Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Finite Element Analysis
Uploaded by
AndrésGonzálezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Finite Element Analysis
Uploaded by
AndrésGonzálezCopyright:
Available Formats
Finite Element Analysis
S313070001W
2014 5
1
Final Course Report
(Andrs Gonzlez)
College of electrical and mechanical engineering
Introduction
The software ANSYS is a powerful tool for solving complex mechanical systems,
from simple static analysis to advanced vibration calculus. It allows to model systems or
solids in a simplified representation, define physical properties, different types of elements
such as springs, solids, dampers, shells, etc. Simulation characteristics like meshing, forces,
displacement constraints, moments can be defined according to the needs.
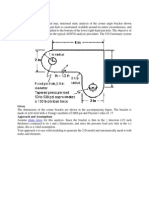
The problem solved for this report consists of a hollow rectangular column, thickness
0.06 meters, under a pressure of 1E9 Pa. The shell material has a Young Modulus of 2E11 Pa
and a Poisson ratio of 0.3. The dimensions of the column are described in Figure 1. The
bottom of the column is completely fixed.
2
0
1
0
1
0
Figure 1. Dimensions of the hollow rectangular column
For the solution of this problem it was assumed that the column has no top and bottom
cover, this noticed from the given drawing. The density was not given in the problem; anyway
it was not assumed neither because it is not needed for the solution.
Modeling
Jobname and title
The first step to solve the given problem was to open the software ANSYS and define
2
a jobname. The chosen name was report4. Then define a title, Final report.
Element type
Preprocessor > Element Type > Add/Edit/Delete > Add > Structural Mass > Shell >
Elastic 4node 63 > OK
This type was chosen because the figure is a polygon of 4 sides and only needs a node on each
corner.
Real Constants
Preprocessor > Real Constants > Add/Edit/Delete > Add > OK
In the Shell thickness at node I box, the thickness of the material (0.06 m) was input. Then
clicked OK to close.
Material Properties
Preprocessor > Material Models > Structural > Linear > Elastic > Isotropic
In this window the real material properties were defined. In the EX box, the Youngs
modulus of 2E1 Pa was introduced. In the PRXY box, the Poissons ratio 0,3 was introduced.
Modeling
Preprocessor > Modeling > Create > Keypoints > In Active CS
In this step, the following keypoints were created:
Keypoint X Y Z
1 0 0 0
2 0 10 0
3 10 10 0
4 10 0 0
5 0 0 20
Figure 2. Keypoints
Creating lines
Preprocessor > Modeling > Create > Lines > Lines > Straight Line
Straight lines were created between keypoints 1-2, 2-3, 3-4 and 4-1. This four lines
3
form the square that is the base of the column. Then, a straight line was created between
keypoints 1 and 5; this line was used later as a guide for extruding the square to create the
column.
Extrusion
Preprocessor > Modeling > Operate > Extrude > Lines > Along Lines
In this step, the 4 lines of the square were chosen as the lines to extrude, then the line 5
(between keypoints 1-5) was selected as the guide. Then, the hollow column was formed.
Meshing
Preprocessor > Meshing > Mesh Tool
In Size Controls > Global > Set > No. of element divisions, the value used was 20.
In Mesh > Areas, the options Quad and Mapped were selected. Then, clicking on the
Mesh button, the four side areas of the column were selected and the mesh was done.
Displacement constraining
Solution > Define Loads > Apply > Structural > Displacement > On Lines
The problem states that the bottom of the column is fully constrained; so the base lines
(1-4) were selected. Then, in the Apply U,ROT on Lines window, the All DOF option
was selected, with a Displacement value of 0 (zero).
Applying loads
Solution > Define Loads > Apply > Structural > Pressure > On Lines
A pressure of 1E9 Pa is applied on the top of the column. Since there is no area on the
top face of the model, the lines 6, 9, 11 and 13 were selected. In the Apply PRES on lines
window, the constant value was introduced.
Solution
Solution > Solve > Current LS
This final step solved the analysis.
Viewing results
General Postproc > Plot Results > Deformed Shape > Def + undeformed
This plots the model after the application of the pressure, plus the shade of the
undeformed shape.
4
General Postproc > Plot Results > Contour Plot > Nodal Solu
In the window that pops up, the von Mises stress data is selected to be plotted. Since
the column is made of a uniform material, the applied pressure is uniform along the top border
and the column is symmetrical, the von Mises stress can show if the stress in the sides of the
column is also uniform.
Results
The first result obtained from this analysis is the displacement, or the deformation in
the Z-axis (along the direction of the force). The figure 3 shows the shape of the column
before and after the application of the pressure. The values can be plotted in a table, to know
the deformation at any node of the model. It is not included because of the size of the table.
Figure 3. Column before and after the load.
The deformation is a vector, composed of the deformation components in each axis.
This vector can also be plotted, shown in figure 4, to compare the symmetry of the
deformation on each face of the column.
5
Figure 4. Displacement vector sum.
The last graph plotted, shown in figure 5, is the distribution of stress in the column;
the selected model was von Mises. The graph shows that, as expected since the column is
made of uniform material and symmetrical geometry, the stresses are distributed
symmetrically. It also shows that the lower corners are the places where the biggest stress
concentration takes place.
A table with the stress values can be plotted, but is not included because of its size.
Figure 5. Von Mises stress on the column.
6
Conclusions and suggestions
The given problem for this report is a simple axial load analysis. The graphs show
symmetry in stress distribution and slow changes in its distribution along Z-axis. These results
let conclude that the selected meshing size is enough for this specific problem. The behavior
of the stress distribution was the expected.
For this specific problem, it can be suggested to use a bigger meshing size. This could
help make the calculations faster and should not affect the results. However, this should not be
done if it is not necessary.
You might also like
- Rectangular Plate With Circular HoleDocument9 pagesRectangular Plate With Circular Holebalusharma1212No ratings yet
- ANSYS Handout: Hole Tutorial: 1. Overview About Plane ProblemsDocument18 pagesANSYS Handout: Hole Tutorial: 1. Overview About Plane ProblemsMuthu PandiNo ratings yet
- Transmissio Tower StructureDocument36 pagesTransmissio Tower StructureAbu SafyanNo ratings yet
- Give Example A TitleDocument8 pagesGive Example A Titleapi-3833671No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Crack ProblemDocument8 pagesTutorial 3 - Crack ProblemImran2109No ratings yet
- Plane Stress Bracket: Problem DescriptionDocument28 pagesPlane Stress Bracket: Problem DescriptionChong JongNo ratings yet
- Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams PDFDocument18 pagesShear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams PDFCholan PillaiNo ratings yet
- CE 463.3 - Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 - SAP2000 Plane ElasticityDocument14 pagesCE 463.3 - Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 - SAP2000 Plane ElasticityMarcelo ElguetaNo ratings yet
- Beam Analysis For Ansys SoftwareDocument18 pagesBeam Analysis For Ansys SoftwareHemant Mahajan100% (1)
- CE 463.3 - Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 - SAP2000 Plane ElasticityDocument14 pagesCE 463.3 - Advanced Structural Analysis Lab 4 - SAP2000 Plane ElasticityOuafi Saha100% (1)
- Static Analysis of A Corner BracketDocument11 pagesStatic Analysis of A Corner BracketFaizan RasoolNo ratings yet
- Residual Stresses of Plate With Holes by ANSYS Analysis - Hani Aziz AmeenDocument14 pagesResidual Stresses of Plate With Holes by ANSYS Analysis - Hani Aziz AmeenHani Aziz AmeenNo ratings yet
- NonLinear MaterialsDocument12 pagesNonLinear MaterialsNafees ImitazNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress BracketDocument18 pagesPlane Stress Bracketdeepak parariyaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Design in ANSYSDocument5 pagesPressure Vessel Design in ANSYSRohan KarandeNo ratings yet
- Cad Exp-7Document12 pagesCad Exp-7Harshal DodkeNo ratings yet
- Non Linear AnalysisDocument53 pagesNon Linear AnalysisdpksobsNo ratings yet
- Handout - Ansys ExamplesDocument13 pagesHandout - Ansys Examplesரா. ராஜ பாண்டிNo ratings yet
- Ansys ManualDocument94 pagesAnsys Manualgmahaadev100% (3)
- Tutorial Tensao Plana - ANSYSDocument29 pagesTutorial Tensao Plana - ANSYSCleytonClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Distributed LoadingDocument6 pagesDistributed LoadingJean David ChanNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Tutorials For MTECH StudentsDocument49 pagesANSYS Tutorials For MTECH StudentsSubbu SuniNo ratings yet
- Practical 4 - FEA LabDocument16 pagesPractical 4 - FEA LabMHK ZarkNo ratings yet
- Cad Exp-6Document12 pagesCad Exp-6Harshal DodkeNo ratings yet
- Ansys 3d Structural TestDocument32 pagesAnsys 3d Structural TestDevendra BangarNo ratings yet
- Plaxis Excercise 2Document17 pagesPlaxis Excercise 2RiadTaftafNo ratings yet
- Module 1.3: Distributed Loading of A 1D Cantilever Beam: Page Number Problem Description 2Document12 pagesModule 1.3: Distributed Loading of A 1D Cantilever Beam: Page Number Problem Description 2nanduslns07No ratings yet
- Mesh Convergence Study Using ANSYSDocument9 pagesMesh Convergence Study Using ANSYSsmvarunmurthyNo ratings yet
- Femap TutorialsDocument9 pagesFemap Tutorialsalexandre oliveiraNo ratings yet
- Preprocessing: Defining The Problem: Keypoint Coordinates (X, Y, Z)Document5 pagesPreprocessing: Defining The Problem: Keypoint Coordinates (X, Y, Z)dsathiyaNo ratings yet
- Buckling in ANSYSDocument18 pagesBuckling in ANSYSNafees ImitazNo ratings yet
- U of A ANSYS Tutorials - NonLinear MaterialsDocument8 pagesU of A ANSYS Tutorials - NonLinear Materialskiran_wakchaureNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of Compression of Thin, High Modulus, Cylindrical Shells With Low-Modulus CoreDocument8 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Compression of Thin, High Modulus, Cylindrical Shells With Low-Modulus CoreGhouse ShaikNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Assignment 1Document14 pagesANSYS Assignment 1Sebastián ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Ansys ExperimentsDocument10 pagesAnsys ExperimentsASIST MechNo ratings yet
- Me 266 Solid Mechanics Laboratory Virtual Tensile Test Tutorial 1 Problem DescriptionDocument9 pagesMe 266 Solid Mechanics Laboratory Virtual Tensile Test Tutorial 1 Problem DescriptionDeva RajNo ratings yet
- An Approach To Finite Element Analysis of Boiler Tube-SheetDocument4 pagesAn Approach To Finite Element Analysis of Boiler Tube-SheetAJER JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Practice - 2DDocument2 pagesPractice - 2DVinícius VitorelliNo ratings yet
- Lab3 PlateDocument8 pagesLab3 PlateffefffeNo ratings yet
- AnsysDocument15 pagesAnsysginupaulNo ratings yet
- Buckling: Nonlinear TutorialDocument27 pagesBuckling: Nonlinear TutorialSwadesh DixitNo ratings yet
- Buckling Analysis: The Theory of BucklingDocument6 pagesBuckling Analysis: The Theory of BucklingKing Everest100% (2)
- Analysis of L BracketDocument18 pagesAnalysis of L Bracketlipi8No ratings yet
- Ansys ManualDocument36 pagesAnsys ManualSaras ChandraNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Method Using Pro ENGINEER and ANSYSDocument11 pagesFinite Element Method Using Pro ENGINEER and ANSYSsunil481No ratings yet
- Analysis & Simulation Lab ManualDocument35 pagesAnalysis & Simulation Lab ManualnarendranNo ratings yet
- Application of Distributed Loads: 1. Open Preprocessor Menu 2. Give Example A TitleDocument6 pagesApplication of Distributed Loads: 1. Open Preprocessor Menu 2. Give Example A Titlesilverknights007No ratings yet
- Standard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationFrom EverandStandard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationNo ratings yet
- Finite Elements for Truss and Frame Structures: An Introduction Based on the Computer Algebra System MaximaFrom EverandFinite Elements for Truss and Frame Structures: An Introduction Based on the Computer Algebra System MaximaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsFrom EverandTheory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Planar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachFrom EverandPlanar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachNo ratings yet
- Method of Moments for 2D Scattering Problems: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsFrom EverandMethod of Moments for 2D Scattering Problems: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Civil 3D - Roads Design: 2From EverandAutoCAD Civil 3D - Roads Design: 2Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Lecture Slides: Shigley's Mechanical Engineering DesignDocument95 pagesLecture Slides: Shigley's Mechanical Engineering DesignpurnaNo ratings yet
- Colis I OnesDocument15 pagesColis I OnesAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides: Fatigue Failure Resulting From Variable LoadingDocument130 pagesLecture Slides: Fatigue Failure Resulting From Variable LoadingABHISHEKSNo ratings yet
- Colis I OnesDocument15 pagesColis I OnesAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- CH 17 Slides MDocument111 pagesCH 17 Slides MAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Shigley CH One SlidesDocument35 pagesShigley CH One Slidesengineer60638100% (2)
- EML3500 CH 2 SlidesDocument71 pagesEML3500 CH 2 SlideshaysamNo ratings yet
- Free-Form Design of Tensegrity Structures by Non-Rigid-Body Motion Analysis PDFDocument4 pagesFree-Form Design of Tensegrity Structures by Non-Rigid-Body Motion Analysis PDFAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Generation of Planar Tensegrity Structures Through Cellular MultiplicationDocument29 pagesGeneration of Planar Tensegrity Structures Through Cellular MultiplicationAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- CH 17 Slides MDocument111 pagesCH 17 Slides MAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Fuller and Clerk Maxwell Rules For Stiff Frames by CalladineDocument12 pagesFuller and Clerk Maxwell Rules For Stiff Frames by CalladineTensegrity WikiNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Slides M PDFDocument77 pagesCH 11 Slides M PDFhajar chouiyakhNo ratings yet
- CH 12 SlidesDocument110 pagesCH 12 SlidesLuis PintoNo ratings yet
- Further Remarks On First Order Infinitesimal Mechanisms PDFDocument4 pagesFurther Remarks On First Order Infinitesimal Mechanisms PDFAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- General Approach For Topology-Finding of Tensegrity Structures PDFDocument16 pagesGeneral Approach For Topology-Finding of Tensegrity Structures PDFAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- First-Order Infinitesimal Mechanisims PDFDocument13 pagesFirst-Order Infinitesimal Mechanisims PDFAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Form-Finding of Tensegrity Structures With Multiple States of Self-Stress PDFDocument17 pagesForm-Finding of Tensegrity Structures With Multiple States of Self-Stress PDFAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Behavior and Vibration Control of A Tensegrity Structure PDFDocument12 pagesDynamic Behavior and Vibration Control of A Tensegrity Structure PDFAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Full Paper Docx 1493361422 PDFDocument8 pagesFull Paper Docx 1493361422 PDFAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Bodyweight Exercises Chart PDFDocument1 pageBodyweight Exercises Chart PDFAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Behavior and Vibration Control of A Tensegrity Structure PDFDocument12 pagesDynamic Behavior and Vibration Control of A Tensegrity Structure PDFAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Modal Analysis of A Tensegrity Structure by Bossens, Callafon, SkeltonDocument20 pagesModal Analysis of A Tensegrity Structure by Bossens, Callafon, SkeltonTensegrity WikiNo ratings yet
- A Rough Guide For Conference AuthorsDocument4 pagesA Rough Guide For Conference AuthorsAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Structural Morphology of Tensegrity SystemsDocument14 pagesStructural Morphology of Tensegrity SystemsAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Total AbsDocument32 pagesTotal AbsDavid Quirós LazarenoNo ratings yet
- Synergy Fuller PDFDocument320 pagesSynergy Fuller PDFAfonso PortelaNo ratings yet
- Form-Finding of Tensegrity Structures Subjected To Geometrical ConstraintsDocument14 pagesForm-Finding of Tensegrity Structures Subjected To Geometrical ConstraintsAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Full Paper Docx 1493361422 PDFDocument8 pagesFull Paper Docx 1493361422 PDFAndrésGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Evolutionary Form Finding of Tensegrity Structures by Paul, Lipson, CuevasDocument8 pagesEvolutionary Form Finding of Tensegrity Structures by Paul, Lipson, CuevasTensegrity WikiNo ratings yet
- Motion 1 TheoryDocument13 pagesMotion 1 TheoryAyaan KachwalaNo ratings yet
- Secmm CC Theme 1 Key Idea 9Document32 pagesSecmm CC Theme 1 Key Idea 9Halima ZernabNo ratings yet
- Anmol Publications - PB Catalog (14-05-2014)Document70 pagesAnmol Publications - PB Catalog (14-05-2014)Beenu BhallaNo ratings yet
- 21.04.24 - Osr - Star Co-Sc - Jee-Adv - 2023 - P1 - Gta-7 (P2) - QPDocument16 pages21.04.24 - Osr - Star Co-Sc - Jee-Adv - 2023 - P1 - Gta-7 (P2) - QPvenkateswararao.yNo ratings yet
- Systemic Functional Linguistics: A Brief Introduction: ArticleDocument4 pagesSystemic Functional Linguistics: A Brief Introduction: ArticleHarinder Singh HundalNo ratings yet
- Theory of Computation - Context Free LanguagesDocument25 pagesTheory of Computation - Context Free LanguagesBhabatosh SinhaNo ratings yet
- Semi-Variogram - Nugget, Range and Sill - GIS GeographyDocument8 pagesSemi-Variogram - Nugget, Range and Sill - GIS GeographyhNo ratings yet
- Numbers and Statistics Guide: 7th EditionDocument2 pagesNumbers and Statistics Guide: 7th EditionMelaniekleineNo ratings yet
- Programs On Loops: A-35 Python AssingmentDocument12 pagesPrograms On Loops: A-35 Python AssingmentA- 08 KaushikiNo ratings yet
- Wolfe ConditionsDocument5 pagesWolfe ConditionsRaviKumarNo ratings yet
- Equations of Circles PDFDocument4 pagesEquations of Circles PDFMAYNo ratings yet
- Spesfeed Express HelpDocument85 pagesSpesfeed Express HelpSalvador Villicaña Maldonado100% (1)
- Puzzle Related To MathDocument2 pagesPuzzle Related To MathBeverlyBandojoNo ratings yet
- 1974 Fast Convolution Using Fermat Number Transforms With Applications To Digital FilteringDocument11 pages1974 Fast Convolution Using Fermat Number Transforms With Applications To Digital FilteringRajesh BathijaNo ratings yet
- HS20Document8 pagesHS20kumarg_19No ratings yet
- Time - PGP DSBADocument43 pagesTime - PGP DSBAvansh guptaNo ratings yet
- Multi Step Questions - PowerPointDocument9 pagesMulti Step Questions - PowerPointbrhNo ratings yet
- Salesforce Interview Questions On TriggerDocument3 pagesSalesforce Interview Questions On TriggerSumit Datta100% (2)
- 201Document5 pages201Mohan Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- USFS Timber Cruising Handbook PDFDocument268 pagesUSFS Timber Cruising Handbook PDFJeffTaborNo ratings yet
- Quest Electrostatics 4 KeyDocument5 pagesQuest Electrostatics 4 KeyCarlos OrtizNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer & Thermodynamics in Nuclear ReactorsDocument26 pagesHeat Transfer & Thermodynamics in Nuclear ReactorsLohith KumarNo ratings yet
- 04 - EGC3173 - EGC3113 - Selection StructuresDocument34 pages04 - EGC3173 - EGC3113 - Selection StructuresLudik CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Bourbaki - Lie Groups and Lie Algebras (Chapters 4-6)Document314 pagesBourbaki - Lie Groups and Lie Algebras (Chapters 4-6)Zoe RossiNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Report Lab2 1Document10 pagesGroup 5 Report Lab2 1Đức TrọngNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanAmlorepava Mary50% (2)
- 10 - Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) PDFDocument56 pages10 - Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) PDFPankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- CursengDocument230 pagesCursengRadu TrimbitasNo ratings yet
- Pauli Paramagnetism and Superconducting StateDocument12 pagesPauli Paramagnetism and Superconducting StatecaktotNo ratings yet
- Biometry Lecture 6 PostedDocument81 pagesBiometry Lecture 6 PostedS. MartinezNo ratings yet