Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modul 1 f4f5
Uploaded by
Tamil ArasuCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modul 1 f4f5
Uploaded by
Tamil ArasuCopyright:
Available Formats
FORCE AND MOTION
A U < W
B F > G
C U > W
D F = G
2. Which graph shows an increasing acceleration?
A
B
C
D
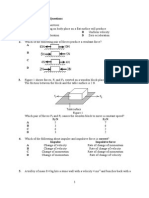
1. The diagram shows an aeroplane flying at a constant velocity. Which relationship between the
forces is true?
3. The diagram shows a book falling down from a table.
Which physical quantity of the book increases while it is falling?
A potential energy
B chemical energy
C mass
D acceleration
E kinetic energy
4. The diagram shows a coconut falls from a coconut tree. The coconut has the least change in
kinetic energy between the positions
A A and B
B A and D
C A and C
D A and E
5. The diagram shows a man climbing up a coconut tree at a constant speed.
Which physical quantity increases while the man is climbing up the staircase?
A potential energy of the man
B momentum of the man
C weight of the man
D kinetic energy of the man
6. A student carried out an experiment using a ticker timer and a trolley. She obtained a chart
from the ticker tape by cutting it into five dot lenghts as shown in the figure.
Which statement describes the motion of the trolley?
A the trolley is coming to a stop with constant deceleration
B the trolley moves from rest with uniform acceleration
C the trolley moves from rest with increasing velocity
7. The figure shows a squid moving forward by discharging a jet of water from its body.
The forward movement of the squid can be explained by
A conservation of energy
B newton's first law of motion
C conservation of momentum
8. What is the difference between mass and weight?
A both mass and weight are vector quantities
B both mass and weight are derived quantites
C unit for mass is kilogram and unit for weight is Newton
9. Which of the following displacement-time graphs shows an object is at rest?
A
B
C
D
E
10. Which of the following statement is true about acceleration due to gravity?
A Increases with increasing height
B
The standard value of the acceleration due to gravity is
C Objects dropped under the influence of the pull of gravity accelerate at a constant rate
11. A stone is dropped from a height in vacuum. Which of he following quantities does not
change?
A mass
B momentum
C velocity
12. Which pair of unit for impulse is correct?
A Ns kgms
-2
B Ns
-1
kgm
C Ns
-1
kgm
3
D Ns kgms
-1
13. Which of the following improves the efficiency of the operation of a car?
A Streamlines the body of the car to reduce air resistance
B Deflate the tyres to the correct pressure to increase friction with the road surface
C Align the wheels of the car to increase resistance to the motion of the car
14. Which of the following is not a safety features in vehicles?
A soft materials in dashboard to reduce injury
B strong reinforced steel in passenger safety cell
C colour of the car
15. Which of the following statements about inertia of an object is false?
A an object with a lesser mass has a lesser inertia
B inertia is the property of matter that causes it to resist any change in its motion or state of
rest
C the SI unit of inertia is kilogram
16. Which of the following can be changed by a force?
A mass
B weight
C shape
17. Which situation relates to inertia?
A
B
C
18. Which of the following is not an example of fossil fuels?
A coal
B petroleum
C natural gas
D oxygen
19. Which of the following is the easiest to stop?
A pencil
B sponge
C iron rod
D car
20. The figure shows John and Subra pulling a rope in the opposite direction with force of
magnitude 50 N and 25 N respectively.
Calculate the magnitude of the resultant force acting on the string.
A 5 N
B 10 N
C 25 N
D 50 N
E 100 N
21. The diagram shows a displacement-time graph for the motion of an object.
The momentum of the object is zero from
A 0 s to 2 s
B 2 s to 4 s
C 2 s to 6 s
D 6 s to 8 s
E 0 s to 8 s
22. The diagram shows a dried leaf and a stone being released at the same time in a cylinder.
Why is the stone reaches the base faster?
A The force of gravity acted on the stone is better to overcome the air resistance compared
to the force of gravity acted on the dried leaf.
B The force of gravity acted on the dried leaf is better to overcome the air resistance
compared to the force of gravity acted on the stone.
C The force of gravity acted on the stone is greater than the force of gravity acted on the
dried leaf.
D The force of gravity acted on the dried leaf is greater than the force of gravity acted on the
stone.
23. Choose the diagram which shows no work being done by the boy.
A
B
C
D
24. In a high jump event, thick mattresses with a soft surface are used to
A increase the stopping time of the body
B increase the impulsive force
C increase the momentum
25.
Which car has the greatest momentum when each of its velocity is ?
A
B
C
D
1. The figure below shows a car traveling on a horizontal road.
The car has a mass of 1000 kg. At a certain moment in its motion, the frictional force between
the car and the road is 500N and its acceleration then is 1.2 ms
-2
.
(a) What is the difference between scalar quantities and vector quantities?
(b) Classify the physical quantities mention above into scalar quantities and vector
quantities.
(c) Calculate the forward driving force that is acting on the car as shown in the figure
above?
(d) Other than frictional force, what other force do you think acts on the car as it is moving?
2. The figure below shows a ticker tape chart obtained from the motion of a trolley down an
inclined plane. Each strip of ticker tape contains 10 ticks. The ticker timer makes 50 ticks per
second.
(a) What type of power supply is used to run the ticker timer?
(b) What is the time interval for 1 tick on the ticker tape?
(c) What is the type of motion shown by the trolley?
SECTION A Structured Items
Instruction: Answer all questions in this section.
(d) What is the average velocity shown by the first strip of ticker tape?
(e) Calculate the acceleration of the trolley.
3. Ahmad cycles to school everyday. The graph below shows a typical velocity-time graph of
Ahmad's journey to school.
(a) During which part of the journey is Ahmad :
(i) Accelerating :.
(ii) Decelerating :
(b) For how long is Ahmad cycling with constant velocity?
(c) How far is Ahmad's school form his house?
(d) What is Ahmad's average velocity for the whole journey?
4. The diagram shows a boy of mass 45 kg running with a velocity of 2.0 ms
-1
towards a
stationary trolley of mass 15 kg. He then jumps onto the stationary trolley.
(a) Name the physics principle involved when the boy jumps onto the trolley.
(b) In what direction will the trolley moves after the boy jumped onto it?
(c) Calculate the velocity of the boy and the trolley after the boy lands on the trolley.
(d) Name one application of the physics principle named in part (a) in the field of sports.
5. The figure below shows the arrangement of the apparatus to study the effect of the extension
of a spring produced by a load hung at the end of the spring.
The results of the experiment is represented by the graph below.
(a) Name the law involved in the relation above.
(b) Mark 'X' on the graph above to show the upper limit to which the law mentioned in (a) is
valid.
(c) What physical quantity is represented by the gradient of the graph?
(d) If the elastic potential energy stored in the spring is represented by the area under the
graph, how much energy is stored when the spring is acted upon by a load of weight 0.5
N?
END OF QUESTION PAPER
You might also like
- Modul 1Document13 pagesModul 1Ms PaulinaNo ratings yet
- T-Forces and Motion AssessmentDocument12 pagesT-Forces and Motion AssessmentGan Hock KiamNo ratings yet
- MODUL 1 FizikDocument14 pagesMODUL 1 FizikMohd HafizuddinNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Modul WAJADocument14 pagesPhysics Form 4 Modul WAJARamanath RamNo ratings yet
- Physics Y10 Term 2 Exam Paper1Document14 pagesPhysics Y10 Term 2 Exam Paper1Ezra Loganathan MuniandiNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Objective QuestionDocument17 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2 Objective Questionqalanis67% (9)
- This Paper Consists of 50 Questions. Each Question Is Followed by Four Options. Choose The Best Option For Each Question Then Blacken The Correct Space On The Answer Sheet. Answer All QuestionsDocument8 pagesThis Paper Consists of 50 Questions. Each Question Is Followed by Four Options. Choose The Best Option For Each Question Then Blacken The Correct Space On The Answer Sheet. Answer All Questionsjoe zulkefliNo ratings yet
- Mid 2nd Term Mathayom 2 ScienceDocument8 pagesMid 2nd Term Mathayom 2 ScienceAbdullohNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Fizik PAT 2016Document15 pagesPaper 1 Fizik PAT 2016Junaidah Mohamad RamliNo ratings yet
- (Momentum, Works and Power) Quiz2023Document14 pages(Momentum, Works and Power) Quiz2023Haigou WaaaahNo ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument7 pagesForce and MotionDavidHutasoit100% (2)
- Physics Test 2Document4 pagesPhysics Test 2WeteachNo ratings yet
- SECTION A: Objective Questions Instruction: Answer All Questions. 1. A B C D 2. A B C DDocument17 pagesSECTION A: Objective Questions Instruction: Answer All Questions. 1. A B C D 2. A B C DNurlailie Md JamilNo ratings yet
- ap-physb_dynamics-multiple-choice-questions_2014-01-05Document10 pagesap-physb_dynamics-multiple-choice-questions_2014-01-05Asma FarooquiNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Physics Final Exam ReviewDocument21 pagesForm 4 Physics Final Exam ReviewMohd AzlanNo ratings yet
- Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011Document19 pagesPeperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011Jill Peary RajuNo ratings yet
- HL Paper1Document21 pagesHL Paper1Proleteriat Dictatorship of Koperia0% (1)
- Physics TestDocument5 pagesPhysics TestAnonymous FH0ak9INfUNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 05 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 05 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Physic's Paper 1 Form4-08Document15 pagesPhysic's Paper 1 Form4-08Salmizam IzamNo ratings yet
- QP 1098Document10 pagesQP 1098Anshul ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument9 pagesDynamicsAbdul WarsiNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Review - DynamicsDocument10 pagesMultiple Choice Review - DynamicsPremkumar NaikarNo ratings yet
- Balanced Forces Worksheet AnswersDocument4 pagesBalanced Forces Worksheet AnswersGeronimo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE PHYSICS PROBLEMSDocument7 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE PHYSICS PROBLEMSNay Lin AungNo ratings yet
- SG Physics PaperDocument18 pagesSG Physics Paperfyzc76tbdxNo ratings yet
- AGA KHAN SCHOOLS PHYSICS EXAMDocument10 pagesAGA KHAN SCHOOLS PHYSICS EXAMHaseeb MirzaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Force, Vector and ScalarDocument10 pagesTopic 3 - Force, Vector and ScalarMac Justine JimenezNo ratings yet
- Review Exam2Document5 pagesReview Exam2EliezerNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Pop Quiz Jan 2013Document4 pagesGrade 11 Pop Quiz Jan 2013Jerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- Physics SampleDocument9 pagesPhysics SamplevipulmuraliNo ratings yet
- Regents Physics Holiday Homework Study GuideDocument9 pagesRegents Physics Holiday Homework Study GuideAashna ShahNo ratings yet
- Forces and NL Practice TestDocument8 pagesForces and NL Practice TestCASIÑO SHANE VAST ANDREINo ratings yet
- B. Meter: Introductory Physics 1 Test #1 - Unit 1 To 3 Multiply Choices - Answer All QuestionsDocument7 pagesB. Meter: Introductory Physics 1 Test #1 - Unit 1 To 3 Multiply Choices - Answer All Questionscondoleeza smithNo ratings yet
- Use The Passage To Answer Questions 4 - 5Document4 pagesUse The Passage To Answer Questions 4 - 5Melvin CabonegroNo ratings yet
- Physics P-22 IgcseDocument20 pagesPhysics P-22 IgcseareebNo ratings yet
- Newton S Laws and FrictionDocument7 pagesNewton S Laws and Frictionapi-275290316No ratings yet
- ETE2_Physics_11W_march2024_ms_RevisedDocument25 pagesETE2_Physics_11W_march2024_ms_RevisedanorchiespendiloveNo ratings yet
- 9th Grade Science ExamDocument3 pages9th Grade Science ExamSalve Gregorio AguirreNo ratings yet
- PretestDocument6 pagesPretestEdna Mae CruzNo ratings yet
- MCQ 2Document5 pagesMCQ 2gaya8404No ratings yet
- Test 2 (August) Physics Form 4Document5 pagesTest 2 (August) Physics Form 4Macita KaoruNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Semester One MC Exam ReviewDocument6 pagesAP Physics Semester One MC Exam ReviewJordana BrenesNo ratings yet
- MCAS Forces and Equilibrium PracticeDocument11 pagesMCAS Forces and Equilibrium PracticeSyd MalaxosNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument2 pagesScienceHaier Koppel SkyworthNo ratings yet
- Physics Cambridge Igcse Year 10 Paper 1Document18 pagesPhysics Cambridge Igcse Year 10 Paper 1Adibah AliasNo ratings yet
- STPM 2015 Term 1 Trial SMK Sultan Abdul Hamid QuestionsDocument9 pagesSTPM 2015 Term 1 Trial SMK Sultan Abdul Hamid QuestionsSouseiseki ChromeNo ratings yet
- SJPO General Round SampleDocument19 pagesSJPO General Round SampleToh Qin KaneNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper +1 Physics September 2022Document7 pagesSample Paper +1 Physics September 2022Sukhwinder KumarNo ratings yet
- 2022 WA2 Sci (Phy) 3EDocument13 pages2022 WA2 Sci (Phy) 3EfinNo ratings yet
- SJPO General Round SampleDocument19 pagesSJPO General Round Sampleronghui009No ratings yet
- 1st Assess 2nd Term 2023 Y9Document10 pages1st Assess 2nd Term 2023 Y9Ahsan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapters 5-6 Conceptual QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapters 5-6 Conceptual QuestionsSatish DhanyamrajuNo ratings yet
- Xi-Physics-Half Yearly Exam (Sample Paper) - Set-Ii-2023-24Document5 pagesXi-Physics-Half Yearly Exam (Sample Paper) - Set-Ii-2023-24jaiswalswayam05No ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Kubong, LimbangDocument14 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Kubong, LimbangDuong Han CalebNo ratings yet
- Jadual Trial UpsrDocument1 pageJadual Trial UpsrTamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- English Lower Primary: Unit Akademik Pusat Tuisyen Seri MindaDocument1 pageEnglish Lower Primary: Unit Akademik Pusat Tuisyen Seri MindaTamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- GV JPN 2013Document79 pagesGV JPN 2013Tamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- B. Tamil Modul Cover f3Document1 pageB. Tamil Modul Cover f3Tamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Jawab Semua Soalan - Tunjukkan Langkah-Langkah Penting.: Answer All The Questions - Show Your WorkingDocument6 pagesJawab Semua Soalan - Tunjukkan Langkah-Langkah Penting.: Answer All The Questions - Show Your WorkingTamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- 12 - Reproduction NotesDocument5 pages12 - Reproduction NotesTamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- 5 Waja 2010 f4 Teachers Copy Lines PlanesDocument17 pages5 Waja 2010 f4 Teachers Copy Lines PlanesTamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) Percubaan Terengganu SPM 2012 Sejarah (67448787)Document41 pages(Edu - Joshuatly.com) Percubaan Terengganu SPM 2012 Sejarah (67448787)Tamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- CR LogoDocument1 pageCR LogoTamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Organelle features in cellsDocument5 pagesOrganelle features in cellsTamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- B. Tamil Modul Cover f3Document1 pageB. Tamil Modul Cover f3Tamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Bio Comparison X Compare The Processes That Take Place in X and YDocument8 pagesBio Comparison X Compare The Processes That Take Place in X and YTamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Sastera Tamil NotesDocument1 pageSastera Tamil NotesTamil Arasu0% (1)
- Form 5 (Subject List) : NO. Nama BM BI Maths SC Add. Maths Chemistry Physics Bio P.A Sej B.T B.T (Lit) EcoDocument1 pageForm 5 (Subject List) : NO. Nama BM BI Maths SC Add. Maths Chemistry Physics Bio P.A Sej B.T B.T (Lit) EcoTamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 f4f5Document13 pagesModul 1 f4f5Tamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Statistics Additional MathematicsDocument2 pagesStatistics Additional MathematicsKishen ReddyNo ratings yet
- Biology Presentataion Form 5: Reproduction and GrowthDocument2 pagesBiology Presentataion Form 5: Reproduction and GrowthTamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Transportation ChargesDocument1 pageTransportation ChargesTamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Add MT f4Document1 pageAdd MT f4Tamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- 6days 5nights Phnom PenhDocument3 pages6days 5nights Phnom PenhTamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Pusat Tuisyen Seri Minda Intelek: YEAR 4 - 5 - 6Document1 pagePusat Tuisyen Seri Minda Intelek: YEAR 4 - 5 - 6Tamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- 6 Coordinate Geometry MasDocument17 pages6 Coordinate Geometry MasTamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Sastera Tamil NotesDocument1 pageSastera Tamil NotesTamil Arasu0% (1)
- Add Math Paper 1 Form 5Document22 pagesAdd Math Paper 1 Form 5Tamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Add Math Paper 1 Form 5Document22 pagesAdd Math Paper 1 Form 5Tamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Paper Trading (Megaprint)Document1 pagePaper Trading (Megaprint)Tamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Sastera Tamil NotesDocument1 pageSastera Tamil NotesTamil Arasu0% (1)
- YEAR 4, 5 & 6 Importance Notes RevisonDocument31 pagesYEAR 4, 5 & 6 Importance Notes RevisonTamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Add Math ExaM FORM 5Document9 pagesAdd Math ExaM FORM 5Tamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Methyl Ester Compound of Biodiesel From Industrial Liquid Waste of Crude Palm Oil ProcessingDocument2 pagesCharacterization of Methyl Ester Compound of Biodiesel From Industrial Liquid Waste of Crude Palm Oil ProcessingrahmanNo ratings yet
- Transformer Test ReportDocument2 pagesTransformer Test Reportprum sophearithNo ratings yet
- 8FG D CE049!21!0608 Electrical Wiring DiagramDocument158 pages8FG D CE049!21!0608 Electrical Wiring DiagramDuong Van HoanNo ratings yet
- Continuous Assessment Cover Sheet Faculty of Engineering: Student Statement and SignatureDocument33 pagesContinuous Assessment Cover Sheet Faculty of Engineering: Student Statement and SignatureAriharan KumaranNo ratings yet
- Generator protection systems guideDocument54 pagesGenerator protection systems guideramanaramNo ratings yet
- Solar TrackerDocument111 pagesSolar TrackerAakankshaSharmaNo ratings yet
- Diesel Fuel InjectionDocument5 pagesDiesel Fuel Injectiondamith21No ratings yet
- Unit 7-Fluid MechanicsDocument27 pagesUnit 7-Fluid MechanicsApechRanger100% (1)
- Resonance ExamplesDocument2 pagesResonance ExamplesEyad A. Feilat0% (1)
- BSR307 WSA PresentationDocument12 pagesBSR307 WSA PresentationSafa HaziqNo ratings yet
- VRF VS Chiller: Technical ManagerDocument38 pagesVRF VS Chiller: Technical ManagerJhon Lewis Pino100% (1)
- 2007 iGCSE Physics Written Paper Question PaperDocument28 pages2007 iGCSE Physics Written Paper Question Paperoscar wildeNo ratings yet
- Convection BLDocument77 pagesConvection BLAHMED EL HAMRINo ratings yet
- Benelux PQ Catalogus With New Warranties CA153003ENDocument108 pagesBenelux PQ Catalogus With New Warranties CA153003ENLeonel CarbonettiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Document32 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Mahmood MustafaNo ratings yet
- Wind turbine & propeller efficiency from actuator disk theoryDocument2 pagesWind turbine & propeller efficiency from actuator disk theoryEdo DestradaNo ratings yet
- Fuse Link CatalogueDocument32 pagesFuse Link CatalogueAnonymous dPNmMNcNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent Protection - Time and Current GradingDocument5 pagesOvercurrent Protection - Time and Current Gradingmoses kakwenaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.2 Electrical Energy ManagementDocument61 pagesUnit 4.2 Electrical Energy ManagementJoeb DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Rasmi LED Lighting Company. LED Light, Indoor, Outdoor, Underwater LED LightDocument30 pagesRasmi LED Lighting Company. LED Light, Indoor, Outdoor, Underwater LED LightRasmi Lighting & Energy India Pvt. Ltd100% (1)
- Tutorial Sheets UEE 801-1Document10 pagesTutorial Sheets UEE 801-1Akshita KamthanNo ratings yet
- Edward k12 Mechdesign DataDocument6 pagesEdward k12 Mechdesign Dataapi-254586275No ratings yet
- Wheeled Inverted Pendulum EquationsDocument10 pagesWheeled Inverted Pendulum EquationsMunzir ZafarNo ratings yet
- Jenny Gas Fired Steam Cleaner: Solving Individual Cleaning Problems WorldwideDocument2 pagesJenny Gas Fired Steam Cleaner: Solving Individual Cleaning Problems WorldwidePawan SehrawatNo ratings yet
- Trouble Shooting Electronic System PC200-10MODocument136 pagesTrouble Shooting Electronic System PC200-10MONaughty Vong100% (1)
- D.22!12!042 Final DecisionDocument48 pagesD.22!12!042 Final DecisionRob NikolewskiNo ratings yet
- Centauro 40, Centauro 50 y Taurus 60 Gas TurbineDocument54 pagesCentauro 40, Centauro 50 y Taurus 60 Gas Turbinebarcaza_13No ratings yet
- Examiners' Report Principal Examiner Feedback October 2017Document16 pagesExaminers' Report Principal Examiner Feedback October 2017Newton JohnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To CourseDocument20 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To CourseSudeep AryalNo ratings yet
- Reheat Furnace Efficiency at Laverton Rod MillDocument12 pagesReheat Furnace Efficiency at Laverton Rod MillJJNo ratings yet