Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Compressor Power Estimation Calcs
Uploaded by
ronny_fernandes363Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Compressor Power Estimation Calcs
Uploaded by
ronny_fernandes363Copyright:
Available Formats
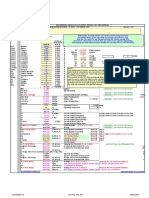
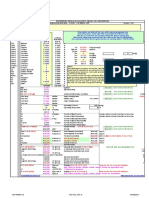
Thermodynamic Equations for gas compressor calculations
Adiabatic compression:
Changes of state
Power P, kW
Theoretical
disch.
temperature, T
2
Isothermal compression:
Changes of state
Power P, kW
Where:
P
1
= Gas pressure before compression (inlet), barA
P
2
= Gas pressure after compression (outlet), barA
V
1
= Gas volume at pressure P
1
, m
3
V
2
= Gas volume at pressure P
2
, m
3
Q
1
= Gas volume flow rate at inlet of compressor, m
3
/s
T
1
= Gas temperature at inlet of compressor, K
T
2
= Gas temperature at outlet of compressor (adiabatic process), K
k = Ratio of specific heat at constant pressure to specific heat at constant volume, C
p
/C
v
P = Theoretical power requirement of compressor, kW
Example of adiabatic compression of air:
k P
1
, barA P
2
, barA T
1
, C T
1
, K Q
1
, m
3
/s P, kW T
2
, K T
2
, C
1.4 1 2 20 293.15 1 76.65 357.35 84.20
1.4 1 3 20 293.15 1 129.06 401.25 128.10
1.4 1 4 20 293.15 1 170.10 435.62 162.47
1.4 1 5 20 293.15 1 204.34 464.30 191.15
Example of isothermal compression of air:
P
1
, barA P
2
, barA T
1
& T
2
, C Q
1
, m
3
/s P, kW
1 2 20 1 69.31
1 3 20 1 109.86
1 4 20 1 138.63
1 5 20 1 160.94
P
2
/P
1
= (V
1
/V
2
)
k
= (T
2
/T
1
)
k-1/k
T
1
*[P
2
/P
1
]
(k - 1/k)
P
2
/P
1
= (V
1
/V
2
)
{P
1
*100000*Q
1
*ln(P
2
/P
1
)}/1000
{(k / k - 1)* P
1
*100000*Q
1
*[ (P
2
/P
1
)
(k - 1/k)
- 1 ]}/1000
ISOTHERMAL COMPRESSION IS FOR ACADEMIC PURPOSE ONLY. CHEMICAL PROCESS INDUSTRY
COMPRESSION APPLICATIONS ARE GENERALLY NOT CONSIDERED AS ISOTHERMAL.
Note: k is both a function of temperature and pressure. At highly elevated temperatures & pressures, k values
will be different than those given at standard conditions of 15C & 1-atm pressure and require to be computed.
P
motor
= P/(h
machine
*h
tr
)
Efficiency
Reciprocating
(piston)
Rotary
(Lobe,
Vane)
Centrifugal
(Dynamic)
h
machine
0.85-0.9 0.7-0.75 0.7-0.75
Efficiency
worm Hydro Gear Belt
Direct
coupling
h
tr
0.7 0.8 0.85 0.97 1
Where:
P
motor
= rating of the driver, kW
h
machine
= compression efficiency of the compressor
h
tr
= efficiency of the speed transmission device.
Specific heat ratio of various gases @15C and 1-atm pressure:
Argon Helium Air Methane Oxygen Nitrogen Hydrogen Ethane
k 1.668 1.66 1.4 1.31 1.4 1.4 1.41 1.22
Prepared by: Ankur Srivastava
Chemical Engineer
e-mail: ankur_2061@hotmail.com
Note: Actual power requirement of driver is a function of the efficiency of the type of compressor & the speed
transmission mechanical device.
Type of compressor
Disclaimer : The information and methods included within this spreadsheet are presented for 'compressor power'
calculations. It is intended to be used by technically skilled persons at their own discretion. I do not warrant the suitability or
accuracy of these methods.
Note: Efficiency values are given as a range and as a general guideline and may differ from the values given in
the table. User is cautioned to check from other resources (compressor manufacturer's literature, handbooks
etc.) for the realistic values of efficiency for the given type of compressor.
Type of speed transmission
Disclaimer : The information and methods included within this spreadsheet are presented for 'compressor power'
calculations. It is intended to be used by technically skilled persons at their own discretion. I do not warrant the suitability or
accuracy of these methods.
You might also like
- Compressor Sizing CalDocument2 pagesCompressor Sizing Calcanada_198020008918No ratings yet
- Compressor Sizing CalDocument2 pagesCompressor Sizing CalSimranjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Compressor Performance Worksheeet USCDocument6 pagesReciprocating Compressor Performance Worksheeet USCTiano BaLajadiaNo ratings yet
- 20120507091359 (1)Document6 pages20120507091359 (1)Noman Abu-FarhaNo ratings yet
- Compressor Performance CalculatorDocument28 pagesCompressor Performance CalculatorEslamShebl100% (2)
- Compressor SizeDocument3 pagesCompressor SizeSubhash KumarNo ratings yet
- API 2000 guidance for inert gas blanketing of tanksDocument2 pagesAPI 2000 guidance for inert gas blanketing of tankssandeshNo ratings yet
- TD HE THE v2020.00Document43 pagesTD HE THE v2020.00Claudia BonocoreNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Compresor CalculationDocument2 pagesCentrifugal Compresor CalculationgrabettyNo ratings yet
- Gas Properties, Flowrate and Conditions: Reciprocating Compressor Calculation SheetDocument5 pagesGas Properties, Flowrate and Conditions: Reciprocating Compressor Calculation SheetNaqqash Sajid0% (2)
- Demister DatasheetDocument1 pageDemister Datasheetdeion29No ratings yet
- Calculation Sheet For Pump Hydraulic (Fps Unit)Document1 pageCalculation Sheet For Pump Hydraulic (Fps Unit)chemical todiNo ratings yet
- UMUECHEM BOOSTER COMPRESSOR SELECTIONDocument2 pagesUMUECHEM BOOSTER COMPRESSOR SELECTIONNicolas CardonaNo ratings yet
- Section 7Document64 pagesSection 7WlopezaNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet Heat Loss from a PipeDocument1 pageSpreadsheet Heat Loss from a PipeJogender DhayalNo ratings yet
- NPSHa Calculation SpreadsheetDocument3 pagesNPSHa Calculation Spreadsheetprasad durgaNo ratings yet
- Pumps Calculation 2Document2 pagesPumps Calculation 2Alchemy EngNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer. Heat Loss From A Pipe in An Indoor LocationDocument29 pagesHeat Transfer. Heat Loss From A Pipe in An Indoor LocationselisenNo ratings yet
- Simple ORC Model SQ110918Document9 pagesSimple ORC Model SQ110918radanpetricaNo ratings yet
- Line Sizing (SI) Gas PhaseDocument10 pagesLine Sizing (SI) Gas PhaseRian Intan SaputraNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet - Gas Blanketed Tanks - Inbreathing Process Calculations & Control Valve Sizing - Rev2Document26 pagesSpreadsheet - Gas Blanketed Tanks - Inbreathing Process Calculations & Control Valve Sizing - Rev2venkatesh801No ratings yet
- Air Receiver SizingDocument4 pagesAir Receiver SizingAnonymous a4Jwz14WNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drop in BendDocument5 pagesPressure Drop in BendfitratulqadriNo ratings yet
- STEAMcalc 12.8 RupiahDocument1,009 pagesSTEAMcalc 12.8 RupiahlightsonsNo ratings yet
- RD 810Document73 pagesRD 810Ashish MishraNo ratings yet
- Section 7 - Separation EquipmentDocument9 pagesSection 7 - Separation Equipmentlulis171No ratings yet
- Selection of Gas Compressors - Part 1Document5 pagesSelection of Gas Compressors - Part 1sauroNo ratings yet
- Calculating Pipe Sizing and Pressure DropDocument12 pagesCalculating Pipe Sizing and Pressure Dropchemkumar16No ratings yet
- GPSAGas PropDocument26 pagesGPSAGas Propxjaf01No ratings yet
- Condensate Line SizingDocument2 pagesCondensate Line SizingAnonymous oVRvsdWzfBNo ratings yet
- Ppgj-Pro-Cal-190 Hot Oil Return Pump (P-1004)Document10 pagesPpgj-Pro-Cal-190 Hot Oil Return Pump (P-1004)Tifano KhristiyantoNo ratings yet
- Piping Pressure Drop and Pump Design Calculation Sheet: Operating Conditions Discharge ConditionsDocument17 pagesPiping Pressure Drop and Pump Design Calculation Sheet: Operating Conditions Discharge ConditionsDhanny Miharja100% (1)
- Cooling Towers & Desiccant Dehumidification GuideDocument23 pagesCooling Towers & Desiccant Dehumidification Guideesojsuil_tgNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pumps: Process Calculation / Data SheetDocument3 pagesCentrifugal Pumps: Process Calculation / Data SheetMurali MuthuNo ratings yet
- Volume Calculation For Pressure Vessel TankDocument2 pagesVolume Calculation For Pressure Vessel Tanksai srikarNo ratings yet
- Control Valve CalcDocument7 pagesControl Valve Calcartneves100% (1)
- Line Size & Pressure Drop CalculationDocument3 pagesLine Size & Pressure Drop Calculationsj_scribdNo ratings yet
- Nonboiling Liq Outflow F Vertical Cyl VesselDocument26 pagesNonboiling Liq Outflow F Vertical Cyl VesselSrihari KodimelaNo ratings yet
- Condenser SizingDocument22 pagesCondenser Sizinglibid_rajNo ratings yet
- Process Storage Tank Lah & Lahh Level Calculation - 1551287770Document1 pageProcess Storage Tank Lah & Lahh Level Calculation - 1551287770wafaNo ratings yet
- Condensation calculations for building envelopeDocument22 pagesCondensation calculations for building envelopelutfi awn100% (1)
- Orifice Plate Flow Calculator Pressure DropDocument6 pagesOrifice Plate Flow Calculator Pressure Droplutfi awnNo ratings yet
- Two Phase Beggs BrillDocument4 pagesTwo Phase Beggs BrillOsmund MwangupiliNo ratings yet
- API520 RVsizingDocument6 pagesAPI520 RVsizingDarshan PatelNo ratings yet
- Tank relief designDocument12 pagesTank relief designsachinumaryeNo ratings yet
- Validation Report On The 2 Phase Line Sizing 3 PDFDocument18 pagesValidation Report On The 2 Phase Line Sizing 3 PDFJoseph MedinaNo ratings yet
- Cvsize (Control Valve Sizing)Document8 pagesCvsize (Control Valve Sizing)EslamSheblNo ratings yet
- Peng Robinson MixturesDocument1 pagePeng Robinson MixturesdckristantoNo ratings yet
- Open TankDocument27 pagesOpen Tankhgagselim2012No ratings yet
- PSV SIZING CALCULATIONS FOR VAPOUR OR GAS RELIEFDocument10 pagesPSV SIZING CALCULATIONS FOR VAPOUR OR GAS RELIEFAlvin SmithNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Load - PumpDocument1 pageNozzle Load - Pumpduf fu0% (1)
- Vertical Separator SizingDocument4 pagesVertical Separator SizingnemprrNo ratings yet
- Compressor CalculationsDocument7 pagesCompressor CalculationsSantosh100% (1)
- Storage Tank Venting CalculationDocument1 pageStorage Tank Venting Calculationام يمنى ايمنNo ratings yet
- Compressor Power Estimation CalcsDocument4 pagesCompressor Power Estimation CalcstedfdfeNo ratings yet
- Memoria de Cálculo CompresoresDocument6 pagesMemoria de Cálculo CompresoresEstuardo Javier Gan Rodríguez100% (1)
- Heat Transfer Lab - 1Document31 pagesHeat Transfer Lab - 1Nikhil JayanthNo ratings yet
- Evaluate centrifugal compressor performanceDocument8 pagesEvaluate centrifugal compressor performanceAnonymous yLPPdPwNo ratings yet
- PressorsDocument8 pagesPressorsManoj MisraNo ratings yet
- Free Excel Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesFree Excel Cheat SheetAlvian0% (1)
- Student Report: Social Studies Class TestDocument4 pagesStudent Report: Social Studies Class Testronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- 16uf BBAinAviationOperationsDocument5 pages16uf BBAinAviationOperationsronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- Payout Request for Surrender/Partial WithdrawalDocument2 pagesPayout Request for Surrender/Partial Withdrawalronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- Packing LabelsDocument4 pagesPacking Labelsronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- St. Michael PrayerDocument1 pageSt. Michael Prayerronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- TechfestDocument16 pagesTechfestronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- Student Report: Math Class TestDocument3 pagesStudent Report: Math Class Testronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- Tux Paint Practice WorksheetDocument5 pagesTux Paint Practice Worksheetronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- AMFI Sample 500 QuestionsDocument36 pagesAMFI Sample 500 Questionssukriti_43784905100% (3)
- 2crsfile MBAinOilandGas1Document5 pages2crsfile MBAinOilandGas1Siva KumarNo ratings yet
- 16uf BBAinAviationOperationsDocument5 pages16uf BBAinAviationOperationsronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- Quality. Safety. Service: 1 Nis Techno Middle East Fze Product PresentationDocument17 pagesQuality. Safety. Service: 1 Nis Techno Middle East Fze Product Presentationronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- AUregular Noprice Group b77040db 834a 4d38 8287 7e1e8f94dc9fDocument7 pagesAUregular Noprice Group b77040db 834a 4d38 8287 7e1e8f94dc9fronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- Buffer and Barrier FluidsDocument10 pagesBuffer and Barrier FluidsFelipeFonckmNo ratings yet
- Couplings, Keys, and SplinesDocument22 pagesCouplings, Keys, and SplinesNaeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Coupling SpecificationDocument4 pagesCoupling Specificationronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
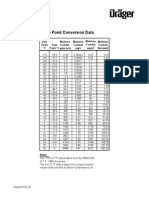
- Dew Point ConversionsDocument1 pageDew Point ConversionsSalvador NegreteNo ratings yet
- Coupling SpecificationDocument4 pagesCoupling Specificationronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- Balancing of Couplings1Document4 pagesBalancing of Couplings1Rittik Chakraborty100% (1)
- Michael M. Calistrat: Safety, Application, and Service Factors As Applied To Shaft Couplings byDocument8 pagesMichael M. Calistrat: Safety, Application, and Service Factors As Applied To Shaft Couplings byronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- Risks of Shaft Driven Oil Pumps on Critical MachinesDocument1 pageRisks of Shaft Driven Oil Pumps on Critical Machinesronny_fernandes363100% (1)
- 2140 Inert Buffer GasDocument2 pages2140 Inert Buffer GasNikola HodakNo ratings yet
- KBBDocument200 pagesKBBronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- Compressor & Turbine Piping Design ManualDocument34 pagesCompressor & Turbine Piping Design Manualsaminasritn100% (2)
- ChemGuide 8677 PDocument32 pagesChemGuide 8677 PPiok Piere TenengNo ratings yet
- Dew Point ConversionsDocument1 pageDew Point ConversionsSalvador NegreteNo ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument37 pagesAir Conditioningronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- API 618 Forced Response StudiesDocument10 pagesAPI 618 Forced Response StudiesKelly EberleNo ratings yet
- This Shall Be 2400mm: Clashing With CoolersDocument1 pageThis Shall Be 2400mm: Clashing With Coolersronny_fernandes363No ratings yet
- LM 2500Document2 pagesLM 2500SLt Shiva Prasad YalalaNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument2 pagesManualDinu RoxanaNo ratings yet
- Horizon Series - Single Stage (SS) / Two Stage (TS) : Reciprocating Air CompressorsDocument1 pageHorizon Series - Single Stage (SS) / Two Stage (TS) : Reciprocating Air CompressorsAnkur Yash100% (1)
- Pumps For SubseaDocument20 pagesPumps For SubseaMartina OrtizNo ratings yet
- Modified Control Philosophy of Arar - 19-2-05Document17 pagesModified Control Philosophy of Arar - 19-2-05srigirisetty208No ratings yet
- Almig Combi GB WebDocument8 pagesAlmig Combi GB WebRomanCHubaNo ratings yet
- Types of Supercharger: Positive DisplacementDocument10 pagesTypes of Supercharger: Positive DisplacementMamdouhAlhanafyNo ratings yet
- Design of Methanol Plant Optimization and Carbon Capture AnalysisDocument25 pagesDesign of Methanol Plant Optimization and Carbon Capture AnalysisAnonymous 0QumXG6NNo ratings yet
- 50LC 6-10 TonDocument72 pages50LC 6-10 TonMauricio Hernandez BolívarNo ratings yet
- Ch-7-W-13-14-VCR and Hyperbar EnginesDocument27 pagesCh-7-W-13-14-VCR and Hyperbar EnginesArkew Bogale100% (3)
- 989-511-02 (Polyclav)Document12 pages989-511-02 (Polyclav)Rizka Dwi Nur VitriaNo ratings yet
- An Exergy Analysis of Small-Scale Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)Document15 pagesAn Exergy Analysis of Small-Scale Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)feraldoNo ratings yet
- Paquete 7.5 - 10.0 Tons Heat PumpDocument36 pagesPaquete 7.5 - 10.0 Tons Heat PumpSeeClaro100% (1)
- Refrigeration System For Food StoragesDocument46 pagesRefrigeration System For Food StoragesFiseha Mengisteab100% (2)
- Air Dryer Ad-9 InstallationDocument24 pagesAir Dryer Ad-9 InstallationCarlos RomeroNo ratings yet
- Wet SealsDocument8 pagesWet Sealsasadiqbal127100% (1)
- 110703pdgs Flyer enDocument4 pages110703pdgs Flyer enSaitejaMechNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Mechanical CompletionDocument123 pagesChecklist For Mechanical CompletionArjun Shantaram Zope100% (3)
- Chicago Pneumatic HN2T 150180 NPDocument37 pagesChicago Pneumatic HN2T 150180 NPhibhavu100% (1)
- Assignment #1Document2 pagesAssignment #1Lary Dela Cruz Guevarra0% (1)
- Mini Gas Turbines Final ReportDocument88 pagesMini Gas Turbines Final ReportRavi Kumar Bandarulanka100% (1)
- 9FA Failures in DabholDocument10 pages9FA Failures in Dabholsenthil031277100% (3)
- Drive Coupling SKFDocument19 pagesDrive Coupling SKFFrank MwafulirwaNo ratings yet
- Aib ZT ZR55 75 90Document138 pagesAib ZT ZR55 75 90nidnitrkl05129650% (2)
- SC15G Standard Compressor R134a 208 A 230V 60HzDocument2 pagesSC15G Standard Compressor R134a 208 A 230V 60Hzgabriel_stachNo ratings yet
- V003t07a005 94 GT 115Document11 pagesV003t07a005 94 GT 115krishan_raj_1No ratings yet
- PDO Guide To Engineering Standards and ProceduresDocument1 pagePDO Guide To Engineering Standards and ProceduresRamesh Ananthanarayanan100% (3)
- Retrofit of Reciprocating Compressors - Hoerbiger ElectricDocument22 pagesRetrofit of Reciprocating Compressors - Hoerbiger ElectricRadu BabauNo ratings yet
- Boiler Soot-Blowing in Power Plants - Compressed Air Best PracticesDocument8 pagesBoiler Soot-Blowing in Power Plants - Compressed Air Best PracticesRoland NicolasNo ratings yet
- Siemens Brochure Centrifugal Compressors en PDFDocument12 pagesSiemens Brochure Centrifugal Compressors en PDFAbbas MohajerNo ratings yet