument5 pagesWeld Cracking PDFjuanNo ratings yet
- P&id NotesDocument17 pagesP&id NotesFitriana SarifahNo ratings yet
- CSWIP Welding Inspection Plate Section PracticalDocument31 pagesCSWIP Welding Inspection Plate Section PracticalManoj Balla100% (3)
- 13.march (GulfJobPaper - Com)Document6 pages13.march (GulfJobPaper - Com)Manoj BallaNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Interpretation: Radiographs of WeldsDocument22 pagesRadiographic Interpretation: Radiographs of WeldsManoj BallaNo ratings yet
- 29 May Assignment Abroad TimesDocument2 pages29 May Assignment Abroad TimesManoj BallaNo ratings yet
- Especificaciones Tanques de AceroDocument6 pagesEspecificaciones Tanques de AcerojhobanybernalNo ratings yet
- ASNT Level III MT Questions and Answers PDFDocument20 pagesASNT Level III MT Questions and Answers PDFManoj Balla100% (5)
- UT Thickness ProcedureDocument8 pagesUT Thickness ProcedureManoj Balla100% (3)
- Pipe Chart PDFDocument2 pagesPipe Chart PDFCarlos Rivera0% (1)
- BS en 1711 (2000)Document24 pagesBS en 1711 (2000)Jindarat KasemsooksakulNo ratings yet
- 19 P PDFDocument9 pages19 P PDFManoj BallaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing For LVL 1 & 2 Vol.2Document48 pagesUltrasonic Testing For LVL 1 & 2 Vol.2Mohd Nazirul Fahmi100% (2)
- Omnibus Rules On LeavesDocument33 pagesOmnibus Rules On Leavesjay dz100% (1)
- Self-Introduction For A CareerDocument11 pagesSelf-Introduction For A Careerabegail libuitNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan High Court rules medical representatives fall under SPE ActDocument6 pagesRajasthan High Court rules medical representatives fall under SPE ActUNIVERSITY LAW COLLEGE BHUBANESWARNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 3Document2 pagesIndividual Assignment 3Mutiara Nuvi NafisahNo ratings yet
- Amonetize LTD Distribution IODocument4 pagesAmonetize LTD Distribution IOMarouane KassemiNo ratings yet
- Dellaportas, S. (2013) PDFDocument11 pagesDellaportas, S. (2013) PDFHans WakhidaNo ratings yet
- Awatin Vs AvantgardeDocument1 pageAwatin Vs AvantgardeJessie Albert CatapangNo ratings yet
- Form Aplly ToyotaDocument6 pagesForm Aplly Toyotaapi-3810279No ratings yet
- WRAP Thesis Lamusse 1982Document457 pagesWRAP Thesis Lamusse 1982Vishal RamlallNo ratings yet
- Mu0012 SLM Unit 15 TextDocument357 pagesMu0012 SLM Unit 15 TextArun MohanNo ratings yet
- CD ActionPlan 12-2jiDocument16 pagesCD ActionPlan 12-2jiJewl AgustinNo ratings yet
- ECON 1002 NOTES ON CHAPTERS 15-17Document52 pagesECON 1002 NOTES ON CHAPTERS 15-17sashawoody167No ratings yet
- Health InsuranceDocument35 pagesHealth InsuranceSujal ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Hospital ManagerDocument3 pagesHospital ManagerOkello George PatrickNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Recruitment and Selection Practice at Commercial Bank of EthiopiaDocument72 pagesEffectiveness of Recruitment and Selection Practice at Commercial Bank of EthiopiaamanuelNo ratings yet
- SIP - Awareness of Financial Planning in Emerging Indian Market On HDFC LifeDocument74 pagesSIP - Awareness of Financial Planning in Emerging Indian Market On HDFC LifeManish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tangazo La Kazi Camartec, January 2022 PDFDocument4 pagesTangazo La Kazi Camartec, January 2022 PDFEmanuel John BangoNo ratings yet
- LLW2602 Exam PreperationDocument11 pagesLLW2602 Exam PreperationNabeelah AngamiaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Authority Ruling on Canteen GSTDocument12 pagesGujarat Authority Ruling on Canteen GSTVivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Employee Shortage in Manufacturing SectorDocument28 pagesA Study On Employee Shortage in Manufacturing Sectordarshak2110No ratings yet
- Tort II Worksheet 1 (Vicarious Liability)Document4 pagesTort II Worksheet 1 (Vicarious Liability)Brian PetersNo ratings yet
- Business CombinationDocument18 pagesBusiness CombinationJoynul AbedinNo ratings yet
- Carpentry: Carpenter (Disambiguation) Carpenters (Disambiguation) Skilled TradeDocument8 pagesCarpentry: Carpenter (Disambiguation) Carpenters (Disambiguation) Skilled Tradeeek.the.katNo ratings yet
- Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited LPG Bottling Plant, Bhitoni TENDER NO. BHTN: LPG: TEND: 26:2021-2022Document31 pagesBharat Petroleum Corporation Limited LPG Bottling Plant, Bhitoni TENDER NO. BHTN: LPG: TEND: 26:2021-2022Tender 247No ratings yet
- How to Achieve Successful Living Through Psychological InsightDocument221 pagesHow to Achieve Successful Living Through Psychological InsightMagicien1No ratings yet
- Industry Code of Practice For Management of Occupational Noise Exposure PDFDocument75 pagesIndustry Code of Practice For Management of Occupational Noise Exposure PDFMohd AbidNo ratings yet
- Hiring A Plant Manager at Dynamo IndustriesDocument4 pagesHiring A Plant Manager at Dynamo IndustriesAshis LambaNo ratings yet
- Lincoln Electric's Failure to Adapt Incentive System InternationallyDocument8 pagesLincoln Electric's Failure to Adapt Incentive System InternationallyHari ShankarNo ratings yet
- Case Study 5 Apple and Its Suppliers Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument4 pagesCase Study 5 Apple and Its Suppliers Corporate Social Responsibilitygopika surendranathNo ratings yet
- Isolation GuideDocument28 pagesIsolation GuidejhoniNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)From EverandAutodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Mastering Autodesk Inventor 2014 and Autodesk Inventor LT 2014: Autodesk Official PressFrom EverandMastering Autodesk Inventor 2014 and Autodesk Inventor LT 2014: Autodesk Official PressRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Geometrical Tolerancing Desk Reference: Creating and Interpreting ISO Standard Technical DrawingsFrom EverandThe Geometrical Tolerancing Desk Reference: Creating and Interpreting ISO Standard Technical DrawingsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- SolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 2 (Surface Design, Mold Tools, and Weldments)From EverandSolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 2 (Surface Design, Mold Tools, and Weldments)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Fusion 360 | Step by Step: CAD Design, FEM Simulation & CAM for Beginners.From EverandFusion 360 | Step by Step: CAD Design, FEM Simulation & CAM for Beginners.No ratings yet
- Beginning AutoCAD® 2020 Exercise WorkbookFrom EverandBeginning AutoCAD® 2020 Exercise WorkbookRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Autodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersFrom EverandAutodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersNo ratings yet