Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Company Name: Calculation Sheet
Uploaded by
Venkatesha HebbarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Company Name: Calculation Sheet
Uploaded by
Venkatesha HebbarCopyright:
Available Formats
COMPANY NAME
Calculation No.
CALCULATION NUMBER
CALCULATION SHEET Project No.
onlinestructuraldesign.com
PROJECT NUMBER
Project Title:
Project Name
Calc. By Date Rev.
Author today 0
Subject/Feature:
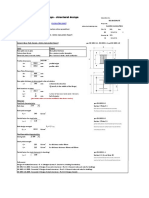
Column Base Plat e Calculat ion
Checked By Date Rev.
Checker today 0
Column Base Plate Calculation per EN 1992-1-1, EN 1993-1-1 and EN 1993-1-8
Input Output
Base plate size in plan Base plate thickness
Column base forces Max. pressure under baseplate
Materials (steel, concrete, bolts) Max. tension in bolts / bolt vericaon
Prole dimensions
HEA340
h = 304.8 mm prole height
b = 304.8 mm prole width
Base Plate Dimensions
H = 600 mm
B = 600 mm
a = 0.95
Base plate thickness is determined in the calculaon
s = 155.22mm
Bolt locaons on plate
f = 241.3 mm
N
B
= 4 number of bolts
= 20 mm bolt diameter
Baseplate http://www.onlinestructuraldesign.com/calcs/Baseplate/Baseplate.aspx
1 of 7 6/11/2013 10:40 PM
Materials
Steel bolt characteriscs per EN 1993-1-8
Bolt class
4.6
Secon 3 Table 3.1
bolt classes recommended bythe Eurocode;
Bold yield strength The Naonal Annexmayexclude certain bolt classes.
f
yb
= 240 N/mm
2
Paral factor for steel bolts per EN 1993-1-8
M2
= 1.25 Secon 2 Table 2.1
paral safetyfactors recommended bythe Eurocode;
Bolt design strength f
yd
=f
y
/
M2 Numerical values for safety factors may be dened
f
yd-b
= 192.0 N/mm
2
in the Naonal Annex
Steel base plate characteriscs
Steel grade S 235
Steel yield strength
f
y
= 235 N/mm
2
for thickness under 40mm
f
y
= 215 N/mm
2
for thickness between 40mm and 80mm
Paral factor for steel elements (in bending) per EN 1993-1-1
M0
= 1.00 Secon 6.1 (1) and Note 2B
value recommended bythe Eurocode; value to be used
can be found in the Eurocode Naonal Annexes
Steel modulus of elascity per EN 1993-1-1
E
s
= 210000 N/mm
2
Secon 3.2.6 (1)
Concrete characteriscs
Concrete class
C12/15
per EN 1992-1-1:2004
f
ck
= 12MPa concrete characterisc cylinder strength Secon 3 Table 3.1
Baseplate http://www.onlinestructuraldesign.com/calcs/Baseplate/Baseplate.aspx
2 of 7 6/11/2013 10:40 PM
References:
Design of Welded Structures - O. W. Blodge (James F. Lincoln Arc Welding Foundaon)
EN 1992-1-1:2004 - Eurocode 2: Design of concrete structures - Part 1-1: General rules and rules for buildings
EN 1993-1-1:2005 - Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures - Part 1-1: General rules and rules for buildings
EN 1993-1-8:2005 - Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures - Part 1-8: Design of joints
COMPANY NAME
Calculation No.
CALCULATION NUMBER
CALCULATION SHEET Project No.
onlinestructuraldesign.com
PROJECT NUMBER
Project Title:
Project Name
Calc. By Date Rev.
Author today 0
Subject
Column Base Plat e Calculat ion Ckd. By Date Rev.
Checker today 0
Paral factor for concrete for ulmate limit states per EN 1992-1-1:2004
Secon 2 Table 2.1N
c
= 1.5
values for Persistent & Transient design situaons
recommended by the Eurocode; values to be used
maybe found in the Eurocode Naonal Annexes
Design compressive concrete strength per EN 1992-1-1:2004
Secon 3.1.6 & Formula 3.15
a
cc
= 1
Coecient taking account of long term eects
f
cd
= a
cc
* f
ck
/ g
c = 8.00MPa on the compressive strength and of unfavourable
eectsresulng fromthe waythe load is applied
value may be found in the EC Naonal Annex
Concrete modulus of elascity
E
cm
= 27GPa for concrete class C12/15 per EN 1992-1-1:2004
Secon 3.1.3 Table 3.1
Aggregates =
quartzite
Secon 3.1.3 (2)
Values in Table 3.1 are given for quartzite aggregates
E
cm
= 27GPa for concrete with quartzite aggregates Values for limestone and sandstone are reduced by10%
Baseplate http://www.onlinestructuraldesign.com/calcs/Baseplate/Baseplate.aspx
3 of 7 6/11/2013 10:40 PM
E
cm
= 27000N/mm
2
and 30%respecvely. For basalt aggregates the value
should be increased by 20%
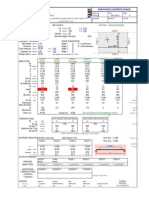
Column base forces
N =
1000
kN axial force pair of column base forces. Mxand Myare not
M =
380
kN*m bending moment considered simultaneous.
e = M/F = 380.0mm
H/6 = 100.00 mm eccentricity
e >H/6 =>Baseplate with large eccentricity
Three equaons, three unknowns: F
b
, Y, s
c
(Axial force in steel hold down bolts, acve area under base plate,
maximum pressure under base plate)
1. Forces equilibrium
Y*s
c
/2 - F
b
-N =0
F
b
+N =Y*s
c
*B/2 (1)
2. Bendingmoment equilibrium
F
b
* f +(F
b
+N) * (H/2 - Y/3) - N * e =0
F
b
=-N * (H/2 - Y/3 -e)/(H/2 - Y/3 +f) (2a)
N =-F
b
* (H/2 - Y/3 -e)/(H/2 - Y/3 +f) (2)
3. Represenngthe elasc behaviour of the concrete
support and the steel hold-down bolt:
a/b = e
b
/e
c
= (s
b
/ E
s
) / (s
c
/ E
c
)
since E
s
= s
b
/ e
s modulus of elascityof steel bolt
E
c
= s
c
/ e
c modulus of elascityof concrete
Baseplate http://www.onlinestructuraldesign.com/calcs/Baseplate/Baseplate.aspx
4 of 7 6/11/2013 10:40 PM
n
b
= 2 number of steel hold down bolts
A
b
= 2* *
2
/4 = 628.3mm
2
area of steel hold down bolts
s
b
= F
b
/ A
b
n = E
s
/ E
c
= 7.78 modular rao of elascity, steel to concrete
References:
Design of Welded Structures - O. W. Blodge (James F. Lincoln Arc Welding Foundaon)
EN 1992-1-1:2004 - Eurocode 2: Design of concrete structures - Part 1-1: General rules and rules for buildings
EN 1993-1-1:2005 - Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures - Part 1-1: General rules and rules for buildings
EN 1993-1-8:2005 - Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures - Part 1-8: Design of joints
COMPANY NAME
Calculation No.
CALCULATION NUMBER
CALCULATION SHEET Project No.
onlinestructuraldesign.com
PROJECT NUMBER
Project Title:
Project Name
Calc. By Date Rev.
Author today 0
Subject
Column Base Plat e Calculat ion Ckd. By Date Rev.
Checker today 0
a/b = (N/A
b
)/(s
c
*n) = N/(A
b
*s
c
*n)
From similar triangles =>
a/b = (H/2-Y+f)/Y
=> N/(A
b
*s
c
*n) = (H/2-Y+f)/Y =>
=> s
c
= F
b
* Y / (A
b
* n *(H/2 - Y +f)) (3)
From(1), (2) and (3)
-F
b
* (H/2 - Y/3 -e)/(H/2 - Y/3 +b) +F
b
= (F
b
* Y
2
* B) / [2 * A
b
* n *(H/2 - Y +f)]
Solve for Y:
Y
3
+3 * (e - H/2) * Y
2
+[(6 * n * A
b
)/B] * (f +e) * Y - [(6 * n * A
b
)/B] * (H/2 +f) * (f +e) =0
Baseplate http://www.onlinestructuraldesign.com/calcs/Baseplate/Baseplate.aspx
5 of 7 6/11/2013 10:40 PM
or
Y
3
+K
1
* Y
2
+K
2
* Y +K
3
=0
where
K
1
= 3 * (e - H/2) = 240
K
2
= [(6 * n * A
b
)/B] * (f +e) = 30362
K
3
= - K
2
* (H/2 +f) = -16435192
Y = 166.5mm
F
b
= 278.92kN (in 2 bolts ) per (2a) hold down bolts max. tension (in all bolts)
F
1.bolt
=F
b
/ 2 = 139.46kN hold down bolt max. tension - in 1 bolt
F
1.bolt
/(*
2
/4) = 443.92N/mm
2
> f
yd-b redimension, bolt eecve stress is larger than bolt design stress
192.0N/mm
2
s
c
= 25.35MPa per (3)
s
c > f
cd f
cd
= 8.00MPa eecve max. pressure under baseplate is compared
redesign base plate length and/or width with the concrete design compressive strength
stress under base plate is larger than the concrete compressive capacity if the max. pressure is higher than the concrete
Design of the Base Plate Thickness
Crical secon locaon
s = 155.22 mm
Stress at the crical secon locaon
s
sc
= s
c
*(Y - s) / Y = 1.72 MPa
Design crical moment - at crical secon
M
Ed.plate
= [(sc*s/2)*(s/3)+(c*s/2)*(s*2/3)]*B 126.31kN*m
M
C,Rd
=M
pl,rd
= (W
pl
* f
y
)/
M0 (4)
per EN 1993-1-1
Secon 6.2.5 (2) Formula 6.13
Design resistance for bending for bending about one
principal axis for class 1 or 2 cross secons
Plasc secon modulus of rectangular secons
Baseplate http://www.onlinestructuraldesign.com/calcs/Baseplate/Baseplate.aspx
6 of 7 6/11/2013 10:40 PM
W
pl
= B*t
pl
2
/4 (5)
(t
pl
=base plate thickness)
from (4) and (5) =>[f
y
* (B*t
pl
2
)/4]/
M0
M
Ed.plate
=>t
pl
[4 * M
Ed.plate
*
M0
/ (B * f
y
)]
=>t
pl
62.58mm (with f
y
= 215N/mm
2
)
References:
Design of Welded Structures - O. W. Blodge (James F. Lincoln Arc Welding Foundaon)
EN 1992-1-1:2004 - Eurocode 2: Design of concrete structures - Part 1-1: General rules and rules for buildings
EN 1993-1-1:2005 - Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures - Part 1-1: General rules and rules for buildings
EN 1993-1-8:2005 - Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures - Part 1-8: Design of joints
Baseplate http://www.onlinestructuraldesign.com/calcs/Baseplate/Baseplate.aspx
7 of 7 6/11/2013 10:40 PM
You might also like
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Structural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsFrom EverandStructural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsNo ratings yet
- Base Plate Calculations IDocument5 pagesBase Plate Calculations Ivarshasdm1987No ratings yet
- Base Plate Cal1,2Document4 pagesBase Plate Cal1,2MyunSu GooNo ratings yet
- Base Plate Cal PDFDocument5 pagesBase Plate Cal PDFMyunSu GooNo ratings yet
- Composite Steel DesignDocument33 pagesComposite Steel DesignALABIADESINA100% (1)
- Steel Structures 3 - Composite Steel-Concrete Structures - Slides Lecture 4 To 6Document46 pagesSteel Structures 3 - Composite Steel-Concrete Structures - Slides Lecture 4 To 6iSoK11No ratings yet
- FW Pipe Rack DocumentDocument38 pagesFW Pipe Rack DocumentSumanthNo ratings yet
- CR 13045 PIER R00 Calculation ReportDocument11 pagesCR 13045 PIER R00 Calculation Reportmusiomi2005No ratings yet
- Rec4 T BeamsDocument3 pagesRec4 T BeamsmillwallandrewNo ratings yet
- Wood Element Axial Bending EC5Document2 pagesWood Element Axial Bending EC5nicolaemariusNo ratings yet
- Column Base Plate Eurocode Ods FileDocument7 pagesColumn Base Plate Eurocode Ods FileSimon LsmNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tank Support StructureDocument44 pagesCooling Tank Support Structurevj8584100% (1)
- 2011 Retaining Wall Design Guide USFS Mohney 5 LVR Slope StabilityDocument559 pages2011 Retaining Wall Design Guide USFS Mohney 5 LVR Slope StabilitySima ViorelNo ratings yet
- Ti809 07Document136 pagesTi809 07smartcad60No ratings yet
- Eurocode 2 - BeamsDocument8 pagesEurocode 2 - Beamsmm507No ratings yet
- Design Parameter:-Geo-ParameterDocument50 pagesDesign Parameter:-Geo-ParameterpandyatusharNo ratings yet
- Composite Steel DesignDocument33 pagesComposite Steel DesignscegtsNo ratings yet
- Beam Identity: GB-6 On Grid W.A1 Beam Data:: (Dead) (Live)Document12 pagesBeam Identity: GB-6 On Grid W.A1 Beam Data:: (Dead) (Live)redscorpion1No ratings yet
- Chapter 24 WexDocument7 pagesChapter 24 WexCiprian VarlanNo ratings yet
- Mathcad V1 BDocument11 pagesMathcad V1 BDoğan ArslanNo ratings yet
- Crack Width BS 8110Document2 pagesCrack Width BS 8110nhulugallaNo ratings yet
- 11 Continuous BeamsDocument55 pages11 Continuous BeamsMelinda GordonNo ratings yet
- Report DSGNDocument2 pagesReport DSGNopulitheNo ratings yet
- Pinned Base As Per AISC-Detail-A-R0Document5 pagesPinned Base As Per AISC-Detail-A-R0Sunil Pulikkal100% (1)
- RC Beam Torsion Design (BS8110)Document2 pagesRC Beam Torsion Design (BS8110)Osarieme Osakue100% (3)
- Acuity Base Frame Anchorage July 3, 2008Document7 pagesAcuity Base Frame Anchorage July 3, 2008GoswandiNo ratings yet
- Raft Slab DesignDocument5 pagesRaft Slab DesignLekins Sefiu Yekini100% (2)
- Evo Design S.R.L.: Calculation SheetDocument1 pageEvo Design S.R.L.: Calculation SheetkhantoNo ratings yet
- Design of Swimming Pool PDFDocument21 pagesDesign of Swimming Pool PDFjanithbogahawatta67% (3)
- PF2Document4 pagesPF2nhulugallaNo ratings yet
- Fin Plate Beam-To-column-flange Connection (GB)Document16 pagesFin Plate Beam-To-column-flange Connection (GB)Vlad MosNo ratings yet
- En Column Base Plate 1.0Document7 pagesEn Column Base Plate 1.0Ali AlomyNo ratings yet
- Element 45 - 1538-NOTE 2Document35 pagesElement 45 - 1538-NOTE 2hadeer youns100% (1)
- Steel Design LSMDocument65 pagesSteel Design LSMStructural SpreadsheetsNo ratings yet
- Base Ring AnalysisDocument9 pagesBase Ring Analysisasirul_meNo ratings yet
- Architectural Fins - Rev 2-5 (1) .9.08Document15 pagesArchitectural Fins - Rev 2-5 (1) .9.08vj8584100% (1)
- 1.2m Box CulvertDocument52 pages1.2m Box Culvertkanishka100% (1)
- Etabs 9.7.2 Shear Wall Design SWD-ACI-318-08Document89 pagesEtabs 9.7.2 Shear Wall Design SWD-ACI-318-08chauhannishargNo ratings yet
- BS ProcedureDocument13 pagesBS ProceduremarahmankhanNo ratings yet
- Base Ring and SkirtDocument8 pagesBase Ring and Skirtduazo2009No ratings yet
- Lessen of Steel DesignDocument34 pagesLessen of Steel DesignMohammed AdelNo ratings yet
- SX019a-En-EU-Example - Column Base Connection Under Axial CompressionDocument5 pagesSX019a-En-EU-Example - Column Base Connection Under Axial CompressionWNo ratings yet
- HiltiDocument10 pagesHiltiAnonymous YDwBCtsNo ratings yet
- Zick Analysis For Saddle SupportDocument8 pagesZick Analysis For Saddle Supportfuransu777100% (1)
- Base Plate Design Metric Units PDFDocument8 pagesBase Plate Design Metric Units PDFVinayak PatilNo ratings yet
- Towerwind Analysis - Anchoragebolt - Base PlateDocument14 pagesTowerwind Analysis - Anchoragebolt - Base PlateJoy lauriaNo ratings yet
- Column Base Plate (Eurocode)Document4 pagesColumn Base Plate (Eurocode)_at_to_No ratings yet
- Exercise EC4Document23 pagesExercise EC4babel_stanNo ratings yet
- EC4 Composite DesignDocument51 pagesEC4 Composite DesignbsitlerNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Elements and AssembliesFrom EverandMachine Design Elements and AssembliesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsFrom EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Steel Buildings: A Practical Guide for Structures and EnvelopesFrom EverandSustainable Steel Buildings: A Practical Guide for Structures and EnvelopesBernhard HaukeNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationFrom EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertNo ratings yet
- Ageing and Life Extension of Offshore Structures: The Challenge of Managing Structural IntegrityFrom EverandAgeing and Life Extension of Offshore Structures: The Challenge of Managing Structural IntegrityNo ratings yet
- Durability Design of Concrete Structures: Phenomena, Modeling, and PracticeFrom EverandDurability Design of Concrete Structures: Phenomena, Modeling, and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Control Equipments: (Design, Manufacture & Commissioning)Document11 pagesAir Pollution Control Equipments: (Design, Manufacture & Commissioning)Venkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Analysis VerificationDocument8 pagesDynamic Analysis VerificationMichael DixonNo ratings yet
- IJEE1497Document11 pagesIJEE1497Muluken TemesgenNo ratings yet
- Beam Splice Design: 1 Input Data: 1.1 Section and Section PropertiesDocument13 pagesBeam Splice Design: 1 Input Data: 1.1 Section and Section PropertiesVenkatesha Hebbar100% (1)
- Structural Steel Design Project: Calculation SheetDocument14 pagesStructural Steel Design Project: Calculation SheetJoey Johnson100% (2)
- TDocument1 pageTVenkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- Scanned by CamscannerDocument25 pagesScanned by CamscannerVenkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- Beam Splice Design: 1 Input Data: 1.1 Section and Section PropertiesDocument13 pagesBeam Splice Design: 1 Input Data: 1.1 Section and Section PropertiesVenkatesha Hebbar100% (1)
- 3Document4 pages3Venkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- KC-5125-01-Foundation Details-AvadiDocument1 pageKC-5125-01-Foundation Details-AvadiVenkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- Load Input File: CHKD VRH Appd VRH Date 13-SEPT-2019Document31 pagesLoad Input File: CHKD VRH Appd VRH Date 13-SEPT-2019Venkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- 24 Sample ChapterDocument14 pages24 Sample ChapterRomyMohanNo ratings yet
- 4Document2 pages4Venkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- KC-5125-01-Foundation Details-AvadiDocument1 pageKC-5125-01-Foundation Details-AvadiVenkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- Air BlastersDocument3 pagesAir BlastersVenkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- KC-5125-01-Foundation Details-AvadiDocument1 pageKC-5125-01-Foundation Details-AvadiVenkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- Moment Connection Beam Column Is Bs Section For Is800Document27 pagesMoment Connection Beam Column Is Bs Section For Is800Ramesh SelvarajNo ratings yet
- 24 Sample ChapterDocument14 pages24 Sample ChapterRomyMohanNo ratings yet
- 08-12-2011 Ambient Data PDFDocument1 page08-12-2011 Ambient Data PDFVenkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Beam/Column Splice: HB-300x300x10x15Document5 pagesCalculation of Beam/Column Splice: HB-300x300x10x15mustika05No ratings yet
- Volume CalculationDocument1 pageVolume CalculationVenkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- (Logistics Team) PDO Oilfield Transport & Interior Based Vehicle SpecificationsDocument22 pages(Logistics Team) PDO Oilfield Transport & Interior Based Vehicle SpecificationsVenkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- XssDocument16 pagesXssVenkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- Recommended Size of Gutter Slopes Draining Roofs Can Be Found in The Table BelowDocument1 pageRecommended Size of Gutter Slopes Draining Roofs Can Be Found in The Table BelowVenkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- Crane Rail Fixing StandardsDocument5 pagesCrane Rail Fixing StandardsVenkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- 740 Single MASSDocument2 pages740 Single MASSVenkatesha HebbarNo ratings yet
- Steel Connection DesignDocument68 pagesSteel Connection DesignPushkar KokaneNo ratings yet
- Ke Building 2009Document639 pagesKe Building 2009JosseNo ratings yet
- CivilBay Crane Load Crane Runway Beam Design 1.0.0 ManualDocument112 pagesCivilBay Crane Load Crane Runway Beam Design 1.0.0 Manualwudongxiao3953100% (2)
- NBC000-1994 State of ArtDocument16 pagesNBC000-1994 State of ArtPrateek Raj PanditNo ratings yet
- IS 2339 - 2013 Aluminium General PurposeDocument9 pagesIS 2339 - 2013 Aluminium General PurposeSudheep DuraiNo ratings yet
- PXE Modes of Operation White Paper V1.0Document7 pagesPXE Modes of Operation White Paper V1.0Davide ToniniNo ratings yet
- Xiaomi Mi 1 (Xiaomi-Shouji) SchematicDocument31 pagesXiaomi Mi 1 (Xiaomi-Shouji) SchematicPino AffeNo ratings yet
- Ports and Protocols - JabberDocument3 pagesPorts and Protocols - JabberCinthya Rocasalvo PerezNo ratings yet
- Call Setup FailureDocument24 pagesCall Setup FailureHien NguyenNo ratings yet
- UML Diagram Step by StepDocument26 pagesUML Diagram Step by StepAnonymous DQbHR4No ratings yet
- Begin Build Oppo PropertiesDocument14 pagesBegin Build Oppo Propertiesディ ローズNo ratings yet
- Atm ProjectDocument18 pagesAtm Projectsujit_ranjanNo ratings yet
- Hydran M2Document2 pagesHydran M2Al De LeonNo ratings yet
- 2018 Sundray Junior Certification Lesson - One - 05 - Fat AP - v3.6.7Document26 pages2018 Sundray Junior Certification Lesson - One - 05 - Fat AP - v3.6.7wendy yohanesNo ratings yet
- RT 1120 Op ManualDocument130 pagesRT 1120 Op ManualfrankNo ratings yet
- Standard For Industrial Enclosed Gear Drives (Metric Edition)Document67 pagesStandard For Industrial Enclosed Gear Drives (Metric Edition)Nicole Suarez50% (2)
- 664 Publist 2014 DecemberDocument15 pages664 Publist 2014 DecemberJ Salvador Calderón BarrancosNo ratings yet
- Series Ap Directly Operated Proportional Valves: Use and Maintenance ManualDocument16 pagesSeries Ap Directly Operated Proportional Valves: Use and Maintenance Manualhazem ab2009No ratings yet
- Is en 1706 - 2010Document9 pagesIs en 1706 - 2010jonathan_scribd12345No ratings yet
- Ansi B1.20.7Document24 pagesAnsi B1.20.7gxbxb100% (2)
- Is 9902 2004Document11 pagesIs 9902 2004cbbasakNo ratings yet
- 9365-AN/910 Manual of All-Weather Operations Second Edition - 1991Document67 pages9365-AN/910 Manual of All-Weather Operations Second Edition - 1991Fran Rodriguez SanchezNo ratings yet
- CME Deleting The Name of The PersonDocument3 pagesCME Deleting The Name of The PersonkhalidNo ratings yet
- Tacoma: Here's The Tacoma TRD Pro 4x4 Double Cab V6 6-Speed Automatic Short BedDocument7 pagesTacoma: Here's The Tacoma TRD Pro 4x4 Double Cab V6 6-Speed Automatic Short Bedk2057282No ratings yet
- RAN18.1 Capacity Monitoring Guide (BSC6910-Based) (02) (PDF) - EN PDFDocument78 pagesRAN18.1 Capacity Monitoring Guide (BSC6910-Based) (02) (PDF) - EN PDFUmar MirNo ratings yet
- Limited Edition XOS - 6060 PDFDocument2 pagesLimited Edition XOS - 6060 PDFEngg.Nafees AhmedNo ratings yet
- BS en 20898-1-1992Document26 pagesBS en 20898-1-1992consultach100% (4)
- PQP Vs ISO 9001 Clauses List PDFDocument1 pagePQP Vs ISO 9001 Clauses List PDFVpln Sarma100% (1)
- 10 Multicast Zone Routing Protocol For Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksDocument6 pages10 Multicast Zone Routing Protocol For Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksakshusvgNo ratings yet
- Fab Idia Baru PDFDocument7 pagesFab Idia Baru PDFQudsiPradyanNo ratings yet
- Huawei HO Parameter OptimizeDocument24 pagesHuawei HO Parameter Optimizerizal0111884120% (2)
- Mag Ss 03152 en m1000 Csi SpecsDocument10 pagesMag Ss 03152 en m1000 Csi SpecsAsad HaiderNo ratings yet
- QML TutorialDocument16 pagesQML TutorialAmanda Carr100% (1)
- LT0098Document8 pagesLT0098mkbijuNo ratings yet