Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pernos Molino Sag Mantos de Oro
Uploaded by
Miguel Lamas Chacana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
160 views49 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
160 views49 pagesPernos Molino Sag Mantos de Oro
Uploaded by
Miguel Lamas ChacanaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 49
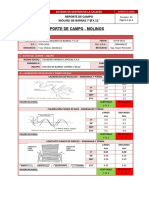
INFORME TECNICO
SIS N 56-1 / 2011
CLIENTE: COMPAA MINERA MANTOS DE ORO
EQUIPO: MOLINO SAG.
COMPONENTES: PERNOS Y TUERCAS
DESCRIPCION: VERIFICACION DE LA CALIDAD MEDIANTE ENSAYOS
MECANICOS, ANALISIS QUIMICO Y OTROS.
CONCLUSIONES Y RECOMENDACIONES.
INFORME TCNICO
SIS N 56-1 / 2011
CLIENTE: COMPAA MINERA MANTOS DE ORO
EQUIPO: MOLINO SAG
DESCRIPCIN: VERIFICACIN DE LA CALIDAD DE 4 CONJUNTOS DE PERNOS Y
TUERCAS. CONCLUSIONES Y RECOMENDACIONES.
1. INTRODUCCIN
Mantos de Oro, ha considerado necesario verificar la calidad de los pernos y tuercas
que se estan utilizando actualmente. Esto debido a que ha observado una mayor
filtracin y sospecha que algo no esta funcionando adecuadamente en el apriete de
los pernos.
Para dicha investigacin Mantos de Oro procede a enviar 4 pernos 2 cabeza
ovalada y 2 cabeza cuadrada con sus correspondientes 4 tuercas. Tambien adjunta
hoja de especificaciones de TORQUE suministrada por el fabricante de los lifter.
Adems informa que estos pernos se compran con especificaciones del fabricante
segn las siguientes normas:
Para Perno 2: SAE J 429 Grado 5
Tuerca 2: ASTM A-194 Grado 2H.
El presente informe detalla los resultados de los anlisis qumicos, ensayos
mecnicos, medicin de durezas y algunas metalografas realizadas a las tuercas, e
Indica las conclusiones finales y agrega algunas recomendaciones.
2. COMENTARIOS SOBRE ENSAYOS DE TRACCIN A 4 PERNOS.
Realizados los ensayos mecnicos a los 4 pernos se puede observar que los
valores de: rea inicial, carga de fluencia, carga mxima, tensin de fluencia, tensin
mxima, alargamiento y reduccin de rea: son cumplidos con largueza por las 4
unidades.
Ms aun, estos pernos estn en un nivel superior a la Norma J 429 la cual no cubre
el dimetro 2(solo alcanza a 1 ).
Los 4 pernos segn sus propiedades mecnicas se clasifican en la norma
ASTM-A-193-B7.
3. ANLISIS QUMICO A LOS 4 PERNOS.
Los resultados de las 4 muestras son muy homogneas y nuevamente cumplen con
las especificaciones validas para ASTM A-193 B7.
Los anlisis indican que el material base de fabricacin es un acero SAE 4140.
La norma J -429 solo indica C 0.28 0.55% y regularmente se utiliza un acero SAE
1040 en su fabricacin.
4. ANLISIS QUMICO DE LAS TUERCAS.
La composicin qumica de las tuercas comparadas con la norma ASTM-A-194
Grado 2H indica:
Ninguna tuerca cumple con el mnimo de carbono, todas se encuentran
levemente bajo el 0.40 especificado como mnimo.
La composicin qumica de las tuercas indicara que se trata de acero
SAE 4140.
5. DUREZA DE PERNOS.
La dureza de pernos segn norma J -429 Grado 5 indica de 19 a 30 HRC.
La dureza de pernos segn norma ASTM A-193 B7 indica solo el mximo 35 HRC.
Las cuatro unidades medidas tienen en promedio entre 30.7 a 33.4 HRC. Esto
nuevamente cumple con la norma ASTM A-193 B7.
6. DUREZA DE LAS TUERCAS.
La norma indicada por el proveedor es la ASTM A-194 Grado 2H y especifica una
dureza entre 25 34 HRC.
Una de las muestras tiene una dureza muy por debajo de la norma con un
promedio de 19.9 HRC.
Las tres muestras restantes estn levemente sobre el mnimo con 25.4;
25.8 y 27.1 HRC.
Esto ltimo asociado a la composicin qumica estara indicando un acero con un
tratamiento trmico deficiente, razn por la que se solicitan 2 metalografas a las
tuercas para confirmar su estructura cristalina.
7. METALOGRAFAS DE LAS TUERCAS.
El resultado de la metalografa es concordante con la dureza medida en la tuerca
blanda.
Presenta una estructura compuesta por perlita fina y presencia de ferrita en los
bordes de grano. Por tanto no tiene tratamiento de temple y revenido y no cumple
con la norma.
8. COMENTARIOS SOBRE EL TORQUE.
Al estudiar la hoja de recomendacin de torque y procedimiento de instalacin
suministrada por el proveedor, nuestros comentarios son:
La tabla indica Recommended Torque Class 7.8 8.8 Grado 5 Standard
Bolts 2800 Nm (2060 ft-lb)
Llama la atencin la propuesta del fabricante de utilizar un torque al 50%
correspondiente al perno Class 8.8.
Se sabe que la aplicacin define el torque; para el caso de tan bajo
torque, se tiende a pensar que se debe a unin con empaquetadura o al
tipo de Lifter?
Ahora si consideramos que el perno que se esta utilizando ASTM A 193 B7 de 2
podemos indicar:
El perno ASTM A 193 B7 ha demostrado la mejor performance en la
aplicacin de corazas de molino, lo que le ha valido el uso generalizado
por su excelente comportamiento a la fatiga.
Su aplicacin molinos con corazas de acero con pernos de 2 de dimetro
se realiza con torques entre 6000 y 7000 lb/pie.
Este torque concuerda con la utilizacin de la norma SAE J 1701 donde el
factor K utilizado alcanza 0.15 a 0.20. (Ver informe USACH)
Por otra parte, para el perno ASTM A 193 B7 es nefasto trabajar con
bajo torque, que en este caso solo alcanza al 33% del torque
recomendado para l.
El bajo torque en los pernos ASTM A 193 B7 causa bsicamente dos
tipos de fallas: Soltura prematura y fractura por fatiga, al aparecer
esfuerzos de flexin sobre el perno.
Llama la atencin la utilizacin de pernos de alta resistencia y la
recomendacin de torque tan bajos.
9. RECOMENDACIONES.
Mantener los pernos ASTM A 193 B7.
Cambiar las tuercas por partidas confiables con certificacin de calidad
segn ASTM A 194 2H con dureza media de 28-30 HRC.
Revisar el torque con el proveedor de los Lifter. Recordamos que el
torque depende de la aplicacin del perno y la recomendacin de la
ingeniera de diseo, ya que solo ella sabe los valores aceptables para los
Lifter, empaquetaduras, etc.
10. DOCUMENTOS ADJ UNTOS.
Este informe incluye certificado AM 4684 0101 de SIMET USACH
que indica, ensayo de traccin, anlisis qumico, dureza y metalografas.
Norma ASTM A 193
Norma ASTM A 194
Recomendacin de torque del proveedor de lifter.
Santiago, 23 de Septiembre 2011.
Mario Fandez Bustos.
Servicios Integrados Sntesis S.A.
INFORME DE RESULTADOS Fecha: 22 de Septiembre de 2011
AM-4684-0101 Revisin: 01.-
SINTESIS Pgina 1 de 15
UNIVERSIDAD DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
Departamento de Ingeniera Metalrgica
Laboratorio de Ensayos e Investigacin de Materiales SIMET-USACH
Av. Ecuador 3769, Estacin Central-Santiago-Chile
Fono-Fax: 56-2-3234780, Email: simet@usach.cl
www.simet.usach.cl
Cliente : Servicios Integrados Sntesis.
Direccin : Eliodoro Ynez N 1984 oficina 305, Providencia, Santiago.
Tipo de Muestra : Material metlico.
Cantidad : 04
Tipo de Ensayo : Ensayo de Traccin,
Qumico y Dureza.
Fecha de Recepcin : 07-09-11
Solicitante : Sr. Mario Faundez. Fecha Emisin Informe : 12-09-11
A.- Identificacin de las Muestras:
ID
ITEM Identificacin del cliente
4684-01 Identificada por el cliente como: Perno 1, cabeza ovalada.
4684-02 Identificada por el cliente como: Perno 2, cabeza ovalada.
4684-03 Identificada por el cliente como: Perno 3, cabeza cuadrada.
4684-04 Identificada por el cliente como: Perno 4, cabeza cuadrada.
4684-05 Identificada por el cliente como: Tuerca 1, Perno cabeza ovalda.
4684-06 Identificada por el cliente como: Tuerca 2, Perno cabeza ovalada.
4684-07 Identificada por el cliente como: Tuerca 3, Perno cabeza cuadrada.
4684-08 Identificada por el cliente como: Tuerca 4, Perno cabeza cuadrada.
La figura A.1 muestra una imagen de los pernos recibidos y su correspondiente
designacin para el anlisis.
La figura A.2 muestra una imagen donde se puede apreciar la identificacin de las
tuercas respectivas de cada perno.
INFORME DE RESULTADOS Fecha: 22 de Septiembre de 2011
AM-4684-0101 Revisin: 01.-
SINTESIS Pgina 2 de 15
UNIVERSIDAD DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
Departamento de Ingeniera Metalrgica
Laboratorio de Ensayos e Investigacin de Materiales SIMET-USACH
Av. Ecuador 3769, Estacin Central-Santiago-Chile
Fono-Fax: 56-2-3234780, Email: simet@usach.cl
www.simet.usach.cl
Figura A.1 Imagen de muestras recibidas e identificacin de los pernos.
Figura A.2 Imagen de muestras recibidas e identificacin de las tuercas.
4684-01
4684-02
4684-03
4684-04
4684-05
4684-06
4684-07
4684-08
INFORME DE RESULTADOS Fecha: 22 de Septiembre de 2011
AM-4684-0101 Revisin: 01.-
SINTESIS Pgina 3 de 15
UNIVERSIDAD DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
Departamento de Ingeniera Metalrgica
Laboratorio de Ensayos e Investigacin de Materiales SIMET-USACH
Av. Ecuador 3769, Estacin Central-Santiago-Chile
Fono-Fax: 56-2-3234780, Email: simet@usach.cl
www.simet.usach.cl
B.- Ensayo de Traccin:
En la tabla B.1 se presenta un resumen de los datos obtenidos del ensayo de
traccin, realizado a los pernos.
Tabla B.1 Resumen de los datos obtenidos.
ID
ITEM
rea Inicial
(mm
2
)
Carga de
Fluencia
0,2 % Def.
(Kgf)
Carga
Mxima
(Kgf)
Tensin de
Fluencia
0,2% Def.
(MPa)
Tensin
Mxima
(MPa)
Alarg.
Sobre 50
mm
(%)
Reduccin
de rea
(%)
4684-T01 119,60 10.854 12.090 890 991 21 58
4684-T02 120,57 10.881 12.200 885 992 19 59
4684-T03 120,96 9.929 11.690 805 948 19 57
4684-T04 119,40 11.043 12.550 907 1.031 17 53
Referencia
ASTM
A193 B7
2 y menor. 720 860 16 50
Referencia
SAE J 429.
Sobre 1 a 1 558 724 14 35
No existen especificaciones mecnicas para un perno de 2 pulg. De dimetro,
segn norma SAE j 429.
C.- Resultados de Anlisis Qumico:
Se realiz anlisis de composicin qumica a los pernos y tuercas.
En la tabla C.1 se muestran los valores resultantes del anlisis qumico para los
pernos y la tabla C.2 muestra los valores resultantes para las tuercas, obtenidos mediante
Espectrometra de Emisin ptica.
INFORME DE RESULTADOS Fecha: 22 de Septiembre de 2011
AM-4684-0101 Revisin: 01.-
SINTESIS Pgina 4 de 15
UNIVERSIDAD DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
Departamento de Ingeniera Metalrgica
Laboratorio de Ensayos e Investigacin de Materiales SIMET-USACH
Av. Ecuador 3769, Estacin Central-Santiago-Chile
Fono-Fax: 56-2-3234780, Email: simet@usach.cl
www.simet.usach.cl
Tabla C.1 Resultados de Anlisis qumico de las muestras de pernos.
ID
ITEM
%C %Si %Mn %P %S %Cr %Ni %Mo %Al %Cu
4684-Q01
0,398 0,291 0,79 0,021 0,019 1,09 0,005 0,160 0,033 0,007
%Co %Ti %Nb %V %W %Sn - - - %Fe
0,004 0,001 <0,0040 0,005 <0,0070 0,006 - - - Resto
ID
ITEM
%C %Si %Mn %P %S %Cr %Ni %Mo %Al %Cu
4684-Q02
0,393 0,288 0,79 0,022 0,020 1,08 0,005 0,159 0,032 0,007
%Co %Ti %Nb %V %W %Sn - - - %Fe
0,004 0,001 <0,0040 0,005 <0,0070 0,006 - - - Resto
ID
ITEM
%C %Si %Mn %P %S %Cr %Ni %Mo %Al %Cu
4684-Q03
0,382 0,233 0,78 0,026 0,026 1,03 0,082 0,179 0,011 0,174
%Co %Ti %Nb %V %W %Sn - - - %Fe
0,008 <0,0005 <0,0040 0,005 <0,0070 0,023 - - - Resto
ID
ITEM
%C %Si %Mn %P %S %Cr %Ni %Mo %Al %Cu
4684-Q04
0,386 0,234 0,79 0,028 0,028 1,03 0,079 0,180 0,010 0,175
%Co %Ti %Nb %V %W %Sn - - - %Fe
0,007 <0,0005 <0,0040 0,005 <0,0070 0,024 - - - Resto
Referencia
SAE J-429
Grado 5
1
%C %Si %Mn %P %S - - - - %Fe
0,28-
0,55
- -
Mx.
0,030
Mx.
0,050
- - - - Resto
Referencia
ASTM A
193 grado
B7
%C %Si %Mn %P %S %Cr - %Mo - %Fe
0,37-
0,49
0,15-
0,35
0,65-
1,10
Mx.
0,035
Mx.
0,040
0,75-
1,20
-
0,15-
0,25
- Resto
INFORME DE RESULTADOS Fecha: 22 de Septiembre de 2011
AM-4684-0101 Revisin: 01.-
SINTESIS Pgina 5 de 15
UNIVERSIDAD DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
Departamento de Ingeniera Metalrgica
Laboratorio de Ensayos e Investigacin de Materiales SIMET-USACH
Av. Ecuador 3769, Estacin Central-Santiago-Chile
Fono-Fax: 56-2-3234780, Email: simet@usach.cl
www.simet.usach.cl
Tabla C.2 Resultados de Anlisis qumico de muestras de tuercas.
ID
ITEM
%C %Si %Mn %P %S %Cr %Ni %Mo %Al %Cu
4684-Q05
0,388 0,178 0,76 0,022 0,020 0,98 0,079 0,155 0,008 0,145
%Co %Ti %Nb %V %W %Sn - - - %Fe
0,005 <0,0005 <0,0040 0,004 <0,0070 0,020 - - - Resto
ID
ITEM
%C %Si %Mn %P %S %Cr %Ni %Mo %Al %Cu
4684-Q06
0,382 0,174 0,76 0,023 0,021 0,97 0,083 0,155 0,008 0,145
%Co %Ti %Nb %V %W %Sn - - - %Fe
0,006 <0,0005 <0,0040 0,004 <0,0070 0,020 - - - Resto
ID
ITEM
%C %Si %Mn %P %S %Cr %Ni %Mo %Al %Cu
4684-Q07
0,391 0,222 0,76 0,021 0,020 0,96 0,084 0,181 0,009 0,099
%Co %Ti %Nb %V %W %Sn - - - %Fe
0,006 <0,0005 <0,0040 0,004 <0,0070 0,015 - - - Resto
ID
ITEM
%C %Si %Mn %P %S %Cr %Ni %Mo %Al %Cu
4684-Q08
0,391 0,221 0,76 0,021 0,020 0,97 0,086 0,182 0,009 0,098
%Co %Ti %Nb %V %W %Sn - - - %Fe
0,006 <0,0005 <0,0040 0,004 <0,0070 0,015 - - - Resto
Referencia
ASTM A-
194 Grado
2H
%C %Si %Mn %P %S - - - - %Fe
Mn.
0,40
Mx.
0,40
Mx.
1,00
Mx.
0,040
Mx.
0,050
- - - - Resto
INFORME DE RESULTADOS Fecha: 22 de Septiembre de 2011
AM-4684-0101 Revisin: 01.-
SINTESIS Pgina 6 de 15
UNIVERSIDAD DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
Departamento de Ingeniera Metalrgica
Laboratorio de Ensayos e Investigacin de Materiales SIMET-USACH
Av. Ecuador 3769, Estacin Central-Santiago-Chile
Fono-Fax: 56-2-3234780, Email: simet@usach.cl
www.simet.usach.cl
D.- Ensayo de Dureza:
La medicin de dureza fue realizada en escala Rockwell C para los pernos y tuercas.
La tabla D.1 muestra los resultados del ensayo realizado a los pernos y la tabla D.2 muestra
los resultados obtenidos para las tuercas.
Tabla D.1 Resultados de las durezas de los pernos.
ID
ITEM
Dureza
HRC
Promedio
4684-D01 30,8 30,8 30,4 30,9 30,7
4684-D02 31,1 30,9 30,7 31,0 30,9
4684-D03 30,8 31,2 30,8 31,3 31,0
4684-D04 32,1 33,1 34,4 33,8 33,4
Referencia
SAE J-429 Grado 5
Sobre 1 a 1
19-30 HRC
Referencia
ASTM A 193 grado B7
Mx. 35 HRC
Tabla D.2 Resultados de las durezas de las tuercas.
ID
ITEM
Dureza
HRC
Promedio
4684-D05 26,0 27,3 23,9 25,0 25,0 25,4 25,4
4684-D06 21,8 19,8 20,1 20,7 18,0 18,8 19,9
4684-D07 25,9 26,0 25,6 25,6 25,7 26,0 25,8
4684-D08 27,8 25,8 26,4 27,3 25,7 29,5 27,1
Referencia
ASTM A-194 Grado 2H
25-34 HRC
INFORME DE RESULTADOS Fecha: 22 de Septiembre de 2011
AM-4684-0101 Revisin: 01.-
SINTESIS Pgina 7 de 15
UNIVERSIDAD DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
Departamento de Ingeniera Metalrgica
Laboratorio de Ensayos e Investigacin de Materiales SIMET-USACH
Av. Ecuador 3769, Estacin Central-Santiago-Chile
Fono-Fax: 56-2-3234780, Email: simet@usach.cl
www.simet.usach.cl
E.- Anlisis Metalogrfico:
Con el objetivo de verificar la microestructura y posible tratamiento trmico, se
procedi a realizar anlisis metalogrfico de dos tuercas, las cuales correspondieron a la
tuerca 2 y tuerca 3.
Tuerca 2:
Para realizar el anlisis de la tuerca 2, se procedi a realizar un desbaste con lija
nmero 120 hasta la nmero 1200 y a continuacin se puli la superficie utilizando almina 1,
2 y 3 respectivamente como abrasivo. Posteriormente la muestra fue observada al
microscopio ptico. La figura E.1 muestra una imagen sin ataque a 100 aumentos de la tuerca
2, donde se pueden observar inclusiones no metlicas.
Figura E.1 Imagen atacada a 100 aumentos de la tuerca 2.
Para poder revelar las fases presentes en la muestra, se ha procedido a atacar
qumicamente la superficie con Nital al 3% (cido Ntrico 3%V/V) durante 20 segundos. La
figura E.2 muestra una imagen atacada a 100 aumentos, en donde se aprecia una estructura
perltica con ferrita en bordes de grano.
200 m
INFORME DE RESULTADOS Fecha: 22 de Septiembre de 2011
AM-4684-0101 Revisin: 01.-
SINTESIS Pgina 8 de 15
UNIVERSIDAD DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
Departamento de Ingeniera Metalrgica
Laboratorio de Ensayos e Investigacin de Materiales SIMET-USACH
Av. Ecuador 3769, Estacin Central-Santiago-Chile
Fono-Fax: 56-2-3234780, Email: simet@usach.cl
www.simet.usach.cl
Figura E.2 Imagen atacada a 100 aumentos de la tuerca 2.
Figura E.3 Imagen atacada a 500 aumentos de la tuerca 2.
40 m
200 m
INFORME DE RESULTADOS Fecha: 22 de Septiembre de 2011
AM-4684-0101 Revisin: 01.-
SINTESIS Pgina 9 de 15
UNIVERSIDAD DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
Departamento de Ingeniera Metalrgica
Laboratorio de Ensayos e Investigacin de Materiales SIMET-USACH
Av. Ecuador 3769, Estacin Central-Santiago-Chile
Fono-Fax: 56-2-3234780, Email: simet@usach.cl
www.simet.usach.cl
La figura E.3 muestra una imagen atacada a 500 aumentos de la tuerca 2, donde se
puede observar una microestructura compuesta por perlita fina y presencia de ferrita en los
bordes de grano.
La estructura no es coincidente con un tratamiento trmico de temple y revenido.
Tuerca 3:
La figura E.4 muestra una imagen sin ataque a 100 aumentos de la tuerca 3, donde
se pueden observar inclusiones no metlicas en el material.
Figura E.4 Imagen atacada a 100 aumentos de la tuerca 3.
Para poder revelar las fases presentes en la muestra, se ha procedido a atacar
qumicamente la superficie con Nital al 3% (cido Ntrico 3%V/V) durante 20 segundos. La
figura E.5 muestra una imagen atacada a 100 aumentos de la tuerca 3, donde se puede
observar una microestructura compuesta por martensita revenida, homogneamente
distribuida.
200 m
INFORME DE RESULTADOS Fecha: 22 de Septiembre de 2011
AM-4684-0101 Revisin: 01.-
SINTESIS Pgina 10 de 15
UNIVERSIDAD DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
Departamento de Ingeniera Metalrgica
Laboratorio de Ensayos e Investigacin de Materiales SIMET-USACH
Av. Ecuador 3769, Estacin Central-Santiago-Chile
Fono-Fax: 56-2-3234780, Email: simet@usach.cl
www.simet.usach.cl
Figura E.5 Imagen atacada a 100 aumentos de la tuerca 3.
Figura E.6 Imagen atacada a 500 aumentos de la tuerca 3.
200 m
40 m
INFORME DE RESULTADOS Fecha: 22 de Septiembre de 2011
AM-4684-0101 Revisin: 01.-
SINTESIS Pgina 11 de 15
UNIVERSIDAD DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
Departamento de Ingeniera Metalrgica
Laboratorio de Ensayos e Investigacin de Materiales SIMET-USACH
Av. Ecuador 3769, Estacin Central-Santiago-Chile
Fono-Fax: 56-2-3234780, Email: simet@usach.cl
www.simet.usach.cl
La figura E.6 muestra una imagen atacada a 500 aumentos de la tuerca 3, donde se puede
observar martensita revenida en su microestructura, caracterstica de un tratamiento trmico
de temple y revenido.
F. Estimacin de Torque para el material ensayado:
El siguiente clculo relaciona el torque especificado para un perno grado 5 de 2
pulgadas de dimetro, segn referencia del cliente especificado en documento PS 1.04.1
Recomended torque and installation procedure.doc
La figura F.1 muestra la tabla 1 del documento en referencia, donde se indica el
torque especificado.
Figura F.1 Imagen de tabla 1, documento en referencia.
INFORME DE RESULTADOS Fecha: 22 de Septiembre de 2011
AM-4684-0101 Revisin: 01.-
SINTESIS Pgina 12 de 15
UNIVERSIDAD DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
Departamento de Ingeniera Metalrgica
Laboratorio de Ensayos e Investigacin de Materiales SIMET-USACH
Av. Ecuador 3769, Estacin Central-Santiago-Chile
Fono-Fax: 56-2-3234780, Email: simet@usach.cl
www.simet.usach.cl
El documento indica segn tabla que el torque recomendado correspondiente para un
perno de 2, es equivalente a 2.800 Nm o 2060 ftlb.
Segn norma SAE J 1701, la relacin y clculo de torque est bajo la siguiente
ecuacin (extracto de norma SAE J 1701).
Para un torque de 2.800 y la ecuacin T=KDW, se obtiene un K=0,0844.
Considerando que los pernos son clasificables como ASTM A193 B7, equivalente a
un perno 9.8 segn norma ISO, es posible establecer que bajo 75% de un proof load de 650
Mpa, se obtiene un torque de 3.571 Nm. Este clculo fue realizado considerando un
K=0,0844 (obtenido a partir de la informacin del fabricante), lo que es considerado un K bajo.
Normalmente el K se encuentra en un rango de 0,10 a 0,15, para materiales con golilla.
Es importante sealar que el factor K, tiene importante significancia en el torque a
aplicar.
La tabla F.1 muestra la variacin del torque aplicado en funcin de la variacin del
factor K.
INFORME DE RESULTADOS Fecha: 22 de Septiembre de 2011
AM-4684-0101 Revisin: 01.-
SINTESIS Pgina 13 de 15
UNIVERSIDAD DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
Departamento de Ingeniera Metalrgica
Laboratorio de Ensayos e Investigacin de Materiales SIMET-USACH
Av. Ecuador 3769, Estacin Central-Santiago-Chile
Fono-Fax: 56-2-3234780, Email: simet@usach.cl
www.simet.usach.cl
Tabla F.1 Variacin del torque en funcin del factor K.
Perno SAE grado 5, SAE J429
Proof load 510 Mpa.
Perno ASTM A 193 grado
B7.
Proof load 650 Mpa.
Factor K Torque Nm Torque Nm
0,0844 2.802 3.571
0,1000 3.319 4.231
0,1500 4.979 6.346
0,2000 6.639 8.461
INFORME DE RESULTADOS Fecha: 22 de Septiembre de 2011
AM-4684-0101 Revisin: 01.-
SINTESIS Pgina 14 de 15
UNIVERSIDAD DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
Departamento de Ingeniera Metalrgica
Laboratorio de Ensayos e Investigacin de Materiales SIMET-USACH
Av. Ecuador 3769, Estacin Central-Santiago-Chile
Fono-Fax: 56-2-3234780, Email: simet@usach.cl
www.simet.usach.cl
G.- Comentarios:
De los anlisis realizados, es posible decir lo siguiente:
G.1 Referente a su clasificacin:
Respecto de los pernos:
Los pernos no son clasificable bajo norma SAE J 429 Grado 5, ya que estos
presentan dimetros superiores a lo especificado por la norma (dimetro menor a 1 ).
Los pernos pueden ser clasificados bajo norma ASTM A 193 grado B7, cumpliendo
con las propiedades mecnicas, composicin qumica y dureza.
Respecto a las tuercas:
Es posible decir que las cuatro muestras, no cumplen con el mnimo exigido en el
porcentaje de carbono, para la norma ASTM A 194 2H.
La tuerca identificada como tuerca 2, perno cabeza ovalada, adems, no cumple con
la dureza exigida por la norma ASTM A 194 2H.
G.2 Referente al anlisis metalogrfico de las tuercas:
Es posible decir que las tuercas analizadas presentaron tratamientos trmicos
diferentes, siendo la tuerca 2 la muestra con menor dureza y una microestructura coherente
con esta baja dureza, compuesta por perlita fina y ferrita en bordes de grano. La tuerca 2 no
presenta un tratamiento trmico de temple y revenido o tratamiento trmico deficiente.
La tuerca clasificada como 3, presenta una microestructura de martensita revenida, lo
que es coherente con un tratamiento trmico de temple y revenido.
G.3 Referente al torque de los pernos:
Es posible decir que en revisin de los torques recomendados para un perno grado 5
segn SAE J 429 y para un ASTM A193 grado B7, los torque tienen diferencias en sus
magnitudes, por lo que es posible suponer que si los pernos clasificados como ASTM A 193
grado B7 fueron torqueados bajo la especificacin de un perno grado 5 SAE J 429, el torque
se encontrara por debajo de lo recomendado.
No es posible establecer el grado de incidencia en la prestacin ya que se
desconocen las condiciones de esfuerzos del conjunto en servicio.
INFORME DE RESULTADOS Fecha: 22 de Septiembre de 2011
AM-4684-0101 Revisin: 01.-
SINTESIS Pgina 15 de 15
UNIVERSIDAD DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
Departamento de Ingeniera Metalrgica
Laboratorio de Ensayos e Investigacin de Materiales SIMET-USACH
Av. Ecuador 3769, Estacin Central-Santiago-Chile
Fono-Fax: 56-2-3234780, Email: simet@usach.cl
www.simet.usach.cl
NOTAS:
Los resultados obtenidos son vlidos slo para las muestras ensayadas y entregadas por el cliente.
Este informe no puede ser reproducido parcial ni totalmente sin la aprobacin escrita del laboratorio.
El laboratorio SIMET-USACH no se responsabiliza por las muestras ensayadas a contar de 30 das de la
fecha de emisin de informe.
Los ensayos de traccin fueron realizados en una mquina de traccin marca Tinius & Olsen Mod. Sper L,
con capacidad para 30 toneladas (certificado de calibracin IDIC N F-792, con fecha 08 julio de 2010).
Los ensayos fueron realizados con un espectrmetro de emisin de lectura directa, modelo
SPECTROMAXx.
Las mediciones de dureza fueron realizadas en un durmetro con reporte de datos digital, marca Emco
Test tipo M4R 075.
Dr. Ing. Alfredo Artigas A.
Gerente Tcnico.
Ing. Alejandro Castillo A.
Departamento de Ing. Metalrgica.
Document type Product Specification Skega Mill Linings
Date 2005-04-27 Version 4
Issued by / version by Lars Furtenbach / Mattias Karlsson Status Approved 2010-10-28
Skega Mill Linings
PRINTED PAPER COPY IS UNCONTROLLED UNAUTHORISED COPYING OR DISTRIBUTION IS PROHIBITED
PS 1.04.1 Recommended torque and
installation procedure.doc
1 (5)
1.04.1 Recommended torque and installation procedure
1.04.1.1 Recommended torque values Rubber and Poly-Met
Torque values for lifter bar attachments
Table 1. Torque values for lifter bar attachments.
Attachment channel and clamp (aluminium and steel)
Recommended
torque*
Attachment types
M
UNC
Class 7.8-8.8/Grade 5
Standard bolts
[Nm] [ftlb]
M12 1/2 70 50
H (RAC) M (RAC) Y
M16 5/8 100 75
A (RAC)
M16 5/8 150 110
L M (RAC) R
M20 3/4 150 110
B (RAC)
M20 3/4 300 220
K
M24 1 500 370
D F F2
M30 1 700 510
F F2
M36 1 1200 880
V (alu) V6 (steel)
M48 2 2800 2060
W6 (steel)
Notes: * Recommended torque is the minimum allowed for bolts of each diameter specified.
Maximum torque not to exceed recommended torque +10% (M12-M20) or +20% (M24-M48).
(RAC) Removable Attachment Clamp No bonding, detachable and recyclable.
(BAC) Bonded Attachment Channel Channel bonded to rubber. All attachments except those
designated (RAC) in table 1.
Document type Product Specification Skega Mill Linings
Date 2005-04-27 Version 4
Issued by / version by Lars Furtenbach / Mattias Karlsson Status Approved 2010-10-28
Skega Mill Linings
PRINTED PAPER COPY IS UNCONTROLLED UNAUTHORISED COPYING OR DISTRIBUTION IS PROHIBITED
PS 1.04.1 Recommended torque and
installation procedure.doc
2 (5)
Torque values for manhole covers
1.04.1.2 Cleaning and lubrication of bolts
Dirt and debris on mating threads will significantly reduce the attachment system pre-load
regardless of whether the recommended torque is attained. The bolt threads must be cleaned
after inserting the bolts through the mill shell and it is recommended that they be lubricated
using grease or heavy oil before tightening the nuts. Lubrication of the contacting surfaces
between the nut and cup washer is also suggested.
1.04.1.3 Recommended torque order
Torque order for Lifter Bar attachments
Poly-Met bars with 3 or more attachments (bolts) must be tightened in a specific order to achieve
a correct and consistent bolt tension on all attachment points. Failure to follow these
recommendations can result in bolt tension variations of 25% or more.
A specific torque order for the final tightening to reach recommended torque is required for
Poly-Met bars with 3 or more attachment points. It is important to always tighten the middle
attachments last. The torque must be applied in a sequence (between all bolts on same lifter) with
at least 2 tightening cycles on each bolt to reach recommended torque.
Final torque order for P-M bars with 3 bolts is 1-3-2.
Final torque order for P-M bars with 4 bolts is 1-4-2-3
Rubber bars or Poly-Met bars with 1 or 2 attachments (bolts) are less sensitive to the order in
which the bolts are tightened. The torque must however be applied in a sequence (between all
bolts on same lifter) with at least 2 tightening cycles on each bolt to reach recommended torque.
Torque 250 Nm / 185 ftlb
(M24 & 1 UNC)
Torque 100 Nm / 75 ftlb
(M16 & 5/8 UNC)
Document type Product Specification Skega Mill Linings
Date 2005-04-27 Version 4
Issued by / version by Lars Furtenbach / Mattias Karlsson Status Approved 2010-10-28
Skega Mill Linings
PRINTED PAPER COPY IS UNCONTROLLED UNAUTHORISED COPYING OR DISTRIBUTION IS PROHIBITED
PS 1.04.1 Recommended torque and
installation procedure.doc
3 (5)
Torque order for manhole covers
The torque must be applied in a sequence (between all pin bolts on same manhole cover) with at
least 2 tightening cycles on each bolt to reach recommended torque.
Document type Product Specification Skega Mill Linings
Date 2005-04-27 Version 4
Issued by / version by Lars Furtenbach / Mattias Karlsson Status Approved 2010-10-28
Skega Mill Linings
PRINTED PAPER COPY IS UNCONTROLLED UNAUTHORISED COPYING OR DISTRIBUTION IS PROHIBITED
PS 1.04.1 Recommended torque and
installation procedure.doc
4 (5)
1.04.1.4 Re-torque recommendations
Re-torque is required to compensate for settling & relaxation of attachment system components.
In many cases it is sufficient to re-torque all nuts just prior to mill start-up, as most of the
relaxation takes place within minutes from initial tightening.
In the case of attachment systems using long bolts (as found on grate walls) additional re-
torque is recommended to compensate for the self-adjustment / settling of components after
the mill has been put into service. Since long bolts tend to act as torsion springs during
tightening with impact tools, it is recommended that such assemblies be tightened at slow
speeds and in the lubricated condition.
Table 2. Re-torque procedure for rubber and Poly-Met linings.
Part of mill
Application
type
- Feed end head
- Shell
- Discharge end head
for overflow mills
- Grate discharge
wall
- Diaphragm wall
AG and SAG Mills
Primary Ball Mills
Rubber +10/3 m
Poly-Met all sizes
Secondary Ball Mills
Rubber +14/4.3 m
Poly-Met all sizes
Prior to start up Prior to start up
and after 2-24 hours
Diaphragm walls
not applicable for this
application
Rod Mills
(shell only)
Prior to start up
Grate discharge walls
not applicable for this
application
Diaphragm walls
not applicable for this
application
Other Mills Not required (rubber)
Prior to start up (P-M)
Prior to start up
and after 2-24 hours
Prior to start up
and after 1-4 days
Recycling Plant Ball Mills
(Waste Mills)
Prior to start up
After 1 week
Check every month
(or 500 hrs) and
retorque if value is
below 60% of
recommended
torque
Prior to start up
After 2-24 hrs
Check every month
(or 500 hrs) and
retorque if value is
below 60% of
recommended
torque
Diaphragm walls
not applicable for this
application
Document type Product Specification Skega Mill Linings
Date 2005-04-27 Version 4
Issued by / version by Lars Furtenbach / Mattias Karlsson Status Approved 2010-10-28
Skega Mill Linings
PRINTED PAPER COPY IS UNCONTROLLED UNAUTHORISED COPYING OR DISTRIBUTION IS PROHIBITED
PS 1.04.1 Recommended torque and
installation procedure.doc
5 (5)
1.04.1.5 Example of general arrangement drawing notes
General drawing note for all assembly drawings
Complete the following table with torque values from table 1 for the applicable bolt dimensions.
Recommended torque for standard hex nuts (7.8 - 8.8 Grade 5):
M12 ______ Nm (or ftlb)
M16 ______ Nm
M20 ______ Nm
M24 ______ Nm
Etc.
Torque must be applied in a sequence (between all bolts on same lifter)
with at least 2 tightening cycles on each bolt to reach recommended torque.
Examples of additional drawing notes depending on application/lining type
Combine the following drawing notes depending on application/lining type.
All lining attachments to be re-tightened to the recommended torque prior to mill start-up.
Nuts on the discharge head to be re-tightened to the recommended torque following two
(2) to 24 hours of mill operation.
Nuts on diaphragm walls to be re-tightened to the recommended torque the following day
or within four (4) days of mill operation.
A specific torque order for the final tightening to reach recommended torque is required
for Poly-Met bars with 3 or more attachment points. It is important to always tighten the
middle attachments last.
Final torque order for P-M bars with 3 bolts is 1-3-2.
Final torque order for P-M bars with 4 bolts is 1-4-2-3
Designation: A 193/A 193M 08b
Standard Specication for
Alloy-Steel and Stainless Steel Bolting Materials for High
Temperature or High Pressure Service and Other Special
Purpose Applications
1
This standard is issued under the xed designation A 193/A 193M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon () indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specication
2
covers alloy and stainless steel bolt-
ing material for pressure vessels, valves, anges, and ttings
for high temperature or high pressure service, or other special
purpose applications. The term bolting material as used in this
specication covers bars, bolts, screws, studs, stud bolts, and
wire. Bars and wire shall be hot-wrought. The material may be
further processed by centerless grinding or by cold drawing.
Austenitic stainless steel may be carbide solution treated or
carbide solution treated and strain-hardened. When strain
hardened austenitic steel is ordered, the purchaser should take
special care to ensure that Appendix X1 is thoroughly under-
stood.
1.2 Several grades are covered, including ferritic steels and
austenitic stainless steels designated B5, B8, and so forth.
Selection will depend upon design, service conditions, me-
chanical properties, and high temperature characteristics.
1.3 The following referenced general requirements are in-
dispensable for application of this specication: Specication
A 962/A 962M.
NOTE 1The committee formulating this specication has included
fteen steel types that have been rather extensively used for the present
purpose. Other compositions will be considered for inclusion by the
committee from time to time as the need becomes apparent.
NOTE 2For grades of alloy-steel bolting material suitable for use at
the lower range of high temperature applications, reference should be
made to Specication A 354.
NOTE 3For grades of alloy-steel bolting material suitable for use in
low temperature applications, reference should be made to Specication
A 320/A 320M.
1.4 Nuts for use with this bolting material are covered in
Section 14.
1.5 Supplementary Requirements S1 through S14 are pro-
vided for use when additional tests or inspection are desired.
These shall apply only when specied in the purchase order.
1.6 This specication is expressed in both inch-pound units
and in SI units. However, unless the order species the
applicable M specication designation (SI units), the material
shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
1.7 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system
must be used independently of the other. Combining values
from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the
specication. Within the text, the SI units are shown in
brackets.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3
A 153/A 153M Specication for Zinc Coating (Hot-Dip) on
Iron and Steel Hardware
A 194/A 194M Specication for Carbon and Alloy Steel
Nuts for Bolts for High Pressure or High Temperature
Service, or Both
A 320/A 320M Specication for Alloy-Steel and Stainless
Steel Bolting Materials for Low-Temperature Service
A 354 Specication for Quenched and Tempered Alloy
Steel Bolts, Studs, and Other Externally Threaded Fasten-
ers
A 788/A 788M Specication for Steel Forgings, General
Requirements
A 962/A 962M Specication for Common Requirements
for Steel Fasteners or Fastener Materials, or Both, Intended
for Use at Any Temperature from Cryogenic to the Creep
Range
B 633 Specication for Electrodeposited Coatings of Zinc
on Iron and Steel
1
This specication is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.22 on Steel Forgings and Wrought Fittings for Piping Applications and Bolting
Materials for Piping and Special Purpose Applications.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2008. Published September 2008. Originally
approved in 1936. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as A 193/A 193M-08a.
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications, see related Speci-
cation SA-193 in Section II of that Code.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standards Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
1
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Thu Oct 2 14:38:16 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
B 695 Specication for Coatings of Zinc Mechanically
Deposited on Iron and Steel
B 696 Specication for Coatings of Cadmium Mechanically
Deposited
B 766 Specication for Electrodeposited Coatings of Cad-
mium
E 18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic
Materials
E 21 Test Methods for Elevated Temperature Tension Tests
of Metallic Materials
E 112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
E 139 Test Methods for Conducting Creep, Creep-Rupture,
and Stress-Rupture Tests of Metallic Materials
E 150 Recommended Practice for Conducting Creep and
Creep-Rupture Tension Tests of Metallic Materials Under
Conditions of Rapid Heating and Short Times
4
E 151 Recommended Practice for Tension Tests of Metallic
Materials at Elevated Temperatures With Rapid Heating
and Conventional or Rapid Strain Rates
4
E 292 Test Methods for Conducting Time-for-Rupture
Notch Tension Tests of Materials
E 328 Test Methods for Stress Relaxation for Materials and
Structures
E 566 Practice for Electromagnetic (Eddy-Current) Sorting
of Ferrous Metals
E 709 Guide for Magnetic Particle Testing
E 606 Practice for Strain-Controlled Fatigue Testing
F 1940 Test Method for Process Control Verication to
Prevent Hydrogen Embrittlement in Plated or Coated
Fasteners
F 1941 Specication for Electrodeposited Coatings on
Threaded Fasteners (Unied Inch Screw Threads (UN/
UNR))
F 2329 Specication for Zinc Coating, Hot-Dip, Require-
ments for Application to Carbon and Alloy Steel Bolts,
Screws, Washers, Nuts, and Special Threaded Fasteners
2.2 ANSI Standards:
5
B18.2.1 Square and Hex Bolts and Screws
B18.2.3.1M Metric Hex Cap Screws
B18.3 Hexagon Socket and Spline Socket Screws
B18.3.1M Metric Socket Head Cap Screws
2.3 AIAG Standard:
6
AIAG B-5 02.00 Primary Metals Identication Tag Appli-
cation Standard
3. General Requirements and Ordering Information
3.1 The inquiry and orders shall include the following, as
required, to describe the desired material adequately:
3.1.1 Heat-treated condition (that is, normalized and tem-
pered, or quenched and tempered, for the ferritic materials, and
carbide solution treated (Class 1), carbide solution treated after
nishing (Class 1A), and carbide solution treated and strain-
hardened (Classes 2, 2B and 2C), for the austenitic stainless
steels; Classes 1B and 1C apply to the carbide solution-treated
nitrogen-bearing stainless steels; Class 1D applies to material
carbide solution treated by cooling rapidly from the rolling
temperature),
3.1.2 Description of items required (that is, bars, bolts,
screws, or studs),
3.1.3 Nuts, if required by purchaser, in accordance with
14.1,
3.1.4 Supplementary requirements, if any, and
3.1.5 Special requirements, in accordance with 7.1.5.1,
7.2.6, 9.1, 14.1, and 15.1.
3.2 CoatingsCoatings are prohibited unless specied by
the purchaser (See Supplementary Requirements S13 and S14).
When coated fasteners are ordered the purchaser should take
special care to ensure that Appendix X2 is thoroughly under-
stood.
4. Common Requirements
4.1 Material and fasteners supplied to this specication shall
conform to the requirements of Specication A 962/A 962M.
These requirements include test methods, nish, thread dimen-
sions, marking, certication, optional supplementary require-
ments, and others. Failure to comply with the requirements of
Specication A 962/A 962M constitutes nonconformance with
this specication. In case of conict between this specication
and Specication A 962/A 962M, this specication shall pre-
vail.
5. Manufacture (Process)
5.1 The steel shall be produced by any of the following
processes: open-hearth, basic-oxygen, electric-furnace, or
vacuum-induction melting (VIM). The molten steel may be
vacuum-treated prior to or during pouring of the ingot or strand
casting.
5.2 QualitySee Specication A 962/A 962M for require-
ments.
6. Discard
6.1 A sufficient discard shall be made to secure freedom
from injurious piping and undue segregation.
7. Heat Treatment
7.1 Ferritic Steels
7.1.1 Ferritic steels shall be allowed to cool to a temperature
below the cooling transformation range immediately after
rolling or forging. Materials to be liquid quenched shall then be
uniformly reheated to the proper temperature to rene the grain
(a group thus reheated being known as a quenching charge),
quenched in a liquid medium under substantially uniform
conditions for each quenching charge, and tempered. Materials
to be normalized and tempered or air-quenched and tempered
shall be reheated to the proper temperature to rene the grain,
cooled uniformly in air to a temperature below the transfor-
mation temperature range and tempered. The minimum tem-
pering temperature shall be as specied in Tables 2 and 3.
4
Withdrawn.
5
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
6
Available from Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG), 26200 Lahser Rd.,
Suite 200, Southeld, MI 48033, http://www.aiag.org.
A 193/A 193M 08b
2
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Thu Oct 2 14:38:16 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements (Composition, percent)
A
Type . . . . . . . . . Ferritic Steels
Grade . . . . . . . . B5 B6 and B6X
Description. . . . . . . . 5% Chromium 12 % Chromium
UNS Designation . . . . . . . . S41000 (410)
Range Product Variation, Range Product Variation
Over or Under
B
Over or Under
B
Carbon 0.10 min 0.01 under 0.080.15 0.01 over
Manganese, max 1.00 0.03 over 1.00 0.03 over
Phosphorus, max 0.040 0.005 over 0.040 0.005 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over
Silicon 1.00 max 0.05 over 1.00 max 0.05 over
Chromium 4.06.0 0.10 11.513.5 0.15
Molybdenum 0.400.65 0.05 . . . . . .
Type . . . . . . . . . . Ferritic Steels
Grade . . . . . . B7, B7M B16
Description . . . . . . . . . Chromium-Molybdenum
C
Chromium-Molybdenum-Vanadium
Product Variation, Product Variation,
Range Over or Under
B
Range Over or Under
B
Carbon 0.370.49
D
0.02 0.360.47 0.02
Manganese 0.651.10 0.04 0.450.70 0.03
Phosphorus, max 0.035 0.005 over 0.035 0.005 over
Sulfur, max 0.040 0.005 over 0.040 0.005 over
Silicon 0.150.35 0.02 0.150.35 0.02
Chromium 0.751.20 0.05 0.801.15 0.05
Molybdenum 0.150.25 0.02 0.500.65 0.03
Vanadium . . . . . . 0.250.35 0.03
Aluminum, max %
E
. . . . . . 0.015 . . .
Type Austenitic Steels,
F
Classes 1, 1A, 1D, and 2
Grade . . B8, B8A B8C, B8CA B8M, B8MA, B8M2, B8M3 B8P, B8PA
UNS Designation . . . . . . S30400 (304) S34700 (347) S31600 (316) S30500
Range
Product Variation,
Over or Under
B
Range
Product Variation,
Over or Under
B
Range
Product Variation,
Over or Under
B
Range
Product Variation,
Over or Under
B
Carbon, max 0.08 0.01 over 0.08 0.01 over 0.08 0.01 over 0.12 0.01 over
Manganese, max 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.010 over 0.045 0.010 over 0.045 0.010 over 0.045 0.010 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over
Silicon, max 1.00 0.05 over 1.00 0.05 over 1.00 0.05 over 1.00 0.05 over
Chromium 18.020.0 0.20 17.019.0 0.20 16.018.0 0.20 17.019.0 0.20
Nickel 8.011.0 0.15 9.012.0 0.15 10.014.0 0.15 11.013.0 0.15
Molybdenum . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.003.00 0.10 . . . . . .
Columbium + . . . . . . 10 x carbon 0.05 under . . . . . . . . . . . .
tantalum content, min;
1.10 max
Type . . . . . . . . . . Austenitic Steels,
F
Classes 1A, 1B, 1D, and 2
Grade . . . . . B8N, B8NA B8MN, B8MNA B8MLCuN, B8MLCuNA
UNS Designation . . . .
. . . . . .
S30451 (304N) S31651 (316N) S31254
Range
Product Variation,
Over or Under
B
Range
Product Variation,
Over or Under
B
Range Product Variation,
Over or Under
B
Carbon, max 0.08 0.01 over 0.08 0.01 over 0.020 0.005 over
Manganese, max 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over 1.00 0.03 over
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.010 over 0.045 0.010 over 0.030 0.005 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over 0.010 0.002 over
Silicon, max 1.00 0.05 over 1.00 0.05 over 0.80 0.05 over
Chromium 18.020.0 0.20 16.018.0 0.20 19.520.5 0.20
Nickel 8.011.0 0.15 10.013.0 0.15 17.518.5 0.15
Molybdenum . . . . . . 2.003.00 0.10 6.06.5 0.10
Nitrogen 0.100.16 0.01 0.100.16 0.01 0.180.22 0.02
Copper . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.501.00 . . .
A 193/A 193M 08b
3
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Thu Oct 2 14:38:16 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
TABLE 1 Continued
Type. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Austenitic Steels
F
, Classes 1, 1A, and 2
Grade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B8T, B8TA
UNS Designation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . S32100 (321)
Range
Product Variation,
Over or Under
B
Carbon, max 0.08 0.01 over
Manganese, max 2.00 0.04 over
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.010 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over
Silicon, max 1.00 0.05 over
Chromium 17.019.0 0.20
Nickel 9.012.0 0.15
Titanium 5 x (C + N) min, 0.70 max 0.05 under
Nitrogen 0.10 max . . .
Type Austenitic Steels
F
, Classes 1C and 1D
Grade B8R, B8RA B8S, B8SA
UNS Designation S20910 S21800
Range
Product Variation,
Over or Under
B
Range
Product Variation,
Over or Under
B
Carbon, max 0.06 0.01 over 0.10 0.01 over
Manganese 4.06.0 0.05 7.09.0 0.06
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.005 over 0.060 0.005 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over
Silicon 1.00 max 0.05 over 3.54.5 0.15
Chromium 20.523.5 0.25 16.018.0 0.20
Nickel 11.513.5 0.15 8.09.0 0.10
Molybdenum 1.503.00 0.10 . . . . . .
Nitrogen 0.200.40 0.02 0.080.18 0.01
Columbium + tantalum 0.100.30 0.05 . . . . . .
Vanadium 0.100.30 0.02 . . . . . .
Type Austenitic Steels
F
, Classes 1, 1A and 1D
Grade B8LN, B8LNA B8MLN, B8MLNA
UNS Designation S30453 S31653
Range
Product Variation,
Over or Under
B
Range
Product Variation,
Over or Under
B
Carbon, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over
Manganese 2.00 0.04 over 2.00 0.04 over
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.010 over 0.045 0.010 over
Sulfur, max 0.030 0.005 over 0.030 0.005 over
Silicon 1.00 0.05 over 1.00 0.05 over
Chromium 18.020.0 0.20 16.018.0 0.20
Nickel 8.011.0 0.15 10.013.0 0.15
Molybdenum . . . . . . 2.003.00 0.10
Nitrogen 0.100.16 0.01 0.100.16 0.01
A
The intentional addition of Bi, Se, Te, and Pb is not permitted.
B
Product analysisIndividual determinations sometimes vary from the specied limits on ranges as shown in the tables. The several determinations of any individual
element in a heat may not vary both above and below the specied range.
C
Typical steel compositions used for this grade include 4140, 4142, 4145, 4140H, 4142H, and 4145H.
D
For bar sizes over 3
1
2 in. [90 mm], inclusive, the carbon content may be 0.50 %, max. For the B7M grade, a minimum carbon content of 0.28 % is permitted, provided
that the required tensile properties are met in the section sizes involved; the use of AISI 4130 or 4130H is allowed.
E
Total of soluble and insoluble.
F
Classes 1 and 1D are solution treated. Classes 1, 1B, and some 1C (B8R and B8S) products are made from solution treated material. Class 1A (B8A, B8CA, B8MA,
B8PA, B8TA, B8LNA, B8MLNA, B8NA, and B8MNA) and some Class 1C (B9RA and B8SA) products are solution treated in the nished condition. Class 2 products are
solution treated and strain hardened.
A 193/A 193M 08b
4
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Thu Oct 2 14:38:16 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
TABLE 2 Mechanical Requirements Inch Products
Grade Diameter, in.
Minimum
Tempering
Temperature,
F
Tensile
Strength,
min, ksi
Yield Strength,
min, 0.2 %
offset,
ksi
Elongation
in 4D,
min, %
Reduction
of Area,
min, %
Hardness,
max
Ferritic Steels
B5
4 to 6 % chromium up to 4, incl 1100 100 80 16 50 . . .
B6
13 % chromium up to 4, incl 1100 110 85 15 50 . . .
B6X
13 % chromium up to 4, incl 1100 90 70 16 50 26 HRC
B7
Chromium-molybdenum 2
1
2 and under 1100 125 105 16 50 321 HB or
35 HRC
over 2
1
2 to 4 1100 115 95 16 50 321 HB or
35 HRC
over 4 to 7 1100 100 75 18 50 321 HB or
35 HRC
B7M
A
Chromium-molybdenum 4 and under 1150 100 80 18 50 235 HB or
99 HRB
over 4 to 7 1150 100 75 18 50 235 BHN or
99 HRB
B16
Chromium-molybdenum-vanadium 2
1
2 and under 1200 125 105 18 50 321 HB or
35 HRC
over 2
1
2 to 4 1200 110 95 17 45 321 HB or
35 HRC
over 4 to 8 1200 100 85 16 45 321 HB or
35 HRC
Grade, Diameter, in. Heat Treatment
B
Tensile
Strength,
min, ksi
Yield
Strength,
min, 0.2
% offset,
ksi
Elongation
in 4 D,
min %
Reduction
of Area,
min %
Hardness,
max
Austenitic Steels
Classes 1 and 1D; B8, B8M, B8P,
B8LN,
carbide solution treated 75 30 30 50 223 HB
C
or 96 HRB
B8MLN, all diameters
Class 1: B8C, B8T, all
diameters
carbide solution treated 75 30 30 50 223 HB
C
or 96HRB
Class 1A: B8A, B8CA, B8MA,
B8PA, B8TA, B8LNA, B8MLNA,
B8NA, B8MNA
B8MLCuNA, all diameters
carbide solution treated in the nished
condition
75 30 30 50 192 HB or 90 HRB
Classes 1B and 1D: B8N, B8MN,
and
carbide solution treated 80 35 30 40 223 HB
C
or 96 HRB
B8MLCuN, all diameters
Classes 1C and 1D: B8R, all
diameters
carbide solution treated 100 55 35 55 271 HB or 28 HRC
Class 1C: B8RA, all diameters carbide solution treated in the nished
condition
100 55 35 55 271 HB or 28 HRC
Classes 1C and 1D: B8S, all
diameters
carbide solution treated 95 50 35 55 271 HB or 28 HRC
Classes 1C: B8SA, carbide solution treated in the nished 95 50 35 55 271 HB or 28 HRC
all diameters condition
Class 2: B8, B8C, B8P, B8T, and
B8N,
D
3
4 and under
carbide solution treated and strain
hardened
125 100 12 35 321 HB or 35 HRC
over
3
4 to 1, incl 115 80 15 35 321 HB or 35 HRC
over 1 to 1
1
4 , incl 105 65 20 35 321 HB or 35 HRC
over 1
1
4 to 1
1
2 , incl 100 50 28 45 321 HB or 35 HRC
Class 2: B8M, B8MN, B8MLCuN
D
3
4 and under
carbide solution treated and strain
hardened
110 95 15 45 321 HB or 35 HRC
over
3
4 to 1 incl 100 80 20 45 321 HB or 35 HRC
Over 1 to 1
1
4 , incl 95 65 25 45 321 HB or 35 HRC
over 1
1
4 to 1
1
2 , incl 90 50 30 45 321 HB or 35 HRC
Class 2B: B8, B8M2
D
2 and under
carbide solution treated and strain
hardened
95 75 25 40 321 HB or 35 HRC
A 193/A 193M 08b
5
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Thu Oct 2 14:38:16 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
TABLE 2 Continued
Grade, Diameter, in. Heat Treatment
B
Tensile
Strength,
min, ksi
Yield
Strength,
min, 0.2
% offset,
ksi
Elongation
in 4 D,
min %
Reduction
of Area,
min %
Hardness,
max
Austenitic Steels
over 2 to 2
1
2 incl 90 65 30 40 321 HB or 35 HRC
over 2
1
2 to 3 incl 80 55 30 40 321 HB or 35 HRC
Class 2C: B8M3
D
2 and under
carbide solution treated and strain
hardened
85 65 30 60 321 HB or 35 HRC
over 2 85 60 30 60 321 HB or 35 HRC
A
To meet the tensile requirements, the Brinell hardness shall be over 200 HB (93 HRB).
B
Class 1 is solution treated. Class 1A is solution treated in the nished condition for corrosion resistance; heat treatment is critical due to physical property requirement.
Class 2 is solution treated and strain hardened. Austenitic steels in the strain-hardened condition may not show uniform properties throughout the section particularly in
sizes over
3
4 in. in diameter.
C
For sizes
3
4 in. in diameter and smaller, a maximum hardness of 241 HB (100 HRB) is permitted.
D
For diameters 1
1
2 and over, center (core) properties may be lower than indicated by test reports which are based on values determined at
1
2 radius.
TABLE 3 Mechanical Requirements Metric Products
Class Diameter, [mm]
Minimum
Tempering
Temperature,
C
Tensile
Strength,
min,
MPa
Yield Strength,
min, 0.2 %
offset,
MPa
Elongation
in 4D,
min, %
Reduction
of Area,
min, %
Hardness,
max
Ferritic Steels
B5
4 to 6 % chromium up to M100, incl 593 690 550 16 50 . . .
B6
13 % chromium up to M100, incl 593 760 585 15 50 . . .
B6X
13 % chromium up to M100, incl 593 620 485 16 50 26 HRC
B7
Chromium-molybdenum M64 and under 593 860 720 16 50 321 HB or
35 HRC
over M64 to M100 593 795 655 16 50 321 HB or
35 HRC
over M100 to M180 593 690 515 18 50 321 HB or
35 HRC
B7M
A
Chromium-molybdenum M100 and under 620 690 550 18 50 235 HB or
99 HRB
over M100 to M180 620 690 515 18 50 235 BHN or
99 HRB
B16
Chromium-molybdenum-vanadium M64 and under 650 860 725 18 50 321 HB or
35 HRC
over M64 to M100 650 760 655 17 45 321 HB or
35 HRC
over M100 to M180 650 690 585 16 45 321 HB or
35 HRC
Class Diameter, mm Heat Treatment
B
Tensile
Strength,
min,
MPa
Yield
Strength,
min, 0.2
% offset,
MPa
Elongation
in 4 D,
min %
Reduction
of Area,
min %
Hardness,
max
Austenitic Steels
Classes 1 and 1D; B8, B8M, B8P, B8LN, carbide solution treated 515 205 30 50 223 HB
C
or 96 HRB
B8MLN, all diameters
Class 1: B8C, B8T, all
diameters
carbide solution treated 515 205 30 50 223 HB
C
or 96HRB
Class 1A: B8A, B8CA, B8MA, B8PA,
B8TA, B8LNA, B8MLNA, B8NA, B8MNA
B8MLCuNA, all diameters
carbide solution treated in the nished
condition
515 205 30 50 192 HB or 90 HRB
Classes 1B and 1D: B8N, B8MN, and carbide solution treated 550 240 30 40 223 HB
C
or 96 HRB
B8MLCuN, all diameters
Classes 1C and 1D: B8R, all diameters carbide solution treated 690 380 35 55 271 HB or 28 HRC
Class 1C: B8RA, all diameters carbide solution treated in the nished
condition
690 380 35 55 271 HB or 28 HRC
Classes 1C and 1D: B8S, all diameters carbide solution treated 655 345 35 55 271 HB or 28 HRC
A 193/A 193M 08b
6
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Thu Oct 2 14:38:16 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
TABLE 3 Continued
Class Diameter, mm Heat Treatment
B
Tensile
Strength,
min,
MPa
Yield
Strength,
min, 0.2
% offset,
MPa
Elongation
in 4 D,
min %
Reduction
of Area,
min %
Hardness,
max
Austenitic Steels
Classes 1C: B8SA, carbide solution treated in the nished 655 345 35 55 271 HB or 28 HRC
all diameters condition
Class 2: B8, B8C, B8P, B8T, and B8N,
D
M20 and under
carbide solution treated and strain
hardened
860 690 12 35 321 HB or 35 HRC
over M20 to M24, incl 795 550 15 35 321 HB or 35 HRC
over M24 to M30, incl 725 450 20 35 321 HB or 35 HRC
over M30 to M36, incl 690 345 28 45 321 HB or 35 HRC
Class 2: B8M, B8MN, B8MLCuN,
D
M20 and under
carbide solution treated and strain
hardened
760 655 15 45 321 HB or 35 HRC
over M20 to M24, incl 690 550 20 45 321 HB or 35 HRC
over M24 to M30, incl 655 450 25 45 321 HB or 35 HRC
over M30 to M36, incl 620 345 30 45 321 HB or 35 HRC
Class 2B: B8, B8M2,
D
M48 and under
carbide solution treated and strain
hardened
655 515 25 40 321 HB or 35 HRC
over M48 to M64, incl 620 450 30 40 321 HB or 35 HRC
over M64 to M72, incl 550 380 30 40 321 HB or 35 HRC
Class 2C: B8M3,
D
M48 and under
carbide solution treated and strain
hardened
585 450 30 60 321 HB or 35 HRC
over M48 585 415 30 60 321 HB or 35 HRC
A
To meet the tensile requirements, the Brinell hardness shall be over 200 HB (93 HRB).
B
Class 1 is solution treated. Class 1A is solution treated in the nished condition for corrosion resistance; heat treatment is critical due to physical property requirement.
Class 2 is solution treated and strain hardened. Austenitic steels in the strain-hardened condition may not show uniform properties throughout the section particularly in
sizes over M20 mm in diameter
C
For sizes M20 mm in diameter and smaller, a maximum hardness of 241 HB (100 HRB) is permitted.
D
For diameters M38 and over, center (core) properties may be lower than indicated by test reports which are based on values determined at
1
2 radius.
7.1.2 Use of water quenching is prohibited for any ferritic
grade when heat treatment is performed after heading or
threading.
7.1.3 Except as permitted below for B6X; material that is
subsequently cold drawn for dimensional control shall be
stress-relieved after cold drawing. The minimum stress-relief
temperature shall be 100 F [55 C] below the tempering
temperature. Tests for mechanical properties shall be per-
formed after stress relieving.
7.1.4 B6 and B6X materials shall be held at the tempering
temperature for a minimum time of 1 h. B6X material may be
furnished in the as-rolled-and-tempered condition. Cold work-
ing after heat treatment is permitted for B6X material provided
the nal hardness meets the requirements of Tables 2 and 3.
7.1.5 B7 and B7M bolting material shall be heat treated by
quenching in a liquid medium and tempering. For B7M
bolting, the nal heat treatment, which may be the tempering
operation if conducted at 1150 F [620 C] minimum, shall be
done after all machining and forming operations, including
thread rolling and any type of cutting. Surface preparation for
hardness testing, nondestructive evaluation, or ultrasonic bolt
tensioning is permitted.
7.1.5.1 Unless otherwise specied, material for Grade B7
may be heat treated by the Furnace, the Induction or the
Electrical Resistance method.
NOTE 4Stress-relaxation properties may vary from heat lot to heat lot
or these properties may vary from one heat-treating method to another.
The purchaser may specify Supplementary Requirement S8, when stress-
relaxation testing is desired.
7.1.6 Material Grade B16 shall be heated to a temperature
range from 1700 to 1750 F [925 to 955 C] and oil quenched.
The minimum tempering temperature shall be as specied in
Tables 2 and 3.
7.2 Austenitic Stainless Steels
7.2.1 All austenitic stainless steels shall receive a carbide
solution treatment (see 7.2.2-7.2.5 for specic requirements for
each class). Classes 1, 1B, 1C (Grades B8R and B8S only), 2,
2B, and 2C can apply to bar, wire, and nished fasteners. Class
1A (all grades) and Class 1C (grades B8RA and B8SA only)
can apply to nished fasteners. Class 1D applies only to bar
and wire and nished fasteners that are machined directly from
Class 1D bar or wire without any subsequent hot or cold
working.
7.2.2 Classes 1 and 1B, and Class 1C Grades B8R and
B8SAfter rolling of the bar, forging, or heading, whether
done hot or cold, the material shall be heated from ambient
temperature and held a sufficient time at a temperature at which
the chromium carbide will go into solution and then shall be
cooled at a rate sufficient to prevent the precipitation of the
carbide.
7.2.3 Class 1DRolled or forged Grades B8, B8M, B8P,
B8LN, B8MLN, B8N, B8MN, B8R, and B8S bar shall be
cooled rapidly immediately following hot working while the
temperature is above 1750 F [955 C] so that grain boundary
carbides remain in solution. Class 1D shall be restricted to
applications at temperatures less than 850 F [455 C].
7.2.4 Class 1A and Class 1C Grades B8RA and B8SA
Finished fasteners shall be carbide solution treated after all
rolling, forging, heading, and threading operations are com-
plete. This designation does not apply to starting material such
A 193/A 193M 08b
7
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Thu Oct 2 14:38:16 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
as bar. Fasteners shall be heated from ambient temperature and
held a sufficient time at a temperature at which the chromium
carbide will go into solution and then shall be cooled at a rate
sufficient to prevent the precipitation of the carbide.
7.2.5 Classes 2, 2B, and 2CMaterial shall be carbide
solution treated by heating from ambient temperature and
holding a sufficient time at a temperature at which the
chromium carbide will go into solution and then cooling at a
rate sufficient to prevent the precipitation of the carbide.
Following this treatment the material shall then be strain
hardened to achieve the required properties.
NOTE 5Heat treatment following operations performed on a limited
portion of the product, such as heading, may result in non-uniform grain
size and mechanical properties through the section affected.
7.2.6 If a scale-free bright nish is required; this shall be
specied in the purchase order.
8. Chemical Composition
8.1 Each alloy shall conform to the chemical composition
requirements prescribed in Table 1.
8.2 The steel shall not contain an unspecied element for
the ordered grade to the extent that the steel conforms to the
requirements of another grade for which that element is a
specied element. Furthermore, elements present in concentra-
tions greater than 0.75 weight/% shall be reported.
9. Heat Analysis
9.1 An analysis of each heat of steel shall be made by the
manufacturer to determine the percentages of the elements
specied in Section 8. The chemical composition thus deter-
mined shall be reported to the purchaser or the purchasers
representative, and shall conform to the requirements specied
in Section 8. Should the purchaser deem it necessary to have
the transition zone of two heats sequentially cast discarded, the
purchaser shall invoke Supplementary Requirement S3 of
Specication A 788.
10. Mechanical Properties
10.1 Tensile Properties:
10.1.1 RequirementsThe material as represented by the
tension specimens shall conform to the requirements pre-
scribed in Tables 2 and 3 at room temperature after heat
treatment. Alternatively, stainless strain hardened headed fas-
teners (Class 2, 2B, and 2C) shall be tested full size after strain
hardening to determine tensile strength and yield strength and
shall conform to the requirements prescribed in Tables 2 and 3.
Should the results of full size tests conict with results of
tension specimen tests, full size test results shall prevail.
10.1.2 Full Size Fasteners, Wedge Tensile TestingWhen
applicable, see 13.1.3, headed fasteners shall be wedge tested
full size. The minimum full size load applied (lbf or kN) for
individual sizes shall be as follows:
W 5 T
s
3 A
t
(1)
where:
W = minimum wedge tensile load without fracture,
T
s
= tensile strength specied in ksi or MPa in Tables 2 and
3, and
A
t
= stress area of the thread section, square inches or
square milimetres, as shown in the Cone Proof Load
Tables in Specication A 962/A 962M.
10.2 Hardness Requirements:
10.2.1 The hardness shall conform to the requirements
prescribed in Table 2. Hardness testing shall be performed in
accordance with either Specication A 962/A 962M or with
Test Methods F 606.
10.2.2 Grade B7MThe maximum hardness of the grade
shall be 235 HB or 99 HRB. The minimum hardness shall not
be less than 200 HB or 93 HRB. Conformance to this hardness
shall be ensured by testing the hardness of each stud or bolt by
Brinell or Rockwell B methods in accordance with 10.2.1. The
use of 100 % electromagnetic testing for hardness as an
alternative to 100 % indentation hardness testing is permissible
when qualied by sampling using indentation hardness testing.
Each lot tested for hardness electromagnetically shall be 100 %
examined in accordance with Practice E 566. Following elec-
tromagnetic testing for hardness a random sample of a mini-
mum of 100 pieces of each heat of steel in each lot (as dened
in 13.1.1) shall be tested by indentation hardness methods. All
samples must meet hardness requirements to permit acceptance
of the lot. If any one sample is outside of the specied
maximum or minimum hardness, the lot shall be rejected and
either reprocessed and resampled or tested 100 % by indenta-
tion hardness methods. Product that has been 100 % tested and
found acceptable shall have a line under the grade symbol.
10.2.2.1 Surface preparation for indentation hardness test-
ing shall be in accordance with Test Methods E 18. Hardness
tests shall be performed on the end of the bolt or stud. When
this is impractical, the hardness test shall be performed
elsewhere.
11. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
11.1 Bolts, screws, studs, and stud bolts shall be pointed and
shall have a workmanlike nish. Points shall be at and
chamfered or rounded at option of the manufacturer. Length of
point on studs and stud bolts shall be not less than one nor more
than two complete threads as measured from the extreme end
parallel to the axis. Length of studs and stud bolts shall be
measured from rst thread to rst thread.
11.2 Bolt heads shall be in accordance with the dimensions
of ANSI B18.2.1 or ANSI B18.2.3.1M. Unless otherwise
specied in the purchase order, the Heavy Hex Screws Series
should be used, except the maximum body diameter and radius
of llet may be the same as for the Heavy Hex Bolt Series. The
body diameter and head llet radius for sizes of Heavy Hex
Cap Screws and Bolts that are not shown in their respective
tables in ANSI B18.2.1 or ANSI B18.2.3.1M may be that
shown in the corresponding Hex Cap Screw and Bolt Tables
respectively. Socket head fasteners shall be in accordance with
ANSI B18.3 or ANSI B18.3.1M.
12. Retests
12.1 If the results of the mechanical tests of any test lot do
not conform to the requirements specied, the manufacturer
may retreat such lot not more than twice, in which case two
additional tension tests shall be made from such lot, all of
which shall conform to the requirements specied.
A 193/A 193M 08b
8
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Thu Oct 2 14:38:16 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
13. Test Specimens
13.1 Number of TestsFor heat-treated bars, one tension
test shall be made for each diameter of each heat represented in
each tempering charge. When heat treated without interruption
in continuous furnaces, the material in a lot shall be the same
heat, same prior condition, same size, and subjected to the
same heat treatment. Not fewer than two tension tests are
required for each lot containing 20 000 lb [9000 kg] or less.
Every additional 10 000 lb [4500 kg] or fraction thereof
requires one additional test.
13.1.1 For studs, bolts, screws, and so forth, one tension test
shall be made for each diameter of each heat involved in the
lot. Each lot shall consist of the following:
Diameter, in. [mm] Lot Size
1
1
8 [30] and under 1500 lb [780 kg] or fraction thereof
Over 1
1
8 [30] to 1
3
4 [42], incl 4500 lb [2000 kg] or fraction thereof
Over 1
3
4 [42] to 2
1
2 [64], incl 6000 lb [2700 kg] or fraction thereof
Over 2
1
2 [64] 100 pieces or fraction thereof
13.1.2 Tension tests are not required to be made on bolts,
screws, studs, or stud bolts that are fabricated from heat-treated
bars furnished in accordance with the requirements of this
specication and tested in accordance with 13.1, provided they
are not given a subsequent heat treatment.
13.1.3 Full Size Specimens, Headed FastenersHeaded
fasteners 1
1
2 in. in body diameter and smaller, with body
length three times the diameter or longer, and that are produced
by upsetting or forging (hot or cold) shall be subjected to full
size testing in accordance with 10.1.2. This testing shall be in
addition to tensile testing as specied in 10.1.1. The lot size
shall be as shown in 13.1.1. Failure shall occur in the body or
threaded section with no failure, or indications of failure, such
as cracks, at the junction of the head and shank.
14. Nuts
14.1 Bolts, studs, and stud bolts shall be furnished with
nuts, when specied in the purchase order. Nuts shall conform
to Specication A 194/A 194M.
15. Rejection and Rehearing
15.1 Unless otherwise specied in the basis of purchase, any
rejection based on product analysis shall be reported to the
manufacturer within 30 days from the receipt of samples by the
purchaser.
15.2 Material that shows defects subsequent to its accep-
tance at the place of manufacture shall be rejected, and the
manufacturer shall be notied.
15.3 Product AnalysisSamples that represent rejected ma-
terial shall be preserved for two weeks from the date of the test
report. In the case of dissatisfaction with the results of the test,
the manufacturer may make claim for a rehearing within that
time.
16. Certication
16.1 The producer of the raw material or nished fasteners
shall furnish a certication to the purchaser or his representa-
tive showing the results of the chemical analysis, macroetch
examination (Carbon and Alloy Steels Only), and mechanical
tests, and state the method of heat treatment employed.
16.2 Certication shall also include at least the following:
16.2.1 Astatement that the material or the fasteners, or both,
were manufactured, sampled, tested, and inspected in accor-
dance with the specication and any supplementary require-
ments or other requirements designated in the purchase order
or contract and was found to meet those requirements.
16.2.2 The specication number, year date, and identica-
tion symbol.
17. Product Marking
17.1 The marking symbol and manufacturers identication
symbol shall be applied to one end of studs
3
8 in. [10 mm] in
diameter and larger and to the heads of bolts
1
4 in. [6 mm] in
diameter and larger. (If the available area is inadequate, the
marking symbol may be placed on one end with the manufac-
turers identication symbol placed on the other end.) The
marking symbol shall be as shown in Table 4 and Table 5.
Grade B7M, which has been 100 % evaluated in conformance
with the specication, shall have a line under the marking
symbol to distinguish it from B7M produced to previous
specication revisions not requiring 100 % hardness testing.
17.2 For bolting materials, including threaded bars, fur-
nished bundled and tagged or boxed, the tags and boxes shall
carry the marking symbol for the material identication and the
manufacturers identication symbol or name.
17.3 For purposes of product marking, the manufacturer is
considered the organization that certies the fastener was
manufactured, sampled, tested, and inspected in accordance
with the specication and the results have been determined to
meet the requirements of this specication.
17.4 Bar CodingIn addition to the requirements in 17.1,
17.2, and 17.3, bar coding is acceptable as a supplementary
identication method. Bar coding should be consistent with
AIAG Standard B-5 02.00. If used on small items, the bar code
may be applied to the box or a substantially applied tag.
18. Keywords
18.1 hardness; heat treatment
TABLE 4 Marking of Ferritic Steels
Grade Marking Symbol
B5 B5
B6 B6
B6X B6X
B7 B7
B7M
A
B7M
B7M
B16 B16
B16 +
Supplement S12
B16R
A
For explanations, see 10.2.2 and 17.1.
A 193/A 193M 08b
9
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Thu Oct 2 14:38:16 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
SUPPLEMENTARY REQUIREMENTS
These requirements shall not apply unless specied in the order and in the Ordering Information,
in which event the specied tests shall be made before shipment of the product.
S1. High Temperature Tests
S1.1 Tests to determine high temperature properties shall be
made in accordance with Test Methods E 21, E 139, and E 292,
and Practices E 150 and E 151.
S2. Charpy Impact Tests
S2.1 Charpy impact tests based on the requirements of
Specication A 320/A 320M, Sections 6 and 7, shall be made
as agreed between the manufacturer and the purchaser. When
testing temperatures are as low as those specied in Speci-
cation A 320/A 320M, bolting should be ordered to that speci-
cation in preference to this specication.
TABLE 5 Marking of Austenitic Steels
Class Grade Marking Symbol
Class 1 B8 B8
B8C B8C
B8M B8M
B8P B8P
B8T B8T
B8LN B8F or B8LN
B8MLN B8G or B8MLN
Class 1A B8A B8A
B8CA B8B or B8CA
B8MA B8D or B8MA
B8PA B8H or B8PA
B8TA B8J or B8TA
B8LNA B8L or B8LNA
B8MLNA B8K or B8MLNA
B8NA B8V or B8MA
B8MNA B8W or B8MNA
B8MLCuNA B9K or B8MLCuNA
Class 1B B8N
B8MN
B8MLCuN
B8N
B8Y or B8MN
B9J or B8MLCuN
Class 1C B8R B9A or B8R
B8RA B9B or B8RA
B8S B9D or B8S
B8SA B9F or B8SA
Class 1D B8 B94
B8M B95
B8P B96
B8LN B97
B8MLN B98
B8N B99
B8MN B100
B8R B101
B8S B102
Class 2 B8 B8SH
B8C B8CSH
B8P B8PSH
B8T B8TSH
B8N B8NSH
B8M B8MSH
B8MN B8YSH
B8MLCuN B0JSH
Class 2B B8M2
B8
B9G or B8M2
B9
Class 2C B8M3 B9H or B8M3
A 193/A 193M 08b
10
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Thu Oct 2 14:38:16 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
S3. 100 % Hardness Testing of Grade B7M
S3.1 Each Grade B7M bolt or stud shall be tested for
hardness by indentation method and shall meet the require-
ments specied in Table 2.
S4. Hardness Testing of Grade B16
S4.1 For bolts or studs 2
1
2 in. [65 mm] or smaller, the
hardness for Grade B16 shall be measured on or near the end
of each bolt or stud using one of the methods prescribed in
10.2.1 for the Brinell or Rockwell C test. The hardness shall be
in the range 253319 HB or 2534 HRC.
S5. Product Marking
S5.1 Marking and manufacturers identication symbols
shall be applied to one end of studs and to the heads of bolts of
all sizes. (If the available area is inadequate, the marking
symbol may be marked on one end and the manufacturers
identication symbol marked on the other end.) For bolts
smaller than
1
4 in. [6 mm] in diameter and studs smaller
than
3
8 in. [10 mm] in diameter and for
1
4 in. [6 mm] in
diameter studs requiring more than a total of three symbols, the
marking shall be a matter of agreement between the purchaser
and the manufacturer.
S6. Stress Relieving
S6.1 A stress-relieving operation shall follow straightening
after heat treatment.
S6.2 The minimum stress-relieving temperature shall be
100 F [55 C] below the tempering temperature. Tests for
mechanical properties shall be performed after stress relieving.
S7. Magnetic Particle Inspection
S7.1 Bars shall be magnetic particle examined in accor-
dance with Guide E 709. Bars with indications of cracks or
seams are subject to rejection if the indications extend more
than 3 % of the diameter into the bar.
S8. Stress-Relaxation Testing
S8.1 Stress-Relaxation Testing, when required, shall be
done in accordance with Test Methods E 328. The test shall be
performed at 850 F [454 C] for a period of 100 h. The initial
stress shall be 50 M psi [345 MPa]. The residual stress at 100
h shall be 17 M psi [117 MPa] minimum.
S9. Grain Size Requirements for Non H Grade
Austenitic Steels Used Above 1000 F
S9.1 For design metal temperatures above 1000 F [540
C], the material shall have a grain size of No. 7 or coarser as
determined in accordance with Test Methods E 112. The grain
size so determined shall be reported on the Certicate of Test.
S10. Hardness Testing of Class 2 Bolting Materials for
ASME Applications
S10.1 The maximum hardness shall be Rockwell C35 im-
mediately under the thread roots. The hardness shall be taken
on a at area at least
1
8 in. [3 mm] across, prepared by
removing threads, and no more material than necessary shall be
removed to prepare the at areas. Hardness determinations
shall be made at the same frequency as tensile tests.
S11. Thread Forming
S11.1 Threads shall be formed after heat treatment. Appli-
cation of this supplemental requirement to grade B7M or the
grades listed in 7.2.4 is prohibited.
S12. Stress Rupture Testing of Grade B16
S12.1 One test shall be made for each heat treat lot. Testing
shall be conducted using a combination test bar in accordance
with Test Methods E 292. Rupture shall occur in the smooth
section of each test specimen. The test shall be conducted at
1100 F [595 C] and 20 ksi [140 MPa]. The test shall be
continued until the sample ruptures. Rupture life shall be 25 h
minimum. Testing is not required on material less than
1
2 in.
[12 mm] thick.
S12.2 When a purchase order for fasteners invokes S12, the
product marking supplied shall be B16R.
S13. Coatings on Bolting Materials
S13.1 It is the purchasers responsibility to specify in the
purchase order all information required by the coating facility.
Examples of such information may include but are not limited
to the following:
S13.1.1 Reference to the appropriate coating specication
and type, thickness, location, modication to dimensions, and
hydrogen embrittlement relief.
S13.1.2 Reference to Specications A 153/A 153M, B 633,
B 695, B 696, B 766, or F 1941, F 2329, or Test Method
F 1940, or other standards.
S14. Marking Coated Bolting Materials
S14.1 Material coated with zinc shall have an asterisk (*)
marked after the grade symbol. Material coated with cadmium
shall have a plus sign (+) marked after the grade symbol.
A 193/A 193M 08b
11
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Thu Oct 2 14:38:16 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
APPENDIXES
(Nonmandatory Information)
X1. STRAIN HARDENING OF AUSTENITIC STEELS
X1.1 Strain hardening is the increase in strength and
hardness that results from plastic deformation below the
recrystallization temperature (cold work). This effect is pro-
duced in austenitic stainless steels by reducing oversized bars
or wire to the desired nal size by cold drawing or other
process. The degree of strain hardening achievable in any alloy
is limited by its strain hardening characteristics. In addition, the
amount of strain hardening that can be produced is further
limited by the variables of the process, such as the total amount
of cross-section reduction, die angle, and bar size. In large
diameter bars, for example, plastic deformation will occur
principally in the outer regions of the bar so that the increased
strength and hardness due to strain hardening is achieved
predominantly near the surface of the bar. That is, the smaller
the bar, the greater the penetration of strain hardening.
X1.2 Thus, the mechanical properties of a given strain
hardened fastener are dependent not just on the alloy, but also
on the size of bar from which it is machined. The minimum bar
size that can be used, however, is established by the congu-
ration of the fastener so that the conguration can affect the
strength of the fastener.
X1.3 For example, a stud of a particular alloy and size may
be machined from a smaller diameter bar than a bolt of the
same alloy and size because a larger diameter bar is required to
accommodate the head of the bolt. The stud, therefore, is likely
to be stronger than the same size bolt in a given alloy.
X2. COATINGS AND APPLICATION LIMITS
X2.1 Use of coated fasteners at temperatures above ap-
proximately one-half the melting point (Fahrenheit or Celsius)
of the coating is not recommended unless consideration is
given to the potential for liquid and solid metal embrittlement,
or both. The melting point of elemental zinc is approximately
780 F [415 C]. Therefore, application of zinc-coated fasten-
ers should be limited to temperatures less than 390 F [210 C].
The melting point of cadmium is approximately 600 F [320
C]. Therefore, application of cadmium-coated fasteners
should be limited to temperatures less than 300 F [160 C].
SUMMARY OF CHANGES
Committee A01 has identied the location of selected changes to this specication since the last issue,
A 193/A 193M 08a, that may impact the use of this specication. (Approved August 1, 2008).
(1) Added new paragraph 1.3 and renumbered subsequent
paragraphs.
(2) Added reference to Specications B 633 and F 2329 to
S13.1.2.
Committee A01 has identied the location of selected changes to this specication since the last issue,
A 193/A 193M 08, that may impact the use of this specication. (Approved May 1, 2008).
(1) Reorganized and edited 7.1 to clarify and separate ferritic
grades from austenitic grades. Claried use of water quenching
for threaded ferritic grades and intent relative to stress relief of
cold worked B6X. Added reference in Section 10 to Table 3
and Specication A 962/A 962M for wedge tensile testing of
metric product.
Committee A01 has identied the location of selected changes to this specication since the last issue,
A 193/A 193M 07, that may impact the use of this specication. (Approved April 1, 2008).
(1) Added new Supplementary Requirement S14. (2) Added Nitrogen for Grades B8T and B8TA in Table 1.
A 193/A 193M 08b
12
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Thu Oct 2 14:38:16 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
Committee A01 has identied the location of selected changes to this specication since the last issue,
A 193/A 193M 06a, that may impact the use of this specication. (Approved March 1, 2007).
(1) Deleted the space between the S and the numbers in the
UNS designations in Table 1.
(2) Added permissible product variations for B8MLCuN and
B8MLCuNA in Table 1.
(3) Added the requirement to report nitrogen for S32100 and
changed the order of the elements in Table 1 for this grade to
be consistent with the other stainless grades.
(4) Corrected the metric yield strength for B16 M100 to M180
in Table 3.
(5) Corrected the metric conversion in S12.
(6) Added reference to Test Method F 1940 and Specication
F 1941, and dropped reference to Specication B 633, in S13.
ASTM International takes no position respecting the validity of any patent rights asserted in connection with any item mentioned
in this standard. Users of this standard are expressly advised that determination of the validity of any such patent rights, and the risk
of infringement of such rights, are entirely their own responsibility.
This standard is subject to revision at any time by the responsible technical committee and must be reviewed every ve years and
if not revised, either reapproved or withdrawn. Your comments are invited either for revision of this standard or for additional standards
and should be addressed to ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the
responsible technical committee, which you may attend. If you feel that your comments have not received a fair hearing you should
make your views known to the ASTM Committee on Standards, at the address shown below.
This standard is copyrighted by ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959,
United States. Individual reprints (single or multiple copies) of this standard may be obtained by contacting ASTM at the above
address or at 610-832-9585 (phone), 610-832-9555 (fax), or service@astm.org (e-mail); or through the ASTM website
(www.astm.org).
A 193/A 193M 08b
13
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Thu Oct 2 14:38:16 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
Designation: A 194/A 194M 08b
Endorsed by
Manufacturers Standardization Society
of the Valve and Fittings Industry
Used in USNRC-RDT Standards
Standard Specication for
Carbon and Alloy Steel Nuts for Bolts for High Pressure or
High Temperature Service, or Both
1
This standard is issued under the xed designation A 194/A 194M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon () indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specication
2
covers a variety of carbon, alloy, and
martensitic stainless steel nuts in the size range
1
4 through 4
in. and metric M6 through M100 nominal. It also covers
austenitic stainless steel nuts in the size range
1
4 in. and M6
nominal and above. These nuts are intended for high-pressure
or high-temperature service, or both. Grade substitutions with-
out the purchasers permission are not allowed.
1.2 Bars from which the nuts are made shall be hot-wrought.
The material may be further processed by centerless grinding
or by cold drawing. Austenitic stainless steel may be solution
annealed or annealed and strain-hardened. When annealed and
strain hardened austenitic stainless steel is ordered in accor-
dance with Supplementary Requirement S1, the purchaser
should take special care to ensure that 8.2.2, Supplementary
Requirement S1, and Appendix X1 are thoroughly understood.
1.3 Supplementary requirements (S1 through S8) of an
optional nature are provided. These shall apply only when
specied in the inquiry, contract, and order.
1.4 This specication is expressed in both inch-pound units
and in SI units. However, unless the order species the
applicable M specication designation (SI units), the mate-
rial shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
1.5 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system
must be used independently of the other. Combining values
from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the
specication. Within the text, the SI units are shown in
brackets.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3
A 153/A 153M Specication for Zinc Coating (Hot-Dip) on
Iron and Steel Hardware
A 276 Specication for Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes
A 320/A 320M Specication for Alloy-Steel and Stainless
Steel Bolting Materials for Low-Temperature Service
A 962/A 962M Specication for Common Requirements
for Steel Fasteners or Fastener Materials, or Both, Intended
for Use at Any Temperature from Cryogenic to the Creep
Range
B 633 Specication for Electrodeposited Coatings of Zinc
on Iron and Steel
B 695 Specication for Coatings of Zinc Mechanically
Deposited on Iron and Steel
B 696 Specication for Coatings of Cadmium Mechanically
Deposited
B 766 Specication for Electrodeposited Coatings of Cad-
mium
E 112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
F 1940 Test Method for Process Control Verication to
Prevent Hydrogen Embrittlement in Plated or Coated
Fasteners
F 1941 Specication for Electrodeposited Coatings on
Threaded Fasteners (Unied Inch Screw Threads (UN/
UNR))
F 2329 Specication for Zinc Coating, Hot-Dip, Require-
ments for Application to Carbon and Alloy Steel Bolts,
Screws, Washers, Nuts, and Special Threaded Fasteners
2.2 American National Standards:
4
B 1.1 Unied Screw Threads
B 1.2 Gages and Gaging for Unied Inch Screw Threads
1
This specication is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.22 on Steel Forgings and Wrought Fittings for Piping Applications and Bolting
Materials for Piping and Special Purpose Applications.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2008. Published September 2008. Originally
approved in 1936. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as A 194/A 194M08a.
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Speci-
cation SA-194 in Section II of that code.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standards Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
4
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
1
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Oct 7 21:36:37 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
B 1.13M Metric Screw Threads
B 18.2.2 Square and Hex Nuts
B 18.2.4.6M Metric Heavy Hex Nuts
3. Terminology
3.1 Denitions of Terms Specic to This Standard:
3.1.1 Austenitic GradesAll grades with a prex of 8 or
9.
3.1.2 Ferritic GradesGrades 1, 2, 2H, 2HM, 3, 4, 6, 6F, 7,
7M, and 16.
3.1.3 LotUnless otherwise specied (see Discussion be-
low), a lot is the quantity of nuts of a single nominal size and
grade produced by the same manufacturing process.
3.1.3.1 DiscussionWhen Supplementary Requirement S5
is invoked on the purchase order, the following denitions of a
lot shall apply:
3.1.3.2 For Grade 8 NutsThe quantity of all the nuts of a
single nominal diameter and grade made from the same heat of
steel and made by the same manufacturing process.
3.1.3.3 For All Other Grade Nuts (see 8.2 and 8.1.2.1)
All the nuts of a single nominal diameter and grade made from
the same heat number and heat treated in the same batch if
batch-type heat treating equipment is used or heat treated in the
same continuous run of not more than 8 h under the same
conditions if continuous-type heat treating equipment is used.
3.1.4 Type
3.1.4.1 For Grade 8 NutsVariations within the grade
designated by a letter and differentiated by chemistry and by
manufacturing process.
3.1.4.2 For Grade 6 NutsVariations within the grade
designated by the letter F as differentiated by chemical addi-
tions made for machineability.
3.1.5 SeriesThe dimensional relationship and geometry
of the nuts as described in ANSI B 18.2.2 or B 18.2.4.6M.
4. Ordering Information
4.1 The inquiry and order for material under this specica-
tion shall include the following as required to describe the
material adequately:
4.1.1 Specication designation, year date, and grade, issue
date and revision letter,
4.1.2 Quantity, number of pieces,
4.1.3 Dimensions (see Section 9),
4.1.4 Options in accordance with 8.2.2.1, 9.1, 9.2, 10.3, and
12, and
4.1.5 Supplementary Requirements, if any.
4.2 CoatingsCoatings are prohibited unless specied by
the purchaser (see Supplementary Requirements S7 and S8).
When coated nuts are ordered, the purchaser should take
special care to ensure that Appendix X2 is thoroughly under-
stood.
4.3 See Supplementary Requirement S3 for nuts to be used
in low temperature applications (Specication A 320/A 320M).
4.4 Proof Load TestingSee Supplementary Requirement
S9 for proof load testing of nuts manufactured to dimensions
and congurations other than those covered in Tables 3 and 4.
5. Common Requirements
5.1 Material and fasteners supplied to this specication shall
conform to the requirements of Specication A 962/A 962M.
These requirements include test methods, nish, thread dimen-
sions, marking, certication, optional supplementary require-
ments, and others. Failure to comply with the requirements of
Specication A 962/A 962M constitutes nonconformance with
this specication. In case of conict between the requirements
of this specication and Specication A 962/A 962M, this
specication shall prevail.
6. Manufacture (Process)
6.1 Stainless steels for all types of Grade 6 and 8 nuts shall
be made by one of the following processes:
6.1.1 Electric-furnace (with separate degassing and rening
optional),
6.1.2 Vacuum induction furnace, or
6.1.3 Either of the above followed by electroslag remelting,
or consumable-arc remelting.
6.2 The steel producer shall exercise adequate control to
eliminate excessive unhomogeneity, nonmetallics, pipe, poros-
ity, and other defects.
6.3 Grades 1 and 2 nuts shall be hot or cold forged, or shall
be machined from hot-forged, hot-rolled, or cold-drawn bars.
6.3.1 All Grade 1 and 2 nuts made by cold forging or by
machining from cold-drawn bars shall be stress-relief annealed
at a temperature of at least 1000 F [538 C].
6.3.2 Grade 1 and 2 nuts made by hot forging or by
machining from hot-forged or hot-rolled bars need not be given
any stress relief annealing treatment.
6.4 Grades 2H, 2HM, 3, 4, 6, 6F, 7, 7M, and 16 nuts shall
be hot- or cold-forged or shall be machined from hot-forged,
hot-rolled, or cold-drawn bars and shall be heat treated to meet
the required mechanical properties. These grades shall be
reheated above the critical range of the steel, quenched in a
suitable medium, and then tempered at a temperature not less
than the following:
Grade
Minimum Tempering Temperature, F
[C]
2H 850 [455]
2HM 1150 [620]
3 1050 [565]
4 1100 [595]
6 and 6F 1100 [595]
7 1100 [595]
7M 1150 [620]
16 1200 [650]
Nuts machined from bar heat treated in accordance with this
specication need not be reheat-treated. For Grade 2HM and
7M nuts, a nal stress relief shall be done at or above the
minimum tempering temperature after all forming, machining,
and tapping operations. This nal stress relief may be the
tempering operation.
6.4.1 Grade 6 and 6F nuts shall be tempered for a minimum
of 1 h at the temperature.
6.5 Grades 8, 8C, 8M, 8T, 8F, 8P, 8N, 8MN, 8R, 8S, 8LN,
8MLN, 8MLCuN, and 9C nuts shall be hot or cold forged, or
shall be machined from hot-forged, hot-rolled or cold-drawn
bars.
A 194/A 194M 08b
2
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Oct 7 21:36:37 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
A,B,C,D
Grade
Symbol
Material
UNS
Number
Carbon,
%
Manga-
nese,
%
Phospho-
rus,
%
Sulfur,
E
%
Silicon,
%
Chromium,
%
Nickel,
%
Molyb-
denum,
%
Tita-
nium,
%
Colum-
bium and
Tanta-
lum, %
Nitrogen,
%
Other
Elements,
%
1 carbon 0.15 min 1.00 0.040 0.050 0.40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2, 2HM,
and 2H
carbon 0.40 min 1.00 0.040 0.050 0.40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 carbon,
molyb-
denum
0.400.50 0.700.90 0.035 0.040 0.150.35 . . . . . . 0.200.30 . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Type 501 0.10 min 1.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 4.06.0 . . . 0.400.65 . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 Type 410 S41000 0.15 1.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 11.513.5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6F Type 416 S41600 0.15 1.25 0.060 0.15
min
1.00 12.014.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6F Type
416Se
S41623 0.15 1.25 0.060 0.060 1.00 12.014.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . Selenium,
0.15 min
7, 7M Type
4140/
4142/
4145,
4140H,
4142H,
4145H
0.370.49 0.651.10 0.035 0.04 0.150.35 0.751.20 . . . 0.150.25 . . . . . . . . . . . .
8, 8A Type 304 S30400 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.020.0 8.011.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8C, 8CA Type 347 S34700 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.019.0 9.012.0 . . . . . . 10 x
carbon
content,
min
. . . . . .
8M, 8MA Type 316 S31600 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.018.0 10.014.0 2.003.00 . . . . . . . . . . . .
8T, 8TA Type 321 S32100 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.019.0 9.012.0 . . . 5 x
(C+N)
min -
0.70
max
. . . 0.10 . . .
8F, 8FA Type 303 S30300 0.15 2.00 0.20 0.15
min
1.00 17.019.0 8.010.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8F, 8FA Type
303Se
S30323 0.15 2.00 0.20 0.06 1.00 17.019.0 8.010.0 . . . . . . . . . Selenium,
0.15 min
8P, 8PA Type 305
with
restricted
carbon
S30500 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.019.0 11.013.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8N, 8NA Type
304N
S30451 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.020.0 8.011.0 . . . . . . . . . 0.100.16
8LN,
8LNA
Type
304LN
S30453 0.030 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.020.0 8.011.0 . . . . . . . . . 0.100.16
8MN,
8MNA
Type
316N
S31651 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.018.0 10.013.0 2.003.00 . . . . . . 0.100.16
8MLN,
8MLNA
Type
316LN
S31653 0.030 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.018.0 10.013.0 2.003.00 . . . . . . 0.100.16
8R, 8RA
F
XM19 S20910 0.06 4.06.0 0.045 0.030 1.00 20.523.5 11.513.5 1.503.00 . . . 0.100.30 0.200.40 Vanadium,
0.100.30
8S, 8SA S21800 0.10 7.09.0 0.060 0.030 3.54.5 16.018.0 8.09.0 . . . . . . . . . 0.080.18
8MLCuN,
8MLCuNA
S31254 S31254 0.020 1.00 0.030 0.010 0.80 19.520.5 17.518.5 6.06.5 . . . . . . 0.180.22 Copper,
0.501.00
9C, 9CA N08367 N08367 0.030 2.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 20.0-22.0 23.5- 25.5 6.0-7.0 0.18-0.25 Copper
0.75
16 Chromium
Molyb-
denum
Vanadium
0.360.47 0.450.70 0.035 0.040 0.150.35 0.801.15 . . . 0.500.65 . . . . . . . . . Vanadium,
0.250.35
Aluminum
B
0.015
A
The intentional addition of Bi, Se, Te, and Pb is not permitted except for Grades 6F, 8F, and 8FA, in which Se is specied and required.
B
Total aluminum, soluble and insoluble.
C
Maximum, unless minimum or range is indicated.
D
Where ellipses () appear in this table there is no requirement.
E
Because of the degree to which sulfur segregates, product analysis for sulfur over 0.060 % max is not technologically appropriate.
F
As described in Specication A 276.
A 194/A 194M 08b
3
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Oct 7 21:36:37 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
6.6 Grades 8A, 8CA, 8MA, 8TA, 8FA, 8PA, 8NA, 8MNA,
8RA, 8SA, 8LNA, 8MLNA, 8MLCuNA, and 9CA nuts shall
be hot- or cold-forged or shall be machined from hot-forged,
hot-rolled, or cold-drawn bars and the nuts shall subsequently
be carbide-solution treated by heating them for a sufficient time
at a temperature to dissolve chromium carbides followed by
cooling at a rate sufficient to prevent reprecipitation of the
carbides.
7. Chemical Composition
7.1 Each alloy shall conform to the chemical composition
requirements prescribed in Table 1.
8. Mechanical Requirements
8.1 Hardness Test:
8.1.1 Requirements:
8.1.1.1 All nuts shall meet the hardness requirements speci-
ed in Table 2.
8.1.1.2 Sample nuts of Grades 1, 2, 2H, 2HM, 3, 4, 7, 7M,
and 16 which have been given the treatment described in 8.1.5
shall meet the minimum hardness specied in Table 2.
8.1.2 Number of Tests (Grades 1, 2, 2H, 3, 4, 7, and 16
and all types of Grade 6):
8.1.2.1 Tests on the number of sample nuts in accordance
with the following table shall be performed by the manufac-
turer following all production heat treatments:
Lot Size Samples
Up to 800 1
801 to 8000 2
8001 to 22 000 3
Over 22 000 5
8.1.2.2 In addition, a hardness test shall be performed by the
manufacturer in accordance with 8.1.5 on one sample nut
selected from each nominal diameter and series from each
grade and heat number following completion of all production
heat treatments.
8.1.3 Number of Tests, Grades 2HM and 7M:
8.1.3.1 Each nut shall be tested by Brinell or Rockwell
methods to ensure product conformance.
5
8.1.3.2 In addition, 8.1.2.2 shall be met.
8.1.4 Number of Tests, All Types of Grade 8Tests on the
number of sample nuts in accordance with 8.1.2.1 shall be
performed by the manufacturer.
8.1.5 Test 2In addition to the testing required by 8.1.2.1
the manufacturer shall also perform hardness tests on sample
nuts after the following test heat treatment. After completion of
all production heat treatments heat the specimen nuts to the
temperatures indicated below for 24 h, then slow cool. Test at
room temperature.
5
An underline as a marking requirement for grades 2HM and 7M has been
removed but is permitted.
TABLE 2 Hardness Requirements
A
Grade and Type
Completed Nuts Sample Nut after Treatment as in 8.1.5
Brinell
Hardness
Rockwell Hardness Brinell
Hardness,
min
Rockwell
Hardness B
Scale, min C Scale B Scale
1 121 min ... 70 min 121 70
2 159 to 352 ... 84 min 159 84
2H to 1
1
2 in. or M36, incl 248 to 327 24 to 35 ... 179 89
2H over 1
1
2 in. or M36 212 to 327 35 max 95 min 147 79
2HM and 7M 159 to 235 ... 84 to 99 159 84
3, 4, 7, and 16 248 to 327 24 to 35 ... 201 94
6 and 6F 228 to 271 20 to 28 ... ... ...
8, 8C, 8M, 8T, 8F, 8P, 8N,
8MN, 8LN, 8MLN,
8MLCuN, and 9C
126 to 300 32 max 60 min ... ...
8A, 8CA, 8MA, 8TA,
8FA, 8PA, 8NA, 8MNA,
8LNA, 8MLNA,
8MLCuNA, and 9CA
126 to 192 ... 60 to 90 ... ...
8R, 8RA, 8S, and 8SA 183 to 271 25 max 88 min ... ...
A
Where ellipses () appear in this table there is no requirement.
A 194/A 194M 08b
4
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Oct 7 21:36:37 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
Grade
A
Temperature,
F [C]
1 850 [455]
2, 2H, 2HM 1000 [540]
3, 4, 7, 7M 1100 [590]
16 1200 [650]
A
Nuts intended to be coated with zinc or cadmium (marked in accordance with
the requirements of Supplementary Requirement S8) are not subjected to the
requirements of 8.1.5 (See Appendix X2).
8.1.5.1 Special Requirement, Grades 2HM and 7M
Preparation of Grades 2HM and 7M nuts for hardness test and
the hardness test itself shall be performed with consideration to
(1) protect legibility of markings; (2) minimize exterior dimen-
sional changes; and (3) maintain thread t.
8.2 Proof Load Test:
8.2.1 RequirementsThe nuts listed in Tables 3 and 4 shall
be capable of withstanding the proof loads specin therein.
Proof load testing of nuts manufactured to dimensions and
congurations other than those covered in Table 3 or Table 4 is
only required when S9 is specied in the order or inquiry.
8.2.2 Number of Tests:
8.2.2.1 The manufacturer shall test the number of nuts
specied in 8.1.2.1 following all production heat treatments.
Nuts that would require a proof load in excess of 160 000 lb/f
or 705 kN may be furnished on the basis of minimum hardness
requirements. Testing of nuts requiring a proof load in excess
of 160 000 lb/f or 705 kN is covered in Supplementary
Requirements S1 amd S4.
8.2.3 Test MethodThe test shall be run using a threaded
mandrel or a test bolt in accordance with Specication A 962/
A 962M.
8.3 Cone Proof Load Test:
TABLE 3 Proof Load Using Threaded Mandrel Inch Series
NOTE 1Proof loads are not design loads.
Nominal
Size, in.
Threads
per Inch
Stress Area
in.
2
Proof Load, lbf
A
Grade 1 Grades 2, 2HM, 6, 6F, 7M Grades 2H, 3, 4, 7, 16
Heavy Hex
B
Hex
C
Heavy Hex
D
Hex
E
Heavy Hex
F
Hex
G
1
4 20 0.0316 4 130 3 820 4 770 4 300 5 570 4 770
5
16 18 0.0524 6 810 6 290 7 860 7 070 9 170 7 860
3
8 16 0.0774 10 080 9 300 11 620 10 460 13 560 11 620
7
16 14 0.1063 13 820 12 760 15 940 14 350 18 600 15 940
1
2 13 0.1419 18 450 17 030 21 280 19 160 24 830 21 280
9
16 12 0.182 23 660 21 840 27 300 24 570 31 850 27 300
5
8 11 0.226 29 380 27 120 33 900 30 510 39 550 33 900
3
4 10 0.334 43 420 40 080 50 100 45 090 58 450 50 100
7
8 9 0.462 60 060 55 440 69 300 62 370 80 850 69 300
1 8 0.606 78 780 72 720 90 900 81 810 106 000 90 900
1
1
8 8 0.790 102 700 94 800 118 500 106 700 138 200 118 500
1
1
4 8 1.000 130 000 120 000 150 000 135 000 175 000 150 000
1
3
8 8 1.233 160 200 148 000 185 000 166 500 215 800 185 000
1
1
2 8 1.492 194 000 170 040 223 800 201 400 261 100 223 800
All Types of Grade 8, Grades 9C and 9CA
Heavy Hex
H
Hex
I
1
4 20 0.0316 2 540 2 380
5
16 18 0.0524 4 190 3 930
3
8 16 0.0774 6 200 5 810
7
16 14 0.1063 8 500 7 970
1
2 13 0.1419 11 350 10 640
9
16 12 0.182 14 560 13 650
5
8 11 0.226 18 080 16 950
3
4 10 0.334 26 720 25 050
7
8 9 0.462 36 960 34 650
1 8 0.606 48 480 45 450
1
1
8 8 0.790 63 200 59 250
1
1
4 8 1.000 80 000 75 000
1
3
8 8 1.233 98 640 92 450
1
1
2 8 1.492 119 360 111 900
A
See limit for proof load test in 8.2.2.1. The proof load for jam nuts shall be 46 % of the tabulated load.
B
Based on proof stress of 130 000 psi.
C
Based on proof stress of 120 000 psi.
D
Based on proof stress of 150 000 psi.
E
Based on proof stress of 135 000 psi.
F
Based on proof stress of 175 000 psi.
G
Based on proof stress of 150 000 psi.
H
Based on proof stress of 80 000 psi.
I
Based on proof stress of 75 000 psi.
A 194/A 194M 08b
5
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Oct 7 21:36:37 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
8.3.1 RequirementsThis test shall be performed only
when visible surface discontinuities become a matter of issue
between the manufacturer and the purchaser. Nuts in the size
range
1
4 to 1
1
2 in. inclusive and M6 to M36 inclusive shall be
proof load tested. Nuts not in this size range and all types of
Grade 8 nuts are not subject to this test. Also, nuts manufac-
tured to dimensions and congurations other than those cov-
ered by Specication A 962/A 962M, ANSI B 1.1, ANSI
B 1.13M, ANSI B 18.2.2, and ANSI B 18.2.4.6M are not
subject to the cone proof load test. The cone proof load applied
shall be determined in accordance with the Cone Proof Load
requirements in Specication A 962/A 962M (tables or formu-
lae or both) based upon the proof stresses shown in Table 5 and
Table 6 of Specication A 194/A 194M.
8.3.2 Number of TestsThe manufacturer shall sample and
test the number of nuts specied in 8.1.2.1. The lot shall be
considered acceptable if the sample nut(s) withstand(s) appli-
cation of the cone proof load without failure.
9. Dimensions
9.1 Nuts shall be hexagonal in shape, and in accordance
with the dimensions for the hex or heavy hex series, as
required, by ANSI B 18.2.2 and ANSI B 18.2.4.6M. Unless
otherwise specied, the American National Standard Heavy
TABLE 4 Proof Load Using Threaded Mandrel Metric
NOTE 1Proof loads are not design loads.
Nominal
Size,
mm
Threads
Pitch
Stress Area
mm
2
Proof Load, kN
A
Grade 1 Grades 2, 2HM, 6, 6F, 7M Grades 2H, 3, 4, 7, 16
Heavy Hex
B
Hex
C
Heavy Hex
D
Hex
E
Heavy Hex
F
Hex
G
M6 1.0 20.1 18.0 16.6 20.8 18.7 29.2 20.8
M8 1.25 36.6 32.8 30.2 37.9 34.0 44.1 37.9
M10 1.50 58.0 51.9 47.9 60.0 53.9 69.9 60.0
M12 1.75 84.3 75.5 69.5 87.3 78.4 101.6 87.3
M14 2.0 115.0 102.9 94.9 119.0 107.0 138.6 119.0
M16 2.0 157.0 140.5 129.5 162.5 146.0 189.2 162.5
M20 2.5 245.0 219.3 202.1 253.6 227.8 295.2 253.6
M22 2.5 303.0 271.2 249.9 313.6 281.8 365.1 313.6
M24 3.0 353.0 315.9 291.2 365.4 328.3 425.4 365.4
M27 3.0 459.0 411.0 378.7 475.1 426.9 553.4 475.1
M30 3.5 561.0 502.1 462.8 580.6 521.7 676.0 580.6
M36 4.0 817.0 731.2 674.0 845.6 759.8 984.5 845.6
All Types of Grade 8, and
Grades 9C and 9CA
Nominal Size, mm Thread Pitch Stress
Area,
mm
2
Heavy Hex
H
Hex
I
M6 1.0 20.1 11.1 10.4
M8 1.25 36.6 20.1 18.8
M10 1.50 58.0 31.9 29.9
M12 1.75 84.3 46.4 43.4
M14 2.0 115.0 63.3 59.2
M16 2.0 157.0 86.4 80.9
M20 2.5 245.0 134.8 126.2
M22 2.5 303.0 166.7 156.0
M24 3.0 353.0 194.2 181.8
M27 3.0 459.0 252.5 236.4
M30 3.5 561.0 308.6 288.9
M36 4.0 817.0 449.4 420.8
A
See limit for proof load test in 8.2.2.1. The proof load for jam nuts shall be 46 % of the tabulated load.
B
Based on proof stress of 895 MPa.
C
Based on proof stress of 825 MPa.
D
Based on proof stress of 1035 MPa.
E
Based on proof stress of 930 MPa.
F
Based on proof stress of 1205 MPa.
G
Based on proof stress of 1035 MPa.
H
Based on proof stress of 550 MPa.
I
Based on proof stress of 515 MPa.
TABLE 5 Proof Stress Using 120 Hardened Steel Cone Inch
Proof Stress psi, Minimum
Type Grade 1 Grades 2,
2HM, 6,
6F & 7M
Grades 2H
3, 4, 7, & 16
Hex 120 000 135 000 150 000
Heavy Hex 130 000 150 000 175 000
A 194/A 194M 08b
6
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Oct 7 21:36:37 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
Hex Series shall be used and nuts shall be either double
chamfered or have a machined or forged washer face, at the
option of the manufacturer, and, conform to the angularity
requirements of ANSI B 18.2.2 and ANSI B 18.2.4.6M.
9.2 Unless otherwise specied, threads shall be in accor-
dance with ANSI B 1.1 or ANSI B 1.13M, and shall be gaged
in accordance with ANSI B 1.2 and ANSI B 1.13M as de-
scribed in 9.2.1 and 9.2.2.
9.2.1 Nuts up to and including 1 in. nominal size shall be
UNC Series Class 2B t. Metric nuts up to and including M24
nominal size shall be coarse thread series tolerance 6H.
9.2.2 Nuts over 1 in. nominal size shall be either UNC
Series Class 2B t or 8 UN Series Class 2B t. Unless
otherwise specied, the 8 UN series shall be furnished. Metric
nuts over M24 nominal size shall be coarse thread series
tolerance 6H.
10. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
10.1 Nuts shall be free of defects and shall be good
commercial nish.
10.2 If visible surface imperfections in size
1
4 through 1
1
2
in. and M6 through M36 and in any grade other than Grade 8
become a matter of issue between the manufacturer and the
purchaser, the cone proof load test described in 8.3 shall be
employed.
10.3 If a scale-free bright nish is required, this shall be
specied on the purchase order.
11. Retests
11.1 Provisions for retests by the purchaser and his repre-
sentative are specied in Supplementary Requirement S2.
12. Certication
12.1 The producer of nuts shall furnish a certication to the
purchaser or his representative showing the results of the
chemical analysis, macroetch examination (Carbon and Alloy
Steels Only), mechanical tests, and the minimum tempering
temperature for nuts of Grades 2H, 2HM, 3, 4, 6, 6F, 7, and
7M.
12.2 Certication shall also include at least the following:
12.2.1 A statement that the fasteners were manufactured,
sampled, tested and inspected in accordance with the speci-
cation and any supplementary requirements or other require-
ments designated in the purchase order or contract and was
found to meet those requirements.
12.2.2 The specication number, year date, and identica-
tion symbol.
13. Product Marking
13.1 All nuts shall bear the manufacturers identication
mark.
13.2 Nuts shall be legibly marked on one face to indicate the
grade and process of the manufacturer, as presented in Table 7.
Marking of wrench ats or bearing surfaces is not permitted
unless agreed upon between manufacturer and purchaser.
13.3 For purposes of identication marking, the manufac-
turer is considered the organization that certies the fastener
was manufactured, sampled, tested, and inspected in accor-
dance with the specication and the results have been deter-
mined to meet the requirements of this specication.
14. Keywords
14.1 bolting; chemical analysis; coated; marking on fasten-
ers; plated
SUPPLEMENTARY REQUIREMENTS
One or more of the following supplementary requirements shall be applied only when specied by
the purchaser in the inquiry, contract, or order. Details of these supplementary requirements shall be
agreed upon in writing by the manufacturer and purchaser. Supplementary requirements shall in no
way negate any requirement of the specication itself.
S1. Strain-Hardened Austenitic Steel Nuts
S1.1 Strain hardened Grades 8, 8C, 8T, 8M, 8F, 8P, 8N, or
8MN nuts may be specied. When Supplementary Require-
ment S1 is invoked in the order, nuts shall be machined from
cold drawn bars or shall be cold forged to shape. No subse-
quent heat treatment shall be performed on the nuts. Nuts made
in accordance with this requirement shall be proof load tested
in accordance with 8.2.2.1 and shall withstand the proof load
specied in Table 8 and Table 9. Testing nuts requiring proof
loads over 160 000 lbf or 705 kN is only required when
Supplementary Requirement S4 is invoked. The hardness
limits of Table 2 do not apply to strain hardened nuts. Nuts
TABLE 6 Proof Stress Using 120 Hardened Steel Cone Metric
Proof Stress MPa, Minimum
Type Grade 1 Grades 2,
2HM, 6,
6F & 7M
Grades 2H
3, 4, 7, & 16
Hex 825 930 1035
Heavy Hex 895 1035 1205
A 194/A 194M 08b
7
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Oct 7 21:36:37 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
made in accordance with this requirement shall be marked with
the Grade symbol underlined.
S2. Retests by Purchasers Representative
S2.1 The purchasers representative may select two nuts per
keg (200-lb unit [90-kg]) for sizes
5
8 in. and M16 and smaller,
one nut per keg for sizes over
5
8 in. and M16 up to and
including 1
1
2 in. and M36, and one nut per every two kegs for
sizes larger than 1
1
2 in. and M36, which shall be subjected to
the tests specied in Section 8.
S3. Low-Temperature Requirements for Grade 4, Grade
7 or Grade 7M Nuts
S3.1 When low-temperature requirements are specied for
Grade 4 or Grade 7 nuts, the Charpy test procedures and
requirements as dened in Specication A 320/A 320M for
Grade L7 shall apply. When low-temperature requirements are
specied for Grade 7M nuts, the Charpy test procedures and
requirements as dened in Specication A 320/A 320M for
Grade L7M shall apply. Depending on the size of nuts, separate
test samples of the same heat may be required and shall be
processed through heat treatment with the nuts for which the
test is to apply. Impact testing is not required when the bar
stock or nut is smaller than
5
8 in. [16 mm] in diameter.
S3.2 An L shall be added to the marking, as shown in
Table 7, for nuts so tested.
S4. Proof Load Tests of Large Nuts
S4.1 Proof load testing of nuts requiring proof loads of over
160 000 lbf or 705 kN is required. Testing shall be performed
in accordance with 8.2 to the loads required in Table 10 and
Table 11. The maximum load will be based entirely on the
equipment available.
S5. Control of Product by Heat Number
S5.1 When control of nuts by actual heat analysis is
required and this supplementary requirement is specied, the
manufacturer shall identify the completed nuts in each ship-
ment by the actual heat number. When this supplementary
requirement is specied, a certicate including the results of
the actual production tests of each test lot together with the heat
chemical analysis shall be furnished by the manufacturer.
S6. Grain Size Requirements for Non H Grade
Austenitic Steels Used Above 1000 F
S6.1 For design metal temperatures above 1000 F [540
C], the material shall have a grain size of No. 7 or coarser as
determined in accordance with Test Methods E 112. The grain
size so determined shall be reported on the Certicate of Test.
S7. Coating on Nuts
S7.1 It is the purchasers responsibility to specify in the
purchase order all information required by the coating facility.
Examples of such information may include but are not limited
to the following:
S7.1.1 Reference to the appropriate coating specication
and type, thickness, location, modication to dimensions, and
hydrogen embrittlement relief.
NOTE S7.1Modication of thread dimensions may result in loss of
load carrying ability.
S7.1.2 Reference to Specications A 153/A 153M, B 633,
B 695, B 696, B 766, F 1941, F 2329, or Test Method F 1940,
or other standards.
S8. Marking Coated Nuts
S8.1 Nuts coated with zinc shall have an asterisk (*) marked
after the grade symbol. Nuts coated with cadmium shall have
a plus sign (+) marked after the grade symbol.
S9. Proof Load Testing
S9.1 Proof load tests of nuts made to dimensions, thread
pitch, and congurations other than those covered in Table 3 or
Table 4 shall be made using loads agreed upon between the
manufacturer and the purchaser.
TABLE 7 Marking of Nuts
A
Grade and
Type
Nuts Hot-
Forged or
Cold-
Punched
Nuts Machined
from Bar
Stock
Nuts Manu-
factured in
Accordance
with 6.6
1 1 1B ...
2 2 2B ...
2H
B
2H 2HB ...
2HM
B
2HM 2HMB ...
3 3 3B ...
4 4 4B ...
4L
C
4L 4BL . . .
6 6 6B . . .
6F 6F 6FB ...
7 7 7B ...
7L
C
7L 7BL ...
7M
B
7M 7MB ...
8 8 8B 8A
8C 8C 8CB 8CA
8M 8M 8MB 8MA
8T 8T 8TB 8TA
8F 8F 8FB 8FA
8P 8P 8PB 8PA
8N 8N 8NB 8NA
8MN 8MN 8MNB 8MNA
8R 8R 8RB 8RA
8S 8S 8SB 8SA
8LN 8LN 8LNB 8LNA
8MLN 8MLN 8MLNB 8MLNA
8MLCuN 8MLCuN 8MLCuNB 8MLCuNA
9C 9C 9CB 9CA
16 16 16B
A
Where ellipses () appear in this table there is no requirement.
B
The letters H and M indicate heat-treated nuts (see Section 6).
C
See Supplementary Requirement S3.
A 194/A 194M 08b
8
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Oct 7 21:36:37 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
TABLE 8 Proof Load Testing of Strain Hardened Nuts Using Threaded Mandrel Inch Series
NOTE 1Proof loads are not design loads.
Proof Load, lbf
A
Nominal
Size, in.
Threads
per in.
Stress Area,
in.
2
Grade 8M
(strain hardened)
Grade 8M
(strain hardened)
All Other Types
of Grade 8
(strain hardened)
All Other Types
of Grade 8
(strain hardened)
Heavy Hex
B
Hex
C
Heavy Hex
D
Hex
B
1
4 20 0.0316 3 480 3 160 3 950 3 480
5
16 18 0.0523 5 760 5 240 6 550 5 760
3
8 16 0.0774 8 510 7 740 9 675 8 510
7
16 14 0.1063 11 690 10 630 13 290 11 690
1
2 13 0.1419 15 610 14 190 17 740 15 610
9
16 12 0.182 20 020 18 200 22 750 20 020
5
8 11 0.226 24 860 22 600 28 250 24 860
3
4 10 0.334 36 740 33 400 41 750 36 740
7
8 9 0.462 46 200 41 580 53 130 46 200
1 8 0.606 60 600 54 540 69 690 60 600
1
1
8 8 0.790 75 050 67 150 82 950 75 050
1
1
4 8 1.000 95 000 85 000 105 000 95 000
1
3
8 8 1.233 110 970 98 640 123 300 110 970
1
1
2 8 1.492 134 280 119 360 149 200 134 280
A
The proof load for jam nuts shall be 46 % of the tabulated value.
B
Based on proof stress of 110 000 psi up to
3
4 in.; 100 000 psi
7
8 to 1 in.; 95 000 psi 1
1
8 to 1
1
4 in.; 90 000 psi 1
3
8 to 1
1
2 in.
C
Based on proof stress of 100 000 psi up to
3
4 in.; 90 000 psi
7
8 to 1 in.; 85 000 psi 1
1
8 to 1
1
4 in.; 80 000 psi 1
3
8 to 1
1
2 in.
D
Based on proof stress of 125 000 psi up to
3
4 in.; 115 000 psi
7
8 to 1 in.; 105 000 psi 1
1
8 to 1
1
4 in.; 100 000 psi 1
3
8 to 1
1
2 in.
TABLE 9 Proof Load Testing of Strain Hardened Nuts Using Threaded Mandrel Metric
NOTE 1Proof loads are not design loads.
Proof Load, kN
A
Nominal
Size, mm
Thread
Pitch
Stress Area,
mm
2
Grade 8M
(strain hardened)
Grade 8M
(strain hardened)
All Other Types
of Grade 8
(strain hardened)
All Other Types
of Grade 8
(strain hardened)
Heavy Hex
B
Hex
C
Heavy Hex
D
Hex
B
M6 1.0 20.1 15.3 13.9 17.3 15.3
M8 1.25 36.6 27.8 25.3 31.3 27.8
M10 1.50 58.0 44.1 40.0 49.9 44.1
M12 1.75 84.3 64.1 58.2 72.5 64.1
M14 2.0 115.0 87.4 79.4 98.9 87.4
M16 2.0 157.0 119.3 108.3 135.0 119.3
M20 2.5 245.0 186.2 169.0 210.9 186.2
M22 2.5 303.0 209.0 187.9 240.9 209.0
M24 3.0 353.0 243.5 218.9 280.6 243.5
M27 3.0 459.0 300.6 268.5 332.7 300.6
M30 3.5 561.0 367.5 328.2 406.7 367.5
M36 4.0 817.0 506.5 449.4 563.7 506.5
A
The proof load for jam nuts shall be 46 % of the tabulated value.
B
Based on proof stress of 760 MPa up to M20 mm; 690 MPa M22 to M24 mm; 655 MPa M27 to M30; and 620 MPa for M36.
C
Based on proof stress of 690 MPa up to M20 mm; 620 MPa M22 to M24 mm; 585 MPa M27 to M30; and 550 MPa for M36.
D
Based on proof stress of 860 MPa up to M20 mm; 795 MPa M22 to M24 mm; 725 MPa M27 to M30 mm; and 690 MPa for M36.
A 194/A 194M 08b
9
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Oct 7 21:36:37 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
APPENDIXES
(Nonmandatory Information)
X1. STRAIN HARDENING OF AUSTENITIC STEELS
X1.1 Strain hardening is the increase in strength and
hardness that results from plastic deformation below the
recrystallization temperature (cold work). This effect is pro-
duced in austenitic stainless steels by reducing oversized bars
to the desired nal size by cold drawing or other process. The
degree of strain hardening achievable in any alloy is limited by
its strain hardening characteristics. In addition, the amount of
strain hardening that can be produced is further limited by the
variables of the process, such as the total amount of cross-
section reduction, die angle and bar size. In large diameter bars,
for example, plastic deformation will occur principally in the
outer regions of the bar, so that the increased strength and
hardness due to strain hardening is achieved predominantly
near the surface of the bar. That is, the smaller the bar, the
greater the penetration of strain hardening. Thus, the mechani-
cal properties of a given strain hardened fastener are dependent
not just on the alloy, but also on the size of bar from which it
is machined.
X2. COATINGS AND APPLICATION LIMITS
X2.1 Use of coated fasteners at temperatures above ap-
proximately one-half the melting point (Fahrenheit or Celsius)
of the coating is not recommended unless consideration is
given to the potential for liquid and solid metal embrittlement,
or both. The melting point of elemental zinc is approximately
780 F [415 C]. Therefore, application of zinc coated fasteners
should be limited to temperatures less than 390 F [210 C].
The melting point of cadmium is approximately 600 F [320
C]. Therefore, application of cadmium coated fasteners should
be limited to temperatures less than 300 F [160 C].
TABLE 10 Proof Load for Large Heavy Hex Nuts Inch
A
Nominal
Size, in.
Threads
per in.
Stress Area,
in.
2
Proof Load, lbf
B
Grade 1 Heavy Hex
Grades 2, 2HM, 6, 6F, 7M
Heavy Hex
Grades 2H, 3, 4, 7, 16
Heavy Hex
1
5
8 8 1.78 231 400 267 000 311 500
1
3
4 8 2.08 270 400 312 000 364 000
1
7
8 8 2.41 313 300 361 500 421 800
2 8 2.77 360 100 415 500 484 800
2
1
4 8 3.56 462 800 534 000 623 000
2
1
2 8 4.44 577 200 666 000 777 000
2
3
4 8 5.43 705 900 814 500 950 250
A
ANSI B 18.2.2 in the size range over 1
1
2 in. provides dimensions only for heavy hex nuts. Refer to 8.3.1.
B
Proof loads for nuts of larger dimensions or other thread series may be calculated by multiplying the thread stress area times the proof stress in the notes to Table
3 or Table 8. The proof load for jam nuts shall be 46 % of the tabulated load.
TABLE 11 Proof Load for Large Heavy Hex Nuts Metric
A
Nominal
Size,
mm
Thread
Pitch
Stress Area,
mm
2
Proof Load, kN
B
Grade 1 Heavy Hex
Grades 2, 2HM, 6, 6F, 7M
Heavy Hex
Grades 2H, 3, 4, 7, 16
Heavy Hex
M42 4.5 1120 1002.4 1159.2 1349.6
M48 5 1470 1315.7 1521.4 1771.4
M56 5.5 2030 1816.9 2101.0 2446.2
M64 6 2680 2398.6 2773.8 3229.4
M72 6 3460 3096.7 3581.1 4169.3
A
ANSI B 18.2.4.6M in the size range over M36 provides dimensions only for heavy hex nuts. Refer to 7.3.1.
B
Proof loads for nuts of larger dimensions or other thread series may be calculated by multiplying the thread stress area times the proof stress in the notes to Table
4 or Table 9. The proof load for jam nuts shall be 46 % of the tabulated load.
A 194/A 194M 08b
10
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Oct 7 21:36:37 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
SUMMARY OF CHANGES
Committee A01 has identied the location of selected changes to this specication since the last issue,
A 194/A 194M 08a, that may impact the use of this specication. (Approved August 1, 2008)
(1) Added reference to Specications B 633 and F 2329 in
S7.1.2.
Committee A01 has identied the location of selected changes to this specication since the last issue,
A 194/A 194M 08, that may impact the use of this specication. (Approved May 1, 2008)
(1) Added new 4.4 and Supplementary Requirement S9 and
revised 8.2.1 for proof load testing for nuts not covered in
Tables 3 and 4.
Committee A01 has identied the location of selected changes to this specication since the last issue,
A 194/A 194M 07b, that may impact the use of this specication. (Approved April 1, 2008)
(1) Added Nitrogen for Grades 8T and 8TA in Table 1.
Committee A01 has identied the location of selected changes to this specication since the last issue,
A 194/A 194M 07a, that may impact the use of this specication. (Approved December 1, 2007)
(1) Added Note S7.1.
Committee A01 has identied the location of selected changes to this specication since the last issue,
A 194/A 194M 07, that may impact the use of this specication. (Approved March 1, 2007)
(1) Added reference to Test Method F 1940 in S7.1.2.
Committee A01 has identied the location of selected changes to this specication since the last issue,
A 194/A 194M 06a, that may impact the use of this specication. (Approved February 1, 2007)
(1) Revised cone proof load test requirements to reference
recent changes to Specication A 962/A 962M and Test Meth-
ods and Denitions A 370.
ASTM International takes no position respecting the validity of any patent rights asserted in connection with any item mentioned
in this standard. Users of this standard are expressly advised that determination of the validity of any such patent rights, and the risk
of infringement of such rights, are entirely their own responsibility.
This standard is subject to revision at any time by the responsible technical committee and must be reviewed every ve years and
if not revised, either reapproved or withdrawn. Your comments are invited either for revision of this standard or for additional standards
and should be addressed to ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the
responsible technical committee, which you may attend. If you feel that your comments have not received a fair hearing you should
make your views known to the ASTM Committee on Standards, at the address shown below.
This standard is copyrighted by ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959,
United States. Individual reprints (single or multiple copies) of this standard may be obtained by contacting ASTM at the above
address or at 610-832-9585 (phone), 610-832-9555 (fax), or service@astm.org (e-mail); or through the ASTM website
(www.astm.org).
A 194/A 194M 08b
11
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Oct 7 21:36:37 EDT 2008
Downloaded/printed by
Universadad Santiago de Chile pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
You might also like
- Pernos Molino Sag Mantos de Oro PDFDocument49 pagesPernos Molino Sag Mantos de Oro PDFJose VidalNo ratings yet
- Cambio de Linner Molino SAGDocument1 pageCambio de Linner Molino SAGAdolfo Popayán VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Mantenimiento chancador SymonsDocument11 pagesMantenimiento chancador SymonsMaritza PomaNo ratings yet
- ES2-MPMA01-785-25062020 Cambio de Corona Molino SAG.Document6 pagesES2-MPMA01-785-25062020 Cambio de Corona Molino SAG.Javiera A Osorio AracenaNo ratings yet
- Bombas WarmanDocument1 pageBombas WarmanMUÑOZ ingenieria y mantenimientoNo ratings yet
- Krebs MillMAXDocument18 pagesKrebs MillMAXPablo Andrés VillalónNo ratings yet
- LCC (Bomba para Pulpa de Minerales GIW)Document27 pagesLCC (Bomba para Pulpa de Minerales GIW)davidgloomNo ratings yet
- Pernos Molino SAG Cabeza ForjadaDocument24 pagesPernos Molino SAG Cabeza ForjadaAlejandro HerreraNo ratings yet
- Bombas NashDocument22 pagesBombas NashDaniel SotoNo ratings yet
- Pernos Molino SagDocument1 pagePernos Molino SagMac SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Cambio de rodillos de HPGR 18 en concentradora C2Document6 pagesCambio de rodillos de HPGR 18 en concentradora C2Jhean TurpoNo ratings yet
- Planta ConcentradoraDocument8 pagesPlanta ConcentradoraOrlando RBNo ratings yet
- Manual de Operacian Bomba Centrafuga WarmanDocument10 pagesManual de Operacian Bomba Centrafuga WarmanEvelyn SupoNo ratings yet
- Reporte de Campo - Molino Barra 7'Ø X 12'Document4 pagesReporte de Campo - Molino Barra 7'Ø X 12'Alex Franco Uriarte ParedesNo ratings yet
- Rubrica Bomba Slurry PDFDocument23 pagesRubrica Bomba Slurry PDFMiiReitap Mmni ChvzNo ratings yet
- Cálculo Correa SKFDocument2 pagesCálculo Correa SKFpafredo007No ratings yet
- Informe Parada de Planta Del 08 y 09 MayoDocument13 pagesInforme Parada de Planta Del 08 y 09 MayoC47050500No ratings yet
- Cambio de cóncavos chancadoras primariasDocument66 pagesCambio de cóncavos chancadoras primariasRAMIRONo ratings yet
- Trilabio Del Molino Sag - MMG Las BambasDocument2 pagesTrilabio Del Molino Sag - MMG Las BambasLeonel Gamero CardenasNo ratings yet
- 01 Bombas de Transferencia Colas Segunda LimpiezaDocument6 pages01 Bombas de Transferencia Colas Segunda LimpiezaMaxwell Carrasco SantiNo ratings yet
- 2.40.2.3 Bomba Centrifuga (310-PPS-0001 - 0002Document5 pages2.40.2.3 Bomba Centrifuga (310-PPS-0001 - 0002bryan gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Bujes - "Taper-Lock"Document6 pagesCatalogo Bujes - "Taper-Lock"tatiana hernandezNo ratings yet
- 4208-Targ-P-Sp-400-001 - 6 Piping Class FDPDocument346 pages4208-Targ-P-Sp-400-001 - 6 Piping Class FDPDeidry Kuu100% (1)
- Acitividad - Reconocimiento de Fallas Chancadora GiratoriaDocument4 pagesAcitividad - Reconocimiento de Fallas Chancadora GiratoriaJOSE ANDRES GARCIA ANDRADE100% (1)
- Materiales para Forros de Molinos en Acero y FierroDocument78 pagesMateriales para Forros de Molinos en Acero y FierroRoger CubasNo ratings yet
- Cambio de forro a trompo de chancadoraDocument2 pagesCambio de forro a trompo de chancadoraCancio FlorezNo ratings yet
- Pm011 Iom ManualDocument47 pagesPm011 Iom Manualvaio1100% (2)
- Cronograma de Avance Pets FlsmidthDocument4 pagesCronograma de Avance Pets FlsmidthBryan CorpseNo ratings yet
- VE (Es-En) Vertical Pump EnsivalDocument9 pagesVE (Es-En) Vertical Pump EnsivalMarco Soto0% (1)
- Informe #2 - Filtro LaroxDocument1 pageInforme #2 - Filtro LaroxAlejandro Castro Arroyo100% (1)
- 4.-Caso de Estudio Bombas SlurryDocument4 pages4.-Caso de Estudio Bombas SlurryAlex Pakito100% (1)
- Poes Botella Porta RodamientosDocument11 pagesPoes Botella Porta RodamientosAndré Fernández QueaNo ratings yet
- Curso Apron FeederDocument51 pagesCurso Apron Feederrodrigo100% (1)
- RDP Cilindros v3Document19 pagesRDP Cilindros v3Pablo RojasNo ratings yet
- Informe Chancadora Trevali RevDocument17 pagesInforme Chancadora Trevali RevDaniel Herrera QuintoNo ratings yet
- Protocolo Mantenimiento de ChancadorasDocument9 pagesProtocolo Mantenimiento de Chancadorasmauro2018No ratings yet
- Mantenimiento molino 6x6 AgropexDocument7 pagesMantenimiento molino 6x6 Agropexchristian huamanNo ratings yet
- Repuestos Bombas 1-MilpoDocument2 pagesRepuestos Bombas 1-MilpoCarlos Rudas RamirezNo ratings yet
- Arranque Sistema de Lubricacion (Marcy 9x12), (Comesa 9 X 12), (Allis Chalmers 10.5x14)Document8 pagesArranque Sistema de Lubricacion (Marcy 9x12), (Comesa 9 X 12), (Allis Chalmers 10.5x14)Jorge Terrones CNo ratings yet
- Pet GPM 01 - R1 PDFDocument39 pagesPet GPM 01 - R1 PDFJesus Manuel Juarez MamaniNo ratings yet
- Procedimiento Desarme y Armado Bomba slurryMAX 20X18-QR 323-PP-101Document10 pagesProcedimiento Desarme y Armado Bomba slurryMAX 20X18-QR 323-PP-101JOSE LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Cambio de Resortes en ZarandaDocument5 pagesCambio de Resortes en ZarandaAlbert Nick Vega LaureanoNo ratings yet
- Pet GPM 23 - R0Document45 pagesPet GPM 23 - R0Jesus Manuel Juarez MamaniNo ratings yet
- 16 Cambio de Piñon, Corona, Bocina Excentrica y Cilindrica de Tritruadoras ConicasDocument4 pages16 Cambio de Piñon, Corona, Bocina Excentrica y Cilindrica de Tritruadoras ConicasOSVALDONo ratings yet
- Catalogo Bombas GouldsDocument20 pagesCatalogo Bombas GouldsEmmanuel Ordenes100% (2)
- OK PTS 36 Cambio Trunnion Alimentacion Molino Bolas ConvencionalDocument7 pagesOK PTS 36 Cambio Trunnion Alimentacion Molino Bolas Convencionalleandro100% (3)
- LCC Giw-KsbDocument48 pagesLCC Giw-Ksbalexandraaraya100% (1)
- Pand ParadaDocument152 pagesPand ParadaJorge Terrones CNo ratings yet
- Retiro de backstop CV-01Document22 pagesRetiro de backstop CV-01Jorge CortesNo ratings yet
- 003 Manual Celda FMI 100 - Milpo Andina - Febrero 2015Document30 pages003 Manual Celda FMI 100 - Milpo Andina - Febrero 2015EduardoNo ratings yet
- Criterio de Diseño FajasDocument18 pagesCriterio de Diseño FajasGiovanna100% (1)
- Nivelación sistema transmisión zarandasDocument19 pagesNivelación sistema transmisión zarandasErnesto El LokoNo ratings yet
- Protocolos Allis Challmers 8-1-08Document4 pagesProtocolos Allis Challmers 8-1-08wilberhuamaniNo ratings yet
- GRAL-MANTENIMIENTO DE BOMBAS CENTRIFUGAS HORIZONTALES EN VOLADIZO Rev.0Document37 pagesGRAL-MANTENIMIENTO DE BOMBAS CENTRIFUGAS HORIZONTALES EN VOLADIZO Rev.0CARLOS GUSTAVO YATACO VILCANo ratings yet
- PET - Cambio Excéntrica y ContraejeDocument73 pagesPET - Cambio Excéntrica y ContraejeJOSE ANDRES GARCIA ANDRADENo ratings yet
- Cot. Cambio de Forros Molino 8X10 N2 Rev 1Document30 pagesCot. Cambio de Forros Molino 8X10 N2 Rev 1Katheryne Sherley NIETO MANCILLANo ratings yet
- Manual de operación y mantenimiento de bomba de doble succiónDocument12 pagesManual de operación y mantenimiento de bomba de doble succiónPaco Orlando Tumbalobos100% (1)
- Informe-De-Reparacion - Ire006-21-Nexa - Reparacion de Mecanismo RCS - 50Document12 pagesInforme-De-Reparacion - Ire006-21-Nexa - Reparacion de Mecanismo RCS - 50Lily Julcapari Rojas100% (1)
- Hydrociclones TOROMOCHODocument1 pageHydrociclones TOROMOCHOBrajham Felix Alberto GarayNo ratings yet
- Resumen API 1104Document14 pagesResumen API 1104Sebastian Vargas80% (5)
- Calibracion de Un MolinoDocument73 pagesCalibracion de Un MolinoMonica Ulloa Lamas100% (6)
- Molienda Convencional y SAGDocument38 pagesMolienda Convencional y SAGOmar Ignacio Carvajal Camaño67% (9)
- Curso de AutocadDocument82 pagesCurso de Autocadapi-3829848100% (1)
- Filtro de Banda Delkor Belt FiltersDocument2 pagesFiltro de Banda Delkor Belt Filtersjpakimsa100% (1)
- Presentacion Final Cesar Parra CorregidaDocument36 pagesPresentacion Final Cesar Parra CorregidaMiguel Lamas ChacanaNo ratings yet
- SAG PebblesDocument19 pagesSAG PebblesNancho Cartes RuminotNo ratings yet
- OS-2012-155-2D Mantos de Oro-Molino Sag-EscaneoLaser-Tapa Descarga (2012-Julio 26)Document8 pagesOS-2012-155-2D Mantos de Oro-Molino Sag-EscaneoLaser-Tapa Descarga (2012-Julio 26)Miguel Lamas ChacanaNo ratings yet
- INF5369 2012 E Tapa Descarga MDODocument4 pagesINF5369 2012 E Tapa Descarga MDOMiguel Lamas ChacanaNo ratings yet
- Molienda Convencional y SAGDocument38 pagesMolienda Convencional y SAGOmar Ignacio Carvajal Camaño67% (9)
- Indicadores de GestionDocument5 pagesIndicadores de GestionMiguel Lamas ChacanaNo ratings yet
- Instructivo para Crear Boletas HonorariosDocument4 pagesInstructivo para Crear Boletas HonorariosMiguel Lamas ChacanaNo ratings yet
- Stokes y GausDocument26 pagesStokes y GausBernardo VegaNo ratings yet
- Calendario de Obra de Construccion de Casa HabitacionDocument1 pageCalendario de Obra de Construccion de Casa HabitacionFrank Monzon83% (12)
- C20-1366 Pharmaplant PDFDocument3 pagesC20-1366 Pharmaplant PDFGenaroNeriNo ratings yet
- Muros: definición, clasificación y materialesDocument55 pagesMuros: definición, clasificación y materialesCritcia SalazarNo ratings yet
- Clasificacion de Electrodos GMAW 1Document3 pagesClasificacion de Electrodos GMAW 1J CazuriNo ratings yet
- Procedimiento de Hormigon ArmadoDocument9 pagesProcedimiento de Hormigon ArmadoCristian Gatica HerreraNo ratings yet
- ContratoModificatorio1Document20 pagesContratoModificatorio1Juvenal Chambi RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Reporte EnvejecimientoDocument17 pagesReporte EnvejecimientoDaniel PesNo ratings yet
- Detalle de Colector PluvialDocument1 pageDetalle de Colector PluvialNestor Luciano ColoniaNo ratings yet
- Cemento Pórtland Morteros, Hormigones y PrefabricadosDocument3 pagesCemento Pórtland Morteros, Hormigones y PrefabricadosGustavo VenturaNo ratings yet
- Normas para El Dibujo MecanicoDocument66 pagesNormas para El Dibujo MecanicoGenesis SznoNo ratings yet
- Memoria de Estructuras NaveDocument25 pagesMemoria de Estructuras NaveJoseline Pamela Chire PostigoNo ratings yet
- Acu Agua PotableDocument18 pagesAcu Agua PotableErlin Noe Sanchez ChavezNo ratings yet
- Válvulas y accesorios fundiciónDocument34 pagesVálvulas y accesorios fundiciónSamuel TrassierraNo ratings yet
- Concreto AutocompactanteDocument11 pagesConcreto AutocompactanteIvan HuamaniNo ratings yet
- 2016-06-17 Document Release 03 - SpecificationsDocument1,415 pages2016-06-17 Document Release 03 - SpecificationsmarcoNo ratings yet
- Recubrimiento Epóxico de Pisos1Document19 pagesRecubrimiento Epóxico de Pisos1LOREN LEON CASALLASNo ratings yet
- Planilla Peso EspecificosDocument4 pagesPlanilla Peso Especificosale MartinezNo ratings yet
- M1-U3 Materiales Construccion PDFDocument74 pagesM1-U3 Materiales Construccion PDFJoseph Louis G. P100% (2)
- Anexo - Listado Equipos para MantenimientoDocument83 pagesAnexo - Listado Equipos para MantenimientoArbyn Grand PumNo ratings yet
- Acu-Lista de Insumos 2pDocument38 pagesAcu-Lista de Insumos 2pGianfranco JHNo ratings yet
- AtletismoDocument8 pagesAtletismoHelpSportNo ratings yet
- Despeje de terreno y excavaciones para jardín infantilDocument98 pagesDespeje de terreno y excavaciones para jardín infantilHector JorqueraNo ratings yet
- Listado PendientesDocument18 pagesListado PendientesCONSORCIO TIMNo ratings yet
- Viguetas y BovedillasDocument12 pagesViguetas y BovedillasPRO-Ingeniería CivilNo ratings yet
- Copia de Wps1778 Rev 0 Hci A SW p1-p8Document4 pagesCopia de Wps1778 Rev 0 Hci A SW p1-p8Gaston Gualdieri100% (1)
- 07 SimonciniDocument9 pages07 SimoncinigacetaNo ratings yet
- HORMIGONDocument9 pagesHORMIGONMarco Antonio AlvisNo ratings yet
- Propiedades de los materiales y conformado plásticoDocument31 pagesPropiedades de los materiales y conformado plásticoAna Cristina Fernandez VigilNo ratings yet
- T Uce 0011 Icf 147 PDFDocument247 pagesT Uce 0011 Icf 147 PDFMilbert ArmasNo ratings yet