Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Project Report 2
Uploaded by
Ark DuttaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Project Report 2
Uploaded by
Ark DuttaCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYSICS PROJECT
REPORT
2013-2014
SUBODH PUBLIC SCHOOL
SUBMITTED BY: GUIDED BY:
SPARSH DUTTA MRS.AJAYSHREESHARMA
S-2A H.O.D(PHYSICS)
ROLL NO: S-3822
CERTIFICATE OF
AUTHENTICITY
This is to certify that SPARSH DUTTA, a student of class XII has
successfully completed the project report on the topic: IR Security
Sensor Using A Full Wave Rectifier Circuit under the
guidance of Mrs. Ajayshree Sharma (Subject Teacher).
This project is absolutely genuine and does not indulge in plagiarism of
any kind. The references taken in making this project have been declared
at the end of this report.
Signature ( Subject Teacher) Signature ( Examiner)
ACKNOWLEGDEMENT
The project could have never been possible without the support
of various sources. It is extremely impossible to thank every
individual who has helped me in completing this project. Some
people have helped in the basic formularization and there were
sources that helped me in giving the ideas a physical
form/shape. I am extremely grateful to my teacher,
Mrs. Ajayshree Sharma, for his invaluable guidance in the
project right from the beginning. Her vital support helped the
project to take a logical and suitable shape.
I take this opportunity to thank the School authorities, for
extending their full support and cooperation in the project.
Last but not the least; I would like to thank everyone who has
offered a helping hand when required.
INTRODUCTION
The IR Security Sensor Using A Full Wave Rectifier
Circuit can be of great use in day to day life. The device
for the circuit uses a full wave rectifier circuit which is
used to rectify all the alternating current components from
A.C Mains into direct current. The two alternating halves
of an alternating current are rectified in full wave rectifier
circuit which is advantage over half wave rectifier. Most
electronic circuit cannot withstand such a huge amount of
power which is coming from A.C Mains.
Therefore this rectifier circuit has a lot of employment in
day to day life.
MATERIAL REQUIRED
Connecting Wires
Plywood
A Transformer
A Capacitor
L.E.Ds
P-N Junction Diodes
Insulating Tapes
Solder Machine, Solder Wax and Flux
IR Security Sensor
Resistors
A Plug Wire -1M
A Toy Car For Demonstration
DETAILS OF MATERIAL REQUIRED
Connecting wires and a plug - A normal insulated copper
wire able to withstand 230 250 v is required.
Single lead wire - Thin wire with one single strand of
copper well Insulated and able to conduct a current of 1
ampere or a D.C current efficiently.
A circuit board -A normal board of mica facilitated with
clips to simplify the connection.
A small box - To place the equipments safely.
A bulb - To test the output voltage whether Direct or not.
A 6-0-6 transformer-Transformer is a device used to
change the voltage of an alternating current. The
transformer which converts low voltage to high voltage is
called a step up transformer whereas the one which
converts high voltage to low voltage is called a step down
transformer. It consists of a laminated core consisting of
two coils, a primary & a secondary coil. In a step up the
number of turns in the secondary is greater that that of the
primary and the reverse in a step down transformer. Here
we use a step down transformer which steps down 230V to
6V between the secondary terminals and the center tap.
A CAPACITOR-The ability of a metal to store electric
charges measures the capacitances of a conductor. It
provides high impedance to Alternating Current and stores
them while all the D.C components are let to pass. There
are different types of capacitors
o PARALLEL PLATE CAPACITOR
o SPHERICAL CAPACITOR
o CYLINDRICLAL CAPACITOR
Here we use capacitor of 1000 m F & 25 v.
A Resistor - A resistor is an electronic components whose
resistance value tells us about the opposition it offers to the
flow of electric current. Resistance is measured in ohms.
P-N junction Diodes -When one side of a semiconductor
crystal (Germanium or silicon) is doped with acceptor
impurity atoms and the other side with donor impurity
atoms a P-N junction is formed. It is also called
semiconductor or crystal diode. When diffusion of the two
regions occur a resultant potential barrier is created
between the two sides due to migration of electrons and
holes. When the diode is connected with P side to positive
terminal of a battery & N side to ve terminal it is said to
be forward biased & reverse biased when reversed. In
forward biasing the applied positive potential repels the
holes and turns a current is made to flow overcoming the
Internal potential Barrier. While in reverse biasing the ve
electrons 1st attract the holes and widen the Barrier and
then only the repulsion between the inner electrons occur
and current flows. So theoretically no current flows
through due to the widening of the Potential barrier but
practically a very
small current does flows through.
Different types of diodes are present
Zener diode
P-N junction diode
LED
LAD
Solar cell
Here we use a P-N junction diode. The grayish ring
indicated the N side and the Black colouration the P side.
Finally, small equipments such as a soldering iron to solder
the lead, Blades, holders, insulation tapes to insulate the
wire from shocking and sand paper to rub the oxidized
wire ends are used.
IR SENSOR- This Sensor is having two diodes in which
continuos current is flowing and one diode is acting as a
thrower of infrared waves and other is receiver of infrared
waves.
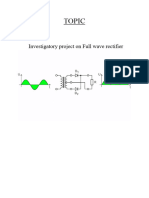
CONNECTION DETAILS
Connections are done as in the circuit. The A.C. supply is
given to both the input wires of the transformer and the
two ends of the secondary coil is given to the P side of the
two diodes and the N side of the diodes are twined and
then connected to one end of the Capacitor and the other
end to the center tap lead and to the resistor.
Further, the other end of capacitor with the diode
connection is connected to the other end of the resistor.
WORKING
1st when the A.C. is supplied to the transformer, it steps down the
220V main supply to 6 volts. It has a capability of delivering a current
of 500mA. The 6 volts A.C. appearing across the secondary is the
RMS value and the peak value is 8.4 volts.
During the 1
st
half cycle of the A.C. input Diode D1 is forward biased
and a current I flows in the circuit in the direction S1D1ABEOS1.
During this time diode D2 is reverse biased. So it does not conduct any
electric current. During the next half cycle the diode D2 is forward and
D1 is reversed. Hence D2 conducts current in the direction
S2D2ABEOS2 and D1 does not conduct any current. In subsequent half
cycles of the A.C current the above processes are repeated. In both the
half cycles it is clear that current flows through the resistor in only one
direction ABE. Even though the voltage across RL is unidirectional it
will still contain a few A.C components. This is filtered and made
smooth using a capacitor, which filters 99% of the A.C current. A
resistor is then used to adjust the output voltage. We can then test the o/p
Voltage using a multi-meter.
By the use of more number of diodes the efficiency can be increase to
a maximum of 94.6%.
Here we only use 2 diodes.
The use of multiple capacitors also nearly filters all A.C components
from the supply and resistance is adjusted for the required output. As
this is a simple circuit, only one capacitor and a resistance is being used.
But there will be slight factor of A.C. current still left in the output but it
is negligible.
RECTIFIED D.C VOLTAGE
PHOTO GALLERY
PHOTO GALLERY
BIBILIOGRAPHY
1) Electronic projects Blog for beginners by A.K Manini
2) H.C VERMA XIIth
3) S.L ARORA PHYSICS XIIth
4) NCERT based CBSE text for XIIth
5) Website: www.Google.com
THANKS TO ALL.
You might also like
- Full Wave Rectifier Constructed to Rectify AC into DCDocument12 pagesFull Wave Rectifier Constructed to Rectify AC into DCManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Phy Project FileDocument16 pagesPhy Project FileCadever Y.T100% (1)
- Full Wave Rectifier Project PDFDocument17 pagesFull Wave Rectifier Project PDFApoorva Panchal100% (6)
- KVS Physics ProjectDocument11 pagesKVS Physics ProjectLokesh MaliNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument14 pagesFull Wave RectifierCYBER HUTNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Cell Internal ResistanceDocument13 pagesFactors Affecting Cell Internal ResistanceHardik RohitNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Class 12 CbseDocument20 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Class 12 Cbsesyed50% (6)
- Transformer (Class 12 Investigatory Project)Document22 pagesTransformer (Class 12 Investigatory Project)Soniya GiriNo ratings yet
- Sanjay Rathore: Wireless Power TransferDocument24 pagesSanjay Rathore: Wireless Power TransferKamleshNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument6 pagesHalf Wave RectifierAnmol Dubey33% (3)
- Computer Investigatory ProjectDocument23 pagesComputer Investigatory ProjectMohammed MustafaNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronics Project on LEDs, Solar Cells and PhotodiodesDocument25 pagesOptoelectronics Project on LEDs, Solar Cells and Photodiodesrahuhl100% (1)
- DC Motor (P)Document16 pagesDC Motor (P)Ankit KumarNo ratings yet
- Automatic Lamp Using Transistor & LDR - Class 12 Physics Investigatory Project Free PDF Downl..Document20 pagesAutomatic Lamp Using Transistor & LDR - Class 12 Physics Investigatory Project Free PDF Downl..Babu Lal100% (1)
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument12 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectGaurav Baman67% (6)
- Converesion of Galvanometer Into VoltmeterDocument5 pagesConveresion of Galvanometer Into VoltmeterMukdar Ka SikanderNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project: by Tarun Singh of XII B, Manav Rachna International SchoolDocument11 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: by Tarun Singh of XII B, Manav Rachna International Schoolraj60% (5)
- Wirelesspowertransferreport2 PDFDocument26 pagesWirelesspowertransferreport2 PDFsuman vvabNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Investigatory ProjectDocument14 pagesPHYSICS Investigatory ProjectRKNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Class 12 On RectifierDocument14 pagesPhysics Project Class 12 On RectifierShubham BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class Xii PDFDocument19 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class Xii PDFRahulNo ratings yet
- Photodiode Project Explains Working and ApplicationsDocument10 pagesPhotodiode Project Explains Working and ApplicationsLokesh MaliNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Internal Resistance/Emf Ofa: Submitted By: Ayushi ShakyaDocument12 pagesFactors Affecting Internal Resistance/Emf Ofa: Submitted By: Ayushi ShakyaAvinash Kumar100% (1)
- Project Semi ConductorDocument20 pagesProject Semi ConductorSahil SinghNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project Physics - Class 12Document7 pagesInvestigatory Project Physics - Class 12Sahana KannanNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Parth Doshi: Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesPresented By: Parth Doshi: Physics Investigatory Projectparth doshiNo ratings yet
- LIFI PROJECT Un-UpdatedDocument15 pagesLIFI PROJECT Un-UpdatedISHIKKA ISHIKKANo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Class 12Document13 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Class 12nidhi sengarNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEDocument21 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEMaverick ShadeNo ratings yet
- Investigatory ProjectDocument9 pagesInvestigatory ProjectMahesh Sahu69% (13)
- On Mutual InductionDocument14 pagesOn Mutual InductionVaishali ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Electromagnetic Train (Hyperloop)Document11 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Electromagnetic Train (Hyperloop)Cherish BinnyNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry NcertSolutions Chapter 11 IntextDocument10 pages12 Chemistry NcertSolutions Chapter 11 IntextAditya kaushikNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula and Notes For Class 12 CBSE Board Chapter 7 ALTERNATING CURRENTDocument11 pagesPhysics Formula and Notes For Class 12 CBSE Board Chapter 7 ALTERNATING CURRENTkaruna25% (4)
- Physics ProjectDocument20 pagesPhysics ProjectJai BansalNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project by Divyam GiriDocument23 pagesInvestigatory Project by Divyam GiriPriyanshu GiriNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Class 12Document16 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Class 12new movies100% (1)
- SIBAN Ip ProjectDocument21 pagesSIBAN Ip ProjectDrezzing GamingNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project: Name: Shantanu Singh Class: 12 C' Kendriya Vidyalaya Pitampura, DelhiDocument26 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Name: Shantanu Singh Class: 12 C' Kendriya Vidyalaya Pitampura, DelhiRitik Kumar NayakNo ratings yet
- Transformer: Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesTransformer: Physics Investigatory ProjectSonu100% (1)
- Cbs Public SchoolDocument17 pagesCbs Public SchoolNawab Jatin YadavNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Project FileDocument26 pagesClass 12 Physics Project FileDeepan KumarNo ratings yet
- Portable Mobile ChargerDocument9 pagesPortable Mobile Chargermohamed AasisNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorsDocument6 pagesSemiconductorsSargam PantNo ratings yet
- Vdocument - in Chemistry Project Class 12 Variation of Conductance of Electrolytes WithDocument22 pagesVdocument - in Chemistry Project Class 12 Variation of Conductance of Electrolytes WithSashi KanthNo ratings yet
- Photodiode Investigatory ProjectDocument25 pagesPhotodiode Investigatory ProjectSajjad AliNo ratings yet
- Working Model of Physics For Class 12 - (Find The Best PDFDocument5 pagesWorking Model of Physics For Class 12 - (Find The Best PDFAnand Kumar0% (2)
- Capacitance and Its ApplicationDocument31 pagesCapacitance and Its ApplicationSuardi F. Seiei0% (1)
- Activity - 2 - To Assemble The Component of An Electric CircuitDocument1 pageActivity - 2 - To Assemble The Component of An Electric CircuitAtul Kumar Mishra100% (1)
- Physics Project BoardDocument31 pagesPhysics Project BoardSukalpo BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project: Pinaki Bandyopadhyay XII - C'Document20 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Pinaki Bandyopadhyay XII - C'Vipin SinghaiNo ratings yet
- Harish Physics ProjectDocument15 pagesHarish Physics Projectjnv bhindNo ratings yet
- Sriaansh Kapoor Sriaansh Kapoor Physics ISC: 2017-18 Physics ISC: 2017-18 Xii-A Xii-ADocument29 pagesSriaansh Kapoor Sriaansh Kapoor Physics ISC: 2017-18 Physics ISC: 2017-18 Xii-A Xii-ASai SangaviNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project: Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierDocument15 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierRitvikTiwariNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument22 pagesFull Wave Rectifierriturajparashar2006No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument11 pagesPhysicspraveensivan22No ratings yet
- Full Wave ProjectDocument23 pagesFull Wave ProjectThe Geruaa100% (1)
- Physics Projec1Document10 pagesPhysics Projec1koshilaranu36No ratings yet
- Critical ReasoningDocument26 pagesCritical ReasoningArk DuttaNo ratings yet
- 05 CollisionsDocument4 pages05 Collisionsmonu991100% (1)
- Effects of Pollution on Human Health and EnvironmentDocument1 pageEffects of Pollution on Human Health and EnvironmentArk DuttaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compound InfoDocument48 pagesChemical Compound InfoArk DuttaNo ratings yet
- Lattice SeminarDocument48 pagesLattice SeminarNaina JabbarNo ratings yet
- Paper H3 - Mock Set 6 - MSchemeDocument17 pagesPaper H3 - Mock Set 6 - MSchemeH Aslam100% (4)
- Legrand BelankoDocument15 pagesLegrand Belankobilja.malaNo ratings yet
- Auto Crane 5005H User ManualDocument98 pagesAuto Crane 5005H User ManualJim RNo ratings yet
- SC1000 60HZ Cummins GeneratorDocument4 pagesSC1000 60HZ Cummins GeneratorChen CarolineNo ratings yet
- Pipelining VerilogDocument26 pagesPipelining VerilogThineshNo ratings yet
- Ciara Mae G. Daguio Civil Engineer ResumeDocument1 pageCiara Mae G. Daguio Civil Engineer ResumeCiara Mae DaguioNo ratings yet
- Energy Landscapes: Applications To Clusters, Biomolecules and Glasses (Cambridge Molecular Science)Document6 pagesEnergy Landscapes: Applications To Clusters, Biomolecules and Glasses (Cambridge Molecular Science)darlyNo ratings yet
- Math8 Q1 Module8of8 SolvingRationalALgebraicEquationsIn2Variables v2Document24 pagesMath8 Q1 Module8of8 SolvingRationalALgebraicEquationsIn2Variables v2Jumar MonteroNo ratings yet
- MV Capacitor CalculationDocument1 pageMV Capacitor CalculationPramod B.WankhadeNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument12 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Genbio 2 Module 1 Genetic Engineering ProcessDocument26 pagesGenbio 2 Module 1 Genetic Engineering Processeaishlil07No ratings yet
- STT041 and STT041.1 PDFDocument59 pagesSTT041 and STT041.1 PDFHayrah Lawi100% (2)
- Rohtak:: ICT Hub For E-Governance in HaryanaDocument2 pagesRohtak:: ICT Hub For E-Governance in HaryanaAr Aayush GoelNo ratings yet
- Xtract V 3 0 8Document72 pagesXtract V 3 0 8Don Ing Marcos LeónNo ratings yet
- Head Barista Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesHead Barista Job Descriptionbarber rocxNo ratings yet
- Last Service ReportDocument4 pagesLast Service ReportSandeep NikhilNo ratings yet
- Contanuity Case StudyDocument14 pagesContanuity Case StudyUsama TariqNo ratings yet
- Interview@InfosysDocument13 pagesInterview@InfosysSudheer KumarNo ratings yet
- Algorithmic Composer: Openmusic and Chaos - Omchaos LibraryDocument11 pagesAlgorithmic Composer: Openmusic and Chaos - Omchaos LibrarysophochaNo ratings yet
- G5 - CLC 30Document5 pagesG5 - CLC 30Phuong AnhNo ratings yet
- Swimming at Key Stages 1 and 2 Schemes of Work and Session Plans For Advanced SwimmersDocument20 pagesSwimming at Key Stages 1 and 2 Schemes of Work and Session Plans For Advanced SwimmersShadrack MutisoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Ob Perception ReDocument23 pagesChapter - 4 Ob Perception Rep bbNo ratings yet
- PGT Lesson Plan#1Document1 pagePGT Lesson Plan#1Bart T Sata'oNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: PhysicsDocument12 pagesSri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: PhysicsSridhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Logistics RegressionDocument14 pagesLogistics RegressiondownloadarticleNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument10 pagesQuestionsmfoNo ratings yet
- 4Ps of Marketing Among Selected Resorts in Cabanatuan CityDocument5 pages4Ps of Marketing Among Selected Resorts in Cabanatuan CityKomal sharmaNo ratings yet
- Biology Thesis by SlidesgoDocument39 pagesBiology Thesis by SlidesgoKristian Hezekiah DuyoganNo ratings yet
- Macro To Roll Exalted 3e Die in Foundry VTTDocument5 pagesMacro To Roll Exalted 3e Die in Foundry VTTtcherban100% (1)