Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organization Study
Uploaded by
sharonjohney0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
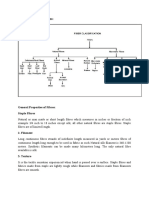
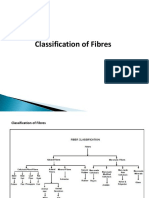
632 views59 pagesYarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibers, suitable for use in the production of textiles, sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, and rope making. Cotton staple is usually between 3 / 8 and 21 / 4 long. The quality of cotton is determined by the length of staple. Long staple means high quality and vice versa.
Original Description:
Original Title
organization study
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentYarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibers, suitable for use in the production of textiles, sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, and rope making. Cotton staple is usually between 3 / 8 and 21 / 4 long. The quality of cotton is determined by the length of staple. Long staple means high quality and vice versa.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
632 views59 pagesOrganization Study
Uploaded by
sharonjohneyYarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibers, suitable for use in the production of textiles, sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, and rope making. Cotton staple is usually between 3 / 8 and 21 / 4 long. The quality of cotton is determined by the length of staple. Long staple means high quality and vice versa.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 59
INTRODUCTION
Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibers, suitable for use in
the production of textiles, sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, and rope
making. Thread is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern
manufactured sewing threads may be finished with wax or other lubricants to withstand the
stresses involved in sewing. Embroidery threads are yarns specifically designed for hand or
machine embroidery.
Cotton Spun Yarn and Cotton Staple(Fiber)
Spun yarn is a kind of yarn made by gathering together a bundle of staple by spinning the
spindles at a very high speed to twist the staples together to form a piece of yarn. The
usual length of the staple of any kind, such as wool, ramie, or any type of synthetic fiber
for spinning should be less than 7. Cotton staple is usually between 3/8 and 2- long.
Cotton staple of less than long is usually not used for quilt, padding or spinning into
yarn because spun yarn of such short staple will have very weak tensile strength which is
not suitable for these fabrics. The quality of cotton is determined by the length of staple.
Long staple means high quality and vice versa.
By quality cotton is basically divided into the following four major groups.
1. Sea Island Cotton: This is the best quality cotton in the world. It has the longest and
finest staple reaching 2- which is the maximum length by nature. It is named so because
this type of cotton is particularly found in South Carolina, Georgia and Florida and many
islands off the coast of these states.
2. Pima Cotton: It is the name given to the cotton of the second longest staple reaching 1-
3/4. It is grown in Peru and Egypt (also called as Peruvian and Egyptian Cotton).
However, it is also grown in the south western U.S.
3. U.S Cotton : generally refers to cotton in United States other than Sea Island cotton .The
staple length varies but may reach 1- .
4. Asian Cotton: This cotton is grown in Asia, Japan, China, Pakistan and India. The staple
length is usually not longer than 1- 1/8
Other than the length of cotton staple which is of great importance, the thickness of it is
important too because only cotton of long and fine staple to make high quality fine fabrics.
The wool thickness varies depending on the kind of wool and origin of it. Synthetic fiber
is made by machine and we can adjust the thickness usually between 0.01 mm and 0.04
mm based on our needs. The staple length of each kind of the above mentioned cotton, can
be substantially shorter than indicated.
Before spinning yarn, cotton of different staple length are sorted into groups such as:
1. Cotton of all long staple length (called as fully combed cotton) are sorted for
making fully combed yarn.
2. Cotton of medium length staple (called as semi combed cotton) for making semi
combed yarn.
3. Cotton of all short staple (called as carded cotton) for making carded yarn.
Fabrics of fully combed yarn would have a smooth silky surface where as fabrics made of
carded yarn would have nubs or dead cotton on the surface, which are usually less color
absorbent. As a result it is coarse and not very soft. Therefore, we usually use combed
yarn to make light weight fabrics such as shirtings etc. but use carded yarn which is
cheaper to make heavy fabrics such as heavy denim canvas. Theoretically, a piece of yarn
can be made of any size, usually from 4 count to 120 count or even heavier than 4 count or
finer than 120 count.1 count yarn means 840 yards to weigh 1 lb. 2 count yarn means
1,680 yards (twice as long as 1 lb), and of 10 count yarn means 8400 yards (10 times as
long) to weigh 1 lb and so on. Therefore split the one count yarn into almost any number
and call it yarn of that count .This is the system used to control the size of the spun yarn of
100% cotton, polyester, wool, acrylic, ramie, rayon or any mixture of them.
Characteristics of textile spun yarn
composed of short staple fibers of definite length
Made from natural cotton, flax or wool staple fibers
Made from natural or man-made filaments which are chopped or cut into short
lengths and referred to as filament staple yarns
Individual fiber length vary
Bigger and wider in diameter than filament fiber yarns
Fuzzy appearance and feel, fiber ends protrude from yarn
Uneven number of fibers throughout
Range from soft, loose construction to hard finished, fine twist yarns
Thick and thin areas highly twisted
Fall apart when untwisted
Dull or flat in appearance
Rough to touch
Natural textural appearance and feel
Bulkier to the feel
Provide good covering power snagging
The Textile and Apparel Supply Chain
Distribution Channel (Export & Domestic Markets)
Garments & Accessories
Process House
Unorganized Segment Composite Mills
Powerlooms Handlooms Knitting
Spinning
Ginning
Man- Made Filament Extraction
Process
Cotton
Wool/Silk Petrochemical
2.3.2 Raw Material Base and Capacity in India
Cotton: Cotton is one of the major raw materials for the Indian textiles industry. India is
the second largest producer of cotton in the world, has the largest cultivated area ofover9
million hectares and accounts for around 20% (4.8 million tons) of globalproduction (over 25
million tons). The performance of the cotton sector has been increasing over the years and
during the cotton season (Aug-Sept) 2007-08, the output recorded was 310 lakh bales (170 kg
each). Even the consumption has been increasing over the years from 195.03 lakh bales in
2004-05 to 245 lakh bale sin 2007-08, by both mill and non -mill sectors. During 2007-08,
India exported 65 lakh bales of cotton. Technology Mission of Cotton (TMC), Mini mission
III, and Mini Mission 1V are some of the developmental measures taken by the Government
in this sector. The cotton sector provides employment to more than 50 million people in
various activities starting from cultivation to trade and processing.
Silk: In the world silk production, India is a distant - second largest producer, with a share
of around 15%, next to China, which holds a share of 82% in the world With a total silk
production of aroundl8, 500 MT in 2006-07, India has the distinction of producing all
varieties of silk, viz; mulberry, en, tasar and muga. Mulberry accounted for nearly 90% of
total silk production in India. The silk sector provides employment to around six million
persons in rural and semi urban areas, and the majority belonging to the economically weaker
sections of the society, including women. With Japanese technology and cooperation, Indian
sericulture industry is able to evolve and popularize Bivoltine silkworm races, which can
yield raw silk, matching the international standards.
Wool: India is the 7th largest producer of raw wool in the world accounting for little
over 2% of the world production. with about 4.2% of the total sheep population. Although
the woolen textile and clothing industry is relatively small compared to the cotton and
man-made fiber based textiles and clothing industry, yet the woolen sector plays an
important role as it is linking the rural sector with the textile manufacturing sector. The
product portfolio is also diverse, ranging from textile intenried.uas to finished textiles.
garments, knitwear, blankets and carpets Indian woolen sector has also a small presence
in manufacture of technical textiles, catering to the civil defense requirements for warm-
clothing Most of the u 001 produced in India (around 85) is of course quality used
mainly in the manufacture of hand-knotted carpets. And 5 a is of apparel grade, and 10%
is of course grade. used mainly for production of blankets.
Jute: India is the largest producer and consumer of raw jute in the world. In the year
2006-07, India imported raw jute worth US S 25 million (over83, 000 tons). During the
period April-February 2007-08, India imported raw jute valued US $31 6million (over
119,000 tons).Export of jute products (including floor coverings) from India was around US
$ 257 million in 2006-07, which has reached to US $ 296milIion, for the period April
February 2007-08. There are 77jute mills in India; 60 in West Bengal, 3 each in Bihar and
Uttar Pradesh, 7 in Andhra Pradesh and one each in Assam, Orissa, Tripura and Chhattisgarh.
Manmade Fibers: The man-made fiber industry comprises fiber and filament yarn
manufacturing units of cellulosic and non-cellulosic origin. The production of man-made
fibers in India has shown an increasing trend in 2007-08, a growth of around 10% over the
previous year. India also imports man-made fibers and synthetic & regenerated fibers for
processing and value addition. In the year 2006-07, India imported man-made fibers valued
US $ 555 million, and synthetic and regenerated fibers worth US $ Q7million. In the year
2007-08, during the period April-February, Indias imports of man-made filament and spun
yarn amounted to US $ 578rnillion, and Indias import of synthetic and regenerated fibers
amounted to US $ 100 million.
Current Scenario
The Indian Textile Industry has an overwhelming presence in the economic life of the
country Apart from providing one of the basic necessities of life; the textiles industry also
plays a vital role through its contribution to industrial output, employment generation, and the
export earnings of the country. The Indian textile industry contributes about 1 4 per cent to
industrial production, 4 per cent to the countries gross domestic product (GDP) and I per cent
to the countrys export earnings. The industry provides direct employment to over 35 million
people and is the second largest provider of employment after agriculture.
The total cloth production is increased by 10.2 percent during September 2010 as compared
to September 2009. The highest growth was observed in the power loom sector (13.2 per
cent), followed by hosiery sector (9 1 per cent). The total cloth production during Apnl-
Septemher2010 has increased by 2 1 per cent compared to the same period of the previous
year. The total textile exports during April July 2010 (provisional) were valued at US $ 7.58
billion as against Us $ 7.21 billion during the corresponding period of the previous
Year. Registering an increase of 5 20 per cent in rupee terms, 1 he share of textile exports in
total expois was 11.04 per cent during April-July 2010. Cotton textiles has registered a owth
of 8.2 per cent during April-September 20 10-lI, while wool, silk and man-made fiber textiles
have registered a growth of 2.2 per cent while textile products including wearing apparel
have registered a growth of 3 per cent.
India has the potential to increase its textile and apparel share in the world trade from the
current level of 4.5 per cent to 8 per cent and reach US$ 80 billion by 2020. Textiles and
apparel industry exports.valued at US$ 20.02 billion (TNR 963.05 billion), contributed about
11.5 per cent to the countrys total exports in 200809. Thus, the growth and all round
development of this industry has a direct bearing on the improvement of the economy of the
nation.
2.4 STATE -SCENARIO
The textile sector comprising of spinning and handloom is the single largest industry in the
state. The textile industry is dominated by handlooms, which enjoy a huge production base
and account for 10 per cent of the country exports. Total sales of the sector accounted for 1.8
per cent of sales by industry in the state in 2010. The handloom industry dominated by
cooperative societies, accounts for 86 per cent of the looms and produces 97 per cent of the
states textiles. Cotton yarn is the most popular product in the state followed by knitted
garments and fabrics such as cotton and wool. The textile-processing complex at
Kanjikode,.the International Apparel Park at Thiruvananthapuram and the Industrial Export
Park at Kochi offer walk- in-and-manufacture environments.
Hardly 20% of the textiles requirement of the state is met by local production. which 3
Coniprises principally of the handloom and khaki sectors, the power loom sector (Which
produces over 75% of the requirement nationally) not having been encouraged Adequately in
Kerala for fear of aggravating the already problematic traditional Sectors. The Government
desires to con-act this policy on the lines of the Government of Indias Textile Policy with
adequate safeguards to prevent massive redundancies in the handloom and khaki sectors.
2.4.1 Profile of Textile Sub-Sectors
Organlied Mill Sector: As of December 31. 2007. there were 1700 conon-Obre and man-
made Oher textiles mills (noii-SS() in the country with a capacity of round 35 milion
spindles, and around 0.5 million rotors. lndas organized mill sector produced about 4000
million kgs of yarn and oer 1 700 million sq. mirs of cloth.
Power looms Sector: The power looms sector provides a wide variety of cloth, both grey as
well as processed fabrics. As on January 3 1, 2008, there was 20.83lakh power looms
distributed in over4.64 lakh units, constituting over0% of the global power loom age. The
sector also contributes around62% to the total cloth production in the country, provides
employment to about 50 lakh people, which constitutes around 14% of the total employment
in the textiles sector and contributes 60% of the fabric, meant for exports.
Handlooms: The handlooms sector has been playing an important role in creating an
awareness of the Indian cultural diversity and fashion, which is unique only to the Indian
textile industry. The handloom cloth production was 6536 million square meters in 2006-07
and dunng2007-08, the production of cloth by handlooms sector was over 7000 million
square meters.
Readymade Garments: The clothing sector is fragmented and predominantly in the small
scale sector. It is estimated that there are over 13,000 apparel units (excluding tailoring units)
in India, majority of which are in the SME sector. The total production of clothing sector was
around 8 billion pieces with a value of Rs. 1 trillion during 2005-06 of which over one fourth
in quantity terms are being exported. The clothing sector is concentrated primarily in 8
clusters ,viz., Tirupur, Ludhiana, Bangalore, Delhi Noida Gurgaon, Mumbai, Kolkata, Jaipur
and Indore. Tirupur, Ludhiana and Kolkata ate major centers for knitwear, while Bangalore,
Delhi/Noida/Gurgaon. Murnbai.Jaipur and Indoreare major centers for woven
clothing.Indias exports of ready-made garments.consisting of cotton, silk, man-made fibres,
wool arid other textile materials showed a marginal increase of 0.8%, from 2005-06 to2006-
07; and it is expected toperform marginally better in the year 2007-08.
Technical Textiles: Textile materials and products, which are used for industrial purposes
and manufactured primarily for their technical performance and functional properties, rather
than for decoration, are called technical textiles. The maximum consumption of technical
textiles is in the USA, Western Europe, China and Japan. These regions account for 65% of
the total consumption of technical textiles in the world. In India, the production of different
items of the technical textile industryha been slowly and steadily increasing All the twelve
items are produced in India in varied quantities. India has also made notable contribution in
the production of textile for strategic applications viz. national security. e.g. parachute
canopy fabric used the carrying human, dropping of supply brake parachute application etc.
that are indigenized and exposed to other countries as well, The market size and potential of
technical textiles was estimated at Rs 19,130 crores in 2003M4, and it is estimated to have
reached Rs 30,000 crores in 2007-08.Being an emerging field, Government of India is
launching a (Rs 1000 crore) Technology Mission on Technical Textiles (TMTT) to ensure
that there are necessary profitable benefits from the enduring investments. To combat the
issue of technology backwardness and infrastructure issues, The Ministry of Textiles,
Government of India, plans to create clusters on technical textiles, so that thenecessary
textiles may be produced with adequate technology, thereby making the products
technologically competitive too.
COMPANY PROFILE
NAME & LOCATION
GTN TEXTILES LTD is incorporated on August 2nd 1962 at Aluva, near Cochin in Kerala
state and commissioned in 1964. The company has its registered office Erumathala near
Aluva in Ernakulum district. The company was started for the manufacture of cotton yarn
with a capacity of 12000 spindles. Company has got roots in the textile business for almost
100 years. GT Narayana Swami was the founder of GTN TEXTILES LTD. In 1966, the
company was taken over by the present management of the company. The founders were
from the raw cotton and yarn trading family business. They entered into manufacturing of
cotton in 1965 by starting GTN TEXTILES LTD in the small town of Aluva, Kerala, in the
southern part of India.
The GTN group which started with a single unit at Aluva has gradually grown into multi
location multi-unittextile group with a spindlage nearing, 1,60.000 GTN Textiles Ltd. Aluva
unit has an installed capacity around 50,000 spindles. GTN Textiles ltd is an ISO
s
PRODUCTS & SERVI CES PROFI LE
GTN Textiles is one the largest cotton yarn exporting organization from
india and is currently exporting at most 100% of its total production to countries like Japam,
Italy, South korea. Taiwan, Indonesia, Singapore, Malaysia and West Germany. The
company pioneered exports of cotton yarn to Japan and Italy where it has maintained its
leadership.
GTNs Product Range
GTN group manufacture 100% cotton yarn/ knitted fabrics:
Yarn of count 30s to 140s
Two for one twisted & Ring double
Knitting & Weaving yarn
Gassed yarn
Gassed and processed yarn
Knitted garments
Activities
Manufacturer, Exporters & Importers of Cotton Yarn, Knitted Fabric and Garments.
Import
Egypt, United States, Austria, Greece
Export
Japan, Italy, South Korea, China, Hong Kong, Austria, Belgium, Israel, Australia, Taiwan,
Malaysia, Mauritius, Turkey
OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
The objectives of the study are divided into two.
Primary Objective
The primary objective of the study is to know the organization structure and the functions of
different department.
Secondary Objectives
To know about the textile industry
To study the structure of the company
The functions of various department
To analyze the strengths weaknesses opportunities and threates of the company
To provide suitable suggestions of the effective functioning of the company
To know the interaction between different departments.
METHODOLOGY OF THE STUDY
Collection of Data
1. Area of Data Collection
The area of data collection is from GTN Textile Ltd Aluva.
2. Source of Data
The data can be classified as:
a. Primary data
For this study the primary data were collected from different departments, by direct
interview. Primary data are those which are collected for the first time. Primary data
collected through discussions and interviews with management personnels of varioys
departments. We collect primary data during the course of doing experimental
research but in case we do research of the descriptive and perform surveys whether
sample surveys or census surveys.
b. Secondary Data
For this study secondary data were collected from published reports of the company
magazines and websites.
Period of study
This study in GTN Textiles Ltd manufacturing company was done from 5
th
August to 10
tth
September. The data was mainly collected through the primary source by interviewing or
having a conversation with the executives and the workers of the organization.
DEPARTMENTAL PROFILE
1. Raw Material Department
2. Quality Assurance Department
3. Production Department
4. Stores Department
5. Maintenance Department
6. Management Information Systems Department
7. Finance Department
8. HR Department
9. Sales, Export/ Marketing Department
10. Security Department
11. Research and Department
8.1 RAW MATERIAL DEPARTMENT
Introduction
Cotton is the sole raw material for the manufacture of cotton yarns. Since it is a
seasonal product and is available only during the months from October- March, the required
quality is purchased and stocked for the production of cotton yarn. The fiber processors seek
to acquire the highest quality at the lowest price, and attempt to meet processing requirements
by blending bales with different average fiber properties.
Blends that fail to meet processing specification show marked increase in processing
distribution and product defect that cut into the profits of the yarn and textile manufacture.
The cotton picked folds are ginned and taken to the factory site from the ginning
centers through agents. The purchase is done on a massive scale, before which the material
undergoes a series of tests. The basic sample considered should satisfy three parameters viz.,
sample length, strength and value. Once the sample clears this high volume instrument
testing, the company goes for bulk purchase on lot basis. These samples again undergo the
quality check which once cleared for delivery. The approval lot again undergoes HVI tests.
Once cleared these lots are accepted for manufacturing.
Functions:-
Verification of properties
Finding suppliers
Import of cotton
Purchase of raw materials
Waste management
Procedures
1. Verification of Properties
Successful processing of cotton depends on appropriate management during and after
harvest of those highly variable fiber properties that have been shown to affect finished
product quality manufacturing efficiency. If fiber-blending specific end uses and profitability,
production managers in textile mills need accurate and effective descriptive and predicative
quantitative measures of both the means and ranges of these highly variable fiber properties.
The components of cotton fiber quality are usually defined as those properties
reported for every bale which currently include length, length uniformly index, strength,
micron ire, and yellowness (+b), and trash content, all quantified by the High Volume
Instrument Line (HVI).
2. Finding Suppliers
Cotton is produced from different cotton producing states of India i.e., Gujarat,
Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Punjab, Haryana, etc. The various
varieties of Indian cotton are J34, S6-S4, Y-1, JAYADHAR, MECH, BRAHMA, DCH,
DIGVIJAY, H-4 etc. A part from these American supima giza42, Giza70, Giza77, Giza76,
Giza85, and Giza80 which are imported from America, Egypt and Sudan are used for
processing cotton yarns.
Earlier the company used to depend solely on Indian cotton, but the quality was not
up to the mark as it was contaminated with foreign particles. Later imported cotton was used
and now 90% of American cotton is used.
3. Import of Cotton
The company purchase more than 40% cotton raw materials from foreign countries
like America and Egypt. The main reason or import is better quality and productivity. Raw
material used for production is Suvin. One of the finest extra-long staple cottons available in
the world. Suvin cotton is superior in all aspects like fineness Staple length, silkiness, and
luster. The exclusive cotton of India origin is a luxury and its products are considered
premium and niche worldwide.
a) Supima
It is a superior, extra-long staple variety of cotton growth in America. Yarns produced
from Supima cotton are used to produce softer and more lustrous fabrics. Supimarepresent
highest quality in cotton yarns. GTN is the first spinning company in India to obtain a
Supima trademark license.
b) Egypt Giza
Giza cotton is a true mark of excellence with extremely superior quality in the extra-
long staple and long staple variety. These varieties are also renowned for their excellent
fitness and feel.
c) Indian Cotton
GTN use high quality verity of MCUS and Shanker cotton known for their superiority
in terms of fitness and goodness.
d) Australian Cotton
Medium staple contamination free, varieties of cotton and one of the best grades of
raw materials from among the best suppliers.
e) American sjv Acala
GTN was the first Indian spinner to be given a cotton USA license. Medium staple
contamination free, varieties of cotton and one of the best grades of raw materials from
among the best suppliers.
4. Purchase of Raw Materials
The purchase is based on three production plan made the departments according to the
forecasted requirements for production. The production plan does not allow shortage as it can
lead to heavy loss. Random samples of purchased cotton, is tested in the quality lab for fiber
quality specification. Test for fibre fitness is conducted as spinning larger number of fitness
fibre together results in stronger, more uniform yarn than if they hard be made up of fewer,
thicker fibers. The 4 ultimate acceptance tests for fibre colour as well as for finished yarns
and fabrics is the human eye. Therefore instrumental colour measurement must be correlated
closely with visual judgment.
5. Waste Management
Long fibres are best suited for yarn production. Short fibre content is defined as the
percentage of fiber less than 12.7mm the short fibers obtained as waste from processing is
packed and sold.
Key factors for success
Procurement of the right quality at right time.
Ability to procure large quantum of raw material and keep long time stock which
ensures consistent quality.
The GTN has an associated concern trading in cotton for the last 40 years which gives
it added advantage.
Organization Structure- Raw Material Department
8.2 QUALITY ASSURANCE DEPARTMENT
Introduction
This department is responsible for the quality assurance of raw materials, quality
assurance in process and quality of finished goods. The department is also responsible for
implementation of research and development quality improvement activities in the
organization and also tries to establish and maintain procedure for inspection, calibration of
measuring and testing equipment.
The department is situated inside the factory with state- of art laboratory for testing
the quality of cotton yarn at various stages of production and the finished goods. Some of the
machines used in the quality assurance department and USER Spin Lab excusing these
machines, testing is done for the raw materials and finished goods. GTN Textiles Ltd., Aluva
Officer
MANAGER
Senior Officer
Supervisors
Workers Workers
Supervisors
is ISO 9002 for quality assures in production, installation and servicing. The company has a
quality manual that makes commitments to the customers that they shall comply with all their
requirements for improvement in all the activities to serve them.
Quality assurance department is the department where the quality is checked and there
are various parameters that affect the quality of cotton fiber, some of them are length,
evenness, fiber strength. These parameters are tested in the quality assurance lab.
Quality Policy
GTN textiles would ensure manufacturing and marketing of cotton yarn by complying
with:
GTN Textiles ltd. Would achieve the highest level of customer satisfaction by
meeting their stated and perceived requirements manufacturing consistency and
timely delivery.
GTN 41 endeavours continual up gradation of product quality and technology
supported by R &D efforts in a cost effective manner.
To meet changing global demands and stay headed in competition GTN would adapt/
innovate methods in its manufacturing activities.
GTN would inculcate a sense of quality awareness at all levels by using appropriate
training and motivation techniques.
GTN would aim at preserving the environmental conditions y adopting eco- friendly
measures in its manufacturing and other activities.
The man activities of QAD are:
Raw material selection and stock
Bale management
Online process monitoring of production and quality.
100% zero/ quantum clearer
UV lamp testing
Duties and responsibilities
Senior Manager: Takes care of the overall administration of the quality assurance
department.
s.
Organization Structure- Quality Assurance Department
Senior Manger
Manager
Assistant Manager
Supervisors
Assistant Manager
Supervisors
Operators
Operators
8.3 PRODUCTION DEPARTMENT
Introduction
Production department is the most important part of this organization. Here
production is carried out in required quality at minimum cost. The production department in
coordination with the marketing divisions does managing and controlling of the production
process. Customer requirement in terms of quality, quantity, delivery, packaging are obtained
an analyzed as per the sales contract from the export division.
Production capacity
GTN have 165000 Spindles Capacity, consisting of 30000 Compact spindles and
135000 Ring Spinning in addition process like twisting Gassing, Dye package winding,
Knitting etc. in- house in order to server different customers requirements effectively.
Product
The reason for success in this competitive environment I that all the products are
customized and are produced on a made to order bases
GTNs Product Range
GTN group manufacture 100% cotton yarn/ knitted fabrics:
Yarn of count 30s to 140s
Two for one twisted & Ring double
Knitting & Weaving yarn
Gassed yarn
Gassed and processed knitted yarn
Knitted garments
Main counts
Over 90% of products are fine and superfine 100% yarns carded and combed with
counts ranging from 30s to 140s, both single and multi-fold, as well as gassed, suitable for
knitting and weaving.
Flow chart of production process
Production process
The production process is mainly going through five stages:
1) Bale opening: In this process cotton are opened, foreign matters are segregated and
processed in the bale- opening machine. From this process, cotton is subject to
maximum.
2) Mixing: Here different varieties of cotton are blended in define proportion. The
objective of blending different varieties of cotton is to spin the required yarn
economically. Unimix is the machine that is used to mix the cotton and to convert in
to chute.
Stack mixing is the best way of doing the mixing compared to using automatic bale
openers which picks up the material from 40-70 bales depending on the length of the
machine and bale size, provided stack mixing is done perfectly. Improper stack
Packaging
Bale Opening Mixing Blow Room
Drawing Combing Carding
Ring Spinning Automatic Cone
Winding
Doubling
Conditional Yarn Singeing Waxing
mixing will lead to shade variation problem, stack mixing with bale opener takes care
of short term blending and two mixers in series take care of long term blending.
3) Blow Room: In this, the mixed cotton is opened, cleaned and made in to a continuous
sheet in the wound from. This product is called Blow Room Lap.
4) Carding: In carding operation, the Blow Room Lap material is cleaned, fibers are
made parallel and then wastes are extracted from fibers and assemble in to a
continuous stand. This stand is called card Sliver. This silver are coiled and stored in
cans. There are two rules of carding.
The fibre must enter the carding machine, be efficiently carded and taken from it in as
little time as possible.
The fiber must be under supervision from entry to exit.
The purpose of carding:-
To open the flocks individual fibers.
Cleaning or elimination of impurities.
Elimination of dust.
Elimination of short fibers
Fiber blending
Fiber orientation or alignment
Sliver formation
5) Combing: The carded sliver is then prepared for combing in Sliver Lap and Ribbon
Lap machines. The product thus prepared is called Ribbon Lap. This Ribbon Lap are
then fed to comber machine. In comber, the short fibers and minute impurities are
removed and the fibers are made parallel and assembled in fro of sliver.
6) Drawing: In drawing process, s definite number of combed sliver is doubled and
drawn together to make the resulting sliver more even and parallelized fibers. The
sliver is stored in cans in coiled form.
7) Simplex: The object of simples or speed frame process is to attenuate the drawn sliver
into a finer strand, twist and wind it on a plastic tube this product is called Roving.
8) Spinning: In ring spinning process the roving is attenuated with the help of drafting
system and the drafted fibers strand is twisted and wound on a tube. The twisting and
winding operations are performed with the help of Ring Traveler and spindle. The
yarn count s also set at this stage. The arrangement is being progress to sin the latest
form of compact yarn by the employment of Elite and Com4 machines.
9) Automatic Cone Winding: In the automatic cone winding process, yarn from the
ring frame cops passed through electronic yarn cleaners to detect and remove
objectionable fault in the yarn. The yarn ends are joined with the splicing provision. A
definite length of yarn will be wounded on ones. Waxing can also be done in this
process.
10) Doubling: In doubling process, two or more single yarns are twisted together. This
consists of two processors- assembly winding and twisting. In assembly winding the
required number of single yarns of definite length is wound in parallel to a single
package. Twisting may be carried out either with Ring Doubling machine or two- for
one twister.
11) Conventional winding: In conventional winding a definite length yarn is wounded on
ones. During winding yarn is passed through electronic yarn cleaner to detect and
remove objectionable yarn fault waxing also can be done in this process.
12) Singeing: In singeing process yarn is passed through a flame at high speed to remove
the protruding fibres. The object of singeing is to make the yarn lustrous, which can
be used for some special end uses. The flame and speed of the should be constant as
ay change can cause damage to the yarn.
13) Conditional yarn: Apart from gassed yarn conditional yarn is also produced.
According to the customer requirement the yarn is conditioned in a conditioning
machine. The yarn conditioned for half n hour in specific temperature and moisture.
The time limit is imported as over conditioning may lead to absorption of moisture by
the yarn and hence may result in poor quality.
14) Precision Winding:- In this process yarn is passed through a special type of tension
assembly to get the package more softly so as to get the dye package directly. The
softness can be increased or decreased as per the requirement.
Organization structure- Production Department
8.4STORES DEPARTMENT
Introduction
Stores department is the department whose main service is maintaining several
types of inventories. Also it functions as maintenance of materials, spare parts and general
store as required. Purchase is made with reputed companies who offer good quality of
products at reasonable cost.
Functions:
Storing of purchased raw material
Assistant
Manager
Production -1
Officers
Supervisors
Workers
Senior Manager
Manager
Assistant
Manager
Production -2
Assistant
Manager
Production -3
Assistant
Manager
Production -4
Officers Officers Officers
Supervisors Supervisors Supervisors
Workers
Workers
Workers
Issuing reorder level
Material inspection
Listing and selling of scrap
Procedure
Storing of raw material
It is the duty of the stores department to store the purchased raw material. All the
purchase are made online. SAP is the software used for this purpose. The purchases are made
through quotations for a period of six months. Quotations are received from dealers who
provide maximum discount.
Mainly 3 type of material are purchased and stored.
Mill stores: this inculds spear parts, bearings, consumable goods etc.
Packing goods: These include material which is used for packing.
Utility item: This include engineering items, electric items etc.
All purchases are made within the limit of 8-12 days and on the same day itself it is fed into
the computer.
Issuing Re Order Level
All the purchase and issue of raw materials are entered in the computer and computer will
show the re order level.
First release
The requirement of each department is listed out by the respective department staff.
This list is then sent to the department head.
Second release
The list prepared b the department is approved by the department head and then sent
to the vice- chairman.
Order Placement
After the second release, the requirement list is sent to the stores department, where
the order is placed. The description and quality of the product is specified in the order
form.
Order release
The store manager places the order with the suppliers and is knows as order release.
The re order time and lead time is estimated with the help of past record. Tax free
goods are specified
Order acceptance
The order acceptance is the receipt of goods ordered. The quality of the item is
checked by the stores department.
Material Inspection
The quality of the items delivered by the suppliers is inspected by the investigation in the
quality assurance department. Then the materaisl are issued to the respective departments.
The purchase entry is also made during this time. The items received by the stores department
are stocked in the stores.
Monthly reports are generated. Consumption reports are generated to find out the
consumption rate. The reports are alsso used to tally the physical stock with consumption.
Listing and selling of scrap
The scrap materials are listed out once in every six months. A call for quotation is made to
find the best price that can be obtained for scarp. ABC analysis is used for regular items,
which directly affect the quality like packaging materials and machinery spares.
Organization structure- stores Department
Stores Manager
Supervisor
Worker
8.5 MAINTENANCE DEPARTMENT
Introduction
GTN being a manufacturing concern, the number of equipment and machines are
involved directly with production process and hence the effective functioning of maintenance
department is inevitable.
The objective of maintenance department includes minimizing long run
maintenance cost, minimizing breakdowns to keep operation stable, providing reliable
conditions for equipment to perform at specified technical conditions through service, repairs
replacement and modifications. They conduct the maintenance program at tervals intended to
reduce the like hood of equipment conditions falling below a required level of acceptability
and also modernization works are done by the department.
In order to assist maintenance department, computer are provided with the details
and reminder dates of the maintenance of a machine in a department and details of its
services and replacement. All the machines are cleaned periodically and their functioning is
checked in order to assure that the machines are working smoothly with no troubles. Other
than daily checks, weekly, monthly or yearly checks are carried out. A time interval is set for
all machines. A monthly schedule is prepared to see which machine is to be attended first and
then at the time the concerned foreman will attend the machine.
GTN Textiles being a manufacture of fine and super fine quality cotton threads,
modernization has become the inevitable part of the production. Replacement of machines
and machine parts also is done by this department. Good quality machines are selected
according to the count rate.
Functions:
Minimizing maintenance cost
Minimizing breakdowns of machines.
Replacement and modification of machine.
Replacement and modification of machines
Providing safer working condition.
Ensure machine are working properly
The maintenance operations are divided into two.
Preventive Maintenance
The manger and other concerned officers will fix the life of all machines spare
parts and will replace the particular spare part at the end of the period. All the machines
used in the company 9Indian as well as imported ones) are under the annual maintenance
contract. So the serious mechanical problems are rectified by the company, who supplied
the machines.
Breakdown maintenance
If any faults occur at any part of the machine, the assigned person from the
maintenance department will check out the problem repair the part.
Levels of maintenance
Mechanical Maintenance
To ensure the protection is carried out in a controlled condition.
Electrical maintenance
Ensure that process equipment or machinery are maintained and fit for the purpose.
Organization Structure- Maintenance Department
8.6 IT MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM DEPARTMENT
Introduction
About 90% of the organization is computerized. The main network is the SAP/
ERP implemented within the raw material finance, export and stores department. Other
applications like Payroll software in Fox Pro and production Control in Visual Basic are
implemented in the organization.
Senior Manager
Manager
Assistant Manager
(Mechanical
Maintenance)
Assistant Manager
(Mechanical
Maintenance)
Supervisors Supervisors
Operators Operators
Functions:
Maintenance: The system has to be maintained and updated according to the increasing
needs of the organization.
Process Monitoring: The production process is completely monitored by the department.
The Payroll Software is handled by the personnel department. The wage and salary
calculation is done using this software. The organization provided intranet facilities for ease
of access of information. The intranet is accessible by the top level management. The main
server is at Cochin through which the transactions are communicated. The information
regarding the transactions are shared and passed to the organization through routers.
Organization Structure: Management Information System Department
8.7FINANCE DEPARTMENT
Introduction
This department has to raise necessary funds, mange them, prepare finance budgets
and administer its working capital. The department functions on public issue of capital,
maintains records for helping the finance manager access the appropriateness of capital
structure. It provides data for the preparation of budget and various financial statements. The
accounting function of the department includes the preparation of trial balance on a yearly
basis. They also prepare managerial reports regarding expenditure of travelling, postal
telephone and courier transactions.
Manager
System Analyst System
Administrator
Programmers
Functions of Finance Department
The company maintains a clear and perfect accounting system. The main activity
of the finance department is working capital management. Preparation of fund flow
statement, cash flow statement, balance sheet, profit and loss accounts are also the activities
of finance department. Secretarial work relating to board comes under the finance
department. Most the activities carried out by the finance department are preparing to long
term and short term requirement of the operation, closing purchase bill, maintaining the
account contractors, subcontractors, income tax, deduction, salary discrepancy, dealing with
the financial institutions with import and exports.
Maintaining Books of Accounts like,
a. Purchase Records
The finance department of the company keeps the account of raw material and
accounting entries are made in the books of accounts of the company. The department
analyses the details of purchase afterwards.
b. Salary accounts
The main function of the department is preparation and disbursement of salary of
officers, office staff and workers. The department keeps salary register pertaining to each of
the above said person and facilities charges in salary due to granting of annul increment and
deduction from the salary. The department is maintaining sub ledgers for deduction made in
the salary such as PF, insurance premium advance and income tax. Another important
function is computation of income tax.
c. Sales and Revenue Accounts
The department functions on calculation of paying sales tax and central excise duty
to the concerned government every year, provision for current tax is made on the basis
estimated taxable income for the current accounting year in accordance with income tax
1961.
d. Cash and bank accounts
The department does all the matters relating to the day to day cash transactions.
They receive and make payment for purchase and sales.
e. Cost sheet
Annual budget and cost sheet is prepared at the outset of every year and the
company is following Process costing method. It helps the company to ascertain the cost of a
product at each stage of the production, i.e., cost at each process through which the raw
cotton passes through for the production of fine years. The total incurred at each stage of
production is carried out to ascertain the final cost. The pricing policy adopted by GTN
textiles is Cost plus- pricing and hence a certain percentage of the profit is added to the final
cost incurred.
f. Depreciation
Department has been provided at the rates and in the manner prescribed in
Schedule XIV to the Companies act 1956. Plant and machinery and electrical installation
have been, on technical assessment, considered as continuous process.
Accounting system
The financial statements are prepared on historical cost and convention.
All fixed assets are states at cot adjusted by revaluation in case of certain land,
building, land and machinery and electrical installation, less accumulated
depreciation.
Long term investments are stated at cost less provision
Values of fixed assets are devalued by technicians
Valuation of investment is done at cost.
Depreciation is done as per the companys act 1956.
Management of Payables and Receivables:
As 90% of the sales are as exports, it takes place with the support of letter of credit
or bank guarantee. Therefore, management of payables and receivables has not been a
problem for the company. In this total amount, 50% of the total amount is written off as bad
depts. Likewise 80% of the raw cotton purchased is imported. So L/C is made us here too.
Local purchase is made by the company for a credit period of 30 to 90 days. The company
claims to have an efficient management of both payables as well as receivables.
Accounting Policies:
Basis of presentation:
The financial statements have been prepared to comply with the mandatory
Accounting Standards issued by the Institute of Charted Accountants of India and the
relevant provisions of the Companys Act 1956. The financial statements have been prepared
under the historical cost convention, 0 the basis of a going concern, on accrual basis.
Use of Estimates:
The preparation of financial statements requires Management to make estimates and
assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of
contingent liabilities on the de of financial statements and reported amounts of revenue and
expense of that year. Actual result could differ from these estimates. Any revision accounting
estimates is recognized prospectively in current and future periods.
Fixed assets:
i. All fixed assets are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Expenditure during
construction period in respect of new project/ expansion is allotted to the respective
fixed assets on their being ready for commercial use. Also refer Policy G and J below.
ii. Impairment of assets the company assesses at each Balance sheet data whether there is
any indication that any asset may be impaired. If any such indication exists, the
carrying value of such assets is reduced to recoverable amount and the impairment
loss is charged to Profit and Loss account. If at the Balance sheet data there is any
deduction thats previously assessed impairment loss on longer exists, then such loss
is reversed and the asset is restated to that effect.
Investments:
Long term investments are stated at cost les provision, if any, for other than temporary
diminution in the value of investments.
Inventories:
Inventories are valued at lower of cost or net reliable value. Cost of Raw Materials is
computed by using Specific identification method and for other inventories Weighted
Average method. The cost includes costs of purchase, cost of convention and other costs
incurred in bringing the inventories to their present location and condition.
Sales:
Sales are recognized as and when risks and rewards of ownership are passed on to the
buyer and ultimate realization of price is reasonable certain. Export sales are inclusive of
deemed exports while local sales a re net of sales Tax/ VAT.
Borrowing Cost:
Borrowing Cost attributable to acquisition and construction of qualifying assets are
capitalized as a part of the cost of such asset up to the date when such asset is ready for its
intended use. Other borrowing costs are charged to profit and Loss Account.
Employee benefit:
Short Term employee benefits including accrued liability for leave Encashment
(other than termination benefits) which are payable within 12 months after the end of the
period in which the employee render service are paid/ provided during the year as per the
Rules of the company.
Foreign currency transactions:
Transactions in foreign currency are recorded at the rate of exchange in force at the
date of transactions. Foreign currency assets and liabilities are stated at the rate of exchange
prevailing at the year- end and resultant gains/ losses are recognized over the life of the
contacts. In accordance, with the AS-11 (revised 2003) the exchange difference arising on the
contacts/ transactions enters into on or after 01-04-2004 on the settlement of monetary items
or on reporting monetary items at rates different from those at which they were initially
recorded during the period, or reported in previous financial statements, is recognized as
income or expenses in the period in which they arise.
Taxation:
Income tax expense comprises current tax and fringe benefit tax (i.e. amount of tax
for the period determined in accordance with the Income Tax Law) and deferred tax charge or
credit reflecting the tax effects of timing difference between accounting income and taxable
income for the year). Deferred tax charge or credit and the corresponding deferred tax
liabilities or assets are recognized using the tax rates that have been enacted or substantively
enacted by the balance sheet date. Deferred tax assets are recognized only if there is a virtual
certainly of realization of such assets. Deferred tax assets are reviewedat each balance sheet
date and written up to reflect the amount that is reasonably I virtually certain as the case may
be to be realized. Tax credit is recognized in respect of Minimum Alternative Tax (MAT) as
per the provisions of section IISJAA of the Income Tax Act, 1961 based on evidence that the
company will pay normal income tax within the statutory time frame and is reviewed at each
balance sheet date.
Costing and pricing:
As GTN textiles Limited is a manufacturing concern and involves a large number of
processes, process costing method is followed. It helps the company ascertain the cost of a
product at each stage of production, i.e. cost at each process through which the row cotton
passes through for the production of fine yarn. The total cost incurred at the each stage of
production is carried out to ascertain the final cost. The pricing method adopted by the GTN
Textile is cost- plus- pricing and hence a certain percentage of the profit is added to the final
cost incurred.
Budget and budgetary control:
Budgets are prepared by this department on a quarterly basis and based in this the
annual budgets are prepared. The budgets can be sales budget, production budget, expenses
budget and the total budget. At the month end, a comparison is made between budgets and
actual right from the raw cotton procurement till the last process. The reasons for variations
(if any) will be found out.
Organization structure- finance Department
8.8 HUMAN RESOURCE DEPARTMENT
Introduction
Personnel Department plays a crucial role in the management of the company. The
department try to create and utilize an able and motivated workforce to accomplish the
organizational goal, and try to satisfy individual and group needs by providing adequate and
equitable wages and incentives, employee, benefit and social security and measures for
challenging work prestige, recognition security, status etc.
The personal department is responsible for recruitment, selection, placemen training
performance, appraisal, promotion and separation. This department is headed by DGM
Manager
Assistant Manager
Accounting
Assistant Manager
Taxation
Assistant
Manager
Costing
Officers Officers Officers
(industrial relations). He is in charge of implementation systematic recruitment procedures
for providing facility for the overall development and motivation of all the employees. He is
also in charge of ensuring safety aspect in the mill and maintaining cordials industrial relation
with the workers. The categories of workers employees in GTN are permanent and
temporary. The recruitment, employment, leave disciplinary actions, retirement etc. are done
as per the standing order. This department is also responsible for training, performance
appraisal compensation and separation.
Work staffs
The company works round the clock in three shifts
1
st
shift : 8 am- 4 pm
2
nd
shift : 4pm- 12 pm
3
rd
shift : 12pm- 8am
Staff shift : 9 am- 5.30 pm
Employees : 721
Staff : 109
For each shift there would be 3 supervisors: 1 shift in charge and supervisors.
Functions of personal department
Recruitment and selection
Induction training procedure
Training
Evaluation
Performance appraisal
Wage and salary Administration
Recruitment and selection
GTN textile Ltd recruits its manpower resources through recruitment agencies and
advertisement in leading newspapers. The other sources are form reference service and
relatives of employees and from apprentices. Recruitment is done b the G.M. of personnel
and industrial Relation Department. At GTN textile selection is done through tests and
interview.
Induction Training Procedure
Technical and non technical fresh recruits are given general exposure to the overall
activities of the organization during initial days. There after they are given in depth training
in assigned areas of work followed by on the job training.
Work men fresh recruits are given general exposure to the overall activities of the
organization. They are on the job training under the supervision of the jobber/ mastery,
guided by supervisors or deputy Manger (training).
Training
Training is given to all workers for developing their skills and proficiency in work.
The probationary period for also workers and office staff is six months. A formal induction
training program is provided for fresh recruits as per the program given in the induction
training manual. Also training is given to each worker when a new machine is installed
respective to their department.
Introduction Program
Induction Report
Training
On the
Job
Off the
Job
Evaluation
On completion of training an evaluation regarding effectiveness of training received is
sought from the department concerned.
Performance Appraisal
Performance appraisal is systematic evaluation of the capacity for development. It is
usually done by the supervisors at GTN. Check list method is used for personnel evaluation.
It helps the superior or the manager to judge the honesty, sincerity, loyalty and responsibility
of the employees. It is usually done in the duration of six months. The performance of each of
the workers, their strengths, merits, weakness etc. is discussed in detail with them and these
are considered for their promotion. However at the managerial level, the through maintains
the performance appraisal system, does not discuss with the officers. It is not carried out in a
transparent manner.
Wage and Salary Administration
GTN follows time rate wage system. For this purpose the attendance records are
maintained strictly also there is card punching system for recording entry and exit of the
employees and workers. The remuneration for the work of service rented by the employees is
paid in the form of salaries, wages or fringe benefit. Wages include both monetary benefits
and non monetary benefits. The employees pay/ wage includes basic pay, DT, TA, HRA,
LTC, PF and ESI for 26 days. A certain percentage of annual earning is distributed as bonus/
of the total pay 12 % is for PF and 1.75% is for ESI. Over time work is also paid at the rate of
1.75 times that of a normal days pay. There is no PF and ESI for over time and holiday
work.
Employee welfare schemes
The company provides all the statutory welfare measure as per the factorys act 1948.
There are general measures and the company also administers activities that come under non-
statutory items.
Employee co-operative society
There is an employee co-operative consumer stores to cater the requirement of
provisions stationary and textile articles. They also arrange for supple of household
appliances like TV, Two wheeler, sewing machines et coin installment basis
Employee credit society
GTN Textile employees credit society advanced loans to the employees ranging from
Rs. 2000/- to 25000/- for various purposes on a reduced rate of interest. They also run
recurring deposit schemes for the employees.
Silver Jubilee educational Assistance
Under the sliver jubilee educational assistance scheme, employees can avail benefits
up to 2 children towards their educational expenses, it ranges form Rs. 600/- up to VII std.
student, RS. 2500/- to medical/ engineering students per year
Marriage assistance
Interest free loans of Rs. 10000/- are being given to the employees in the event of
marriage of their daughter.
Insurance linked gratuity scheme
The company has adopted insurance liked gratuity scheme for the benefit of the
employees. Under the scheme, in case of death of an employee, his dependents will be
eligible to receive full gratuity for the total calculated period of service including the
balance of years of service after death.
Holidays
Each employee can avail 13 paid holidays in a calculating year. List of holidays will
be notified each year.
Canteen
A subsidized canteen managed by the employee representatives is taken care of
catering needs of the employees. Meals, snacks, coffee/ tea are available in the canteen
during the prescribed timings.
Quality Circles
Quality circle activities are being organized in Aluva Unit with the effective
participation of the employees.
Safety
Safety, housekeeping activities are arrived out on a continuous basis. A part from the
statutory compliance; a safety committee is effectively working.
GTN textiles employee welfare fund
There is fund constituted for the welfare of the employees. There are different benefits
like death benefit, retirement benefit, disablement benefit, loans assistance, etc. contemplated
under the scheme
Assistance for the handicapped children
There is a scheme to assist the handicapped children of employees; this includes
supply of artificial limbs, aids or any other assistance to such cases.
Blood Donor Group
Blood Group of almost all employees has been ascertained. In case of emergency,
employees will come forward to donate blood.
Suggestion scheme
The company conducts suggestion scheme in the areas of productivity, housekeeping,
quality, safety, etc. employees who submit suggestions are being properly rewarded
Attendance award
To recognize the employees to attend word regularly special prices given every year.
Membership in professional bodies
The company has membership in various professional bodies viz. SIMA, ATIRA,
SASMIRA, SITRA, Kerala state productivity Council Etc.
Subscription to News Paper and Journals
Various News papers and journals are being subscribed for the benefit of employees
Anti addiction program
The company provides all assistance to employees who wish to come out form their
addiction habit.
Worker Education through worker
In association with central board of workers education, employees are given classes in
batches for a period of 2-3 months on various subjects. There are trained worker teacher who
take such classes.
Standing orders
There is an approved standing order, which regulates the conditions of employment
Excursion tours
Excursion tours are arranged regularly for the staff member and for the participation
the workers education classes
Twenty years service award
As a token of appreciation for the continuous service put in, the employees are given
memento after completion of 20 years of service.
Family planning program
Encouragement like special level of finance incentive is given to employees in the field of
family planning activities.
Conveyance facility
Subsidized conveyance facility is provided between Alwaye and factory for the
second and third shifts.
Social Activities
The company take care of the need of the local people with due consideration. This
includes construction of building ,waiting shed ,donation to various charitable organization
etc. Steps are taken for pollution control.
First Aid Facilities
The company has direct touch towards he nearby hospital the company can use the
service of the hospital in case of emergence.
Welfare office
Welfare activities are under the supervision of the welfare officer MR. Wilson Joseph
appointed by the company.
Health and safety
There is a safety committee for looking after the safety of the workers drinking water
drinking water facilities are priced different spots inside the company.
Employee state insurance scheme
ESI scheme is unique multidimensional self financing social security scheme in which
every contributor is a benefactor and beneficiary. This integrated scheme of health insurance
prides comprehensive medical cover and cash benefit in contingencies of sickness, maternity,
disablement and health.
Trade unions
There are four registered and one unregistered union in the organization
INTUC (Alwaye Textiles Employee Association)
AITUC (Alwaye Textiles Workers Union)
CITU (AlwayeMekhala District Textiles Labour Union)
BMS (BharathiyaMasdoorSangam)
The unregistered union is GTN Workers (Jobbers) Association
Organization structure- personnel department
8.9 EXPORT AND MARKETING DEPARTMENT
Introduction
Export department is serving as a link between the customers. The main duties of the
department includes sales enquiry conformation, sales contract, preparation of work order
which in turn aids the preparation of production plan sending samples and finally shipment.
Thus the export department does not have separate marketing department. Once the lot is
ready the production department makes arrangements for lot dispatch. The goods are shipped
in containers, which undergo house stuffing or port stuffing; the cartons are covered with
Hessian Cloth and loaded in to trucks by experienced personnel under the supervision of the
factory trained expert more over the truck is covered with water proof tarpaulins to protect
GM Personnel
Security Officer Personnel Officer Manager Training
Security Guards Junior Officer
Time Keeper Assistant
the cartons while transpiration. The containers used for transportation is of international
standards, which are leased and provided to shipping line.
The customer of the company include consumer who are directly use the product for
further processing and trader who sell it to other customers. The company promotion efforts
include MDs visit to foreign countries and participation in Textile exhibition abroad. Their
major customers are Italy, japan, China, Australia, Spain and UK etc.
The payments of almost of all the transactions are through the letter of credit system.
The export department office is at Cochin where the transaction re carried out. The
information regarding the transaction are shared and passed to the organization through
routers. The main server of the company is at Cochin.
India continues to be dominant supplier of cotton yarn in the world. However,
Pakistanis closely following India and it may outpace India because of its advantageous
factors like favourable exchange rate, cheaper power tariff and lower wages. Of late, Pakistan
has started importing extra long staple cottons for manufacture of finer counts of yarn for
exports. Therefore, India will have to become more cost- effective to withstand Pakistani
competition in this segment. Chinas imports of cotton yarn are raising Cotton. India is now
poised to become a prominent exporter of raw cotton and cotton yarn.
Export procedure
The export transaction of GTN textiles ltd starts with the receipt of an intent or order
from the foreign importer. After obtaining the license and complying with the exchange
regulations, they proceed to assemble the product as per the terms of the indent. Once the lot
is ready, the production department makes necessary arrangement for lot dispatch and
arrange the secure shipping space on convenient terms and obtain shipping order after
complying with the customer formalities, i.e. paying customs duty and obtaining customs
export pass the company goes for bill or lading certificate of origin and insurance policy.
Finally they prepare invoice showing the price, quantity and description of the product and
negotiates with the bank with necessary documents for securing payment under letter of
credit agreement. The procedure is:
Export procedure chart
The GTN textiles ltd has a well established and managed export department under the
control of well qualified professionals. Its strict delivery schedules, consistent quality and
after sales service had given the company an important position in the textile export area.
Even though there is no separate marketing department for the company the marketing
activities of the company are performed by the export department.
Marketing
Receipt of Indent /Order
Production, Packing &
Forwarding of Goods
Secure Shipping Order
Customer Formalities
Obtain B/L, Certificate
of Origin & Insurance
Negotiates with Bank for
Payment L/C
GTN textiles ltd continues to maintain its leadership in exports of fine and superfine-
combed cotton compact yarns. It has export to cover 25 countries across the world selling
high value and high quality products to the niche market. With a substantially large export
market and a growing domestic presence, GTN certainly has its quality control measure and
production standards in place. Not surprisingly the company has been the recipient of
Texprocil Gold award excellence in exporting for 18 years.
The company has been constantly focusing its efforts to carter to high priced end user
in sophisticated markets. Apart from predominant exports of cotton yarn to Japan and Italys
companys yarn has also been well received in other countries viz. South Korea, China, Hong
Kong, USA, Austria, Belgium, Israel, Australia, Taiwan, Malaysia, Mauritius among others.
The company enjoys excellent relations with all its overseas customers, which have been
assiduously quality and providing prompt after sales service. For the past few years, the
company has been aggressively marketing its products to high end users in the domestic
market who have set up downstream projects for export of high value fabrics, made- ups and
garments.
The tie up with Japan has not only helped in penetrating the Japanese market, but also
in other parts of the o\world where ITOCHU, the marketing conglomerate has officers. The
connection has helped the company is sewing up business opportunities.
Supplier to Higher and market
Used for- shirting, stretch fabrics, voiles, velvets, velour, fine bed liner, fashion
knitwear, lingerie
Worldwide customer list- mark & spencer, gap, Benetton, Victorias secret, Ann
Taylor
The payment of almost all the transaction is through the letter of credit of credit
system. The export department office at Cochin, where the transactions are shared and passed
o the organization through routers. The main server of company is at Cochin.
Major markets
Table
Sl No Markets % Share
1. Japan 36
2. Italy 15
3. Korea 12
4. Israel 10
5. China 6
6. Hong Kong 1
7. Taiwan 1
8. Malaysia 4
9. UK 1
10. Portugal 2
11 Germany 1
12 Austria 2
13. Australia 2
14. Mauritus 1
15 Chile 2
16 SriLanka 5
Organization structure export department
General Manager
(Export)
Manager (Export)
Deputy Manager
(Export)
Assistant Manager
(Export)
Officers
8.10 SECURITY DEPARTMENT
Through security is a part of the personnel department, the functions performed by
them are above that of just as guard. The main functions of security department are:
Security keeping
Fire finding
First- aid
The company has only one gate through which entry and exit of men and material is
permitted. The workers should compulsorily punch during entry and exit. Use of rugs and
smoking is strictly prohibited inside the company. Breath analysers are used for this purpose.
Vehicles are also checked during entry and exit for inflammable materials
There are 173 free extinguishers placed at various places inside the company. Apart
from this, the guards are trained for fire finding.
Five guards are trained for administering first- aid in case of any accidents. A first aid
kit is available in the security officers room
There is one security officer, one head guard and 12 guards. There will be four guards
in each shift. During the night shift to ensure that the guards are going for patrolling an Anglo
Swiss watch is used. This is placed at different laces outside the company. The time of
patrolling is recorded using this, at times of accidents; immediate action is taken by the
security officer.
8.11 RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT DEPARTMENT
The research and development department of GTN Textiles Ltd is well equipped with
latest testing and measuring equipment. The R&D Manger is the Head of the Department.
The supervisors follow him the technicians assist them.
Product design
One way to build the image of the product is done through its design. A distinctive
design may be the only feature that significant differentiates the product many firms and done
product design by considerable glamour and general promotional appeal in product design
and designers name. In the case of GTN product design is done as operate requirements of
the customers.
Product development
Organizations are increasing by recognizing the necessity and advantage of regularly
developing new products and services. Product development must be done because of
declining their product sale the department head should control it.
Duties research and development manner
The person who manages the R&D Department has the role to translating customers
quality requirements in to achievable specification and to continuously improve product
quality and reliability based n information feedback on product performance.
The responsibilities of R&D Manager are:-
Distribute the various stage wise works among the staff in the department and ensure
timely completion.
Regularly oversee the works carried out by the staff and guide them to achieve the
desired goals.
Clear the techniques doubts arising during the designing of requirement by interacting
with the Managing director.
Discuss the testing procedures of prototype samples with managing Directors and
engineers.
Conduct reviews between various stages of design and manage all the verification and
validation processes.
Verify drawing, product specifications and records maintained by research and
development department
Control of documents and amendments to such documents.
Growth profile
1962- GTN Textiles ltd was incorporated for the manufacturing of Cotton yarn.
1966- The company was taken over by the promoters, the Patodia family of GTN Group.
1983- The company ltd has established a unit at Chitkul Village, Medak District in
Andhra Pradesh.
1993- The company had promoted Patspin India Limited, a 100% EOU as a joint venture
along with an equity participation of ITOCHU Corporation, Japan and KSIDC,
Trivandrum.
1995- The company had acquired Cotton Spinning Unit Nagpur, Maharashtra during
1994-95 by7 virtue of amalgamation of Perfect Spinners Limited with the company.
1997- It further set up a yarn dyeing and mercerizing unit at Shadsnagar, Andhra Pradesh.
2004- The company was ranked 63
rd
in the BB 100 Cross Forex listing.
The company ranked 327
th
in Industry 2.0s second annual listing of top 500
manufacturing companies in India
The company had received a compostie score of 12 out of a possible 15 in Industry
2.0s SCM Metrics study.
2005- GTN Industries was incorporated as a public Limited company on 28
th
March,
2005 under the Companies Act, 1956.
It obtained the certificate for commencement of business on 6
th
April 2005.
GTN Industries Limited had changed its name to GTN Textiles Limited and vice
versa through the fresh certificate of incorporation 27
th
December 2005, issued by the
Register of Companies Kerala.
2007- On 26
th
July 2007, company had authorized the board to borrow money for and on
behalf of the company in any manner from time and without prejudice.
Future Plans
Reduce cost of production
Sell improved quality cost efficient products.
Focus more on export of cost efficient cotton yarns and less on promotional activities.
Upgrading the present quality of products to international quality standards.
SWOT ANALYSIS
STRENGTH, WEAKNESS, OPPORTUNITIES AND THREATS ANALYSIS
The overall evaluation of Companys strengths, weakness, opportunities and threat is
called SWOT analysis. In general, a business unit has to monitor key macro environment
forces (demographic, economic, technological, political- legal and socio cultural) and
significant micro environment factors (customers, competitors, distributors and suppliers) the
affect its ability to earn profits each business needs to evaluate its internal strength and
weakness periodically.
Strength
Latest technology
Well accepted brand
Market leader
Financially sound, profit making company
Experienced and committed personnel
95% capacity utilization
Foreign collaboration
ISO Certified
Large reserve
Decades of experience in trading cotton and yarn before venturing into this line of
activity.
Weakness:-
Raw material prices are increasing
Lack of commitment
Labour unrest
Less transportation facility of employees
Absence of user interactive system
Less interaction between marketing and other departments
Money machines have become obsolete
The operating expenses are on the higher side.
Opportunities:
India has the largest cultivation and hence a great scope in the textile market.
Globalization increased opportunity for export of textile.
Increased demand of cotton garments in India and abroad.
Availability od cheap labour
Technology can be adopted to maximize quality production.
Threats:
Growing competition from foreign brands
Rising prices of raw materials
Inflexible Government policies and regulations
Global warming and the resultant changes in the climate have affected the cotton
cultivation
Changing technology
Entering of new players from outside
CONCLUSION
The project entitled organization study with reference to GTN Textiles Aluva, gives
information about the organization. The study gives information about the manufacturing
process, organizational; structure of the company, departmental functions and gives a good
knowledge about the financial position of the company. The company continues to be a
significant player in the medium, fine and superfine segment in the world cotton yarn market
and is continuously innovating new value- added products, like compact yarn and other
specialty yarns. With at most respect to human values, company served its human resources
with integrity, through a variety of services by giving appropriate training, moti8vation
techniques and employee welfare activities. The co-operation and interactions extended by
the employees and management of GTN have made it possible for the in depth organisation
study, which would be of much use in the future.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Marketing management- Philip Kotler
Human Resource management- P. SubbRao
Business Research Methods- Willian G Zikmund(Business research methods the
Dryden press series in management, edition5- illiutrated, reprint, publisher- Dryden
1997)
Operation Management Norman Gaither, Greg Frazier(Edition9, Illustrated,
Publisher- south western/ Thomas learning, 2002)
Human Resource Management- VSP Rao (Publisher- Excel Book, 2002)
Wikipedia
Accounting Reports of GTN Textiles limited
Standing orders of workers GTN Textiles
www.gtntextiles.com
CONTENTS
SL NO
1. INTRODUCTION
2. INDUSTRY PROFILE
3. COMPANY PROFILE
4. PRODUCTS & SERVICES PROFILE
5. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
6. METHODOLOGY OF THE STUDY
7. ORGANISATIONAL CHART
8. DEPARTMENTAL PROFILE
9. SWOT ANALYSIS
10. CONCLUSION
BIBLIOGRAPHY
You might also like
- Petite Pit Bull Amigurumi: by LyzardDocument6 pagesPetite Pit Bull Amigurumi: by LyzardMaría Paz Gallardo63% (8)
- Free Textile Books PDFDocument9 pagesFree Textile Books PDFTextile Learner60% (5)
- Textile Basics NotesDocument33 pagesTextile Basics Notesparthraj89100% (3)
- Business PlanDocument2 pagesBusiness PlanShradha Gupta100% (1)
- Engleski TTF Skripta 1 SemestarDocument6 pagesEngleski TTF Skripta 1 SemestarAndrea VekarićNo ratings yet
- Textile IndustryDocument31 pagesTextile IndustryMamta Shah88% (16)
- Fiber, Yarn, Fabrics 3Document18 pagesFiber, Yarn, Fabrics 3Mahadi HabibNo ratings yet
- Project SreenathDocument42 pagesProject SreenathSreenath SudhakaranNo ratings yet
- Assignment: BGMEA University of Fashion & Technology Course Code: TEX2105Document12 pagesAssignment: BGMEA University of Fashion & Technology Course Code: TEX2105NeFariOus ArYan AraFat AnikNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Job Satisfaction by KishoreDocument83 pagesProject Report On Job Satisfaction by KishoreYellaturi Siva Kishore ReddyNo ratings yet
- Open End SpinningDocument8 pagesOpen End SpinningVikrant Kanugonda100% (1)
- Textile Industry in PakistanDocument13 pagesTextile Industry in Pakistanraoumar100% (3)
- Classification of FibresDocument12 pagesClassification of FibresARYAN RATHORENo ratings yet
- Industry ProfileDocument6 pagesIndustry Profilerams191989No ratings yet
- Sulur Ranga TextilesDocument38 pagesSulur Ranga TextilesraviNo ratings yet
- Finished The Industry Profile in Spinning MillDocument11 pagesFinished The Industry Profile in Spinning MillMukesh kannan MahiNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Study of Textile From Fiber To FashionDocument10 pagesComprehensive Study of Textile From Fiber To Fashiondeepakshi.inNo ratings yet
- Operations Research ReportDocument30 pagesOperations Research ReportVenkatesh RajuNo ratings yet
- Study On Textile FibersDocument9 pagesStudy On Textile FibersAbid hasanNo ratings yet
- Properties Natural FibresDocument46 pagesProperties Natural FibresanishaNo ratings yet
- Types of FibresDocument34 pagesTypes of FibresmehrasunilNo ratings yet
- Indian Cotton & Needs of Spinning Industry, Cotton Research Journal, Vol. 5 (2), 2013Document5 pagesIndian Cotton & Needs of Spinning Industry, Cotton Research Journal, Vol. 5 (2), 2013abisheck444No ratings yet
- Statement of The Problem:: Fiber Seeds Genus Cellulose Shrub Americas Africa India Mexico Australia AfricaDocument7 pagesStatement of The Problem:: Fiber Seeds Genus Cellulose Shrub Americas Africa India Mexico Australia AfricaMark Angelo DiazNo ratings yet
- Mid Term TEX 111Document8 pagesMid Term TEX 111Mainur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Seed FiberDocument57 pagesSeed FiberMurad HossainNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Cotton MKT BDDocument7 pages1.4 Cotton MKT BDKAWSER RAFINo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Natural Fibers and Methods of ObtainingDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Natural Fibers and Methods of ObtainingResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- Abirami Exports Manufacturing ProcessDocument76 pagesAbirami Exports Manufacturing ProcesseswariNo ratings yet
- Abirami Exports Manufacturing ProcessDocument76 pagesAbirami Exports Manufacturing ProcessMeena SivasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Textile IndustryDocument25 pagesTextile IndustryArjun VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Raw CottonDocument3 pagesRaw CottonShoaib ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Cotton Waste - Gin MotesDocument5 pagesCotton Waste - Gin MotesDilhani pereraNo ratings yet
- Term Paper OF Operation MANAGEMENT: TopicDocument39 pagesTerm Paper OF Operation MANAGEMENT: Topicshilpygoyal10No ratings yet
- TextileDocument67 pagesTextileBunty NagapNo ratings yet
- Cotton FiberDocument33 pagesCotton Fibermaruf.hossain14101993No ratings yet
- SivanesanDocument42 pagesSivanesanKp PrakashNo ratings yet
- What Is Cotton????????: Ndefined Undefined, UndefinedDocument5 pagesWhat Is Cotton????????: Ndefined Undefined, UndefinedArsalan Ahmed SheikhNo ratings yet
- CottonDocument6 pagesCottonrim3lNo ratings yet
- InternshipDocument66 pagesInternshipArjunvanneri AshokNo ratings yet
- Indian Garment Industry - An Overview: 3.1 History of TextileDocument15 pagesIndian Garment Industry - An Overview: 3.1 History of TextileKrupaNo ratings yet
- What Is CottonDocument6 pagesWhat Is CottonShailendra MishraNo ratings yet
- A Treatise On Cotton FiberDocument5 pagesA Treatise On Cotton FiberRobotrixNo ratings yet
- FiberDocument10 pagesFiberShresha DasNo ratings yet
- Jute ProcessingDocument13 pagesJute ProcessingNikhil Nani100% (1)
- Textile Industry: Submitted By: Unnati PatelDocument31 pagesTextile Industry: Submitted By: Unnati Patelpalak rathoreNo ratings yet
- Textile Project NiDS PDFDocument40 pagesTextile Project NiDS PDFnidspune.inNo ratings yet
- Sam Chapter - IIDocument16 pagesSam Chapter - IIsamsanthanamNo ratings yet
- Training Report On Textile Wet ProcessingDocument38 pagesTraining Report On Textile Wet ProcessingMunazza SohailNo ratings yet
- Fibre To Fabric Notes 1Document3 pagesFibre To Fabric Notes 1Mohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH TEKSTIL 1 Softfile BingDocument10 pagesMAKALAH TEKSTIL 1 Softfile BingHuswatun HasanaNo ratings yet
- Fibres To FabricDocument23 pagesFibres To FabricPallavi Luthra KapoorNo ratings yet
- JuteDocument16 pagesJuteAviral VermaNo ratings yet
- CottonDocument2 pagesCottonXeniya777No ratings yet
- Rearing TechnologyDocument142 pagesRearing TechnologyAdita AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Ntural and Man Made FibreDocument46 pagesNtural and Man Made FibreRemyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cotton FibreDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Cotton FibreDebasish GhoshNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Study On Jute FiberDocument51 pagesA Comprehensive Study On Jute FiberAsad Amir100% (1)
- Manufacture of Narrow Woven Fabrics - Ribbons, Trimmings, Edgings, Etc. - Giving Description of the Various Yarns Used, the Construction of Weaves and Novelties in Fabrics Structures, also Desriptive Matter as to Looms, Etc.From EverandManufacture of Narrow Woven Fabrics - Ribbons, Trimmings, Edgings, Etc. - Giving Description of the Various Yarns Used, the Construction of Weaves and Novelties in Fabrics Structures, also Desriptive Matter as to Looms, Etc.No ratings yet
- Textiles, for Commercial, Industrial, and Domestic Arts Schools: Also Adapted to Those Engaged in Wholesale and Retail Dry Goods, Wool, Cotton, and Dressmaker's TradesFrom EverandTextiles, for Commercial, Industrial, and Domestic Arts Schools: Also Adapted to Those Engaged in Wholesale and Retail Dry Goods, Wool, Cotton, and Dressmaker's TradesNo ratings yet
- Jirafa ColoresDocument12 pagesJirafa ColoresJULIANA MATEUS SAENZNo ratings yet
- Felted Knit Tulip Amigurumi PatternsDocument2 pagesFelted Knit Tulip Amigurumi PatternsCrafty AlienNo ratings yet
- Crochet Doll Body Pattern: MamaknitkaDocument41 pagesCrochet Doll Body Pattern: MamaknitkaMarina Assa100% (2)
- Dressmaking 9-Module 1 Draft and Cut Pattern For Sleeping Garment-EditedDocument63 pagesDressmaking 9-Module 1 Draft and Cut Pattern For Sleeping Garment-EditedAbegail Maratas100% (3)
- SSM TK2-20CT - 1 X 30 SPDL - 18-14-63-00354-01 - 200114 PDFDocument5 pagesSSM TK2-20CT - 1 X 30 SPDL - 18-14-63-00354-01 - 200114 PDFAhmed Ali Hefnawy0% (1)
- Group 3 Art AppreciationDocument55 pagesGroup 3 Art AppreciationLSRC JAYSONNo ratings yet
- 151023-02 KM WARP PREPARATION View PDFDocument24 pages151023-02 KM WARP PREPARATION View PDFDSSidgiddiNo ratings yet
- Humanities Chapter 2 - Aesthetic Arts and CraftsDocument4 pagesHumanities Chapter 2 - Aesthetic Arts and Craftsjane100% (3)
- Chemical and Enzyme Treatment of Enset Yarn For Technical Textile ApplicationsDocument8 pagesChemical and Enzyme Treatment of Enset Yarn For Technical Textile ApplicationsUNITED CADDNo ratings yet
- Scottish Fold CatDocument11 pagesScottish Fold CatSanti YuanitaNo ratings yet
- Marcador Giraffe - BookmarkDocument10 pagesMarcador Giraffe - BookmarkJessica FagundesNo ratings yet
- Warping CalculationsDocument26 pagesWarping CalculationsBineth T Liyanage80% (5)
- Apparel Quality Management Case Study Analysis PDFDocument36 pagesApparel Quality Management Case Study Analysis PDFNadarajNo ratings yet
- TE 05034 Fabric Analysis (Sample Answer)Document15 pagesTE 05034 Fabric Analysis (Sample Answer)Mritunjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Knitted Baby YodaDocument6 pagesKnitted Baby YodaDorian BöseNo ratings yet
- Garmentdyeingtechniques 120621040800 Phpapp01Document28 pagesGarmentdyeingtechniques 120621040800 Phpapp01Monjur MorshedNo ratings yet
- Solutions For The Draw Textured Yarn ProductionDocument32 pagesSolutions For The Draw Textured Yarn ProductionrabiulfNo ratings yet
- Tuazon, Christian Jay G PDFDocument11 pagesTuazon, Christian Jay G PDFBryan YuNo ratings yet
- 2021 08 01HolidayCraftsDocument100 pages2021 08 01HolidayCraftsmaria0% (2)
- MJ's Off The Hook - Unicorn Blanket & CowlDocument7 pagesMJ's Off The Hook - Unicorn Blanket & CowlMilagros QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Evoquench Upgrade: For Microfiber Yarn ProductionDocument2 pagesEvoquench Upgrade: For Microfiber Yarn Productionanil kapadiaNo ratings yet
- Get The Skinny Scarves-ADocument3 pagesGet The Skinny Scarves-AAlexandra Popa100% (1)
- CM0128Document3 pagesCM0128monicag7773No ratings yet
- Costume and History in Highland EcuadorDocument417 pagesCostume and History in Highland EcuadoranahichaparroNo ratings yet
- Frozen Booklet 1Document40 pagesFrozen Booklet 1Agatha Liberte100% (1)
- LINEN Housekeeping DepartmentDocument14 pagesLINEN Housekeeping DepartmentpranithNo ratings yet
- Q-SKINbyFULGAR ENDocument10 pagesQ-SKINbyFULGAR ENAsif imtiaz islamNo ratings yet
- Aatcc TM20-2021Document20 pagesAatcc TM20-2021Kunal ShingalaNo ratings yet