Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHAPTER 4a Vector
Uploaded by
makiyoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 4a Vector
Uploaded by
makiyoCopyright:
Available Formats
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
1
CHAPTER 4: Vectors
4.1 Vectors
A vector is a quantity that has magnitude and direction.
Example:
AB is a vector whose magnitude is the same as the length of AB and whose direction is
from A to B.
Vector AB can be denoted as a and its magnitude is written as a or
AB
.
Zero or null vector is a vector with zero magnitude and is denoted as 0
Negative vector of AB is a vector with the same magnitude as AB but in a direction
opposite to AB, that is, AB = BA
Two vectors are equal if they have the same magnitude and direction.
The product of vector a by a scalar k is a vector whose magnitude is k times the
magnitude of a , and is written as k a
i) k a is in the same direction as a if k is positive
ii) k a is in the a direction the opposite to a if k is negative.
Example 1
Based on the diagram above, express the vectors PQ , RS and UT in terms of v .
Solution:
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
2
Two vectors are parallel if one vector is a scalar multiple of the other vector and vice
versa
i) a is parallel to b , if a = b , is a constant.
ii) a = b , if a is parallel to b
Example 2
Based on the diagram above, determine whether vector PQ is parallel to each of the
following vectors.
a) RS b) TU c) WV
Solution:
Example 3
Given that PQ = 2v andAB =
3
5
v , determine whether vectors PQ and AB are parallel.
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
3
If AB = BC where is a constant, then the points A, B and C are collinear.
Example 4
a) Given that MN = 4uand NP = 7u,
show that points M, N and P are
collinear.
b) Given that AB = 3a and AC = 5a ,
show that points A, B and C are collinear.
If ha kb = where a and b are non zero vectors and not parallel, then h = k = 0
Example 5
a) Given that ( 3) (2 7) p q | = + where
and are constants, find the values of
and if vectors p and q non -zero and
non- parallel.
b) Given that (2 1) 3 3 9 h a kb a b + = +
where h and k are constants, find the
values of h and k if vectors a and b non
-zero and non- parallel.
A
B
C
a
a
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
4
Example 6
Vectors p and q are non-parallel and non-zero. Given that
(2 4 1) ( 4 6 3) m n p m n q + = where m and n are constants, find the values of m and n.
Practice 4.1
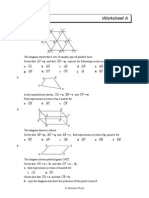
1.
The diagram above shows eight vectors, a , b , PQ , RS , u, v , MO, ON
. Determine
whether each of the following pairs of vectors are equal.
a)
a
and
b
b)
b
and
RS
c)
a
and
RS
d)
v
and
PQ
e)
PQ
and
u
f)
MO
and
ON
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
5
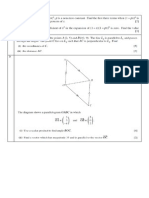
2.
In the diagram above, PQRS is a parallelogram. PR and SQ are the diagonals of the
parallelogram which is intersect at point T. State the vector which is equal to each of the
following vectors.
a) RQ
b) TQ
c) SR
d) TR
3.
Based on the diagram above, express each of the following vectors in terms of
r
.
a) PQ
b) RS
c) TU
d) VW
4. a)
Given that PQ = 4 v
and
SQ =
1
4
v
, determine whether vectors
PQ
and
SQ
are
parallel.
b) Given that
MN = 5 a
,
RS = 4 b
and
PQ =
2
3
RS
,determine whether vectors
MN
and
PQ
are parallel.
5. Given that
PQ = 8p
and
PR = 4p
, show that points P, Q and R are collinear.
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
6
6. P, Q and R are three collinear points. Given that
PR =
10u
and point Q divides PR
internally in the ratio 2 : 3, express each of the following vectors in terms of
u
a) PQ
b) RQ
7. Given that
(2 3) (4 6 ) m a n b + =
where m and n are constants, find the value of m and n if
vectors
a
and
b
are non-parallel and non-zero.
8
. Given a and
b
are two non-parallel and non-zero vectors. Find the values of h and k if
2
( 4) ( 4) h a h k b = +
.
9. Vectors
a
and
b
are non-parallel and non-zero. Given that
2 4 5 9 ua a vb b + =
where u
and v are constants, find the values of u and v.
10. Vectors
p
and
q
are non-zero and non parallel. Given that
2 4 3 3 hp kp p kq hq q + = +
where h and k are constants, find the values of h and k.
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
7
4.2 Addition and Subtraction of Vectors
Resultant vector of two parallel vectors
- when two or more vectors are combined and represented by a single vector, the single
vector is known as the resultant vector such as and | | | | | | c a b c a b = + = +
Example 7
Given that AB = 4v and CD = 7v , find
a) vector 3AB + CD in terms of v
b)
3AB + CD
if 4 units v =
Example 8
In the diagram above, PQRS is a trapezium. PQ is parallel to SR. Given that PQ =
5
3
SR,
PQ = 5 and | | 6 units, m m = find
a) vector PQ + SR in terms of m
b)
PQ + SR
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
8
Resultant vector of two non-parallel vectors
Example 9
In the diagram above, PQR is a triangle, P S = 3n, RP = 5m and SQ =2r .
a) State the vector which is equal to vector
3 2 n r + .
b) Find the resultant vector of vectors P S
and SR in terms of m
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
9
Example 10
In the diagram above, PQRS is a parallelogram. Given that PQ = 2a and P S =3b ,
determine
a) the resultant vector of vectors 2a and 3b
2 3 a b + =
b) vector PT in terms of a and b
PT =
1
2
PR
Resultant vector of three or more vectors
Polygon Law
Example 11
The diagram above shows a heptagon PORSTUV. Find each of the following resultant
vectors.
a) PQ + QR + RS = b) PV + VU + UT + TS =
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
10
Subtracting two vectors
the subtraction of vectors that is a b is the addition of vector a and the negative vector
of b .
a b = ( ) a b +
Example 12
In the diagram above, AB and RS are two parallel vectors. RS = 5a and AB =3a
a) If PQ = RS AB ,find vector PQ in
terms of a and hence mark point Q.
PQ = RS AB
b) If PM = RS 2AB find vector PM in
terms of a and hence mark point M.
PM = RS 2AB
Example 13
In the diagram above, PQRS is a trapezium. PQ is parallel to SR. Given that PQ =2a ,
PR =5b and SR = 2PQ.
a) Determine each of the following vectors in terms of a .
i) PR QR
PR QR = PR +
\
|
QR
.
|
|
ii) SR
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
11
b) Find the vectors which is equal to vector 4 5 a b
4 5 a b =
Example 14
In the diagram PQRS is a parallelogram. It is given that 2 PQ a = and 2 QR b = . PRand QS
intersect each other at point M. Find each of the following vector in terms of a and b
a) PR b) SQ c) MQ
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
12
Example 15
In the diagram above, PTR and QSR are straight lines. Points S and T lie on QR and PR
respectively such that S is the midpoint of QR and 3PT = PR. Given that PQ = 4 and a
PR = 6 , express each of the following vectors in terms of and b a b
a) QR
QR = QP + PR
= PQ + PR
b) RS
c) P S
d) QT
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
13
Example 16
In the diagram above, 8 OP x = , 6 OQ y = and S is a midpoint of OQ . Given that point R and
point T are on the line PQand line ORrespectively such that 3 5 OP OR = and 7 5 OT OR = .
i)Express each of the vector in terms of x and y .
a) QR b) OT
c) PT d) PS
ii) Prove that P, T and S are collinear and determine the ratio : PT PS
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
14
Practice 4.2A
1. Find each of the following resultant vectors.
a) 4 6 x x + b)
2
8 5
3
m m m + +
2. Given that PQ =6u and RS =3 , u find
a) vector 5 PQ + 2RS in terms of u
b)
5PQ + 2RS
if | | 5 units u =
3. Given OABC is a rectangle, where OA = 4 units and OC = 3 units. If OA = a and OB =
b , find
a) AC b) | | b a
4. Given A, B and C are collinear, where AB = (3 3) and k a BC =3b . If
AB
= 2
BC
and 4 , b a = find the value of k.
5.
In the diagram above, points P, Q and R are collinear. Given that PQ =uand
PQ : QR = 1 : 3, find vector PR in terms of u. Hence, find
PR
if | | 5 units. u =
6. A, B and C are three collinear points such that point B lies between points A and C, and
AB: BC = 1 : 4. Given that
AB = 5 , determine each of the following in terms of . m m
a) BC
b) AB + BC
c) AC + CB
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
15
7.
The diagram above shows a triangle PQR. TS is parallel to PQ such that 5TS=3PQ. Given
that PQ =8a, find the resultant vector of vectors PQ and TS in terms of a .
8.
In the diagram above, PQR is a triangle and S is the midpoint of PR. PQ =4a and SP =3b .
a) State the vector which is equal to vector 4 3 . a b +
b) Find each of the following vectors in terms of b
i) RS ii) PQ + QR
9.
In the diagram above, PQRS is a trapezium. SR is parallel to PQ and point T lies on PQ
such that PT : TQ = 1 : 3, PT =4mand TS =6n .
a) Determine each of the following vectors in terms of and m n .
i) PQ ii) SP + PT
b) If 2SR = PQ, find the resultant vector of vectors TS and SR in terms of and m n
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
16
10.
In the diagram above, PQST and PQRS are parallelograms, PQ =9p and PT =6q
a) State the vector which is equal to vector 9 6 p q + .
b) Determine the resultant vector of vectors PQ and P S in terms of and p q
11.
In the diagram above, PQRSTU is a hexagon. State each of the following resultant vectors.
a) PQ + QR + RS b) QP + PU + UT
c) UT + SR + TS + RQ
12.
In the diagram above, PQRS is a parallelogram. T is the midpoint of SR. Given that
PQ =8a and P S =6b, determine each of the following vectors in terms of and/or a b .
a) PQ SQ b) QS TS
c) P S RS
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
17
13.
In the above diagram, OA = 7a , OB = 7b and BX : XA = 3 : 4. Find OX in terms of
and a b.
14.
In the above diagram, CP: PA = 3 : 1 and the line PQ is parallel to the line AB. M is the
midpoint of the line PQ. If AC =8a and BC =16 , b express PM in terms of and a b .
15. The diagram below shows ABC. E is the midpoint of AB and D is a point on CB such
that CD =
1
3
CB.
Given that CA =4a and CD =4b . Find
a) BE b) CE
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
18
16.
The diagram above shows a triangle PQR. Point S lies on RQ such that 4SQ = 5RS.
Given that PQ =3d and PR =2e , determine each of the following vectors in terms of
and d e.
a)
RQ
b) SQ c) P S
17.
In the diagram above, PQRS is a trapezium and PTRS is a parallelogram. T is a midpoint
of PQ. Given that PT =5m and P S = 4n , express each of the following vectors in
terms of and m n .
a) PR b) RQ c) SQ
18.
In the diagram above, PQR is a triangle. Point S lies on PQ such that 4PS = SQ and point
T lies on RQ such that 2RT = 3TQ. Given that PQ =5a and PR =4b , find each of the
following vectors in terms of and a b
a) RQ b) QT c) SR d) TS
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
19
19.
In the diagram above, PQRS is a trapezium. T and U are points lying on SR and PS
respectively, such that T is the midpoint of SR and
5
2
PU
PS
= . Given that PQ =5r , P S
= 4s andQR = PU, express each of the following vectors in terms of and . r s
a) SU b) QU c) ST d) PT
20.
In the diagram above, 8 OA x = , 8 OB y = , : 3:1 OS SB = , : 3:1 AR RB = and
: 4:1 OT TR = . Express each of the following vectors in terms of x and y .
a) AB b) SR c) AS d) AT
Then show that A, T and S are collinear and determine : AT AS
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
20
Example 17
In the above diagram E is a point on the line BD such that
1
4
DE DB = . The line AB is parallel
to the line DC,
4
3
DC AB = , 12 AB a = and 4 AD b =
a) Express each of the following vectors in terms of a and b .
i) DB ii) AE iii) BC
b) Hence, prove that BC is parallel to AE.
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
21
Example 18
In the above diagram, N is the midpoint of the line RT, 6 PQ a = , 6 PT b = ,
2
3
TS PQ = and
1
2
QR PT = .
a) Express each of the following vectors in terms of a and b
i) PS ii) NS
b) Determine whether the points P, N and S are collinear.
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
22
Example 19
In the diagram above, OSR and PSQ are two straight lines. OP =5p , OQ =10 , q
PS : SQ = 2 : 3, PR = mOQ and OS = nOR.
a) Express vector OR in terms of
i) m, and p q ii) n, and p q
b) Hence, find the value of m and n.
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
23
Example 20
In the above diagram, OA =3x and OB =5y . OA is produced to C such that OC = 3OA.
OB is produced to D such that OD =2OB.The lines AD and BC intersect at P.
a) Find each of the following vectors in terms of and x y
a) AD b) BC
b) Given that AP = mAD and BP = nBC , express OP in terms of
a) m, and x y
OP = OA + AP
b) n, and x y
OP = OB + BP
c) Hence, find the value of m and of n.
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
24
Practice 4.2b
1.
In the diagram,
1
4
OS OQ = , PQis parallel to ORand
3
4
PQ OR = . Given that 8 OP p =
and 12 OQ q = , express each of the following vectors in terms of p and q .
a) OR b) PS c) QR
Hence, prove that PS is parallel to QR.
2. In the diagram, below, ABCD is a trapezium and E is the midpoint of AC.
It is given that 12 AD a = , 6 CD b = and BC k AD = , where k is a constant.
a) Find CE in terms of a and b .
b) Find BEin terms of k, a and b . Hence, find the value of k is BE is parallel to CD.
3. In the diagram, M and N are midpoints of OP and MQ respectively. Given that
2
3
OR OQ = , 6 Op a = and 3 OQ b = , find each of the following vectors in terms of a and b .
a) RN b) RP
Hence, prove that the points R, N and P are collinear.
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
25
4.
In the diagram, ABC is a straight line such that 4 AC AB = . The point T on the line BD is
such that 3 BD BT = . The point S on the line DC is such that 3 CD SD = . It is given that
2 AB x = and 3 AD y = .
a) Express
i) AS ii) TC
in terms of x and y
b) Determine whether the point A, T and S are collinear.
5.
In the diagram above, OPQ is a triangle. OTR and PTS are two straight lines. OP =3p ,
OQ =4q , PR : RQ = 1 : 2 and 3SQ = OS.
a) Express each of the following vectors in terms of and p q
i) PQ ii) OR iii) P S
b) If OT = mOR and PT = nPS, express vector OT in terms of
i) m, and p q ii) n, and p q
c) Hence, find the values of m and n .
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
26
6.
In the diagram above, OPQR is a parallelogram. OUS and PUT are two straight lines. The
length of RS is three times the length of SQ and T is the midpoint of OR. OP =5p and
OR = 6r .
a) Express each of the following vectors in terms of and/or . p r
i) OT ii) PT iii) RS iv) OS
b) Given that OU =hOS and PU =kPT, express vector OU in terms of
i) h, and . p r ii) k, and . p r
c) Hence, find the value of h and k.
d) If the area of OPU = 36 unit
2
, find the area of OPS
7. In the diagram, OA =8a, OB =10b and AP = 4b .
a) Express each of the following vectors in terms of and a b
i) OP ii) BA
b) Given that OR = mOP and BR = nBA , express OR in terms of
i) m, and a b ii) n, and a b
c) Hence, find the value of m and n.
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
27
8.
In the diagram, ABCD is a quadrilateral such that the line DB intersects the line XC at Y.
It is given that DX =
2
5
DA , AB =
1
2
XC , DA =10x and DC =10y .
a) If DY = mDB and DY = DX + nXC, find the value of m and of n.
b) Hence, find AB : XY.
9.
In the diagram, OA =3a and OB =5b . The point C lies on OA such that OC: CA = 2 : 1
while the point D lies on OB such that OD : OB = 2 : 3 . The straight lines AD and BC
intersect at point E. It is given that AE = hAD and BE = kBC , where h and k are constant.
a) Express OE in terms of
i) h, and a b ii) k, and a b
b) Hence, calculate the value of h and of k.
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
28
10. In the diagram below, OA =2a , OB =6band OP =
1
3
OB. M is the midpoint of AB.
a) Express each of the following vectors in terms of and a b
i) AP ii) O M
b) Given that OQ = pO M , express OQ in terms of p, and a b
c) Given that AQ = kAP, express OQ in terms of k, and a b.
d) Hence, find the value of p and k.
11. The diagram below shows a triangle OXY. The straight line AY intercepts the straight
line BX at C. It is given that OX = x, OY = y , OA=
1
3
OX and OB = BY.
a) Express each of the following vectors in terms of and x y .
i) AB ii) BX iii) AY
b) Given that BC = hBX and AC = kAY , find the value of h and of k.
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
29
12. The diagram below shows a triangle OAB such that OA = 6a and OB =6b. Point C lies
on the straight line AB such that AC: CB = 2 : 1 and D is the midpoint of OB.
a) Find each of the following vectors in terms of and a b:
i) DA ii) OC
b) OC is produced to point E such that DA is parallel to BE. Given that OE = hOC and
BE = kDA , express OE in terms of
i) h, and a b ii) k, and a b
c) Hence, find the value of h and k.
13.
In the diagram above, OABC is a parallelogram with OA a = and OC b = . ABR is a
straight line with 2 BR AB = . Express each of the vectors in terms of and a b .
a) OB b) OR
Given also CT CB = and OT OR = , express OT
c) in terms of , a and b
d) in terms of , a andb . Hence, find the value of and
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
30
4.3 Vectors in a Cartesian Plane
Vectors in the form xi yj +
- In Cartesian plane, vector i magnitude of 1 unit towards the positive direction of x- axis
vector j magnitude of 1 unit towards the positive direction of y- axis
- Vectors i and j are known as unit vectors in the horizontal and the vertical directions
respectively.
In the diagram, PR = 7 i and RQ = 3 j
PQ = PR + RQ
= 7 3 i j +
- The vector in a Cartesian Plane which proceeds from point A
1 1
( , ) x y to point B
2 2
( , ) x y is:
2 1 2 1
( ) ( ) AB x x i y y j = +
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
31
Example 21
The diagram above shows three vectors, PQ, RS and TU , in a Cartesian plane. Express
each of these vectors in the form xi yj + .
Example 22
a) Given points P(5, 1) and Q(2, 4), express
vector PQ in the form xi yj +
b) The coordinates of A and B are (3, 4) and
(2, 1) respectively. O is the origin.
Express each of the following in the form
xi yj + .
i) OA ii) OB
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
32
Vector in the form
\
|
x
y.
|
|
- Vector in a Cartesian plane can also be expressed in the form
\
|
x
y.
|
|
xi yj + =
\
|
x
y.
|
|
- The vector in a Cartesian Plane which proceeds from point A
1 1
( , ) x y to point B
2 2
( , ) x y is:
AB =
\
|
x
2
x
1
y
2
y
1
.
|
|
Example 23
For each of the following, express vector PQ in the form
\
|
x
y.
|
|
a)
i) PQ = 6 5 i j
ii) P = (4, 6) and Q = ( 3, 7)
b) Given OP =
\
|
5
3.
|
|
and OQ =
\
|
2
6.
|
|
Magnitudes of Vectors
Example 24
Determine the magnitude of each of the following vectors.
a) 3 8 a i j = +
b) b =
\
|
9
-7.
|
|
2 2
a x y = +
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
33
Unit vectors in given direction
Vector AB is in the direction of vector a and has a magnitude of 1 unit. Vector AB is
known as the unit vector in the direction of a
Unit vector in the direction of a is a
If a xi yj = + , unit vector in the given direction of a is
2 2
1
( )
| |
a
a xi yj
a
x y
= = +
+
Example 25
a) Determine the unit vector in the direction
of uif 4 7 u i j =
b) Given that v =
\
|
-2
-4.
|
|
, find v
c) Find the unit vector in the direction of
OP =
\
|
-12
5 .
|
|
d) Given 3 4 r i j = + . Find the unit vector in
the direction of r
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
34
Adding and Subtracting two or more vectors
Example 26
a) Given that 3 2 a i j = + , 4 b i j = + , 6 9 c i j = and 6 d i j = + , find
i) a b + ii) b c d + +
b) Given that
2
5
p
| |
=
|
\ .
,
4
2
q
| |
=
|
\ .
,
7
4
r
| |
=
|
\ .
and
1
8
s
| |
=
|
\ .
, find
i) p r + ii) p q s + +
c)
i) Given that 6 3 , 8 , a i j b i j = = + find
a b
ii) Given that
9
4
p
| |
=
|
\ .
and
6
2
q
| |
=
|
\ .
, find
p q
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
35
Multiplying vectors by scalars
( ) or
x mx
m xi yj mxi myj m
y my
| | | |
+ = + =
| |
\ . \ .
Example 27
a) Given that 4 8 a i j = + , find
i) 3a
ii)
1
2
a
b) Given that
9
2
b
| |
=
|
\ .
, find
i) 6b
ii)
2
3
b
Combined operations on Vectors
Example 28
a) Given that 2 3 , 4 5 a i j b i j = + = and 5 9 c i j = + , find
i) 3 2 a b c + ii) | 2 | b c
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
36
b) Given that
7 4 3
, and ,
1 6 8
p q r
| | | | | |
= = =
| | |
\ . \ . \ .
find
i) 2 4 p q r + ii) the unit vector in the direction of 2r p +
Example 29
a) Given
3 2
12
p
a
+
| |
=
|
\ .
and
2
3
b
| |
=
|
\ .
. Calculate the values of p if
i) | | 15 a b = ii) and a bare parallel
b) If ( 2) ( 1) a n i n j = + + and 4 10 b i j = , find the value of n if vectors and a b are
parallel.
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
37
Practice 4.3
1.
In the diagram above, vectors , , , , , , and a b c d e f g hare drawn in a Cartesian plane.
Express each of these vectors in the form xi yj + .
2. For each of the following pairs of points P and Q, express vector PQ in the formxi yj + .
a) P(3, 4) Q(7, 9) b) P(2, 3) Q(2, 7)
c) P(5, 1) Q(9, 2) d) P(6, 3) Q(1, 6)
3.
The diagram above shows vectors, , , , , , , and a b c d e f g hin a Cartesian plane. Express each
of these vectors in the form
x
y
| |
|
\ .
.
4. Express each of the following vectors in the form
x
y
| |
|
\ .
.
a) 4 7 AB i j = +
b) PQsuch that P = (4, 6) and Q = (9, 1)
c) 8 9 RS i j =
d) UV such that U is the origin and V = (3, 5)
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
38
5. Determine the magnitude of each of the following vectors.
a) 4 6 a i j = + b) 8 3 b i j =
c) 9 c i j = + d)
5
7
d
| |
=
|
\ .
e)
2
9
e
| |
=
|
\ .
f)
4
2
f
| |
=
|
\ .
6.
In the diagram above, vectors , , , and a b c d are drawn in a Cartesian plane. Determine the
magnitude of each of these vectors.
7. For each of the following vectors, determine the unit vector in the direction of the vector.
a) 6 8 a i j = + b) 9 12 b i j =
c) 5 12 c i j = + d)
7
2
d
| |
=
|
\ .
e)
3
4
e
| |
=
|
\ .
f)
6
4
f
| |
=
|
\ .
8. Given that 5 4 , 2 6 , 3 8 a i j b i j c i j = + = + = and 2 10 d i j = + , find
a) a b + b) c d + c) a c d + +
9. Given that
3
6
p
| |
=
|
\ .
,
2
11
q
| |
=
|
\ .
,
12
5
r
| |
=
|
\ .
and
2
9
s
| |
=
|
\ .
, find
a) p r + b) q s + c) p q s + +
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
39
10.
In the diagram above, OPQR is parallelogram. Given that 5 OP i j = + and
2 3 OR i j = + , determine vector OQ.
11. Given that 5 11 a i j = , 3 10 b i j = + and 5 6 c i j = , find
a) a b b) b c c) c a
12. Given that
10
3
p
| |
=
|
\ .
,
8
10
q
| |
=
|
\ .
and
9
1
r
| |
=
|
\ .
, find
a) q p b) r q c) p r
13. Given that 8 4 OA i j = + , 3 6 OB i j = + and 3 OC i j = , determine each of the
following vectors.
a) AB b) BC
14. Given that 6 9 a i j = + , find
a) 4a b)
3
2
a c)
5
6
a
15. Given that
8
12
PQ
| |
=
|
\ .
, find
a) 8PQ b)
3
4
PQ c)
2
3
PQ
16. Given that 3 2 a i j = , 8 3 b i j = + and 4 c i j = + , find
a) 2 3 a b c +
b) | 3 4 | b c
c) the unit vector in the direction of 2b a +
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
40
17. Given that
8
2
p
| |
=
|
\ .
,
3
7
q
| |
=
|
\ .
and
4
11
r
| |
=
|
\ .
, determine
a) 2 3 p q r +
b) the magnitude of vector 2 3 q r
c) the unit vector in the direction of 3r p +
18.
In the diagram above, OAB is a triangle. 4 , 6 5 OA i j OB i j = = + and point C lies
on AB such that AC : CB = 2 : 3
19. In the Cartesian plane with O as the origin, 7 2 , 5 OA i j OB i j = + = and
2
3
OC AB = .
a) Determine each of the following vectors.
i) AB ii) OC iii) AC iv) BC
b) Hence, find the unit vector in the direction of BC
20. If 10 5 , 7 4 p i j q i j = = and 16 7 r i j = + , determine
a) the values of m and n if mp nq r + =
b) the vector that is parallel to vector 2q p and has a magnitude of 15 units.
21. Given that 11 PQ hi j = and 14 2 PR i j = , find the possible values of h if
a) | | 15 QR = units
b) points P, Q and R are collinear
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
41
22. Given that O is the origin,
6
7
PQ
| |
=
|
\ .
,
1
4
OQ
| |
=
|
\ .
and
6
m
RS
| |
=
|
\ .
, find
a) the coordinates of point P
b) the unit vector in the direction of OP
c) the value of m if vector RS is parallel to vector PQ
23. PQRS is a parallelogram.
9
2 3 ,
2
PQ i j PR hi j = + = + and 5 , PS i kj = + where h and k
are constants.
a) Find the value of h and k
b) Calculate the length of the diagonal PR
24. It is given that 6 AB pi j = + and 16 6 CB i j = where p is a constant. Find the possible
value of p if
a) | | 15 Ac =
b) the points A, B and C are collinear.
25. It is given that 2 2 , 2 , a i j b i j = = + P(1, 3) and Q(5, 2). If PQ ha kb = + , where h
and k are constants, find
a) the value of h and k
b) the unit vector in the direction of PQ
26. If 2 a i j = + and 3 b i j = , find the value of m if 3 2 a mb + is parallel to the x-axis.
27. Given that 2 ( 3) r i p j = + + and ( 5) 8 s p i j = , find the value of p if r is parallel to
s
28. It is given that 3 v i j = + and 3 w i j = + . The coordinates of the points P and Q are
(2, 4) and (8, 2) respectively. Given that PQ mv kw = + , where k is a constant, find
a) the value of m and k
b) the unit vector in the direction of PQ
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
42
Answer:
Practice 4.1
1a) Yes b) No
c) Yes d) No
e) Yes f) Yes
2a) SP b) ST
c) PQ d) PT
3a) r b) 2r
c)
5
2
r d)
3
2
r
4a) Yes b) No
6a) 4u b) 6u
7. m =
3
2
, n =
2
3
8. h = 2, k = 2; h = 2. k = 6
9. u = 2, v =
9
5
10. h =
1
2
,k =
1
2
Practice 4.2A
1a) 10x b)
41
3
m
2a) 36u b) 180 units
3a) 2 b a b) 3 units
4. k = 9
5. PR = 4u ,
PR
= 20 units
6.a) 20m b) 25m c) 5m
7.
64
5
a
8a) SQ
b)i) 3b ii) 6b
9a)i) 16m ii) 6n
b) 8 6 m n +
10a) P S b) 18 6 p q +
11a) P S b) QT c) UQ
12a) 6b b) 6 4 b a
c) 8 6 a b +
13. 3 4 a b +
14. 3 6 a b
15a) 2 3 a b b) 2 3 a b +
16a) 3 2 d e b)
5 10
3 9
d e
c)
4 10
3 9
d e +
17a) 5 4 m n + b) 5 4 m n
c) 10 4 m n
18a) 5 4 a b b)
8
2
5
b a
c) 4b a d)
8
2
5
a b
19a)
8
7
s b)
20
5
7
s r
c)
5 4
2 7
r s d)
5 24
2 7
r s +
20a) 8 8 x y + b) 2x
c) 6 8 y x d)
24 32
5 5
y x
: 4: 5 AT AS =
Practice 4.2B
1.a)
32
16
3
p q + b) 8 3 p q +
c)
32
4
3
q p
2.a) 3 6 b a
b) ( )
1
12 6 3 ,
2
k a b k + =
3.a) ( )
1
3
2
b a + b)
( ) 2 3 b a +
1
4
RN RP = R,N and P are collinear
4.a)i)
8
2
3
y x + ii)
20
3
y x +
b) 2 AS AT = A, T and S are collinear
5.a) i) 4 3 q p ii)
4
2
3
p q +
iii) 3 3 q p
b) i)
4
2
3
mp mq + ii) 3(1 ) 3 n p nq +
c) m =
9
10
, n =
2
5
6a)i) 3r ii) 3 5 r p
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
43
iii)
15
4
p iv)
15
6
4
p r +
b) i)
15
6
4
hp hr + ii) 5(1 ) 3 k p kr +
c) k =
8
11
,h =
4
11
d) 99 unit
2
7a)i) 8 4 a b + ii) 10 8 b a +
b)i) 8 4 ma mb + ii) (10 10 ) 8 n b na +
c) m = n =
5
7
8a) m=
2
5
, n =
1
5
b) 5 : 2
9a) i) (3 3 ) 2 h a hb +
ii) (5 5 ) 2 k b ka +
b) h =
5
11
, k =
9
11
10a) i ) 2 2 a b + ii) 3 a b +
b) 3 pa pb + c) (2 2 ) 2 k a kb +
d) k =
3
4
, p =
1
2
11a)i)
1 1
3 2
x y + ii)
1
2
y x +
iii)
1
3
x y + b) h =
1
5
, k =
2
5
12a) i ) 3 6 b a + ii) 2 4 a b +
b) i) 2 4 ha hb + ii) (6 3 ) 6 k b ka +
c) k =
2
5
h =
6
5
13) a) a b + b) 3 a b +
c) b a + d)
( ) 3 a b +
1 1
,
3 3
= =
Pactice 4.3
1. 2 , 4 2 , 4 , a i j b i j c i j = = + = +
6 2 , 3 2 , 5 d i j e i j f i j = = + =
3 3 , 2 3 g i j h i j = + = +
2a) 4 5 i j + b) 4 10 i j
c) 14 3 i j + d) 5 3 i j
3a)
2 5
,
2 1
a b
| | | |
= =
| |
\ . \ .
,
4
3
c
| |
=
|
\ .
,
5
2
d
| |
=
|
\ .
3 3
,
5 6
e f
| | | |
= =
| |
\ . \ .
,
1 5
,
3 2
g h
| | | |
= =
| |
\ . \ .
4a)
4
7
| |
|
\ .
b)
13
5
| |
|
\ .
c)
8
9
| |
|
\ .
d)
3
5
| |
|
\ .
5a) 7.21 units b) 8.54 units
c) 9.06 units d) 8.60 units
e)9.22 units f) 4.47 units
6. | | 5 a = units, | | 6.08 b = units,
| | 4.47 c = units, | | 5.39 d = units
7a)
3 4
5 5
i j + b)
3 4
5 5
i j
c)
5 12
13 13
i j + d)
7
53
2
53
| |
|
|
|
|
\ .
e)
3
5
4
5
| |
|
|
|
|
\ .
f)
3
13
2
13
| |
|
|
|
|
\ .
8a) 3 10 i j + b) 5 2 i j + c) 10 6 i j +
9a)
9
1
| |
|
\ .
b)
0
2
| |
|
\ .
c)
3
4
| |
|
\ .
10. 7 4 i j +
11a) 8 21 i j b) 8 16 i j + c) 5 j
12a)
18
13
| |
|
\ .
b)
1
9
| |
|
\ .
c)
19
4
| |
|
\ .
13a) 11 2 i j + b) 4 3 i j
14a) 24 36 i j + b)
27
9
2
i j +
c)
15
5
2
i j +
SCKung
M.Sc (Teaching Maths)
B. Edu (Acct & Maths) FORM 5 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS TEL: 012 5349153
44
15a)
64
96
| |
|
\ .
b)
6
9
| |
|
\ .
c)
16
3
8
| |
|
|
|
\ .
16a) 26 4 i j b) 5 65 units
c)
19 4
377 377
i j +
17a)
29
14
| |
|
\ .
b) 685 units c)
20
1361
31
1361
| |
|
|
|
|
\ .
18a) i) 2 6 i j + ii)
4 12
5 5
i j
iii)
24 7
5 5
i j + b)
24 7
25 25
i j +
19a) i) 8 7 i j ii)
16 14
3 3
i j
iii)
37 20
3 3
i j iv)
13 1
3 3
i j +
b)
13 1
170 170
i j +
20a) m =
113
, 30
5
n = b) 12 9 i j
21a) 2, 26 b) 77
22a) (5, 3) b)
5 3
34 34
i j c)
36
7
23a) h = 7, k =
1
1
2
b) 8.322
24a) p= 25 or 7 b) p= 16
25a) h =
1
2
, k = 3 b)
4 5
41 41
i j +
26. m = 3
27. p = 1
28a) m =
2
2
5
, k =
1
1
5
b)
1 1
2 2
i j +
You might also like
- Math Review: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandMath Review: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Master The SAT Subject Test-Math Level 1 and 2Document404 pagesMaster The SAT Subject Test-Math Level 1 and 2vmsgr100% (2)
- VectorsDocument26 pagesVectorsAditya Bansal0% (1)
- Earth and Life Science, Grade 11Document6 pagesEarth and Life Science, Grade 11Gregorio RizaldyNo ratings yet
- Solomon C4 VectorsDocument11 pagesSolomon C4 Vectorssim887No ratings yet
- Mongodb TutorialDocument106 pagesMongodb TutorialRahul VashishthaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics SPM Forecast PapersDocument13 pagesMathematics SPM Forecast PaperswhywhyqNo ratings yet
- Coordinate GeometryDocument5 pagesCoordinate Geometrynaisha kumarNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Examination The Contemporary WorldDocument2 pagesPreliminary Examination The Contemporary WorldJane M100% (1)
- Types of Intermolecular ForcesDocument34 pagesTypes of Intermolecular ForcesRuschan JaraNo ratings yet
- Learning Module - Joints, Taps and SplicesDocument9 pagesLearning Module - Joints, Taps and SplicesCarlo Cartagenas100% (1)
- Geopolymer Book Chapter1 PDFDocument37 pagesGeopolymer Book Chapter1 PDFDick ManNo ratings yet
- Scalar Quantity, Such As Area, Volume, Mass, Temperature andDocument10 pagesScalar Quantity, Such As Area, Volume, Mass, Temperature andFazlina MustafaNo ratings yet
- Presentation TMPDocument93 pagesPresentation TMPIzzyan NasruddinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 Baru 1 Tutorial and All QuestionsDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 9 Baru 1 Tutorial and All QuestionsMizaZainalNo ratings yet
- Vector Theory EDocument26 pagesVector Theory EthinkiitNo ratings yet
- O4Qvec - c4 SoomenxDocument11 pagesO4Qvec - c4 SoomenxKapilanNavaratnamNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Lines and Angles Assignment 4Document11 pagesCBSE Class 9 Lines and Angles Assignment 4SarthakDiwanNo ratings yet
- SPM F5 Ch4 PDF - UnlockedDocument11 pagesSPM F5 Ch4 PDF - UnlockedkokleongNo ratings yet
- Juj 2009 PDFDocument36 pagesJuj 2009 PDFMohd Khir ZainunNo ratings yet
- S4 Amath 1Document6 pagesS4 Amath 1Teo Liang WeiNo ratings yet
- E4Qvec XDocument11 pagesE4Qvec XFarisNo ratings yet
- 5 LinesDocument16 pages5 Linesamanda_edithNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument30 pagesVectorsbd87glNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument9 pagesVectorsImash MinokaNo ratings yet
- VECTORSDocument31 pagesVECTORSAlicia HaughtonNo ratings yet
- PGCE Secondary Mathematics Pre-Interview Task: 1 Dividing by FractionsDocument8 pagesPGCE Secondary Mathematics Pre-Interview Task: 1 Dividing by Fractionsjfpowell100% (1)
- 100 - Vectors - 9Document6 pages100 - Vectors - 9whyreadNo ratings yet
- Maths Practice Paper Class 9 CBSE SA1Document4 pagesMaths Practice Paper Class 9 CBSE SA1gurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- Addmath VectorDocument4 pagesAddmath Vectornurhayati8860No ratings yet
- Vectors: Cloned SPM Question (Paper 1)Document7 pagesVectors: Cloned SPM Question (Paper 1)Samuel LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Test: Achievement Category QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 6 Test: Achievement Category QuestionsAnonymous AtyZD9DS1mNo ratings yet
- 4.vektor 2015 (2003 - 2010)Document14 pages4.vektor 2015 (2003 - 2010)Zuraidah BasriNo ratings yet
- Science & Maths (IX)Document12 pagesScience & Maths (IX)Sundeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Vectors and The Geometry of SpaceDocument34 pagesVectors and The Geometry of Spacefara7788No ratings yet
- Vectors - SPM Questions (1) : J I K R J K I SDocument2 pagesVectors - SPM Questions (1) : J I K R J K I SAzizah Haji KamarNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Chapter 07 Coordinate Geometry Practice Paper 07 Answers 1Document8 pagesMaths Class X Chapter 07 Coordinate Geometry Practice Paper 07 Answers 1G.sathasivam MahaNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Resultant VectorsDocument3 pagesWeek 6 Resultant VectorsVeeno DarveenaNo ratings yet
- Coordinate PP KEY 2021Document11 pagesCoordinate PP KEY 2021Mayur GowdaNo ratings yet
- Revision Tingkatan 4Document10 pagesRevision Tingkatan 4Suriani SayuaakhiNo ratings yet
- Program Add MathsDocument20 pagesProgram Add MathsAbdul Manaf100% (1)
- F3 Challenging Exercise 11Document3 pagesF3 Challenging Exercise 11pgkbgjrh5pNo ratings yet
- Jemh 107Document18 pagesJemh 107myNo ratings yet
- Vectors Mixed Practice 12ıb HDocument8 pagesVectors Mixed Practice 12ıb HNil HamaviogluNo ratings yet
- Salomon VectorsDocument2 pagesSalomon Vectorsjsy7w7z8q7No ratings yet
- Find The Midpoints of Each Side Connect Them in OrderDocument23 pagesFind The Midpoints of Each Side Connect Them in OrderRedzuan Saidi0% (1)
- VECTORSebk 1Document13 pagesVECTORSebk 1Tinashe MuzukwaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Revision QuestionsDocument16 pagesMathematics: Revision Questionsdarwisyah.yunosNo ratings yet
- 73 Vector & 3d Part 6 of 6Document9 pages73 Vector & 3d Part 6 of 6sabhari_ramNo ratings yet
- Past Year SPM QuestionsDocument6 pagesPast Year SPM QuestionsLee ElaineNo ratings yet
- Cordinate GeometryDocument14 pagesCordinate GeometryShalini GaneshNo ratings yet
- LPKPM SPM Jun 2008 Mathematics Paper 1,2sqDocument10 pagesLPKPM SPM Jun 2008 Mathematics Paper 1,2sqSelva GanesanNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument5 pagesVectorsZahid RajaNo ratings yet
- FGJLKGFLKHFGFDDocument9 pagesFGJLKGFLKHFGFDIlario CutajarNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Numerical Expressions Math Presentation in Light Blue Math Do - 20240121 - 223657 - 0000Document17 pagesInterpreting Numerical Expressions Math Presentation in Light Blue Math Do - 20240121 - 223657 - 0000tamorromeo908No ratings yet
- Interpreting Numerical Expressions Math Presentation in Light Blue Math Do - 20240121 - 223657 - 0000Document17 pagesInterpreting Numerical Expressions Math Presentation in Light Blue Math Do - 20240121 - 223657 - 0000tamorromeo908No ratings yet
- Vector Algebra Exempler PDFDocument16 pagesVector Algebra Exempler PDFamiNo ratings yet
- f4 Maths Revision c5 Straight LineDocument20 pagesf4 Maths Revision c5 Straight Lineshavnair87No ratings yet
- Gce As/A Level - New: Monday, 13 May 2019 - Afternoon Further Pure Mathematics ADocument3 pagesGce As/A Level - New: Monday, 13 May 2019 - Afternoon Further Pure Mathematics Ajack murairwaNo ratings yet
- MATH 123 - Exercises 2 2018 2019Document2 pagesMATH 123 - Exercises 2 2018 2019Trevor ChilmanNo ratings yet
- Geometry Practice First Sem - 2021Document5 pagesGeometry Practice First Sem - 2021Shivaji ThubeNo ratings yet
- 12nov Test Class9 MathDocument2 pages12nov Test Class9 Mathraonish001No ratings yet
- Vectors Worksheet (A+Astar) - Clip 180Document5 pagesVectors Worksheet (A+Astar) - Clip 180Dominic Bonkers StandingNo ratings yet
- Add Math Vectors 2020 With MC PDFDocument6 pagesAdd Math Vectors 2020 With MC PDFVivek BachuNo ratings yet
- 2012 OctDocument1 page2012 OctmakiyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 ElectronicDocument9 pagesChapter 9 ElectronicmakiyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ElectromagneticDocument14 pagesChapter 8 ElectromagneticmakiyoNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 1Document3 pagesPhysics Chapter 1makiyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 WavesDocument11 pagesChapter 6 WavesmakiyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ElectricDocument18 pagesChapter 7 ElectricmakiyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 LightDocument13 pagesChapter 5 LightmakiyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ForceDocument35 pagesChapter 2 ForcemakiyoNo ratings yet
- MCQ Chapter 1Document7 pagesMCQ Chapter 1makiyoNo ratings yet
- Academic Content For ShirleyDocument2 pagesAcademic Content For Shirleynicole1003No ratings yet
- P1 Extra Test 2Document7 pagesP1 Extra Test 2makiyoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2238785423001345 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S2238785423001345 MainHamada Shoukry MohammedNo ratings yet
- Bobcat E34 - E35Z Brochure - Adare MachineryDocument8 pagesBobcat E34 - E35Z Brochure - Adare MachineryNERDZONE TVNo ratings yet
- Sidomuncul20190313064235169 1 PDFDocument298 pagesSidomuncul20190313064235169 1 PDFDian AnnisaNo ratings yet
- MSDS Formic AcidDocument3 pagesMSDS Formic AcidChirag DobariyaNo ratings yet
- Aashirwaad Notes For CA IPCC Auditing & Assurance by Neeraj AroraDocument291 pagesAashirwaad Notes For CA IPCC Auditing & Assurance by Neeraj AroraMohammed NasserNo ratings yet
- RseDocument60 pagesRseH S Vishwanath ShastryNo ratings yet
- Weekly Lesson Plan: Pry 3 (8years) Third Term Week 1Document12 pagesWeekly Lesson Plan: Pry 3 (8years) Third Term Week 1Kunbi Santos-ArinzeNo ratings yet
- Listening Tests 81112Document13 pagesListening Tests 81112luprof tpNo ratings yet
- 5000-5020 en PDFDocument10 pages5000-5020 en PDFRodrigo SandovalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Translation ExposureDocument14 pagesChapter 10 Translation ExposurehazelNo ratings yet
- Oral Com Reviewer 1ST QuarterDocument10 pagesOral Com Reviewer 1ST QuarterRaian PaderesuNo ratings yet
- Model No. TH-65JX850M/MF Chassis. 9K56T: LED TelevisionDocument53 pagesModel No. TH-65JX850M/MF Chassis. 9K56T: LED TelevisionRavi ChandranNo ratings yet
- Schermer 1984Document25 pagesSchermer 1984Pedro VeraNo ratings yet
- Spring 12 ECON-E370 IU Exam 1 ReviewDocument27 pagesSpring 12 ECON-E370 IU Exam 1 ReviewTutoringZoneNo ratings yet
- Introduction of ProtozoaDocument31 pagesIntroduction of ProtozoaEINSTEIN2D100% (2)
- Project On Mahindra BoleroDocument35 pagesProject On Mahindra BoleroViPul75% (8)
- Reviewer in EntrepreneurshipDocument6 pagesReviewer in EntrepreneurshipRachelle Anne SaldeNo ratings yet
- Technology 6 B Matrixed Approach ToDocument12 pagesTechnology 6 B Matrixed Approach ToNevin SunnyNo ratings yet
- GladioDocument28 pagesGladioPedro Navarro SeguraNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of The KVM Hypervisor Running On Arm-Based Single-Board ComputersDocument18 pagesPerformance Evaluation of The KVM Hypervisor Running On Arm-Based Single-Board ComputersAIRCC - IJCNCNo ratings yet
- Ce Licensure Examination Problems Rectilinear Translation 6Document2 pagesCe Licensure Examination Problems Rectilinear Translation 6Ginto AquinoNo ratings yet
- Teambinder Product BrochureDocument7 pagesTeambinder Product BrochurePrinceNo ratings yet
- Coc 1 ExamDocument7 pagesCoc 1 ExamJelo BioNo ratings yet
- Load Schedule: DescriptionDocument1 pageLoad Schedule: Descriptionkurt james alorroNo ratings yet