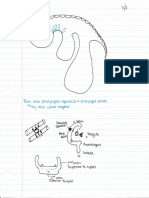
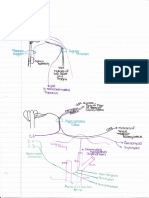
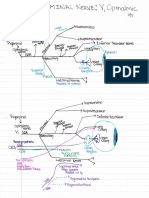
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genetic Diseases
Uploaded by
Beck33ers5826Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Genetic Diseases
Uploaded by
Beck33ers5826Copyright:
Available Formats
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
Rubinstein-
Taybi Syndrome
- broad/angulated thumbs
and big toe
- short stature
- moderate to severe mental
retardation (avg IQ: 35-50)
- Hirsutism (hairyness)
- high arching palate
- grimacing smile
- breaked nose with
columella extending below
nares
- undescended male testes
- down-slanting palpebral
fissures
- undescending testes
- Autosomal Dominant
CREB-Binding
Protein
(CREBBP)
- located on
16p13.3
- most
common
E1A-associated
protein p300
(EP300)
- located at
22q12
CREBBP:
1) provides molecular bridge between
regulatory transcription factors and
general transcription factors and RNA
polymerase.
2) Represses transition from G1 to S phase
3) histone Acetyltransferase activity
allowing transcription factors to access
DNA
EP300:
1) produces protein p300:
- functions as transcription co-factor
for some nuclear proteins
- histone acetyltransferase that
functions as a tumor suppressor
Rett Syndrome - hallmark: apraxia
(inability to carry out
purposeful movement)
- ringing of hands
- hand and foot deformities
- normal psychomotor
development first 6-18
months followed by rapid
regression in language and
motor skills
- autistic features
- females: progressive
neurological disorder
- males: lethal
- X-linked Dominant
Methyl-CpG-
binding protein
2 (MECP2)
- located at
Xq28
1) mediate transcriptional silencing and
epigenetic regulation of methylated DNA
- associated with 5-m-C rich
heterochromatin
2) recruit histone deacetylases by
interacting with co-repressor Sin3A
3) binds to methylated CpG dinucleotides
- important for X-chromosomes
inactivation
4) may play a role in mediating splicing
Fragile X
Syndrome
Males: mental retardation
- large head ; long face ;
protruding ears; large
testes
Females: mild mental
retardation
X-linked Dominant Trinucleotide
expansion
disorder of
FMR1 gene
- located on
Xq27.3
Alleles with more than 230 CGG repeats
usually have hypermethylation of the
repeats and the adjacent FMR1 promotor
- hypermethylation inactivates FMR1
promotor, causing loss of FMRP
expression
- example of anticipation
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
Charcot-Marie
Tooth Type IA
- demylinating peripheral
neuropathy
- distal muscle weakness
- sensory loss
- slow nerve conduction
velocity
- enlarged nerves; especially
ulnar at olcranon groove
& auricular nerve
- bilateral foot drop
- cant walk on heels
- pes cavus foot deformity
- difficulty walking on
toes
- symptoms appear btwn
ages 5 and 25
Autosomal Dominant
- just need one copy of this
gene
Peripheral
myelin protein
22 (PMP22)
- integral
membrane
glycoprotein
- duplication of PMP22 gene usually
causes this syndrome
- >90% arise during male meiosis
- has 3 instead of 2 copies
- over expression of PMP22 results in
inability to form and maintain
compact myelin
Bloom
Syndrome
- severe prenatal/postnatal
growth retardation
- sun sensitive erythematous
skin butterfly lesions
on face
- unusually small individual
that develops cancer
Autosomal Recessive Blood Syndrome
Protein
(BLM)
- located on
15q26.1
- BLM gene contains a domain of several
DNA and RNA helicases
- absence of BLM gene causes an
abnormally high rate of hypermutation
and hyperrecombination in somatic cells
Ashkenazi
Jews
Familial
Mediterranean
Fever (Type 1)
- Hyper-reactive immune
system
- age of onset: 15-17 usually
- recurring fevers plus:
- Abdominal pain, Chest
pain, Joint pain, Skin
eruption
- history of recurrent
inflammatory attacks
- Skin erruptions
- favorable response to
colchicines treatment
Autosomal Recessive Pyrin Protein
(MEFV)
- located on
16p13
Pyrin Gene:
1) Encodes a transcript that is expressed in
granulocyte white blood cells and are
important for immune response
2) Assists in controlling inflammation by
deactivating immune response
Mediterrane
an decent:
- North
African
Jews
-Armenians
- Turks
- Arabs
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
Amyotrophic
Lateral Sclerosis
- Neurodegenerate disorder
- wasting of peripheral
muscles
- intelligence is normal
- person usually does not
survive after initial onset
- hallmark: hard time
gripping things
Autosomal Dominant Superoxide
dismutase (Cu-
Zn)
SOD1 gene
Converts superoxide to hydrogen peroxide
and molecular oxygen
- prevents oxidative damage to cells by
reducing free radicles
Miller-Dieker
Syndrome
- age of onset: prenatal
- facial dysmorphism
- severe metal retardation
- seizures
- early death (by age 2)
- Lissencephaly (smooth
brain)
- early death
Autosomal Dominant
LIS1
microdeletion
LIS1 encodes for the ! subunit of PAFAH
(platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase).
- PAFAH inhibits cortical
neuronal migration causing a
thickened, hypercellular cerebral
cortex with poorly developed gyri
(Lissencephaly- smooth brain)
- cells go to places they do not belong
Aniridia - heterozygotes:
- absence of an iris
- homozygotes:
- absence of complete
eye structure
Autosomal Dominant PAX-6 loss of
function
mutation
PAX-6 gene encodes a transcription factor
that initiate and orchestrate programs of
eye development in both the optic cup and
the lens placode.
Waardenburg
Syndrome
(Type I & 2)
- reduction/deficiency in
neural crest derivatives:
- melanocytes in hair,
eyes, inner ears
- white forelock
- pale/asymmetrically
colored eyes
- sensorineural deafness
- Type 1: fold of eyelid
displaced
- Type 2: higher frequency
of deafness, but no
eyelid displacement
Autosomal Dominant
Type 1:
Heterozygous
for PAX-3 loss
of function
mutation
Type 2:
Microphthalmia-
associated
transcription
factor (MITF)
mutation
PAX-3 gene is expressed in neural crest
development and in the dermatomyotomal
component of somites (give rise to skeletal
muscle and dermis).
- upstream regulator of MITF
MITF gene encodes transcription factor
that binds to and activates genes required
for pigment cells.
Most
likely to
be found
at an
organizati
on dealing
with
hearing
loss
problems
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
Synpolydactyly Heterozygotes:
- interphalangeal
webbing (fusion)
- extra digits
Homozygotes:
- additional bony
malformations of
hands, wrists, feet,
ankles
Autosomal Dominant
Addition of
alanines to the
amino-terminal
domain of
HOXD13
HOX genes determine regional identity
along specific body axes during
development.
Cornelia de
Lange Syndrome
- growth/mental retardation
- hirsutism (excess body and
facial hair)
- cryptorchidism (failure of
testes to decend)
- upper limb deficiencies
- excessive eyebrow growth
Autosomal Dominant
NIPBL Plays a role in directing development
before birth
CHARGE
syndrome
- C: Coloboma of iris,
retina, optic disc, or
optic nerve
- H: Heart defects
- A: Atresia of Choanae
- R: Retardation of growth
and development
- G: Genital abnormalities
- E: Ear abnormalities
Autosomal Dominant
Chromodomain
helicase DNA
binding protein
(CHD7) coding
region mutations
- CHD7 gene is a member of the
chromadomain helicase DNA-binding
gene.
- have effects over eye, cochlea, brain,
CNS, stomach, intestine, skeleton,
heart, kidney, lung and liver
Smith-Lemli-
Opitz Syndrome
- lipid synthesis disorder
- microcephaly (small head)
- mental retardation
- underdeveloped external
genetalia
- temporal narrowing
- post-axial polydactyly
- prenatal/postnatal growth
retardation
Autosomal Recessive DHCR7 gene
causing a
7-dehydro-
cholesterol
reductase
deficiency.
The DHCR7 gene provides instructions for
making an enzyme called 7-
dehydrocholesterol reductase. This enzyme
is responsible for the final step in the
production of cholesterol.
Example of a malformation
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
Adult Polycystic
Kidney Disease
- abnormal cell polarity
- Bilateral renal cysts
- cysts in other organs:
- liver, seminal vesicles,
pancreas
- renal failure
- urinary tract infection
Autosomal Dominant Polycystin
(PKD1) or
(PKD2) gene
mutations
Polycystin-1 is expressed in down
regulation of the epithelia of maturing
tubules in the kidney .
- Expression also found in smooth,
skeletal, and cardiac muscle (suggesting
extrarenal manisfestation)
Stickler
Syndrome
- myopia
- scooped out face
- micrognathia (small jaw)
- U shaped palate
- early onset of arthiritis
- short stature
- mitral valve prolapse
Autosomal Dominant
COL2A1,
COL11A1,
COL11A2
Genes encode for collagen type II
- mutation is usually on alpha subunit of
collagen type II
- one cause of Robin Sequence
- U shaped cleft palate secondary to
micrognathia
Phenylketonuria
(PKU)
- profound mental
retardation
- if untreated
- brain damage if
PAH<5% normal
- high phenylalanine plasma
levels:
- PKU level: 2-3mM
- normal PKU: <1mM
- low tyrosine plasma levels
- causes low melanin levels
- infant developmental delay
- behavior disturbances
- hyperactivity
- musty or mousy odor
- microcephaly
- organ damage
- unusual posture
- in maternal PKU:
- compromise pregnancy
Autosomal Recessive Mutations in
both alleles for
PAH gene on
chromosome 12
(2-3%) caused
by BH
4
deficiency
(usually also
deficient in
catecholamines,
& serotonin)
- causes
classic PKU
- treatment: dietary restriction of
phenylalanine & galactose
- PAH gene mutation leads to a deficiency
in
phenylalanine hydroxylase
- causes build up of phenylalanine in
body
- phenylalanine hydroxylase converts
phenylalanine to tyrosine
- Neonatal screening- test performed a few
days after birth to check for abnormal
phenylalanine/tyrosine levels in blood
- classic PKU- homozygous condition
- low levels of PAH (<5%) present in
blood
- maternal PKU- children of women with
PKU that do not maintain low
phenylalanine
diets have babies with PKU abnormalities:
- genetically normal children with
teratogenic effects from high phenylalanine
levels
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
Cystic Fibrosis - chronic obstructive lung
disease
- bronchiectesis
- pancreatic insufficiency
- deficient secretion of
pancreatic enzymes
- jaundice
- meconium ileus- postnatal
lower intestinal tract
obstruction
-congenital bilateral
absence of vas deferen
- males are infertile
- sweat chloride > 60mEq/L
- salty taste to skin
Autosomal Recessive - "F508 deletion
(3 base pair
deletion) in
Cystic Fibrosis
Transmembrane
Coductance
Regulator gene
(CFTR gene)
- NBD1 domain
of CFTR most
commonly
mutated
- treatment: curcumin for "F508 mutation
- reduces ER destruction of "F508
- gentamicin- skips over nonsense
stop codons
- used in CFTR alleles
- 1:2000 caucasians
- 1/22 are carriers
- pulmonary disease caused by thick
secretions & recurrent infections
- CFTR gene:
- chloride channel gene
- has two transmembrane domains:
- NBD1 is the most common domain
mutated in caucasians
- phosphorylated to activate chloride
channel
- *NBD is sometimes called NBF
Tay Sachs - motor and mental
retardation at about 6
months of age
- blindness
- cherry red spot in the
retina
- accumulation of lipids in
retina
Autosomal Recessive Mutation in !
subunit of
hexosaminidase
A enzyme
- type of lysosomal storage disease
- # subunit of hexosaminidase A enzyme
degrades GM2-gangliosides
- causes GM2-ganglioside accumulation in
central and autonomic nervous system and
retina
Ashkenazi
Jews
Gauchers
Disease
- severe mental retardation
- osteoperosis
- zebra bodies in inclusions
- foamy macrophages
- anemia
- enlarged liver & spleen
- frequent infections,
bleeding,
bruising
- bone disease
Autosomal Recessive - 4 base pair
shift mutation
in
glucocerebrosid
ase gene
- type of lysosomal storage disease
- glucocerebroside (fat) accumulation in
inclusion bodies
- in later onset variants:
- vision and intelligence is normal
- less lower motor neuron dysfunction
and ataxia
- psychosis in 1/3 of patients
- two forms: adult & infant
Ashkenazi
Jews (1 in
27)
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
X-linked
Ichthyosis
- small, dark, firmly
adherent scales on skin
- spares face, palms, & soles
- undescended testes (20%)
- mental retardation is rare
- white spots in cornea
(50%)
X-linked recessive - mutation in
steroid
sulfatase gene
- scales are distinctly worse in dry weather
Red-Green
Color Blindness
- inability to differentiate
red and green
X-linked recessive Misalignment
and
recombination
leading to
duplication and
deletion on X
chromosome
- unequal intragenic recombination
between a pair of X chromosomes
- red and green pigments are very similar
- normal: each chromosome has one red
pigment and one, two, or three green
pigments
- *if red and green merge, it will cause
only red colorblindness if there are other
green pigments still present
- *blue colorblindness is autosomal
recessive on chromosome 7
8% of
Caucasian
men
Down Syndrome - Brushfield spots around
eye iris
- mental retardation (IQ 30
60)
- short neck with loose skin
- furrowed protruding
tongue
- simian crease (single
crease on palm)
- associated with
Alzheimers
- heart disease in 1/3
- 15fold increase risk of
leukemia
- 95%: Trisomy
of chromosome
21 (47
chromosomes)
- 4%:
Robertsonian
translocation
between 21q
(long arm) and
chromosome
14 (46
chromosomes)
- 90% of cases: trisomy occurs during
maternal meiosis I
- 10% of cases: trisomy occurs in during
paternal meiosis II
- 1:800 live births in mothers under 35
years old
- likelihood increases with increased
maternal age
- most common cause of mental retardation
- 47 chromosomes in most patients
- if caused by robersonian translocation:
- 1.4% risk of downs in women < 30
- recurrence risk if it occurred in first child
is higher than the risk of a woman >35
having a baby with downs
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
DiGeorge
Syndrome
(Velocardiofacial
Syndrome;
Conotruncal
anomaly face
syndrome)
CATCH- 22
C: Cardiac (tetralogy of
fallot)
A: Abnormal Face
T: Thymic hypoplasia
- immune-deficiencies
C: Cleft Palate
H: Hypocalcemia
Microdeletion
Transmitted in an
autosomal dominant
fashion
Microdeletion in
chromosome 22
Duplication in
chromosome 22
- 1: 2000 to 1:4000 births
- CGH or FISH used to detect deletion
- usually arise from misalignment during
crossing over
Sickle-cell
Anemia
- Heterozygote: sickle cell
trait
- usually normal
- RBCs may sickle in low
O
2
environments
- Homozygotes: sickle cell
anemia
- sickle shaped cells
- deoxygenated hemoglobin
- vascular occlusions and
hemolysis
- trouble walking (hands
and feet hurt)
- repeated infection
- anemia
Autosomal Recessive Glu6Val
mutation on the
! chain of
hemoglobin
HbS
- more prominent in malaria areas
- GAG !GTG
- two different HpaI restriction fragment
lengths
exist:
- 13kb (began western Africa)
- 7.6 (multiple origins)
African
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritence Pathogenesis Notes Ethnic
Group
Congenital Adrenal
Hyperplasia
- pseudohermaphrodites
- masculanization because of
excess androgen production
- salt wasting
- vomiting, dehydration
- cardiac arrhythmias
- females:
- enlarged clitoris
- labial fusion
- failure to menstruate at
puberty
Autosomal Recessive in
both boys and girls
- deficiency in
adrenal gland
21-hydroxylase on
chromosome 6
Treatment: Dexamethasome (cortisol analogue)
- 46XX with ambiguous genetalia
- deficiency in cortisol and aldesterol
- overproduction of androgen
- death within 1-6 weeks after birth if salt wasting
is not treated
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
- males:
- enlarged penis
- puberty at 2-3 years of age
- small testes at puberty
Familial
Hypercholesterolemia
- hyperlipidemia
- coronary heart disese
- seen more in males than
females
- increased risk of atherosclerosis
- lead to myocardial infarction
- type II hyperlipoproteinemia
xanthelasma
- cutaneous xanthomas
- heterozygotes:
-total cholesterol:
- 300-600mg/dL
- homozygotes:
- total cholesterol:
- 600-1200mg/dL
- ischemic heart disease at
early age
Autosomal Dominant Most common cause:
- LDL receptor
mutation
other causes:
- Apoprotein B-100
loss of function
mutation
- ARH adapter
protein loss of
function mutation
- PCSK9 protease
gain of function
mutation
Treatment:
- Heterozygotes:
- combination of bile acid-binding resin
& HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor
- statins
- Homozygotes:
- LDL apheresis (column filtration removal of
LDL from plasma)
- normal cholesterol: 180mg/dL
- homozygotes are much more likely to have
artherosclerotic plaques
- PCSK9 protease gene mutation:
- lowers LDL levels protecting person
against coronary heart disease
- does not cause hypercholesterolemia
- statin drugs:
- given to block HMG CoA reductase (dec.
intracellular formation of cholesterol) &
increase LDL receptors (increase up take of
cholesterol from circulation
- oral medication given to absorb cholesterol
from bile to reduce cholesterol reuptaken
through bile
Hereditary
Hemochromatosis
- if no intervention, can effect
heart
- cirrhosis (liver cancer)
- fatigue, weakness
- weightloss
- abdominal pain
- arthralgia (joint pain)
- gray bronze skin pigmentation
- heart failure
- chronic abdominal pain
- diabetes is common
Autosomal Recessive Cys282Tyr mutation in
HFE gene
- treatment: phlebotomy to remove Fe
- tyrosine replaces cystine at position 282 on the
HFE gene
- causes excessive absorption and storage of
iron
- effects women less because menstruation
releases majority of iron
- alcohol amplifies effects
- iron overload effecting liver and pancreas first
- primarily effects males (and post-menapausal
females)
Caucasians
in US
Lebers hereditary - rapid onset of blindness Mitochondrial Mutation in ND4 or - 50% males (vs. 10% females)
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
optic neuropathy - optic nerve atrophy
- painless bilateral loss of vision
may be multifactorial
ND1 subunit of
complex I
have visual loss
- maternal inheritance (mitochondrial)
- increased penetrance in males
- alcohol & tobacco use increases probability of
blindness in carriers
- associated with homoplasmy
Spinobulbar muscular
atrophy (Kennedy
disease)
- weakness of tongue and mouth
muscles (earlier on)
- gradual increase in limb
weakness
- muscular atrophy & spasms
X-linked CAG expansion triplet
disorder effecting the
androgen receptor gene
(gain of function
mutation)
- same receptor effected as Androgen
Insensitivity syndrome
- generally effects males (females rarely effected)
- example of anticipation (age of onset varies)
Huntingtons Disease - progressive dimentia
- loss of motor control
- hyper-reflexia
- depression
- chorea
- abnormal eye movement
- personality changes
- neuronal loss in caudate &
putamen
Autosomal Dominant Mutation in the HD
gene (IT15 gene)
- example of delayed age of onset disease
- patient develops symptoms in 30s & 40s
- CAG repeat expansion causes abnormal function of
HD gene
- HD CAG length: 36-121 repeats
- normal CAG length: 9-29 repeats
- example of anticipation
Friedreich ataxia - gait disturbance (ataxia)
- dysarthria
- diminished tendon reflex
- nystagmus
- scoliosis and foot deformities
- heart disease
- thinning of spinal cord
Autosomal Recessive GAA repeat expansion
in intron 1 within the
frantaxin gene
- nerve cells lose some myelin sheaths
- impairment of splicing (AG) signals
- frantaxin gene- involved in iron metabolism
- F.A. GAA repeat length: >100-1200 repeats
- normal GAA length: 5-34 repeats
Myotonic dystrophy - muscle wasting (dystrophy)
- cardiac conduction defect
- reduced GI perisalsis
- lack of facial expression
- cataracts
- endocrine changes
- myotonia
- increased muscle spasms
- frontal balding
- testicular atrophy
- congenital form:
- respiratory disress
- hypotonia, talipes
- Autosomal Dominant CTG repeat expansions
effecting the 3 UT
(untranslated) region of
DMPK (myotonic
dystrophy protein
kinase) gene
- example of anticipation
- can occur at any age (occurs at earlier ages of onset
as it is passed through successive generations)
- lack of penetrance and variable expressivity
- DMPK: found in heart and skeletal muscle
- associated with intracellular conduction &
impulse transmission
- M.D. CTG length: >50 repeats
- normal CTG length: 30-35 repeats
myotonic dystrophy 2 (DM2):
- same as DM1, but no congenital form
- due to expansion of CCTG tetranucleotide in
intron 1 of the gene encoding zinc finger protein 9
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
Neurofibromatosis
Type I
- cafe-au-lait spots
- 6 or more atleast 15mm apart
- growth of multiple benign/fleshy
tumors (neurofibrosarcomas,
astrocytomas, schwann cells)
- mental retardation in some
- neurofibromas
- Lisch nodules of eyes iris
- prone to cancer of nervous
system or muscles
- Autosomal Dominant
- *more often caused by
new mutations
NF-1mutation
- example of variable expressivity
- penetrance is age dependent
- 100% in adults
- NF-1 gene: codes for GAP like protein
- normally deactivates Ras by dephosphorylating
GTP to GDP
- regulates cell proliferation
Marfans Syndrome - Skeletal abnormalities
- Heart diseases
- dilation of ascending aorta
- aortic rupture
- congestive heart failure
- Eye abnormalities
- myopia & detached lenses
- elongated limbs
- pectus exavatum (funnel chest)
- normal intelligence
Autosomal Dominant - mutation in fibrillin
gene
- 1 : 10,000 individuals
- example of pleiotropy
Angelman Syndrome
happy puppet
syndrome
- unusual facial appearance
- short stature
- always happy
- severe mental retardation
- spasticity
- seizures
- wide based stance
- Genetic imprinting
- deletion of AS/PWS
region
- uniparental disomy
Genomic Imprinting
disease involving
15q11-p13 gene
Abnormal chromosome 15 is inherited from mother.
- Microdeletion disorder on maternal
chromosome 15
- most common (70%)
- Uniparental Disomy of paternal gene
- inherit two copies of father and none of
mother (30%)
Beckwith-Wiedmann - macrosomia- very large body
- macroglossia- enlarged tongue
- protrusion of umbilicus
- severe neonatal hypoglycemia
- Wilms Tumor malignancies in
the kidney
autosomal dominant
-* usually caused by a
new mutation
Uniparental disomy or
genetic imprinting on
chromosome 11
- hypomethylation of maternal KCNQOT1 gene
- most common (60%)
- hypermethylation of maternal H19gene
- results in excess IGF
2
expression (30%)
Prader-Willi
Syndrome
- obesity
- excessive and indiscriminate
eating habits
- small hands and feet
- hypogonadism
- mental retardation
Genomic Imprinting
disease involving
15q11-p13 gene
Abnormal chromosome 15 is inherited from father.
- Microdeletion disorder on paternal
chromosome 15
- most common (70%)
- Uniparental Disomy of maternal gene
- inherit two copies of mother and none of
father (30%)
Becker Muscular - male children: onset at 12-13 X-linked recessive - partial loss of - elevated creatin kinase levels (from atrophied
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
Dystrophy years of age
- slow progressive muscle
weakness
- awkward gait
- inability to run quickly
- inability to climb stairs
- pseudohypertrophy of calf
- calves increase in size but are
filled with fat & fibrous tissue
instead of muscle
dystrophin gene muscles)
- Gower Maneuver:
- raise self from floor by using other muscles
other than those of the legs
- dytrophin: linker protein that holds receptors of
cell membranes to the underlying
cytoskeleton
- western blots & immunostaining used to
observe mutations
Duchenne Muscular
Dystrophy
- male children: onset at 3-5 years
of age
- slow progressive muscle
weakness
- awkward gait
- inability to run quickly
- inability to climb stairs
- pseudohypertrophy of calf
- calves increase in size but are
filled with fat & fibrous tissue
instead of muscle
X-linked recessive - complete loss of
dystrophin gene
- elevated creatin kinase levels (from atrophied
muscles)
- *1/3 are from new mutations (non-carrier
mothers)
- DMD gene has high mutation rate
- Gower Maneuver:
- raise self from floor by using other muscles
other than those of the legs
- dytrophin: linker protein that holds receptors of
cell membranes to the underlying cytoskeleton
- western blots & immunostaining used to
observe mutations
Hemophilia A - predominantly effects males
- spontaneous hemorrhages into
joints (hemarthrosis)
- easy bruising and hematoma
formation after minor trauma
- severe prolonged bleeding
X-linked recessive Mutation in
Factor 8 on the
X chromosome
- factor 8 required for activation of factor X in
intrinsic coagulation pathway
Hemophilia B - predominantly effects males
- spontaneous hemorrhages into
joints (hemarthrosis)
- easy bruising and hematoma
formation after minor trauma
- severe prolonged bleeding
X-linked recessive Mutation in
Factor 9 on the
X chromosome
Vitamin D-Resistant
Rickets
(X-linked
Hypophosphatemic
Rickets)
- low plasma/high urinary
phosphate levels
- males effected more seriously
than females
X-linked Dominant
Disorder
Defective gene
products: endopeptidase
family
- *may develop even with adequate dietary intake
of vitamin D
- impaired ability of kidney tubules to reabsorb
filtered phosphate
Ornithine
transcarbamylase
(OTC) Deficiency
- males:
- lethal neonatal
hyperammonemia
- complete deficiency of OTC
Incompletely dominant
X-linked Dominant
Disorder
Deficiency in Ornithine
Transcarbamylase
(OTC)
- 50% of the obligate carriers show
nonpenetrance (asymptomatic)
- thus is incompletely dominant
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
- females:
- deficiency of OTC may vary
Dyschondrosteosis - skeletal dysplasia
- disproportionate short stature
- form of dwarfism
- deformity of forearm
Pseudoautosomal
Inheritance
Mutation in the SHOX
transcription factor
gene
- mutations in a pseudoautosomal gene on the X
and Y chromosome (often cross over from one
to the other)
- pedigree looks like autosomal dominant
Albright Hereditary
Osteodystrophy
(Pseudohypo-
parathyroidism)
- short stature
- shortened 4th & 5th metacarpals
- round face
Autosomal dominant - kidney does not respond to parathyoid hormone
- elevated parathyroid hormone in blood stream
Edwards Syndrome - mental retardation
- failure to thrive
- severe malformation of heart
- hypertonia
- prominent occiput on back of
head
- receding jaw
- fist-clench & rocker-bottom feet
- simian crease
- large malformed/low set ears
Trisomy of
chromosome 18
- 1:8000 incidence rate in women under 35
- 95% are aborted spontaneously
- 80% of surviving patients are female
- likelihood increases with increased maternal age
Patau Syndrome - growth & mental retardation
- severe nervous system
malformations
- cleft lip and cleft palate
- postaxial polydactyly hands/feet
- rocker-bottom feet
- clenched fist
- ocular abnormalities
- i.e. absence of eye
- microcephaly / open sutures
Trisomy of
chromosome 13
- 20% caused by unbalanced translocation
- 1:20,000 incidicence rate
- most patients die within the first month
- likelihood increases with advanced maternal age
- low recurrence risk (<2%)
Cri du Chat
Syndrome
- infant crying sounds like a cat
- epicanthal folds (loose skin)
- hypertolerism
- microcephaly
- low-set ears with pre-auricular
tags
- most are sporadic
Macro-deletion of
chromosome 5
- 10-15% are offspring of translocation carriers
- deletions are large enough to be seen with
G-banding
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
- micrognathia (small jaw)
- severe mental retardation
- heart defects
Williams Syndrome -elfin like facial feature
- heart and blood vessel problems
- dental and kidney abnormalities
- hyperacusis
- musculoskeletal problems
- low IQ
- remarkable musical and verbal
abilities
- very social
Microdeletion
Transmitted in an
autosomal dominant
fashion
Microdeletion on
chromosome 7, deleting
the gene for elastin and
the gene LIM kinase
- CGH or FISH used to detect deletion
- usually arise from misalignment during crossing
over
- elastin deletion: causes musculoskeletal
problems
- LIM kinase: strongly expressed in brain
-causes impaired visuospatial cognition
Klinefelter Syndrome
(XXY males)
- Tall / thin males
- infertile (failed germ cell
development)
- learning / language difficulties
in some patients
- poor psychosocial adjustment
(self conscious/ poor body image)
- hypogonadism (begins at
puberty)
- underdeveloped secondary
sexual characteristics
- Gynecomastia
X-linked - karyotype: 47, XXY
- 1:1000 male births
- have Barr Bodies
- 50% result from errors during paternal meiosis
- due to failure of normal Xp/Yp
recombination
- 15% have mosaic karyotypes
- other variants:
- XXXY, XXYY, XXXXY
- greater the number of Xs, the greater the
phenotypical defects
Turner Syndrome
(X0) females
- Short female
- webbed neck
- broad chest
- infertile
- renal & cardiovascular problems
- coarcation of aorta &
hypoplastic left-sided heart
- average to above average
intelligence
- extra sensitive
- rare behavioral problems
X-linked XO genotype - 50%: Karyotype: 45,X
- 25%: mosaic karyotype (isochrome X)
- 1:4000 female births
- worse social cognition skills if X chromosome
is derived from mather (instead of father)
- small ring X chromosome sometimes seen
instead with extra information of the missing X
- if ring no XIST center
- mental retardation is seen
- if XIST center exists
- extra information is blocked: no mental
retardation
SRY Sex Reversal - XY female
- XX male
X/Y translocation Translocation of SRY
from Y to X
chromosome
- SYR gene: its presence triggers the production of
male gonadal genetalia
- XY females with no SRY in Y chromosome
- excess DAX1 suppresses SRY leading to
ovarian development
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
- XX males with SRY in X chromosome
- excess SRY leads to testis formation
Camptomelic
Dysplasia
- anterior bowing of femur and
tibia (bow legs)
- flat face
- eleven pairs of ribs
- narrow, bell shaped chest
- long and narrow skull
- club feet
- lack of development of cartilage
rings of bronchial tree
- leads to respiratory distress
- lethal skeletal malformations
Autosomal dominant SOX9 gene mutation - SOX9 gene involved in testes formation
- 75% of 46XY patients with this are sex reversed
and are phenotypic females
5 alpha-reductase
Deficiency
- one cause of male
pseudohermaphroditism
- normal testicular development
- small penis
- blind vaginal pouch
Autosomal Recessive - deficiency in
5#-reductase
- 5#-reductase converts testosterone to active
form
Congenital Adrenal
Hyperplasia
- pseudohermaphrodites
- masculanization because of
excess androgen production
- salt wasting
- vomiting, dehydration
- cardiac arrhythmias
- females:
- enlarged clitoris
- labial fusion
- failure to menstruate at
puberty
- males:
- enlarged penis
- puberty at 2-3 years of age
- small testes at puberty
Autosomal Recessive in
both boys and girls
- deficiency in
adrenal gland
21-hydroxylase on
chromosome 6
- 46XX with ambiguous genetalia
- deficiency in cortisol and aldesterol
- overproduction of androgen
- death within 1-6 weeks after birth if salt wasting
is not treated
Androgen
Insensitivity
-another cause of male
pseudohermaphroditism
X-linked recessive - lack of androgen
receptors in target
- 46XY individual (looks female)
- also known as testicular feminization
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritance Pathogenesis Gene Product Function Ethnic
Group
Syndrome - normal female genitalia
- blind vagina
- no uterus or uterine tubes
- sparse pubic hair
- testes present within abdomen or
inguinal canal
cell
-mutation in DNA
binding domain (zinc
fingers) of androgen
receptor
- undescended testes sometimes mistaken for
hernias in babies that appear to be normal
females
WAGR Syndrome - Wilms tumor predispostition
- Aniridia (absence of iris)
- cataracts, ptosis
- Genital abnormalities
- gonadal (testes/ovarian)
tumors
- Retardation (mental)
Autosomal Dominant Deletion of PAX6 gene
on chromosome 11
Achondroplasia - short limbed dwarfism
- small stature, large head
- low nasal bridge prominent
forehead
- lumbar lordosis
- heterozygotes:
- normal longevity, mental, sexual
health
- homozygotes:
- fetal death soon after birth
Autosomal Dominant
*more often caused by
a new
mutation than genetics
Mutation in Fibroblast
Growth Factor
Receptor 3 (FGFR3)
gene on chromosome 4
- achondroplastic people tend to prefer to have
achondroplastic children, and thus usually prefer
achondroplastic significant other
- 1:10,000 incidence
- *80% are due to new mutations
- increased risk with late paternal age
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritence Pathogenesis Notes Ethnic
Group
Wilsons Disease
(hepatolenticular
degeneration)
- liver disease (most common
symptom in children)
- neurological disease (most
common symptom in adults)
- tremor, rigidity
- drooling, difficulty w/ speech
- abrupt personality changes
- grossly inappropriate behavior
- kayser-fleischer ring- deep
copper ring in cornea of eye
Autosomal Recessive - defect in wilsons
gene (ATP7B) on
chromosome 13
- disorder of copper transport
- results in copper accumulation and toxicity to liver
and brain
Treatment:
- zinc acetate
- blocks copper absorption
- increase copper excretion
- penicillamine- chelation of Cu
Acute Intermittent
Porphyria
- decreased heme in liver cells
- increased cytochrome p450 in
liver cells
- abdominal pain
- vomiting
- mental disturbance
Autosomal Dominant Deficiency in
porphobilinogen
deaminase (PBG
deamines)
porphobilinogen deaminase- enzyme in the
biosynthetic pathway for heme
- mutation causes reduced uroporphyrinogen I
synthase
- decreased heme levels, but increased hepatic
cytochrome p450 (heme precursor) levels
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritence Pathogenesis Notes Ethnic
Group
- confusion
- emotional upset
- hallucinations
- no photosensitivity
- darker urine seen sometimes
- precipitating events that may causes this disease:
- barbiturates (do not give this to AIP patients)
- birth control pills
Variegate Porphysia - photosensity
- propensity to develop acute
neuropsychiatric attacks with
abdominal pain
- vomiting
- contrinpation
- tachycardia
- hypertension
- quadriplegia
Autosomal Dominant
(incomplete penetrace)
- protoporphyrinogen
oxidase deficiency
- Decreased protoporphyrinogen oxidase activity South
Africans
Homocystinuria - increased homocysteine &
methionine plasma levels
- homocysteine accumulation in
urine
- mental retardation (if untreated)
- osteoporosis
- thromboembolis in veins &
arteries
- increased coronary artery risk
- lens dislocation
- similar to marfans syndrome
features (i.e. pectus excavatum)
Autosomal Recessive Deficiency in
cystathionine "-
synthetase enzyme
Methionine synthase
and cofactor (B
6
or
folate & B
12
)
deficiencies could also
cause it
- one of the first diseases to show to be vitamin
responsive
- administration of larges amounts of pyridoxine
reduces abnormalities and disease
Lesch-Nyhan
Syndrome
- high uric acid levels in joints,
kidneys, and CNS
- caused by overproduction of
uric acid
- choreoathetosis
- spasticity
- uric acid overproduction
- gout (in patients with partial
phenotypes)
- self-mutilating behaviors
& other behavior disturbances
- neurologic dysfunction
- poor muscle control
- moderate mental retardation
- arthritis
- renal symptoms
- sometimes: megaloblastic anemia
X-linked recessive - mutation in HPRT1
gene
- HPRT1 gene codes for the enzyme hypoxanthine-
guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
- produce purines in biochemical pathway
- females who inherit one copy only are not inherited
- accumulation of uric acid that is normally recycled
into purines
- causes gout & kidney/bladder problems
Hunters Syndrome - similar features to Hurlers except
- no corneal clouding
- physical deformities
- glycosaminoglycan (GAG) build
up in cells
- large head
- hearing loss
- thickening of heart valves
- obstructive airway disease
- sleep apnea
- enlarged liver and spleen
- enlarged abdomen
- nervous system problems
X-linked recessive - defect in the
iduronate-2-sulfatase
(IS2) gene
- type of mucopolysaccharide disorder
- also known as : mucopolysaccharidosis II
- inability to degrade dermatan/heparin sulfate
Alkaptonuria - disorder of tyrosine metabolism
- homogentisic acid accumulation
- black urine
- ochronosis- dark pigments in
connective tissue
- arthritis in spine and large joints
- arthralgia deposits in joints
- cause joint pain
- heart problems, kidney problems,
prostate stones
Autosomal Recessive - defect in
homogentisate 1,2-
dioxygenase enzyme
- homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase:
- converts homogentisic acid (tyrosine product)
to maleylacetoacetate (eventually converted
to TCA cycle component
Slovakia &
Dominican
Republic
X-linked Adreno-
leukodystrophy
- attention deficit disorder (ADD)
- dementia
- progressive behavior disturbances
- vision loss
- worsening of handwriting
- difficulty understanding spoken
language
X-linked Recessive Mutation in ATP
binding cassette of
subfamily D, member 1
(ABCD1)
- example of a peroxisomal disorder
- example of a peroxisomal disorder
- mostly boys effected
- Defective integral membrane protein that transports
very long fatty acid chains into peroxisomes for
!-oxidation
- most common misdiagnosis: ADD
- treatment: lorenzos oil
Fabrys Disease - reddish purple skin rash
- kidney and heart failure
- pain in lower extremities
- vascular cutaneous lesions
- proteinuria
X-linked recessive - deficiency in
!-galactosidase
- type of lysosomal storage disease
- increased levels of globosides
- does not involve GAG breakdown
Menkes Syndrome - cerebral degeneration
- whitish and kinked hair
- scalp and eyebrow hair is
short, sparse, coarse, twisted,
and lightly pigmented
- looks like steel whool cleaning
pad
- sagging cheeks
- pectus excavatum
- umbilical hernia
- hypotonia & failure to thrive
- seizures at 6-10 weeks of age
X-linked recessive Mutations in the
copper-transporting
ATPase gene (ATP7A)
- collagen disorder
- decreased in cells ability to absorb copper
- lysyl oxidase (needed for collagen crosslinking) is
defective
- caused by inability of copper to bind
- clinical heterogeneity
- defects in two different copper-transport
proteins lead to different disorders
Age-Related Macular
Degeneration (AMD)
- progressive degeneration of the
portion of the retina responsible
for central vision
- accumulation of extracellular
protein deposits (drusen) in the
macula (behind retina)
- inability to perform fine vision
(i.e. reading)
- eventually leads to blindness
Autosomal Dominant - Tyr402His mutation in
the complement factor
H (CFH) gene
- cigarette smokers have an increased risk of age-
related macular degeneration
- rarely seen in people younger than 55
- variants of the factor B (CFB) gene and
complement component 2 (C2) genes significantly
reduce the risk of AMD
Cleft lip and cleft
palate
- failure of fusion of the frontal
process with the maxillary
process on the 35
th
day of
gestation
Multifactorial - maternal smoking is a known risk factor for this
disease
Alzheimer - progressive memory loss,
confusion, disorientation
- inability to remember facts or
events
- rigidity, mutism, incontinence
- usually bedridden
- amyloid bearing plaques outside
the cell
- neurofibrillary tangles inside the
cell
- hypophosphorylation of tau
proteins causes this
- Neuronal dystrophy and loss
- fatal neurogenerative disease
- onset is usually after age 60
- earlier onset usually means
homozygous form is present
Multifactoria
7-10% are Autosomal
Dominant
mutation in $4 allele
of apolipoprotein E
!-Amyloid precursor
protein (!APP) on
chromosome 21
mutations causing
cleavage abnormalities
mutations in Presenilin
(PS1 on chromosome
14 & PS2 on
chromosome 1) genes
leading to increased
AB42 peptide
production
- most common neurodegenerative disorder
- 50% of people >70 that have dementia have
alzheimers
- twice as common in women
- ApoE: component of low density LDL particles
- help clear LDL through the liver
- $2 protects you against alzheimers
- $4 predisposes you for alzheimers
- SORL1- helps recycle "APP so that it can be
recut by secretases
- monozygote twin concordance: 40-60%
- "APP gene: single-pass transmembrane protein that
is normally cleaved by one of 3 proteases:
- !- secretase- cleaves 90% of them
- " & #-secretase- cleaves remaining 10%
- form non-toxic AB40 or neurotoxic AB42
PS1 & PS2: modify decretase activity
- PS1 age of onset: 35-60 years
- most common mutation
- PS2 age of onset: 40-85 years
!
1
-Antitrypsin
deficiency
- defect in #
1
-antitrypsin
- deposition of excess #
1
-
antitrypsin cells in liver and
decrease in #
1
-antitrypsin activity
in heart and lungs
- emphysema and/or COPD
- shortness of breath
- liver diseases
- liver cirrhosis
Autosomal Recessive - mutations in
SERPINA1 gene
- SERPINA1 gene encondes for #
1
-antitrypsin
Cerebral Venous
Thrombosis
- occlusion of cerebral veins in the
absence of an infection or tumor
- abnormal coagulabiltiy of the
clotting system
Multifactoria - mutation in factor V,
prothrombin as well as
the use of oral
contraceptives
- requires 2 mutations + 1 environamental effect
- prothrombin- clotting factor
- mutation occurs on 3 untranslated region
- causes increased prothrombin translation
- prothrombin and factor V mutations are also
associated with placental artery thrombosis and
deep venous thrombosis
Digenic Retinitis
Pigmentosa
- retinal degeneration
- night blindness, then tunnel
vision, and then complete
blindness
Multifactorial - patient must be
heterozygous for both
Rom 1 and peripherin
photoreceptor
membrane proteins
Crohn Disease - heterozygotes:
- 1.5 4 fold increase in
disease risk
- homozygotes or compound
heterozygotes:
- 15 40 fold increase in
disease risk
- form of irritable bowl syndrome
- night stomach pains
- diarrhea
- gradual weight loss
- non GI symptoms:
- arthritis of spine and joints
- uveitis- inflammation of skin
and eye
- reduced ability of
NOD2 protein
- NOD2 protein binds to gram negative bacteria
walls and activates NF-$B transcription factor in
leukocytes, assisting in the inflammation response
to bacteria
- 50% of cuacasians with chrons disease have the
NOD2 variant
- increased risk of adenocarcinoma of the intestine
and ulcerated colitis
Caucasian
Galactosemia - reduced galactose-1-phosphate
uridyltransferase (GALT) activity
- feeding problems
- failure to thrive
- hepatocellular damage (jaundice)
- verbal dyspraxia (strange speech)
- abnormal motor function
Autosomal Recessive - GALT gene mutation - treatment: avoid lactose/galactose in diet
Glucose-6-Phosphate
Dehydrogenase
Deficiency
- low levels of G6PD enzyme
- non-immune hemolytic anemia
- favism
- fever, headache, abdominal
pain in response to broad
beans
- neonatal jaundice
- acute renal failure
- often seen in response to diabetic
ketoacidosis
X-linked recessive African
Americans
&
Mediteranni
an descent
Hirschsprung Disease - complete absence of the
parasympathetic ganglion cells in
the submucosal and myenteric
plexuses along intestine
- severe constipation
- intestinal obstruction
- dilation of colon
- delayed passage of meconium
- fatal if untreated
Multifactorial,
Autosomal Dominant,
Autosomal Recessive
Most common
mutation: Ret Gene
- males have 2 times higher risk than females
- Ret gene- tyrosine kinase receptor
- other mutations include:
- ligand gdnf, endothelin B receptor and its
ligand endothelin3
Insulin-dependent
(Type I) Diabetes
Mellitus
- autoimmune destruction of islet
!-cells causing insulin deficiency
- high blood glucose levels
- polydipsia (excessive thirst)
- polyuria (excessive urination)
- ketoacidosis
Multifactorial - linkage disequilibrium
between HLA-DR3 &
HLA-DQB1*0201
allele or HLA-DR4 &
HLA-DQB1*0302
allele
- MHC haplotypes account for 1/3 of genetic
contribution (other genes must be involved)
- combination of genetic susceptibility +
environmental insult
- male / female ratio is about equal
caucasians
Long QT Syndrome - prolonged repolarization
followed by depolarization of
cardiac ventricles
- ventrical arrhythmias
- cause syncope (fainting) and
sudden death
- prolonged QT interval in EKG
Autosomal Dominant
or Autosomal
Recessive
Mutation in
LQT1(KCNQ1) gene is
the most common (40-
55% of cases)
Non-Insulin-
Dependent (type II)
Diabetes Mellitus
- elevated glucose & insulin levels
- NO ketoacidosis
- artherosclerosis
- peripheral neuropathy
- renal disease
- cataracts & retinopathy
Multifactorial - more females get it than males
- if one sibling is affected, risk of acquiring disease
increases to 10% (from 6 -7% in US)
- if a sibling and another 1
st
degree relative is
effected, risk is 20%
- monozygotic twins: risk is 50-100%
African
American &
Mexican
Pyloric Stenosis - projectile vomiting in babies
within a few weeks of life
- gastric outlet obstruction due to
hypetrophic pylorus impairs
emptying of gastric contents into
duodenum
Multifactorial - deficiency of neurons
containing nitric oxide
synthase, abnormal
myenteric plexus,
infantile
hypergastrinemia, and
exposure to macrolide
antibiotics can all
cause pyloric stenosis
- males more commonly effected than females (4:1) Jewish
ancestry
"-thalassemia Type 1: 10% normal !-chain
Type 2: 50% normal !-chain
Type 3: >50% normal !-chain
- beta thalssemia major:
-severe hypochromic microcytic
anemia during 1
st
year(Hb <7g/dL)
- low HbA, high HbF + HbA2
- characteristic skeletal changes
- hypertrophy maxilla and
prominent cheek bone chipmunk
face
-beta thalassemia minor:
- minimal or mild anemia
- increased HBA2 & HbF
Splicing abnormalities
leading to abnormal
Beta chain
May also be caused by
deletion mutations
- onset is not apparent until few months after birth
- only HbA is effected
- treatment: bone marrow transplant, transfusion,
iron chelation (deferiprone;
deferoxamine)
- hemapoeitic stem cell transplantation in
nonstorage diseases
Type 1:
Mediterran.,
middle east,
Indian
Type 2:
west Africa,
Black
American
Type 3:
Italy,
Greece,
Middle East
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritence Pathogenesis Notes Ethnic
Group
!-thalasemia - destruction of alpha chains
- excess !-chains form from
inclusion bodies
- silent carriers: ## / #
- #-thalassemia trait: ##/-- or #-/ #-
- minimal anemia
- microcytosis hypochromia
- HbH disease: # -/ --
- moderate anemia
- hepatosplenomegaly
- no iron overload
- no blood transfusion needed
- Hydrops Fetalis: -- / --
- no alpha chain
- die in utero (Hb cant carry O
2
)
- ATRX-syndrome:
- only effected male
- mental retardation
- skeletal & facial abnormalities
- urogenital malformations
Autosomal Recessive
ATRX syndrome:
X-linked
ZF deletion that
removes 3 end on
LUC7L gene
ATRX-syndrome:
- mutations in ATRX
gene leading to
reduced expression of
chromatin remodeling
protein (ATRX)
Alpha thalsemmia trait:
- ##/--: homozygous deletion
-offspring may have hydrops fetalis
- #-/ #-: does not lead to hyrops fetalis
- antisense transcription is associated with
methylation of #2-globin CpG islands
- causes silencing of #2-globin expression
##/--:
- SE asians
#- /#-:
- Africans
##/ # -:
- Africans
ATRX:
- european
Multiple Endocrine
Adenomatosis, type 2
Type A:
- 60% chance of developing
medullary carcinoma of the
thyroid
- also associated with
pheochromocytoma or benign
parathyroid adenomas
Type B:
- additional thickening of nerves
and the development of benign
neuromas n mucosal surface of
mouth and lip
autosomal dominant Activating mutation of
the RET gene
Ret gene- tyrosine kinase receptor
- binds neurturina and gdnf
Chronic Myelogenous
Leukemia
- cancer of blood cells
- replacement of bone marrow with
malignant leukemic cells
- enlargement of spleen, liver, and
other organs
Translocation between
chromosome 9 and 22
(philedelphia
chromosome)
- creates BCR-ABL fused gene
- abnormally locates tyrosine kinase activity
treatment: Gleevac
- inhibits BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase activity
Burkitt Lymphoma - often induced by Epstein barr
virus (EBV)
- most commonly
caused by
- translocation puts MYC gene under influence of an
enhancer from immunoglobin genes
Young
children in
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritence Pathogenesis Notes Ethnic
Group
translocation between
chromosomes 8 and
14
- can also be between 2
and 8 or 22 and 8
- chromosome 14: heavy chain
- chromosome 2: kappa light chain
- chromosome 22: lamda light chain
central
africa
Follicular B-cell
lymphoma
Translocation between
chromosomes 14 and
18
- results in upregulation of BCL2
- promotes cell survival
Retinoblastoma - 400 times more likely to develop
mesenchymal tumors
- even higher risk if child is
exposed to radioactivity
- large number of primordial
retinoblasts (tumors) in eyes with
a rapid rate of proliferation
Autosomal Dominant - mutation in Rb tumor
suppressor gene
- incomplete penetrance (2
nd
hit is by chance)
- 60% are non-inheritable
- inherited retinoblastoma occurs earlier than sporatic
- inherited more likely to effect both eyes than
sporatic
- Rb gene regulates G1!S phase
- found mutated in several non-hereditary cancers
- i.e. lung, breast, bladder cancer
Li-Fraumeni
Syndrome
- unusually early infliction of rare
cancers (bone & soft tissue
cancer, sarcoma, breast cancer,
brain tumors, adrenocarcinoma,
leukemia, etc..)
Autosomal Dominant - mutation in the TP53
gene
- TP53 gene codes for p53
- requires mutations in both alleles to inactive
TP53
- can be sporadic or familial
Familial breast
cancer, type 1
- if family member is effected,
increased risk of developing
breast cancer
- associated with breast cancer as
well as ovarian cancer in females
Autosomal Dominant Mutation in BRCA1
gene found on
chromosome 17
- causes less than 5% of breast cancer
- 50% of autosomal dominant inherited breast
cancer
- if inherited: both breasts usually effected
- if sporatic: only one initially effected
- BRCA: tumor suppressor gene that is involved
with repair of double stranded DNA
- environmental or genetic influence may play a role
in ultimate penetrance
Familial breast
cancer, type 2
- if family member is effected,
increased risk of developing
breast cancer
- associated with breast cancer as
well as ovarian cancer in females
- also associated with breast cancer
as well as prostate cancer in
males
Autosomal Dominant Mutation in BRCA2
gene found on
chromosome 13
- causes less than 5% of breast cancer
- 33% of autosomal dominant inherited breast
cancer
- environmental or genetic influence may play a role
in ultimate penetrance
Autoimmune
lymphoproliferative
syndrome (ALPS)
- massive lymphadenopathy and
splenemegaly (especially in
children)
- development of autoimmune
Autosomal Dominant Dominant negative
mutation in one allele
of either fas receptor or
fas ligand
- the mutation causes a deficiency of apoptotic
signaling and massive expansion of immature T
lymphocytes (double negative)
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritence Pathogenesis Notes Ethnic
Group
disease like antibody mediated
thrombocytopenia or hemolytic
anemia
- increased frequency of B-cell and
Hodgekins lymphoma
Cowden Syndrome - type of PTEM Hamartoma
Tumor Syndrome
- increased risk of benign and
malignant thyroid, breast,
endometrium tumors
- macrocephaly, trichilemmomas,
and papillomatous papules seen
by age 20
Autosomal Dominant Mutation in PTEN
tumor suppressor gene
- PTEN dephosphorylates PIP3 (back to PIP2),
activating as a negative control on PKB/Akt
proto-oncogene activation
Von Hippel-Lindau
syndrome
- abnormal growth of blood vessels
- knots of blood capillaries
(angiomas) occur
- cysts or tumors may develop
around angiomas
- growths may develop in retina,
spinal cord, adrenal glands, etc..
- symptoms: headaches, vertigo,
dizziness, limb weakness, vision
problems, high blood pressure
- higher risk than normal for
developing kidney cancer
Autosomal Dominant VHL gene on
chromosome 3
- VHL acts as a gate keeper tumor suppressor gene
Wilms' tumor - embryonal malignancy of the
kidney
- abdominal mast in an otherwise
well-appearing child
Mutation in the WT1
gene (causes WAGR
syndrome)
- most common renal neoplasm of children
- 6% of pediatric cancers
- similar to retinoblastoma:
- inherted vs. sporadic determines if tumors are
bilateral, early age of onset, etc..
- has a lower penetrance rate than retinoblastoma
- only about 50% of individuals with a germline
mutation predisposing wilms tumor develop the
disease
- WT1 gene encodes for four zinc finger motifs
- functions in transcription regulation
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritence Pathogenesis Notes Ethnic
Group
Familial Polyposis
Coli (familial
adenomatous
polyposis)
- results in colorectal cancer
- numerous benign polyps are seen
in colon of heterozygous
individuals by age 20
- each polyp has 1% chance of
becoming malignant
Autosomal Dominant Mutation in
Adenomatous Polyposis
Coli (APC) gene on
chromosome 5
- treatment: colectomy (to prevent malignancies)
- APC gene- encodes a cytoplasmic protein that
regulates !-catenin
- !-catenin- linker protein that holds E-cadherin
to microfilaments
Hereditary
Nonpolyposis Colon
Cancer (HNPCC)
- cause 2-4% of colon cancers
- heterozygous males have 90%
risk of developing colon cancer
- heterozygous females have 70%
chance of developing colon
cancer, 40% chance of
endometrial cancer, and 10-20%
risk of biliary, urinary, or ovarian
cancer
Autosomal Dominant - mutations in one of 5
DNA mismatch repair
genes:
- MLH1
- MSH2
- PMSL1
- PMSL2
- MSH6
- MLH1 & MSH2 account for 60%of HNPCC
- HNPCC genes are caretaker tumor suppressor
genes
- Replication error positive phenotype (RER+):
- 3, 4, or more alleles of a given microsatellite
polymorphism are seen in a single tumor
Xeroderma
pigmentosum
- sun sensitivity
- ocular involvement
- greater than 1000 fold increased
risk of cutaneous and ocular
neoplasms
- severe sunburn with blistering
and persistant erthyema with
minimal sun exposure
- freckling of the face
Autosomal recessive Mutation in nucleotide
excision repair pathway
responsible for
correcting DNA
damage caused by UV
light
- mutation results in the formation of pyrimidine
dimers in response to sunlight
Fanconi anemia - progressive bone marrow failure
- myelodysplasia (spinal cord)
- acute myelogenous leukemia
- physical abnormalities:
- short stature
- abnormal skin pigmentation
- skeletal, organ, eye problems
- hearing loss
- hypogonadism
- developmental delay
- increased risk of developing solid
tumors in head, neck, skin, GI
tract, and genital tract
Autosomal Recessive Defect in DNA repair
pathway
- patients are extremely sensitive to DNA damaging
agents (i.e. chemotherapy & radiation)
Ataxia telangiectasia - children appear normal at birth
- first sign: ataxia
Autosomal Recessive Caused by mutation in
the human ATM gene
ATM gene- involved in cellular response to DNA
damage (DNA repair)
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritence Pathogenesis Notes Ethnic
Group
- lack of muscle control
- slurred speech
- telangiectasia- tiny red spider
veins
- on corner of eyes or ears &
cheeks exposed to sunlight
- mild diabetes mellitus
- premature graying of hair
- difficulty swallowing
- normal intelligence
- immunodeficiency leading to
recurrent respiratory infections
- deficient IgA & IgE antibodies
- pneumonia is common cause
of death
- predisposed to developing blood
malignancies:
- lymphoma, leukemia
on chromosome 11
Peutz-Jeghers
Syndrome
- gastro-intestinal polyps
- mucocutaneous pigmentation
- melanin spots (small, flat, brown
or dark blue freckle like spots -
elevated risk of colon cancer)
- symptoms:
- repeated abdominal pain
- precocious puberty
- bowel obstruction
Autosomal Dominant Germline mutation
causing inactivation of
STL11/LKB1
(serine/threonine kinase
11) gene on
chromosome 19
- gene shows variable penetrance
- STL11 inactivation:
- causes APC/beta-catenin and p53 pathways
Hurlers Syndrome - corneal clouding
- coarse facial features
- skeletal abnormalities
- linear growth stops by age 3
- hearing loss
- mental retardation
- cardiorespiratory failure usually
causes death within first 10 years
Autosomal Recessive %-L-iduronidase
deficiency
- type of mucopolysaccharide disorder
I-Cell Disease - unusual facial features
- skeletal changes
- severe growth retardation
- mental retardation
Autosomal Recessive Defect in golgi-specific
phosphotransferase
- type of lysosomal storage disease
- loss in the ability to traffic proteins
- lack of mannose-6-phosphate tags
- fibroblasts release lysosomal enzymes
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritence Pathogenesis Notes Ethnic
Group
- high number of acid hydrolases in
body fluid
- children live for 5-7 years
extracellularly
- loss of glycosylation
- cultured skin fibroblasts have many abnormal
lysosomes throughout the cytoplasm
Maple Syrup Urine
disease
- increased plasma & urine
branched chain amino acid
(valine, leucine, isoleucine) levels
- maple syrup like odor from urine
- vomiting in newborns
- death within few weeks
- if untreated
Autosomal Recessive Deficiency in branched
chain !-keto acid
dehydrogenase
branched chain !-keto acid dehydrogenase:
- breaks down branched chain amino acids (i..e
valine, luecine, isoleucine) to eventual TCA
components
treatment: reduced intake of valine, leucine,
isoleucine
Niemann-Pick
(type A & B)
- halt in psychomotor development
after 12 months of age followed
by neurological deterioration
- elevated sphigomyelin levels
- enlarged spleen & liver
- jaundice
- mental retardation
- cherry red spot of retina macula
- fatal in early life
Autosomal Recessive Deficiency in
sphingomyelinase
- type of lysosomal storage disease
- sphingomyelin accumulation in inclusing bodies
- harmful amounts of fatty substances accumulate
in spleen, liver, lungs, bone marrow, sometimes
brain
- Type A: occurs in infants (most common type)
- brain is effected along with liver and spleen
- Type B: occurs in juveniles
- brain is uneffected
Sandhoffs Disease - slow development and
progressive muscle weakness
after 6 months of age
- loss of motor functions
- exaggerated startle reaction to
loud noises
- cherry red spot
- seizures, vision or hearing loss,
mental retardation, paralysis
- may have enlarged organs
Autosomal Recessive Mutation in !-subunit
that is common to both
Hexosaminidase A & B
- type of lysosomal storage disease
- results in a deficiency in Hexosaminidase A & B
Retinoblastoma - 400 times more likely to develop
mesenchymal tumors
- even higher risk if child is
exposed to radioactivity
- large number of primordial
retinoblasts (tumors) in eyes with
a rapid rate of proliferation
Autosomal Dominant - mutation in Rb tumor
suppressor gene
- incomplete penetrance (2nd hit is by chance)
- 60% are non-inheritable
- inherited retinoblastoma occurs earlier than sporatic
- inherited more likely to effect both eyes than
sporatic
- Rb gene regulates G1!S phase
- found mutated in several non-hereditary cancers
- i.e. lung, breast, bladder cancer
Osteogenesis
imperfecta
Type I:
- most common & mildest
- bones more prone to fracture
- normal stature
- blue/purple/gray tinted sclera
- no bone deformities
Autosomal Dominant
mostly
Mutations in structural
#
1
or #
2
chain genes or
in genes for post-
translational
modification of type I
collagen
- inherited collagen disorder
- caused by substitutions of glycine residues in
pro-alpha chains
- null mutations:
- promoter, splice signal, mRNA stability
mutations
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritence Pathogenesis Notes Ethnic
Group
- brittle teeth (dental problems)
- hearing loss
- triangular faces
- loose joints; low muscle tone
- normal collagen structure:
- less than normal collagen
Type II:
- more severe form
- missense in C-terminal end
- often lethal (b/c of respiratory
problems) - death in utero
- numerous fractures
- underdeveloped lungs
- collagen is improperly formed
Type III:
- bone fractures present at birth
- blue/purple/gray tinted sclera
- barrel shaped ribs
- spinal curvature
- some respiratory problems
- severe bone deformities
- collagen improperly formed
Type IV:
- more severe than type I
- less severe than type III
- bone fractures easily
- most occur before puberty
- sclera is white, or near white
- shorter than avg. stature
- barrel shaped ribs
- collagen improperly formed
- missense glycine substitution mutations
- more severe phenotypes if:
- glycine substitutions are near C-terminus
- helix formation: you start at C-terminus
- substituted amino acid is charged
- substituted amino acid is bulkier than glycine
- locus heterogeneity & allelic heterogeneity
associated
To differentiate from child abuse:
- ask parent if they had the problem
- family history
- look at sclera (for bluish tint)
- look for triangular face
- do collagen analysis
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritence Pathogenesis Notes Ethnic
Group
Krabbess Diseases - elevated galactocerebroside
levels
- mental retardation
- blindness, deafness
- paralysis
- almost complete absence of
myelin
- globoid bodies in white matter of
brain
Autosomal Recessive Deficiency in
galactosylceramidase
(galactocerebrosidase)
- type of lysosomal storage disease
Disease Clinical Feature Mode of Inheritence Pathogenesis Notes Ethnic
Group
Adenosine Deaminase
Deficiency
- may lead to SCIDs Autosomal Recessive - lack of adenosine
deaminase on
chromosome 20
- accounts for 25% of SCIDs cases
- adenosine deaminase is needed for purine
metabolism
X-linked severe
combined
immunodeficiency
- both B and T cells in adaptive
immunity do not work
- bubble boy
- extreme vulnerability to
infections
- severe, recurrent infections
- low or absent T & NK cells
- non-functional B cell
X-linked recessive - mutations in the gene
encoding for the
common gamma chain
for receptors of IL-2, 4,
7, 9, 11, 21.
- JAK3 kinase gene
mutation can also
cause this
Wiskott-Aldrich
Syndrome
- platelets do not function properly
and are removed by the spleen
- eczema
- thrombocytopenia (low platelets)
- bloody diarrhea
- small platelet size
- splenomegaly
X-linked recessive - mutation of the
WASP gene
WASP gene: codes for wiskott-aldrich syndrome
protein that codes for hemapoietic cells
Hereditary
Spherocytosis
Malignant
Hyperthermia
MCAD deficiency
X-linked (Burton)
Agammaglobulinemia
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Subclavian Artery BranchesDocument1 pageSubclavian Artery BranchesBeck33ers5826No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Neck Sympathetic ChainDocument1 pageNeck Sympathetic ChainBeck33ers5826No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Pharyngeal Arches 1Document1 pagePharyngeal Arches 1Beck33ers5826No ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- CN 10 VagusDocument1 pageCN 10 VagusBeck33ers5826No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- CN 11 and CN 12Document1 pageCN 11 and CN 12Beck33ers5826No ratings yet
- CN 5 V1 Opthalmic NerveDocument1 pageCN 5 V1 Opthalmic NerveBeck33ers5826No ratings yet
- CN 5 V2 Maxillary NerveDocument1 pageCN 5 V2 Maxillary NerveBeck33ers5826No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Bucknell at Mews at Laurel Creek Options: First FloorDocument1 pageThe Bucknell at Mews at Laurel Creek Options: First FloorBeck33ers5826No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Pulmonary Journal ClubDocument19 pagesPulmonary Journal ClubBeck33ers5826No ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Abdominal Arteries ChartDocument1 pageAbdominal Arteries ChartBeck33ers5826No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Diabetic Ulcers Wagner GradesDocument2 pagesDiabetic Ulcers Wagner GradesBeck33ers5826No ratings yet
- Acid-Base Disorders Worksheet: This Is: Na - CL - HCO) If They Do, Then They Have A Metabolic Acidosis inDocument1 pageAcid-Base Disorders Worksheet: This Is: Na - CL - HCO) If They Do, Then They Have A Metabolic Acidosis inBeck33ers5826100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Pediatrics Clerkship Shelf ReviewDocument78 pagesPediatrics Clerkship Shelf Reviewlcaskidsn12s100% (1)
- Cell Power ManualDocument95 pagesCell Power ManualKeith McFarlaneNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Movement Disorders Types - Mayo ClinicDocument1 pageMovement Disorders Types - Mayo ClinicdrrajmptnNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Endocrine System Notes - NCERT BasedDocument8 pagesEndocrine System Notes - NCERT Basedpallab mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Nor Azril Izza Bin Mohd NoorDocument1 pageNor Azril Izza Bin Mohd NoorEe SamadNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- PLE Review OBGYN Chap 1 Overview of ObstetricsDocument2 pagesPLE Review OBGYN Chap 1 Overview of ObstetricsRemelou Garchitorena Alfelor100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Free Microbiology Practice Questions - Help Your Microbiology Test ScoreDocument3 pagesFree Microbiology Practice Questions - Help Your Microbiology Test ScoreDalbir SinghNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Adaptive Immunity: Shimelis Teshome (BSC MLS)Document31 pagesAdaptive Immunity: Shimelis Teshome (BSC MLS)Shimelis Teshome AyalnehNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Glossary SPM BiologyDocument11 pagesGlossary SPM BiologyMus Staqim Besut100% (1)
- Roche GlucoseDocument4 pagesRoche GlucoseDiep LeNo ratings yet
- What Is Sleep Paralysis ?Document7 pagesWhat Is Sleep Paralysis ?Alle LOBSNo ratings yet
- Immunology - SyllabusDocument3 pagesImmunology - SyllabusAlaa' Al-AbdulrazzaqNo ratings yet
- Synergy InteractionDocument11 pagesSynergy InteractionDasagrandhi ChakradharNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Immunology Pokhara University Syllabus NOCDocument2 pagesMicrobiology and Immunology Pokhara University Syllabus NOCDinesh SubediNo ratings yet
- Teratology: Handbook ofDocument478 pagesTeratology: Handbook ofmaria5basNo ratings yet
- 9 SC TissueDocument8 pages9 SC Tissuevishesh1997No ratings yet
- Organoiron 1 PDFDocument10 pagesOrganoiron 1 PDFSherly Marcia DevanaNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Prevalence and Species Spectrum of Pulmonary Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Isolates at A Tertiary Care CenterDocument6 pagesPrevalence and Species Spectrum of Pulmonary Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Isolates at A Tertiary Care CenterHiroj BagdeNo ratings yet
- 1 WhydowefallillDocument9 pages1 WhydowefallillAbhimanyu BahreeNo ratings yet
- Medical NuggetsDocument8 pagesMedical NuggetsDrGandhi Bhaskar Patrudu LankaNo ratings yet
- GenpathDocument10 pagesGenpathNatural Science BiologyNo ratings yet
- Practice Test in LET BIOLOGYDocument24 pagesPractice Test in LET BIOLOGYCrisencio M. Paner100% (4)
- Carvone Why and How Should One Bother To Produce This TerpeneDocument10 pagesCarvone Why and How Should One Bother To Produce This TerpeneanamambriNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review On Nanoparticle-Based VaccinesDocument8 pagesA Comprehensive Review On Nanoparticle-Based VaccinesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- OLIGOHIDRAMNIOSDocument20 pagesOLIGOHIDRAMNIOSJorge Luis Sánchez AlarcónNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Plasticity: Windows of Opportunity in The Developing BrainDocument26 pagesCerebral Plasticity: Windows of Opportunity in The Developing BrainRebeca FloresNo ratings yet
- Bio Generics & IndiaDocument38 pagesBio Generics & Indiagupta1704100% (8)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Subject: Leukemia Professor: Ia Marashkhia Researcher: Alireza Farhadiyeh (1701940)Document14 pagesSubject: Leukemia Professor: Ia Marashkhia Researcher: Alireza Farhadiyeh (1701940)alirezaNo ratings yet
- Capsicum Annuum: Antibacterial Activities of Endophytic Fungi From L. (Siling Labuyo) Leaves and FruitsDocument10 pagesCapsicum Annuum: Antibacterial Activities of Endophytic Fungi From L. (Siling Labuyo) Leaves and FruitsMeynard Angelo M. JavierNo ratings yet
- Aquaculture in The Middle & AfricaDocument335 pagesAquaculture in The Middle & AfricaZaky MfaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma On Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology - A Rare Case ReportDocument5 pagesDiagnosis of Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma On Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology - A Rare Case ReportEditor_IAIMNo ratings yet