Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Verra, Vicmar M. Sept.28 0659pm
Uploaded by
Vic Verra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views116 pagesall topics about microeconomics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentall topics about microeconomics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views116 pagesVerra, Vicmar M. Sept.28 0659pm
Uploaded by
Vic Verraall topics about microeconomics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 116
Presented by:
Verra, Vicmar M. BSBA-OM BAOM 202
Presented to:
Ms. Abigael C. Medina-Miranda
CHAPTER 1
o commodity or service being in a short supply,
relative to its demand
o It pertains to the limited availability of economic
resources relative to societys unlimited demand for
goods and services.
o A science that deals with the management of
scarce resources.
o It is simply scarcity and choice.
Greek roots
oikos - household
nomus - system or management
Oikonomia or oikonomus - management of
household
The study of economics was generally founded in
order to address the issue of resource allocation
and distribution, in response to scarcity.
Ceteris Paribus means all other things held
constant or else equal.
This assumption is used as a device to analyze the
relationship between two variables while the other
factors are held unchanged.
Birth of Economic Theory:
Adam Smith
Father of
Economics
his book, Wealth
of the Nations is
known as the
bible in
economics
John Stuart Mill
developed the basic
analysis of the political
economy
Leon Walras
- the general economic system.
Alfred Marshall
- his book Principles in Economics
- his concept of marginalism
John Maynard
Keynes
His influential book,
The General Theory
of Employment,
Interest and Money
John Hicks
His analysis of the IS-
LM model
simply answers the question
what is.
Positive Economics
answers the question what
should be.
Normative Economics
1. What to produce?
2. How to produce?
3. How much to produce?
4. For whom to produce?
Economics is considered the queen of all
social sciences.
o Business Management
o History
o Finance
o Physics
o Sociology
o Psychology
o Efficiency
Refers to productivity and proper allocation of economic
resources.
o Equity
Means justice and fairness.
o Effectiveness
Means attainment of goals and objectives.
oTo understand the Society
oTo understand Global Affairs
oTo be an Informed Voter
o Wealth
-anything that has functional value.
o Consumption
-direct utilization of the available goods and
services.
o Production
-the formation by firms of an output.
o Exchange
-process of trading goods or services for
money.
o Distribution
-process of allocating scarce resources.
Deals with the
individual
decisions of
units of the
economy.
Involved in
understanding the
behavior of the
society as a whole.
o Land
Refers to all natural resources.
o Labor
Any form of human effort exerted in the production.
o Capital
Man-made goods used in the production.
o Entrepreneurship
An economic good that commands a price.
Opportunity Cost refers to the foregone value of the next
best alternative.
o Consumption
The basic decision problem that the consumers must always deal
with in their day to day activities.
o Production
Generally a concern of producers.
o Distribution
Primarily addressed to the government.
o Growth over Time
The last basic decision problem that a society or nation must deal
with.
o Traditional Economy
A subsistence economy.
o Command Economy
The manner of production is dictated
by the government.
o Market Economy
Factors of production are owned and controlled
by individuals.
o Socialism
Key enterprises are owned by the state.
o Mixed Economy
A mixture of market system and the command
system.
CHAPTER 2
o Wet Market
Is where people usually buy vegetables, meat etc.
o Dry Market
Is where people buy shoes, clothes, or other dry
goods.
It is where buyers and sellers meet and their transaction takes
place.
It implies three things:
o desire to possess a thing
o the ability to pay for it
o willingness in utilizing it
Quantity of a good or service
that people are ready to buy at
a given price.
It states that if price goes up, the quantity
demanded will go down. Conversely, if
price goes down, the quantity demanded
will go up.
A table that show the relationship of prices and the
specific quantities demanded at each f these prices.
It is a graphical representation showing the
relationship between price and the quantities
demanded per time period.
It shows the relationship between demand for a
commodity and the factors that determine this
demand.
QD = f (own price, income, price of related goods, etc.)
o Change in Quantity Demanded
There is change in quantity demanded if the
movement is along the same demand curve.
o Change in Demand
There is a change in demand if the entire
demand curve shifts to the right side
resulting to an increase in demand.
o Taste or preferences
o Changing incomes
o Occasional or seasonal products
o Population change
o Substitute goods
o Expectations of future prices
Quantity of goods or services that firms
are ready and willing to sell at a given
price within a period of time.
It states that if the price of a good or service
goes up, the quantity supplied for such good
or service will also go up; if the price goes
down the quantity supplied also goes down.
It is schedule listing the various prices of
a product and the specific quantities
supplied at each of these prices.
It is a graphical representation showing the
relationship between the price of the product
and the quantity supplied per time period.
A form of mathematical notation that link
the dependent variable (Qs) with various
independent variables which determine
quantity supplied.
Qs = f (own price, number of sellers, price of
factor inputs, technology, etc.)
o Change in Quantity Supplied
There is a change in quantity supplied if the
movement is along the same supply curve.
o Change in Supply
There is a change in supply when the entire
supply curve shifts rightward or leftward.
o Optimization in the use of factors of
production
o Technological change
o Future expectations
o Number of sellers
o Weather conditions
o Government policy
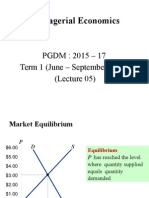
Refers to the meeting of supply and demand.
Pertains to a balance that exists when quantity
demanded equals quantity supplied.
The price agreed by the seller to offer its good
or service for sale and for the buyer to pay for it.
o Surplus
Quantity supplied is more than the
quantity demanded.
o Shortage
Quantity demanded is higher than
supplied.
o Floor Price
It is the legal minimum price imposed by
the government.
o Price Ceiling
It is the legal maximum price imposed
by the government.
Equation System:
o Demand Equation: QD = a bP
o Supply Equation: Qs = -c + dP
o Equilibrium Condition: QD = QS
o 3 equations & unknowns: (QD,QS,P)
Chapter 3
Measures the responsiveness of one
variable to a certain change of another
variable.
Elasticity = percentage change in variable X
percentage change in variable Y
Elastic Inelastic
Unitary
elasticity
Perfectly
elastic
Perfectly
inelastic
Measures the percentage change in
quantity with respect to percentage in price.
measures the responsiveness of the quantity
demanded with respect to its price.
Price Elasticity of Demand = Q2 Q1 P1
P2 P1 Q1
ARC = Q2 Q1 (P1 + P2)/2
P2 P1 (Q1 + Q2)/2
Measures the responsiveness of
quantity demanded in response to a
change in income.
y = %Qd
%y
TYPES OF GOODS
INCOME ELASTICITY
COEFFICIENT
Normal Good Positive elasticity (>0)
Inferior Good Negative elasticity (<0)
Normal, Luxury good Positive elasticity (>1)
Normal, Necessity good Positive elasticity (<1)
measures the responsiveness of quantity
demanded of a good to a change in the
price of another good.
xy = %Qdx
%Py
Chapter 4
o One who demands goods and services.
o Objective is to maximize satisfaction given the
limited budget.
o King in the capitalist or free-market economy.
Consumer sovereignty refers to power to
determine what is produced since consumer are
the ultimate purchasers of goods and services.
o satisfy the needs and wants of consumers
In order to earn profits.
o referred as passive agents simply obey
the wishes and desires of consumers
o Goods refer to
anything that provides
satisfaction to the
needs, wants and
desires of the
consumer.
o Services are any
intangible economic
activities that
contribute to the
satisfaction of human
wants.
These are the goods that yield satisfaction directly
to any consumer. These are primarily sold for
consumption.
These are goods that satisfy the
basic needs of man.
Essential or necessity
goods
Those which men may do without,
but are used to contribute to
comfort and well-being.
Luxury goods
It has value attached to it and a
price has to be paid for its use.
Economic good
Satisfy everyones needs without
paying for it
Free good
Determined
by age,
income,
gender,
occupation,
customs and
tradition.
Tastes
Are the
choices
made by
consumers
as to which
products or
services to
consume.
Preferences
o It is the name, term or symbol given to a
product by a supplier in order to
distinguish his offering from that of similar
products supplied by competitors.
Self-
actualization
needs
Esteem needs
Social needs
Safety needs
Physiological needs
o Utility refers to the satisfaction or pleasure
that an individual or consumer gets from the
consumption of a good or service
purchased.
o Utility theory explains how our satisfaction
or utility as consumer decline when we try
to consume more and more of the same
good at a particular point in time.
The additional satisfaction
that an individual derives
from consuming an extra
unit of a good or service.
Marginal
utility
The total satisfaction derives
from the consumption of a
given quantity of a good or
service.
Total
utility
This law states that as a consumer gets more
satisfaction in the long-run, he experiences a
decline in his satisfaction for goods and
services.
Marginal utility is simply the change in total utility
divided by the change in quantity.
MU = TU
Q
The difference between the total amount that we
are willing and able to pay and the total amount
that we actually pay.
Chapter 5
o Refers to any economic activity, which
combines the four factors of production.
o It is the process of converting inputs into
outputs.
Natural resources represent the gift of
nature to our productive processes.
Land
Mental and physical ability used in the
production of goods and services.
Labor
Goods that are used in the production
of other goods and services.
Capital
resources
One who manages the factors of
production.
Entrepreneur
o These are commodities and services
that are used to produce goods and
services.
Fixed inputs
Components of production
which do not change
Variable inputs
Changeable resources in
the production
o Are the various useful goods and services
that result from the production process.
Body of knowledge applied to how goods
are produced.
Utilizes more
labor resources
than capital
resources.
Labor
intensive
Utilizes more capital
resources than labor
resources.
Capital
intensive
Short run
Period of time so
short that there is
at least one fixed
input
Long run
Period of time so
long that all inputs
are considered
variable.
Known as the
planning horizon.
o The functional relationship between
quantities of inputs used in the production
and outputs to be produced.
Qdress = f(fabrics, sewing machine,
sewer, thread, buttons, etc.)
Total product
Total output
produced after
utilizing the fixed
and variable
inputs.
Marginal
product
Extra output
produced by 1
additional unit of
that input while
other inputs are
held constant.
Average
product
Total product
divided by total
units of input
used.
o Holds that we will get less and less extra
output when we add additional amount of
an input while holding other inputs fixed.
Constant
return to scale
A change in all inputs leads to a proportional change
in output
Increasing
return to scale
Also called economies of scale
An increase in all inputs leads to a more than
proportional increase in the level of output.
Decreasing
return to scale
A balanced increase in all inputs leads to a less than
proportional increase in total output
o Cost refers to all expenses acquired
during the production of goods or services.
Profit = Sales Costs
or
Profit = Total Revenue Total Costs
Explicit and
implicit costs
Explicit costs
Payments to non-
owners of a firm for
their resources.
Implicit costs
Opportunity costs
of using resources
owned by the firm.
Fixed
cost
Expenses which
are spent for the
use of fixed factors
of production.
Sometimes called
sunk costs
Variable
costs
Expenses which
change as a
consequence of a
change in quantity
of output produced.
Total fixed cost (TFC)
Costs that do not vary as output varies and that must be
paid even if output is zero.
Total variable cost (TVC)
Costs that are zero when output is zero and vary as
output increases(decreases).
Total cost (TC)
The sum of total fixed cost and total variable cost at each
level of output.
TC = TFC +TVC
AFC = FC / Q
Average
fixed cost
AVC = VC / Q
Average
variable cost
ATC = TC / Q
Average
total cost
o The cost of producing one additional unit
of output.
MC = TVC
Q
Defined as the difference that arises
when a firms total revenue is greater
that of its total cost.
The process by which a firm
determines the price and output level
that returns the greatest profit.
Chapter
7
o A classification system for the key traits of
a market, including the number of firms,
the similarity of the products they sell, and
the ease of entry into and exit from the
market share.
o A market structure characterized by:
a large number of small firms
homogenous product
very easy entry or exit from the
market
o The opposite extreme of perfect competition.
o Market structure characterized by:
a single seller or producer
a unique product
impossible entry into the market
o A type of market structure characterized by:
many small firms
differentiated products
easy market entry and exit
o A market structure characterized by:
few sellers
homogenous or differentiated
products
difficult market entry
o A market situation comprising one seller and only one buyer.
o A market condition with a significant degree of seller
concentration and a significant degree of buyer concentration.
o A market situation in which there are only two buyers but many sellers.
o A subset of oligopoly describing a market situation in which thee
are only two suppliers.
o A form of buyer concentration, that is, a market situation in
which a single buyer confronts many small suppliers.
Chapter
10
International trade
is defined as the exchange of
Goods and services among
countries.
Differences in a countrys resources
Natural resources
Labor resources
Capital stock
Differences in Tastes and Preferences
Differences in Relative Costs of Production
o This principle explains why trade will still
take place even though a country is able
to produce both goods efficiently.
o A country is said to have a comparative
advantage when it has either higher
relative efficiency or lower opportunity
costs.
Defined as the rate at which exports can be
exchanged for imports.
In terms of prices, it is also defined as the ratio
of export price index to import price index.
High transport as well as
handling costs might eliminate
potential gains from
specialization and trade
Limitations
of
Specialization
and Trade
There is some degree of immobility to
the factors of production.
They risk adverse impacts to the economy when prices of
exports fall below the desired level.
There must be adequate demand to support the production.
Refers to the shielding of domestic
industries from foreign competition through
the use of trade barriers.
Tax levied on imports and it could be in the form
of either a specific tax or an ad valorem tax.
tariff
Usually given by the government to local
producers to increase local production.
subsidies
Refers to the limit in which quantity of a certain
product cold enter the country in a given year.
quota
Subtle forms of protectionism that a country could
impose to protect its domestic industries
Administrative barriers
Has the ability to cause black market for foreign
exchange to form in in the country.
Exchange controls
Complete bans on certain import products.
embargoes
o Protectionism of Infant industry
Infant industry is an industry which has not realized its full
potential but could gain economies of scale or comparative
advantage in the future.
o Diversification
o Prevention of Dumping
Dumping is the export of a countrys goods to another market at
a price below average or production cost.
o Protect Employment
o Correction of Temporary Deficit in the Balance of
Payments (BOP)
BOP shows the annual inflow and outflow of foreign currencies.
Protecting Key Industries
Political Motivations
Social and Moral Reasons
Chapter 12
The act of levying a tax that is the
process or means by which the
sovereign, through its law-making
body, raises income to defray the
necessary expenses of the
government.
to raise revenue to the government to cover
its own expenditure on the provision of social
services
as an instrument of fiscal policy in regulating
the level of total spending in the economy
to alter distribution of income and wealth
to control volume of imports into the country
Taxes are used by the government
for a variety of purpose.
Taxes levied by
government on the
income and wealth
received by
households and
businesses
Direct
taxes
Taxes levied by
government on
goods and
services
Indirect
taxes
Taxes that place a greater burden on those best
able to pay and little or no burden on the poor
Taxes that place an equal burden on the rich,
the middle class, and the poor.
Taxes that fall heavily on the poor than on the
rich.
The Basic Principles of Taxation
basic concepts by which a government is
meant to be guided in designing and
implementing an equitable taxation regime
Taxes should be
just enough
Adequacy
Taxes should be
spread over as
wide as possible to
all sectors of the
population or
economy
Broad
basing
Taxes should
be
coordinated
Compatibility
Taxes should be
enforced in a
manner that
facilitates
voluntary
compliance to
the maximum
extent
Convenience
Tax revenue from a
specific source should
be dedicated to a
specific purpose only
when there is a direct
cost-and-benefit link
between tax source and
expenditure.
Earmarking
Tax collection
efforts of
government
should not cost
an inordinately
high percentage
of tax revenues
Efficiency
Taxes should
equally burden
all individuals
and entities in
similar
economic
circumstances
Equity
Taxes should not favor
any one group or sector
over another, and should
not be designed to
interfere with or influence
individual decision
making.
Neutrality
Collection of taxes should
reinforce their inevitability and
regularity
Predictability
Tax exemptions must only be
for specific purposes and for a
limited period
Restricted
exemptions
Tax assessment and
determination should be easy
to understand by an average
taxpayer
Simplicity
proposed by Jean
Jacques Rouseau, Jean
Baptiste Say and John
Stuart Mill
states that taxation
should be levied
according to an
individuals ability to pay
usually the basis for
progressive taxation
Ability to
pay principle
developed by Thomas
Hobbes, John Locke
and Hugo Grotius
proposes that taxation
should be levied
broadly in relation to
the benefits that
people receive in
public services
Benefit
approach
proposed mainly by
the Physiocrats
Proposes that the
major duty of a tax
system is to analyze
the effect of a
particular tax on the
distribution of tax
welfare
Tax
incident
approach
A tax on a persons income, emoluments,
profits arising from property, practice of
profession, conduct of trade or business or
on the pertinent items of gross income
specified in the Tax Code of1997
You might also like
- As of 050120 - Essential Wedding Package 2020-21Document2 pagesAs of 050120 - Essential Wedding Package 2020-21Vic VerraNo ratings yet
- Mae Ungcad EconomicsDocument141 pagesMae Ungcad EconomicsVic VerraNo ratings yet
- Governor's Drive, General Trias, Cavite Contact Number: (046) .484.8091 To 94 Website: WWW - Lpu.edu - PHDocument1 pageGovernor's Drive, General Trias, Cavite Contact Number: (046) .484.8091 To 94 Website: WWW - Lpu.edu - PHVic VerraNo ratings yet
- Development Trust of Barangay JavaleraDocument9 pagesDevelopment Trust of Barangay JavaleraVic VerraNo ratings yet
- Questions: " - ! You're Stepping On My Foot." (Expressing Pain) A. B. C. D. EDocument7 pagesQuestions: " - ! You're Stepping On My Foot." (Expressing Pain) A. B. C. D. EVic VerraNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- (A) Explain How The Incidence of An Indirect Tax Depends On The Price Elasticity of Demand and The Price Elasticity of Supply. (10 Marks)Document4 pages(A) Explain How The Incidence of An Indirect Tax Depends On The Price Elasticity of Demand and The Price Elasticity of Supply. (10 Marks)anamNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument10 pagesElasticityAbegail OcampoNo ratings yet
- Level I of CFA Program 1 Mock Exam June 2020 Revision 1Document75 pagesLevel I of CFA Program 1 Mock Exam June 2020 Revision 1JasonNo ratings yet
- A Dashboard For Online PricingDocument22 pagesA Dashboard For Online PricingAsh SitaramNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Elasticity of DemandDocument6 pagesModule 3 Elasticity of DemandAbhinab GogoiNo ratings yet
- MBA-105 Question PaperDocument9 pagesMBA-105 Question PaperTushar JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Assignment Week 1Document10 pagesAssignment Week 1victoriabhrNo ratings yet
- FORD MOTOR COMPANY v. FUJIKURA LTD. and FUJIKURA AUTOMOTIVE AMERICA LLCDocument39 pagesFORD MOTOR COMPANY v. FUJIKURA LTD. and FUJIKURA AUTOMOTIVE AMERICA LLCsahmed_anNo ratings yet
- Monopoly: Meaning, Definitions, Features and CriticismDocument11 pagesMonopoly: Meaning, Definitions, Features and CriticismShah AlamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Market Equlibrium and Concept of Elasticity of Demand and Its ApplicationDocument80 pagesLecture 5 - Market Equlibrium and Concept of Elasticity of Demand and Its ApplicationnivecNo ratings yet
- Summary Chapter 4Document5 pagesSummary Chapter 4Lalit SoniNo ratings yet
- 2011 AP Microeconomics ExamsDocument47 pages2011 AP Microeconomics ExamsjoshNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Topic 5Document65 pagesManagerial Economics Topic 5Anish Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Demand AnalysisDocument73 pagesDemand AnalysisSuganya VenurajNo ratings yet
- WK 3Document42 pagesWK 3Shivarni KumarNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment On Elasticity of DemandDocument3 pagesHome Assignment On Elasticity of DemandSk Ahasanur Rahman 1935043681No ratings yet
- Applied Economics 1st Quarter TestDocument2 pagesApplied Economics 1st Quarter TestdhorheeneNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 4Document38 pagesPertemuan 4M Arif IlyantoNo ratings yet
- Marketing in TourismDocument24 pagesMarketing in TourismYulvina Kusuma PutriNo ratings yet
- Effect of TaxDocument2 pagesEffect of TaxrudraarjunNo ratings yet
- Kelloggs Edition 6 Full Case StudyDocument2 pagesKelloggs Edition 6 Full Case Studynarenmadhav100% (1)
- JAIBB 97th 2023 103. - Principles of Economics POEDocument3 pagesJAIBB 97th 2023 103. - Principles of Economics POERanjan GhoshNo ratings yet
- ch4 - Demand ElasticityDocument6 pagesch4 - Demand ElasticityAhmed DabourNo ratings yet
- Assignement 1-Calculating The Impact of Price Change On SoftDocument3 pagesAssignement 1-Calculating The Impact of Price Change On Softparth limbachiyaNo ratings yet
- BBA IB Revised Syllabus - 24.062019Document33 pagesBBA IB Revised Syllabus - 24.062019Atharva ShahaneNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics PPT Module 4Document26 pagesApplied Economics PPT Module 4Jiell Renon VigiliaNo ratings yet
- Review Questions - OVWL 2023Document8 pagesReview Questions - OVWL 2023zitkonkuteNo ratings yet
- Sol 61Document11 pagesSol 61Navin GolyanNo ratings yet
- 3.1. Elasticity and Its ApplicationDocument26 pages3.1. Elasticity and Its ApplicationSamantha Cinco100% (2)
- PomDocument63 pagesPomAllen Fourever50% (2)