Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Signal and System 2014
Uploaded by
pitapitul0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pagessinyal sistem questions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsinyal sistem questions
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pagesSignal and System 2014
Uploaded by
pitapitulsinyal sistem questions
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Signals and Systems
1 Know how to calculate period of a signal, Fourier
coefficients of a signal
2 Know how to calculate convolution of two signals.
3 Know how to calculate the Fourier transformation of
signals
Know how to use the relationship !etween convolution
in time domain and multiplication in Fre"uency domain to
solve practical pro!lems.
# Know the sampling theory
Examples:
The fundamental period of the signal ( ) sin(20 1) cos(5 1) x t t t = + + is ( ).
When the input signal of an LT s!stem is
10
( )
j t
x t e = " the output signal is
10
2
j t
e
. f
10 5
( ) 5
j t
x t e
+
= " the output signal is ( ) .
The non#$ero %ourier series coefficients for the periodic sinusoidal signal
0
cos t are (
).
the %ourier transform of the signal
0
& ' n n is ( ).
%ind the %ourier (oefficients of the signal
0 0 0
( ) 1 sin 2cos cos() ) x t t t t = + + + .
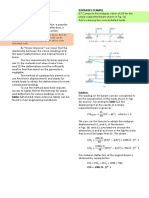
(onsider a continuous#time signal ( ) x t *hose
spectrum is sho*n in the left figure. + periodic impulse
train
( ) ( # )
n
p t = t nT
+
=
is used for its sampling" and
generates the sampled signal
( ) ( ) ( )
p
x t x t p t =
"
(1) Let
2
s
T
= ,e sampling fre-uenc!" s.etch the spectrum of
( )
p
x t
*hen
" 2 " )
s M M M
= .
(2) f a sine *a/e signal *ith fre-uenc! 50$ is sampled *ith sampling rate 10$" after reco/er the
$ %& ( )* 1 + 2
signal *ith lo* pass filter (stop fre-uenc! is half of the sampling rate)" *hat is the fre-uenc!
of the reco/ered signal2 f the sampling rate is 120$" *hat is the fre-uenc! of the reco/ered
signal2 3.etch the spectrum and explain *h!.
(onsider a LT s!stem *ith the impulse response ( ) ( )" 0
t
h t e u t
= > . Let the input signal ,e
( ) ( )" 0
t
x t e u t
= > "find the output signal of the s!stem.
+ s!stem is affected ,! an un.no*n signal ( ) x t and generates an output signal
( ) ( ) ( )
t t
y t e u t e u t
= . f the s!stem is a causal LT s!stem *ith the impulse response
( ) ( )
t
h t e u t
= " determine the input signal ( ) x t .
Basic Formula List
(on/olution
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) " & ' & ' & ' & ' & ' y t x t h t x h t d y n x n h n x k h n k
k
= = = =
=
%ourier 3eries
2
2
1
( ) " ( )
jk t
jk t
T
x t a e a x t e dt T
k
T
k
T
k
= =
=
%ourier Transform
1
( ) ( )
2
( ) ( ) "
j t j t
x t X j e d X j x t e dt
= =
$ %& ( )* 2 + 2
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- AyanamsaDocument30 pagesAyanamsahari1833% (6)
- Syllabus - ME 512 Airconditioning and Ventilation Systems - Not DetailedDocument2 pagesSyllabus - ME 512 Airconditioning and Ventilation Systems - Not DetailedallovidNo ratings yet
- Metering - Manual - Eastern - RegionDocument65 pagesMetering - Manual - Eastern - RegionAmit PathakNo ratings yet
- 3 3 Tipping-Bucket-Rain-Gauge JGormanDocument42 pages3 3 Tipping-Bucket-Rain-Gauge JGormanpitapitul100% (1)
- Automatic Rain GaugeDocument9 pagesAutomatic Rain GaugepitapitulNo ratings yet
- Sdoquezon Adm SHS12 Stem GP1 Q1M4 1 68Document68 pagesSdoquezon Adm SHS12 Stem GP1 Q1M4 1 68Zeicel Allijah De Los SantosNo ratings yet
- SOGC (Society of Obstetri and Gnecology of Canada)Document11 pagesSOGC (Society of Obstetri and Gnecology of Canada)pitapitulNo ratings yet
- Tyrotoxicosis. The Main Antithyroid Drugs Are The Thionamides, Such As PropylthiouracilDocument18 pagesTyrotoxicosis. The Main Antithyroid Drugs Are The Thionamides, Such As PropylthiouracilpitapitulNo ratings yet
- UT OO: Preventing Postpartum Hemorrhage: Managing The Third Stage of LaborDocument8 pagesUT OO: Preventing Postpartum Hemorrhage: Managing The Third Stage of LaborpitapitulNo ratings yet
- Transcranial Doppler: An Introduction For Primary Care PhysiciansDocument7 pagesTranscranial Doppler: An Introduction For Primary Care PhysiciansdediNo ratings yet
- Alogorithm PosterDocument1 pageAlogorithm PosterpitapitulNo ratings yet
- Booklet Renewables Links Version FINAL 061913 PDFDocument8 pagesBooklet Renewables Links Version FINAL 061913 PDFpitapitulNo ratings yet
- Malaria Treatment (Current WHO: Recommendations & Guidelines)Document35 pagesMalaria Treatment (Current WHO: Recommendations & Guidelines)pitapitulNo ratings yet
- MillerDocument7 pagesMillerpitapitulNo ratings yet
- B-Lynch Poster PDFDocument1 pageB-Lynch Poster PDFpitapitulNo ratings yet
- WHO Dengue Guidelines 2013Document160 pagesWHO Dengue Guidelines 2013Jason MirasolNo ratings yet
- Antituberculosis DrugsDocument38 pagesAntituberculosis DrugspitapitulNo ratings yet
- Dlight ManualDocument44 pagesDlight ManualpitapitulNo ratings yet
- Analisis PenggunaanDocument14 pagesAnalisis PenggunaanpitapitulNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (KULIAH)Document90 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever (KULIAH)pitapitulNo ratings yet
- Measurement System BehaviourDocument48 pagesMeasurement System BehaviourpitapitulNo ratings yet
- 2 Indian Guidelines DENGUEDocument39 pages2 Indian Guidelines DENGUEAmanda WrightNo ratings yet
- Diphtheria, Pertusis, Exanthema Subitum 2Document37 pagesDiphtheria, Pertusis, Exanthema Subitum 2pitapitulNo ratings yet
- Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733: 1 TrajectoriesDocument9 pagesClass Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733: 1 TrajectoriesVashish RamrechaNo ratings yet
- Intercultural Communication CourseDocument31 pagesIntercultural Communication CoursepitapitulNo ratings yet
- Intercultural Adaptation Model of Indonesian Foreign Students in ChinaDocument4 pagesIntercultural Adaptation Model of Indonesian Foreign Students in ChinapitapitulNo ratings yet
- Instrumen and SensorDocument39 pagesInstrumen and SensorpitapitulNo ratings yet
- Measurement System BehaviourDocument48 pagesMeasurement System BehaviourpitapitulNo ratings yet
- Typing Bucket Using AtmegaDocument2 pagesTyping Bucket Using AtmegapitapitulNo ratings yet
- Matlab Basics: ECEN 605 Linear Control Systems Instructor: S.P. BhattacharyyaDocument36 pagesMatlab Basics: ECEN 605 Linear Control Systems Instructor: S.P. BhattacharyyapitapitulNo ratings yet
- Fourier Theory TransformDocument87 pagesFourier Theory TransformpitapitulNo ratings yet
- 1350 ArgDocument29 pages1350 ArgDarlis WidodoNo ratings yet
- KOMPASDocument3 pagesKOMPASpitapitulNo ratings yet
- RFID and GPS Technologyand ApplicationsDocument85 pagesRFID and GPS Technologyand ApplicationspitapitulNo ratings yet
- Cfy CRP (2125) - pt-2 B Lot - Iitjee Stage-RDocument16 pagesCfy CRP (2125) - pt-2 B Lot - Iitjee Stage-RRitvik RajNo ratings yet
- Maya RigDocument329 pagesMaya Rigskynet24100% (2)
- Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles in Cellulose Acetate Polymer and The Reaction Chemistry of Silver Complexes in The PolymerDocument4 pagesPreparation of Silver Nanoparticles in Cellulose Acetate Polymer and The Reaction Chemistry of Silver Complexes in The Polymer1No ratings yet
- XII Maths Exercise 3.1 (Solution)Document11 pagesXII Maths Exercise 3.1 (Solution)mansoor100% (5)
- A Facile Synthesis, Characterization of N-Substituted 7-Methoxy 3-Phenyl 4 (3-Piperzin - 1-Yl-Propoxy) Chromen-2-OneDocument21 pagesA Facile Synthesis, Characterization of N-Substituted 7-Methoxy 3-Phenyl 4 (3-Piperzin - 1-Yl-Propoxy) Chromen-2-OneNalla Umapathi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Vectors 05 Notes PDFDocument21 pagesVectors 05 Notes PDFADSaksoulNo ratings yet
- Topic 4. Binary DistillationDocument123 pagesTopic 4. Binary DistillationAngela Lorena DíazNo ratings yet
- Mollier Diagram BeginDocument3 pagesMollier Diagram BeginKalu BhaiNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Heald Frame Motion Generated by Rotary Dobby and Crank & Cam Shedding MotionsDocument6 pagesComparison of Heald Frame Motion Generated by Rotary Dobby and Crank & Cam Shedding MotionsKannan KumarNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument2 pagesProblem SetCrystal DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Rajshahi University of Engineering and Technology, RajshahiDocument9 pagesRajshahi University of Engineering and Technology, RajshahiShakil Ahmed100% (1)
- 750 Multilin Feeder Management Relay ManualDocument446 pages750 Multilin Feeder Management Relay ManualFerdinandja100% (1)
- Kemira, Leonard Dan Bethel Acid FormicDocument22 pagesKemira, Leonard Dan Bethel Acid FormicBen Yudha SatriaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: OpticsDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Opticsronald100% (1)
- FuelDocument172 pagesFuelImtiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Applications and Interpretation Higher SpecimensDocument80 pagesApplications and Interpretation Higher SpecimensJAKE THE DOGNo ratings yet
- Manual On Experimental Stress AnalysisDocument31 pagesManual On Experimental Stress AnalysisrmontandonNo ratings yet
- Nano RamDocument7 pagesNano Ramसाहिल विजNo ratings yet
- ECBC Implementation Experience Case StudyDocument16 pagesECBC Implementation Experience Case StudysiddharthaNo ratings yet
- PERSIAN PROBABILITY FUNCTION For Helping Users Understand Statistical ModelsDocument35 pagesPERSIAN PROBABILITY FUNCTION For Helping Users Understand Statistical ModelsNicola ChieffoNo ratings yet
- Chapter V Beam Deflections 5.4Document3 pagesChapter V Beam Deflections 5.4Joshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- History of MaichewDocument2 pagesHistory of MaichewSehabom Geberhiwot100% (1)
- Dow Elite 5401G TDSDocument3 pagesDow Elite 5401G TDSAli RazuNo ratings yet
- 2019 STEM Applications - FinalDocument81 pages2019 STEM Applications - FinalDavid BumphisNo ratings yet
- Assignment N1Document9 pagesAssignment N1Rania ChNo ratings yet
- CHEM 212 - RecrystallizationDocument16 pagesCHEM 212 - RecrystallizationkristaNo ratings yet