Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EDDL vs FDT/DTM Technologies for DCS Systems
Uploaded by
kamy0010 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views7 pagesThis document discusses and compares EDDL (Electronic Device Description Language) and FDT/DTM (Field Device Tool/Device Type Manager) technologies. EDDL uses text files called EDDs to describe field devices, while FDT/DTM uses executable software modules called DTMs. The document outlines the architecture of each technology, how they are supported, their strengths and weaknesses, differences between them, and how they can coexist in modern DCS (distributed control system) for both regulatory control and asset management applications.
Original Description:
Original Title
2 Introduction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses and compares EDDL (Electronic Device Description Language) and FDT/DTM (Field Device Tool/Device Type Manager) technologies. EDDL uses text files called EDDs to describe field devices, while FDT/DTM uses executable software modules called DTMs. The document outlines the architecture of each technology, how they are supported, their strengths and weaknesses, differences between them, and how they can coexist in modern DCS (distributed control system) for both regulatory control and asset management applications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views7 pagesEDDL vs FDT/DTM Technologies for DCS Systems
Uploaded by
kamy001This document discusses and compares EDDL (Electronic Device Description Language) and FDT/DTM (Field Device Tool/Device Type Manager) technologies. EDDL uses text files called EDDs to describe field devices, while FDT/DTM uses executable software modules called DTMs. The document outlines the architecture of each technology, how they are supported, their strengths and weaknesses, differences between them, and how they can coexist in modern DCS (distributed control system) for both regulatory control and asset management applications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
EDDL or FDT/DTM
WIB Workshop EDDL or FDT/DTM
4 October 2006, Utrecht
Characteristics of EDDL and FDT/DTM
Agenda
WIB Workshop EDDL or FDT/DTM
4 October 2006, Utrecht
Architecture of a modern DCS System
EDDL - Electronic Device Description Language
FDT/DTM - Field Device Tool / Device Type Manager
Differences between EDDL and FDT/DTM
Coexistence EDDL and FDT/DTM
Conclusion
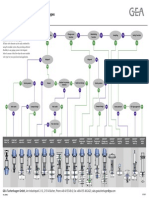
Architecture of a modern DCS system
WIB Workshop EDDL or FDT/DTM
4 October 2006, Utrecht
Fault tolerant communication
system
Fault tolerant communication
system
Level1/Level2 isolation (Control firewall)
Field Instruments. Level 0
Fieldbus
I/O equipment
Level 1
Basic Regulatory Control Network
Level 2
Application
server
Human Machine Interface
(Operator Stations)
History
server
Router
Level 3
Supervisory Control Network
Advanced Control Network
Asset
Management
DMC RTO
Plant
Simulator
Commercial Ethernet
Network
Firewall
Business Network Level 4
Commercial Ethernet
Network
Shadow
History
Server Level 4 desktop users
Operation &
Production
Management
Control and
Database
server
EDDL Electronic Device Description Language
WIB Workshop EDDL or FDT/DTM
4 October 2006, Utrecht
First used in process control in 1992 with the HART
Communication Protocol
In 2004 the Electronic Device Descriptor Language (EDDL)
becomes an approved international standard: IEC 61804-2
The EDD is a text file and operating system independent
However for each Fieldbus system a specific Device EDD is
required
Only functions as described in IEC 61804-2 are possible
Requires a specific EDDL Interpreter for each DCS vendor
In one DCS system all EDDL instruments have the same look and
feel
EDDL Architecture
WIB Workshop EDDL or FDT/DTM
4 October 2006, Utrecht
Smart Field Instruments
Fieldbus
I/O equipment
Basic Regulatory Control Network. Level 1/2
Router
Advanced Control Network. Level 3
Asset
Management
Server
Operator Station
Basic Control and
Database server
Operating System
DCS Operating
Software
EDDL
Interpreter
Workstation
EDD
File 1
EDD
File 2
EDDL -Electronic Device Description Language
WIB Workshop EDDL or FDT/DTM
4 October 2006, Utrecht
Standardization: Recently IEC 61804-3 is released which
gives Enhanced User Interfaced, Graphing System and
Persistent Data Storage
Support of EDDL technology
No single user organization
EDD testing is an independent multi part activity
Weak points of EDDL technology
Functionality is restricted by standard IEC 61804-x. Additional
device functionality requires proprietary plug-ins and snap-ons
Eventually device intelligence can reach the stage that devices
cannot be adequately described via DDs
Testing of EDD file against Fieldbus protocols is well organized
by the Fieldbus organizations. However EDD files are not
independently tested against EDDL interpreters
FDT/DTM - Field Device Tool / Device Type Manager
WIB Workshop EDDL or FDT/DTM
4 October 2006, Utrecht
Requires following parts:
FDT Frame Application (one per DCS system)
CommDTM (one per Fieldbus system)
Device DTM (one per field device type)
DTMs are executable software (drivers)
DCS vendors will require to run the FDT software in another
server than the basic Control and Database server
The Device DTM is independent of the DCS system or the
Fieldbus system
FDT/DTM Architecture
WIB Workshop EDDL or FDT/DTM
4 October 2006, Utrecht
Smart Field Instruments
Fieldbus
I/O equipment
Basic Regulatory Control Network. Level 1/2
Router
Advanced Control Network. Level 3
Asset
Management
Server
Operator Station
Operating System
FDT Frame application
CommDTM
Device
DTM 1
Device
DTM 2
Device
DTM 3
Application Server
Basic Control and
Database server
Operating System
DCS Operating
Software
Workstation
FDT/DTM - Field Device Tool / Device Type Manager
WIB Workshop EDDL or FDT/DTM
4 October 2006, Utrecht
Support of FDT technology: FDT Group, which has
currently appr. 55 members (vendors and users)
Consistent look and feel of different DTMs: Device
manufacturers will follow the FDT Style Guide
Certification of DTMs: By the FDT Group.
Certified DTM are listed on the FDT Groups website
Weak points of FDT technology:
Windows upgrades
Version control
Architectural differences
WIB Workshop EDDL or FDT/DTM
4 October 2006, Utrecht
DCS Control and
Database Server
Field
device 1
FDT/DTM
Field
device 2
EDDL
FDT Frame
Application
EDDL
Interpreter
Operating System
(Windows)
DCS Operating Software
Asset Management
Server
Text file
Executable software
Device
DTM
Device
EDD
Differences of both technologies
Yes, file copy Yes, installation of
software. In general no
restart is required. No
registry changes
Installation
procedures
Dependant on host system.
Must be supported by DCS
vendor. Possibly restricted
functionality for more
complex device types
Is determined by DTM.
Therefore full functionality
for all device types
Presentation of
device functionality
High for host system
manufactures, low for
device manufacturers
High for device
manufacturers, non for
host system
manufacturers
Flexibility for adding
newfunctionality
Host systemmanufacturers Field device and
component manufacturers
Functionality of field
device determined by
Text, data Program Structure/type
EDD/DD FDT/DTM Item
Differences of both technologies
Item FDT/DTM EDD/DD
Dependency on
operating system
Yes, FDT frame and
DTM must be verified
against operating
system
No, but host application
(EDDL interpreter) may
be dependent on host
operating system
User interface
DTM style guide
Proprietary, determined
by host system
Support of open
systems
Strong
Weak
Supported protocols All HART, Foundation
Fieldbus, Profibus
International Standard By end of 2007 IEC 61804-3
Current interoperability
experience
No problems
Often problems arise
when loading non DCS
vendor related DDs
Coexistence EDDL and FDT/DTM
WIB Workshop EDDL or FDT/DTM
4 October 2006, Utrecht
In a DCS system which has provisions for EDDL
technology and FDT/DTM technology as well (a truly open
system), both technologies can coexist.
Then we can use EDDL instruments for regulatory control
applications and FTD/DTM instruments for Asset
Management applications (which require more process
information and device information)
Conclusion
WIB Workshop EDDL or FDT/DTM
4 October 2006, Utrecht
For the optimization of Life-Cycle-Costs, Asset Management
Systems and smart field instruments are required
To transport the instrument data to the Asset Management
System, two technologies are available: EDDL and FDT/DTM
These two technologies are not compatible
Some instruments may be available only in EDDL technology,
others only in FDT/DTM technology
However, a truly open DCS system can handle both
technologies simultaneously.
To avoid future problems when implementing Asset
Management Systems, a DCS system shall be chosen which
supports EDDL technology as well as FDT/DTM
technology
You might also like
- Self-Locking & Self-Sealing Fasteners HandbookDocument48 pagesSelf-Locking & Self-Sealing Fasteners Handbookkamy001No ratings yet
- Fa 2086e Selection Scheme 0512Document1 pageFa 2086e Selection Scheme 0512kamy001No ratings yet
- Peli Atex GuidelinesDocument4 pagesPeli Atex Guidelineskamy001No ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Material PropertiesDocument4 pagesStainless Steel Material PropertiesMohammed RiyazNo ratings yet
- Safebook 1 - Functional Safety in The Process IndustryDocument170 pagesSafebook 1 - Functional Safety in The Process Industrykamy001100% (1)
- (FCENBR0003AQ) - Natural Gas Industry LRDocument12 pages(FCENBR0003AQ) - Natural Gas Industry LRkamy001No ratings yet
- Best Practices For Rupture Disc (RD) / Pressure Relief Valve (PRV) CombinationsDocument4 pagesBest Practices For Rupture Disc (RD) / Pressure Relief Valve (PRV) Combinationskamy001No ratings yet
- Model TL THROUGH CONDUIT KNIFE GATE VALVEDocument12 pagesModel TL THROUGH CONDUIT KNIFE GATE VALVEkamy001No ratings yet
- Bump Gas Offering Iss1 June14 GB EUROPE WEB PDFDocument4 pagesBump Gas Offering Iss1 June14 GB EUROPE WEB PDFkamy001No ratings yet
- Hart ImsDocument1 pageHart Imskamy001No ratings yet
- Rupture Pin vs Rupture Disk: Which is Best for Pressure ReliefDocument6 pagesRupture Pin vs Rupture Disk: Which is Best for Pressure Reliefkamy001No ratings yet
- Flow Ehandbook Finalv2Document19 pagesFlow Ehandbook Finalv2kamy001No ratings yet
- Sizing of Pressure Relief ValveDocument9 pagesSizing of Pressure Relief Valvekenoly123100% (3)
- Control EngineeringDocument4 pagesControl Engineeringkamy001No ratings yet
- Selecting The Right Act - WebDocument1 pageSelecting The Right Act - Webkamy001No ratings yet
- Alfa Laval Pump Handbook PDFDocument257 pagesAlfa Laval Pump Handbook PDFkashifwarsiNo ratings yet
- Rupture DiscsDocument5 pagesRupture Discskamy001No ratings yet
- Flow EhandbookDocument12 pagesFlow Ehandbookkamy001No ratings yet
- Class II-Dust Class III-Fibers Class I - Gases or Vapors: Hazardous Locations GuideDocument2 pagesClass II-Dust Class III-Fibers Class I - Gases or Vapors: Hazardous Locations Guidekamy001No ratings yet
- Wireless EhandbookDocument9 pagesWireless Ehandbookkamy001No ratings yet
- Pressure Regulator Selection Strategy (Flow Curves)Document4 pagesPressure Regulator Selection Strategy (Flow Curves)kamy001No ratings yet
- 6 Tips For Critical Sight Glass Applications: White PaperDocument4 pages6 Tips For Critical Sight Glass Applications: White Paperkamy001No ratings yet
- Guide To RegulatorsDocument20 pagesGuide To Regulatorskamy001No ratings yet
- ARCA Fly Gruppe GBDocument16 pagesARCA Fly Gruppe GBkamy001No ratings yet
- Ball Valve Selection Sheet Rev2Document1 pageBall Valve Selection Sheet Rev2kamy001No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Modicon Premium Automation Platform: CatalogDocument459 pagesModicon Premium Automation Platform: CatalogOth ManeNo ratings yet
- PDS Installation & Configuration ChecklistDocument41 pagesPDS Installation & Configuration Checklistpareen9No ratings yet
- MyQ Smart Quick Setup GuideDocument32 pagesMyQ Smart Quick Setup GuideKbolero BotweNo ratings yet
- Using Yocto Project With BeagleBone Black - Sample ChapterDocument25 pagesUsing Yocto Project With BeagleBone Black - Sample ChapterPackt Publishing100% (1)
- H12 211 PDFDocument18 pagesH12 211 PDFAlly RoyNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference Guide: Hikvision Network SwitchDocument2 pagesQuick Reference Guide: Hikvision Network Switchmas zak danielNo ratings yet
- How To DockerDocument3 pagesHow To DockeralfonzsoNo ratings yet
- Verde 4 Admin GuideDocument176 pagesVerde 4 Admin GuidemillajovavichNo ratings yet
- ExpaDocument119 pagesExpaudayakumarNo ratings yet
- 1 2Document10 pages1 2vcdiniesh14No ratings yet
- HCIA-openGauss V1.0 Lab GuideDocument138 pagesHCIA-openGauss V1.0 Lab GuideRush OunzaNo ratings yet
- Behrooz ParhamiDocument510 pagesBehrooz ParhamiSanath KolaganiNo ratings yet
- Dba 101Document35 pagesDba 101akash raj81100% (1)
- Instruction Manual For Windows 11 / Windows 10 Recovery Image Download ServiceDocument28 pagesInstruction Manual For Windows 11 / Windows 10 Recovery Image Download ServiceRolànd AmberleyNo ratings yet
- BSA 1 TrainingDocument305 pagesBSA 1 TrainingSrinidhi RaoNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Subnet Mask From IP AddressDocument7 pagesHow To Calculate Subnet Mask From IP AddressVivekananda GNNo ratings yet
- Computer Awareness Questions Collection: List of Commonly Used Computer AbbreviationsDocument106 pagesComputer Awareness Questions Collection: List of Commonly Used Computer AbbreviationsSamar SinghNo ratings yet
- Module Uvm Connect Session1 Introduction AericksonDocument27 pagesModule Uvm Connect Session1 Introduction AericksonsandraNo ratings yet
- Versa N24Document12 pagesVersa N24rafitamxNo ratings yet
- FlexiPacket Hub 800 Customer Release Notes R2.0EP1 PU7 R2.0 - 1.15.0Document21 pagesFlexiPacket Hub 800 Customer Release Notes R2.0EP1 PU7 R2.0 - 1.15.0Ahmed RaadNo ratings yet
- Multiprocessor Architectures and ProgrammingDocument89 pagesMultiprocessor Architectures and ProgrammingKULDEEP NARAYAN MINJNo ratings yet
- Local Administrator Password Management Detailed Technical SpecificationDocument20 pagesLocal Administrator Password Management Detailed Technical SpecificationAntony Zurita curahuaNo ratings yet
- MQTT VulneribilitiesDocument6 pagesMQTT VulneribilitiesAbdul HadiNo ratings yet
- WISP-68: 802.11bg High-Power Outdoor AP/CPE User ManualDocument39 pagesWISP-68: 802.11bg High-Power Outdoor AP/CPE User ManualLynn DavisNo ratings yet
- Arduino - TroubleshootingDocument6 pagesArduino - TroubleshootingManiraj PerumalNo ratings yet
- Ansible Automation SA Technical Deck Q2FY19Document43 pagesAnsible Automation SA Technical Deck Q2FY19daniel_vp21No ratings yet
- Network management procedures for routing and protocolsDocument257 pagesNetwork management procedures for routing and protocolsAlexanderNo ratings yet
- Work Spreadsheet PDFDocument39 pagesWork Spreadsheet PDFMohan MNo ratings yet
- Current LogDocument19 pagesCurrent LogCrisNo ratings yet
- Wiring Diagram of The Cpu 314 Ifm - Siemens SIMATIC S7-300 Series Reference Manual (Page 72) - ManualsLibDocument1 pageWiring Diagram of The Cpu 314 Ifm - Siemens SIMATIC S7-300 Series Reference Manual (Page 72) - ManualsLibazzeddine eddhahraouy20100% (1)