Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Seismic Inversion
Uploaded by
jose_regueiro_4100%(5)100% found this document useful (5 votes)
503 views44 pagesPaper by Carlos CObos
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPaper by Carlos CObos
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(5)100% found this document useful (5 votes)
503 views44 pagesSeismic Inversion
Uploaded by
jose_regueiro_4Paper by Carlos CObos
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 44
Seismic Inversion
Pre and Post Stack
Carlos Cobos
September 2010
Outline
What is Seismic Inversion?
Vertical Resolution
Low Frequency Model Estimation
Post Stack Seismic Inversion
Pre Stack Seismic Inversion
Observations
Outline
What is Seismic Inversion?
Vertical Resolution
Low Frequency Model Estimation
Post Stack Seismic Inversion
Pre Stack Seismic Inversion
Observations
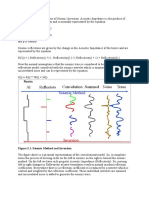
What is Seismic Inversion?
Seismic inversion is the process of
converting seismic reflection data
into seismic impedance (volumetric
rock properties).
Seismic Inversion Classification
Seismic
Inversion
Deterministic
Stochastic
Band Limited Inversion
Generalized Linear Inversion
Sparse Spike
Parametric (Gaussian)
Non-Parametric
Post-Stack
(Single)
Pre-Stack or
Elastic
(Simultaneous)
Post-Stack
(Single)
General Seismic Inversion Work Flow
Low Frequency
Model
Seismic
Data
Wavelet
Extraction
Inversion
QC Impedance
Data
Seismic Inversion Limitations
Vertical Resolution: The vertical resolution
of the seismic impedance is limited by the
bandwidth of the input seismic data.
Low Frequency Model: The accuracy of
the calculated impedance volume is
affected by artifacts in the low frequency
model.
Outline
What is Seismic Inversion?
Vertical Resolution
Low Frequency Model Estimation
Post Stack Seismic Inversion
Pre Stack Seismic Inversion
Observations
Vertical Resolution
A typical deterministic inversion exhibits
a vertical resolution of approximately
/4. At a frequency of 30 Hz and
assuming a P-wave velocity of 9000 ft/s,
the tuning wavelength (/4) is 75 ft.
Vertical Resolution
1 20 Hz Ricker Wavelet
2 30 Hz Ricker Wavelet
3 40 Hz Ricker Wavelet
4 60 Hz Ricker Wavelet
5 80 Hz Ricker Wavelet
Inverted with Generalized
Linear Inversion
1 20 Hz Ricker Wavelet
2 30 Hz Ricker Wavelet
3 40 Hz Ricker Wavelet
4 60 Hz Ricker Wavelet
5 80 Hz Ricker Wavelet
Original Seismic Data
Central Frequency: 30 Hz
Average Velocity: 12500 ft/sec
Vertical Resolution: 104 ft
High Resolution Spectral Inversion
Central Frequency: 310 Hz
Average Velocity: 12500 ft/sec
Vertical Resolution: 10 ft
Original Seismic Data
Central Frequency: 30 Hz
Average Velocity: 12500 ft/sec
Vertical Resolution: 104 ft
High Resolution Spectral Inversion
Central Frequency: 310 Hz
Average Velocity: 12500 ft/sec
Vertical Resolution: 10 ft
Outline
What is Seismic Inversion?
Vertical Resolution
Low Frequency Model Estimation
Post Stack Seismic Inversion
Pre Stack Seismic Inversion
Observations
Low Frequency Model
Due to the band limited nature of the
seismic data, seismic inversion cannot find
a unique solution. Therefore, two types of
data are needed for the inversion process:
the seismic data and a low impedance
model that constrains the possible
solutions.
Low Frequency Model
Low frequency models are derived from well log
data, NMO or pre-stack time migrated velocities.
Low frequency models generated from well log data
are influenced by the amount of wells and the
interpolation algorithm used for the model creation.
On the other hand, seismic velocities models are, in
many cases, too smooth for a high resolution
inversion process.
Raw Dense Interval Velocities
Interval Velocities
After Spatial Smoothing
Interval Velocities After REVEL
Interval Velocities After REVEL
with Seismic Overlay
Outline
What is Seismic Inversion?
Vertical Resolution
Low Frequency Model Estimation
Post Stack Seismic Inversion
Pre Stack Seismic Inversion
Observations
General Inversion Process
Relative
Impedance Trace
Absolute
Impedance Trace
Wavelet
Reflectivity Trace
Seismic Trace
Synthetic Trace
Low Frequency
Model
High Resolution Velocity Model
Post Stack Inversion Generalized
Linear Inversion
[m*g]/[cc*sec]
High Resolution Post Stack Inversion
Generalized Linear Inversion
[m*g]/[cc*sec]
Post Stack Inversion Generalized
Linear Inversion
[m*g]/[cc*sec]
High Resolution Post Stack Inversion
Generalized Linear Inversion
[m*g]/[cc*sec]
Outline
What is Seismic Inversion?
Vertical Resolution
Low Frequency Model Estimation
Post Stack Seismic Inversion
Pre Stack Seismic Inversion
Observations
Why Pre-Stack Inversion?
1. The seismic inversion process is better
constrained if S-wave information is
included into the minimization process.
2. Information carried by a pair of seismic
attributes is typically more robust than
the information obtained by a single
seismic attributes.
Why Pre-Stack Inversion?
0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.2
8000
8500
9000
9500
10000
10500
11000
Probability Density
V
p
[
f
t
/
s
e
c
]
0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.2
3500
4000
4500
5000
5500
6000
Probability Density
V
s
[
f
t
/
s
e
c
]
0.4 0.2 0 0.2 0.4
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.5
2.6
2.7
Probability Density
B
u
l
k
D
e
n
s
i
t
y
[
g
r
/
c
c
]
0.2 0.1 0 0.1 0.2
1.9
2
2.1
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.5
x 10
4
Probability Density
A
c
o
u
s
t
i
c
I
m
p
e
d
a
n
c
e
Sands-Shales Elastic Properties
AVO Intercept-Gradient Statistic
Success
Rate
Brine
Success
Rate
Gas
Success
Rate
Shale
Success
Rate
Total
Information
Entropy
Intercept 0.52 0.84 0.54 0.61 0.33
Gradient 0.47 0.63 0.62 0.59 0.30
Inter-Grad 1 1 1 1 1.09
Why Pre-Stack Inversion?
1 2 3 4
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
Ro G Rp Rs AI EI Ip Is
Information Carried By single
Attribute
0.9
0.95
1
1.05
1.1
1.15
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
R0-G
Rp-Rs
AI-EI
Ip-Is
Information Carried By Pair of
Attributes
Fusions Flow for High Resolution
Simultaneous Absolute Impedance Inversion
BRAVO
TM
REVEL
TM
Low Frequency Models
P-Impedance S-Impedance
Reflectivity Sections
P-Reflectivity S-Reflectivity
High Resolution
Reflectivity Sections
P-Reflectivity S-Reflectivity
High Resolution
Impedance Sections
P-Impedance S-Impedance
Rock Properties Analysis
Rock Properties Analysis
Outline
What is Seismic Inversion?
Vertical Resolution
Low Frequency Model Estimation
Post Stack Seismic Inversion
Pre Stack Seismic Inversion
Observations
Observations
1. The combination of high resolution velocity
residual analysis and high resolution spectral
inversion coupled with seismic inversion
engines improve the accuracy and vertical
resolution of the final absolute impedance
volume.
2. Simultaneous elastic inversion is the most
robust deterministic inversion method because
it is better constrained by the inclusion of S-
wave information into the minimization
process.
You might also like
- Seismic Inversion PDFDocument73 pagesSeismic Inversion PDFAiman Zaini100% (1)
- Seismic Inversion Techniques for Improved Reservoir CharacterizationDocument10 pagesSeismic Inversion Techniques for Improved Reservoir Characterizationbambus30100% (1)
- Seabed Seismic Techniques: QC and Data Processing KeysFrom EverandSeabed Seismic Techniques: QC and Data Processing KeysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Post-stack Seismic InversionDocument174 pagesPost-stack Seismic Inversionsantosmonetta2100% (2)
- SEISMIC INVERSIONDocument122 pagesSEISMIC INVERSIONanima1982No ratings yet
- Seismic Inversion and AVO applied to Lithologic Prediction - Shear Wave Analysis and InversionDocument48 pagesSeismic Inversion and AVO applied to Lithologic Prediction - Shear Wave Analysis and Inversionanima1982100% (1)
- 586 Joint Inversion OverviewDocument36 pages586 Joint Inversion OverviewMustapha Chettouh100% (1)
- Session 11 - Seismic Inversion (II)Document78 pagesSession 11 - Seismic Inversion (II)RizkaNo ratings yet
- Interpretation Seismic Amplitude Anomaly-AVODocument175 pagesInterpretation Seismic Amplitude Anomaly-AVODRRPRASADNo ratings yet
- Measuring AVO UncertaintyDocument45 pagesMeasuring AVO Uncertaintyagus_smrNo ratings yet
- Interpretation Seismic Amplitude Anomaly-AVO - DR - rpraSADDocument190 pagesInterpretation Seismic Amplitude Anomaly-AVO - DR - rpraSADDRRPRASADNo ratings yet
- Seismic Attributes - TectonicsDocument56 pagesSeismic Attributes - TectonicsMirza Ali100% (1)
- Seismic Inversion Basics, Procedure, & LimitationDocument25 pagesSeismic Inversion Basics, Procedure, & LimitationNafees UllahNo ratings yet
- Aapg Cusc - Geophysics For GeologistsDocument175 pagesAapg Cusc - Geophysics For GeologistsalimahrougNo ratings yet
- AVO Analysis and Lithology PredictionDocument64 pagesAVO Analysis and Lithology Predictionanima1982No ratings yet
- Migration Techniques and Principles ExplainedDocument48 pagesMigration Techniques and Principles Explainedniksr91100% (2)
- Seismic Inversion2Document43 pagesSeismic Inversion2Djibril Idé AlphaNo ratings yet
- Seismic Inversion in CarbonatesDocument6 pagesSeismic Inversion in Carbonatesmohamed_booksNo ratings yet
- QBB-2043 Seismic VelocityDocument65 pagesQBB-2043 Seismic VelocityredwanasisNo ratings yet
- HAGI - Velocity Model Building PresentationDocument58 pagesHAGI - Velocity Model Building PresentationAgung Sandi AgustinaNo ratings yet
- Seismic migration problems and solutionsDocument77 pagesSeismic migration problems and solutionsnaivedya_mishra100% (2)
- Seismic Processing 3Document169 pagesSeismic Processing 3Temitayo Ologun100% (1)
- Seismic ReflectionDocument84 pagesSeismic Reflectionginozky100% (5)
- A review of key principles and developments in AVO analysisDocument24 pagesA review of key principles and developments in AVO analysisMohamed Abdel-FattahNo ratings yet
- 6b. AVO TheoryDocument32 pages6b. AVO Theorymohammad_khazaidiNo ratings yet
- Seismic Inversion WorkflowDocument12 pagesSeismic Inversion WorkflowNurlia AduNo ratings yet
- 3D Structural Geology in "X" Area PDFDocument55 pages3D Structural Geology in "X" Area PDFzamridNo ratings yet
- Basic AVO TheoryDocument8 pagesBasic AVO Theoryprincess0607100% (1)
- The Seismic Inversion MethodDocument128 pagesThe Seismic Inversion Methodgodfrey edezuNo ratings yet
- Seismic Velocity, Attenuation (Q), and AnisotropyDocument22 pagesSeismic Velocity, Attenuation (Q), and Anisotropyintang pingkiNo ratings yet
- Making sense of AVO and seismic inversionDocument57 pagesMaking sense of AVO and seismic inversiona1341365100% (2)
- 10 Seismic StratigraphyDocument48 pages10 Seismic Stratigraphyzemabder100% (2)
- Depthteam Express: Fast and Easy Depth Conversion For InterpretersDocument140 pagesDepthteam Express: Fast and Easy Depth Conversion For InterpretersVladutiu RaduNo ratings yet
- Inversion LandL InTouchDocument19 pagesInversion LandL InTouchAdi Danu100% (3)
- PE20M004 - Seismic Amplitude Interpretation and AVO AnalysisDocument32 pagesPE20M004 - Seismic Amplitude Interpretation and AVO AnalysisNAGENDR_006100% (3)
- Seismic ExplorDocument45 pagesSeismic Explorzeze_13No ratings yet
- AVO AnalysisDocument23 pagesAVO Analysisوجدي بلخيرية0% (1)
- 7 AVO Cross PlotDocument63 pages7 AVO Cross Plotanima1982No ratings yet
- Interpretation of Seismic Amplitudes and Hydrocarbon SignaturesDocument65 pagesInterpretation of Seismic Amplitudes and Hydrocarbon SignaturesAiman ZainiNo ratings yet
- InterpretationDocument171 pagesInterpretationDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Quick QC of Velocities in PetrelDocument6 pagesQuick QC of Velocities in PetrelVeronica Arrigoni100% (1)
- Technical Note: Ardmore Field Extended Elastic Impedance StudyDocument22 pagesTechnical Note: Ardmore Field Extended Elastic Impedance StudyAz Rex100% (1)
- Anisotropic PSDM in PracticeDocument3 pagesAnisotropic PSDM in PracticehimanshugstNo ratings yet
- Seismic Inversion1Document23 pagesSeismic Inversion1Djibril Idé Alpha100% (1)
- Improved AVO Fluid Detection and Lithology Discrimination Using Lamé Petrophysical Parameters - CSEG Recorder OnlineDocument6 pagesImproved AVO Fluid Detection and Lithology Discrimination Using Lamé Petrophysical Parameters - CSEG Recorder OnlinesusisoburNo ratings yet
- StrataDocument286 pagesStrataVivekSonker100% (1)
- Seismic Interpretation MNADocument68 pagesSeismic Interpretation MNAShahbaz Gul100% (3)
- Methods of Seismic Data ProcessingDocument410 pagesMethods of Seismic Data ProcessingAaron Gamboa100% (1)
- Wavelets Lecture - CleanDocument31 pagesWavelets Lecture - CleanquangNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Inversion of PP and PS Seismic DataDocument40 pagesSimultaneous Inversion of PP and PS Seismic DataMahmoud Eloribi100% (1)
- Reservoir Characterization Using Seismic InversionDocument18 pagesReservoir Characterization Using Seismic InversionMASAGUS MANGKU GAMANo ratings yet
- Seismic Velocity Sources Depth Conversion MethodsDocument32 pagesSeismic Velocity Sources Depth Conversion MethodsDavid John MarcusNo ratings yet
- An Inversion PrimerDocument8 pagesAn Inversion Primerlagrima_baNo ratings yet
- Advances in Subsurface Data AnalyticsFrom EverandAdvances in Subsurface Data AnalyticsShuvajit BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Structural Geological Interpretation from Seismic ImagesFrom EverandAtlas of Structural Geological Interpretation from Seismic ImagesAchyuta Ayan MisraNo ratings yet
- Tectonics of Sedimentary Basins: Recent AdvancesFrom EverandTectonics of Sedimentary Basins: Recent AdvancesCathy BusbyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Understanding the Bouguer Anomaly: A Gravimetry PuzzleFrom EverandUnderstanding the Bouguer Anomaly: A Gravimetry PuzzleRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Time Lapse Approach to Monitoring Oil, Gas, and CO2 Storage by Seismic MethodsFrom EverandTime Lapse Approach to Monitoring Oil, Gas, and CO2 Storage by Seismic MethodsNo ratings yet
- Complex Seismic Trace Analysis: M. T. Taner, F. Koehler, and R. E. SheriffDocument23 pagesComplex Seismic Trace Analysis: M. T. Taner, F. Koehler, and R. E. Sheriffjose_regueiro_4No ratings yet
- By Jose Regueiro S. Universidad Simbn Bolivar Caracas, KzezuelaDocument3 pagesBy Jose Regueiro S. Universidad Simbn Bolivar Caracas, Kzezuelajose_regueiro_4No ratings yet
- Geote Appl (: SofarDocument5 pagesGeote Appl (: Sofarjose_regueiro_4No ratings yet
- AVO en Norte de PariaDocument10 pagesAVO en Norte de Pariajose_regueiro_4No ratings yet
- Middle Magdalena prospects technical reviewDocument3 pagesMiddle Magdalena prospects technical reviewjose_regueiro_4No ratings yet
- Essential petrophysical formulaeDocument12 pagesEssential petrophysical formulaeJuan Francisco ViveirosNo ratings yet
- Seismic Facies and Hydrocarbon Potential of Carbonate Reservoirs in Ramp SettingsDocument13 pagesSeismic Facies and Hydrocarbon Potential of Carbonate Reservoirs in Ramp SettingsRuth Santos NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Recommended Hardware for HRS 10.3Document1 pageRecommended Hardware for HRS 10.3jose_regueiro_4No ratings yet
- Curriculumvitae December 2017 EnglishDocument4 pagesCurriculumvitae December 2017 Englishjose_regueiro_4No ratings yet
- Seismic Studio Tutorial - Part 4 "Stack QC": Boulder, Colorado USA November, 2004Document33 pagesSeismic Studio Tutorial - Part 4 "Stack QC": Boulder, Colorado USA November, 2004jose_regueiro_4No ratings yet
- Pseudo-Sonics, Synthetics and The Lay of The LandDocument4 pagesPseudo-Sonics, Synthetics and The Lay of The Landjose_regueiro_4No ratings yet
- Seismic Data Processing Using VISTA 2D-3D - v10-CM-Dlw-houstonDocument140 pagesSeismic Data Processing Using VISTA 2D-3D - v10-CM-Dlw-houstonLili89% (9)
- Tuning Strech AVODocument14 pagesTuning Strech AVOjose_regueiro_4No ratings yet
- Venezuela Atlas 2004 Example PagesDocument12 pagesVenezuela Atlas 2004 Example Pagesjose_regueiro_4No ratings yet
- Avo BackgroundDocument102 pagesAvo Backgroundjose_regueiro_4No ratings yet
- CentroLago Line 142Document1 pageCentroLago Line 142jose_regueiro_4No ratings yet
- Kalkomey 1997 TLEDocument5 pagesKalkomey 1997 TLEPatrick EllisNo ratings yet
- The Rolle of Surgery in Oncology: Surgery Departement Medical Faculty Ukrida UniversityDocument25 pagesThe Rolle of Surgery in Oncology: Surgery Departement Medical Faculty Ukrida UniversityGian Alodia RisamasuNo ratings yet
- Qualitative data measurements are measurements of categorical variables and can be displayed as types. Qualitative data are non-numerical measurementsDocument22 pagesQualitative data measurements are measurements of categorical variables and can be displayed as types. Qualitative data are non-numerical measurementsnew rhondaldNo ratings yet
- Sharpe RatioDocument7 pagesSharpe RatioSindhuja PalanichamyNo ratings yet
- Bollinger, Ty M. - Cancer - Step Outside The Box (2009)Document462 pagesBollinger, Ty M. - Cancer - Step Outside The Box (2009)blah80% (5)
- KM UAT Plan - SampleDocument10 pagesKM UAT Plan - Samplechristd100% (1)
- Sea Creatures List, Prices, Shadow Sizes, and Times ACNH - Animal Crossing New Horizons (Switch) Game8Document1 pageSea Creatures List, Prices, Shadow Sizes, and Times ACNH - Animal Crossing New Horizons (Switch) Game8botonlouietNo ratings yet
- John 1.1 (106 Traduções) PDFDocument112 pagesJohn 1.1 (106 Traduções) PDFTayna Vilela100% (1)
- Quarter 3 - Module 8: The Power (Positivity, Optimism and Resiliency) To CopeDocument3 pagesQuarter 3 - Module 8: The Power (Positivity, Optimism and Resiliency) To Copejonalyn felipe100% (1)
- BOSS OS SeminarDocument23 pagesBOSS OS Seminarparam tube100% (1)
- Soal Uts Clea 2022-2023Document2 pagesSoal Uts Clea 2022-2023estu kaniraNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Resolution Day SpeechDocument1 pagePakistan Resolution Day SpeechTariq Hayat100% (10)
- Marxist Approaches in AnthropologyDocument30 pagesMarxist Approaches in AnthropologyLions_Read_Theory100% (1)
- Jsi Eng Paper 1Document4 pagesJsi Eng Paper 1Sharifah Jannatul AjilahNo ratings yet
- Aug. 16, 2019 - Friday Aug. 16, 2019 - FridayDocument3 pagesAug. 16, 2019 - Friday Aug. 16, 2019 - FridayYssh GozumNo ratings yet
- Collage of Business and Economics Department of Management (MSC in Management Extension Program)Document4 pagesCollage of Business and Economics Department of Management (MSC in Management Extension Program)MikealayNo ratings yet
- Ipw - Proposal To OrganizationDocument3 pagesIpw - Proposal To Organizationapi-346139339No ratings yet
- 50 Apo Fruits Corp V Land Bank of The PhilippinesDocument5 pages50 Apo Fruits Corp V Land Bank of The PhilippinesRae Angela GarciaNo ratings yet
- THE PHILIPPINE JUDICIAL SYSTEM: PRE-SPANISH AND SPANISH PERIODDocument17 pagesTHE PHILIPPINE JUDICIAL SYSTEM: PRE-SPANISH AND SPANISH PERIODFranchesca Revello100% (1)
- Action Plan For My Long Term GoalsDocument4 pagesAction Plan For My Long Term Goalsapi-280095267No ratings yet
- Part 3. Scaffolding Children's Understanding and Use of Language PDFDocument7 pagesPart 3. Scaffolding Children's Understanding and Use of Language PDFMaksym BuchekNo ratings yet
- Cultural Identity and Diaspora in Jhumpa Lahiri's The NamesakeDocument10 pagesCultural Identity and Diaspora in Jhumpa Lahiri's The NamesakeOlivia DennisNo ratings yet
- Pastors Sunday MessageDocument4 pagesPastors Sunday MessageDiana Janica Magalong100% (1)
- Workshop 3-6: RCS of A Cube: Introduction To ANSYS HFSSDocument11 pagesWorkshop 3-6: RCS of A Cube: Introduction To ANSYS HFSSRicardo MichelinNo ratings yet
- SQL RenzDocument11 pagesSQL RenzRenz VillaramaNo ratings yet
- Stories of Narada Pancaratra and Lord Krishna's protection of devoteesDocument9 pagesStories of Narada Pancaratra and Lord Krishna's protection of devoteesPedro RamosNo ratings yet
- Remedial 2 Syllabus 2019Document11 pagesRemedial 2 Syllabus 2019Drew DalapuNo ratings yet
- Sociology of Behavioral ScienceDocument164 pagesSociology of Behavioral ScienceNAZMUSH SAKIBNo ratings yet
- Metaverse in Healthcare-FADICDocument8 pagesMetaverse in Healthcare-FADICPollo MachoNo ratings yet
- Mrs.V.Madhu Latha: Assistant Professor Department of Business Management VR Siddhartha Engineering CollegeDocument14 pagesMrs.V.Madhu Latha: Assistant Professor Department of Business Management VR Siddhartha Engineering CollegesushmaNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Unit 6Document3 pagesGrammar - Unit 6Fátima Castellano AlcedoNo ratings yet