Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Symptoms Which Panic
Uploaded by
VelayuthamGunasekaranOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Symptoms Which Panic
Uploaded by
VelayuthamGunasekaranCopyright:
Available Formats
A A A
Share this
Font size:
Select An Article All Subchapter Articles:
Laryngospasm: Causes, symptoms and treatments
Laryngospasmhappens when the muscles of the vocal cords seize up, restricting the flow of air into the lungs.
This may happen during the night, with a person waking up unable to speak or breathe.
This condition is relatively rare. Although it can be frightening, it usually clears up after a few minutes.
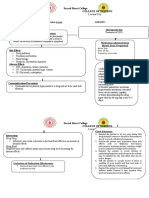
Laryngospasm causes
Laryngospasm can be caused by allergic reactions, foreign bodies in the throat or infections, such as epiglottitis.
Laryngospasm can also be related to gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD). GORD is a condition that occurs when th
ring-like muscle that normally closes to keep the stomach's contents from backing up doesn't work correctly. With GORD,
harsh acids from the stomach rise up into the oesophagus and cause irritation.
Regular exposure to stomach acids can damage and inflame the delicate lining of the oesophagus. This damage can lead to
momentary spasms of the vocal cords, which close the airway and prevent air and oxygen from getting into the lungs.
When stomach acids reach the larynx, the condition is called laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR). The tissues of the larynx are
even more delicate and prone to injury than the oesophagus. Coughs from a cold can push more acid into the larynx. So a
recent or current upper respiratory infection may increase the likelihood of developing laryngospasm.
Laryngospasm may also be a complication of surgery. Anaesthesia used during the surgery can irritate the vocal cords,
especially in children.
Laryngospasm caused by anaesthesia can be life-threatening.
What are the symptoms of laryngospasm?
When laryngospasm occurs people are unable to breathe or speak. Sometimes the episodes occur in the middle of the nigh
A person may suddenly awaken feeling as though he or she is suffocating. This condition is called sleep-related
laryngospasm. It also is related to GORD. Some people will actually lose consciousness during these episodes.
As the airways slowly open, the person will make a high-pitched breathing sound (called stridor). The entire episode lasts on
a minute or two before breathing returns to normal. But the experience can be terrifying.
In addition to experiencing laryngospasm episodes, people with this condition will typically have symptoms of GORD, which
include:
Chest pain
Coughing
Difficulty swallowing
Heartburn
Hoarseness
Nausea
Sore throat
How is laryngospasm treated?
If GORD is the problem, treating the condition can help manage laryngospasm. Doctors often prescribe proton-pump inhibito
that reduce the production of stomach acids to make the fluids from the stomach that do back up into the oesophagus less
corrosive. Another option is prokinetic agents. These stimulate movement in the digestive tract to reduce the amount of ac
available.
Patients who don't respond to these treatments may need a surgical procedure called fundoplication. This is a procedure tha
wraps the upper part of the stomach (fundus) around the oesophagus to prevent acids backing up.
I consent to cookies! close
Article Link: http://www.webmd.boots.com/heartburn-gord/guide/laryngospasm-causes-symptoms-and-treatments
Page 1of 2 Laryngospasm: Causes, symptoms and treatments
5/17/2014 http://www.webmd.boots.com/heartburn-gord/guide/laryngospasm-causes-symptoms-and-t...
Further Reading:
Treatment tips for severe, chronic heartburn
Endoscopy for GORD diagnosis
The special risks of night-time heartburn
Heartburn: 10 questions to ask your doctor
Heartburn organisations
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD)
Effects of uncontrolled heartburn
See All GORD Topics
WebMD Medical Reference
You can also relieve GORD and LPR, and help prevent laryngospasm, by following these lifestyle tips:
Avoid common heartburn triggers such as fruit and fruit juices, caffeine, fatty foods and peppermint.
Eat smaller meals, and stop eating at least three hours before bedtime.
If you smoke, stop. Also limit alcohol consumption.
Raise the head of your bed 15cm (6in) by putting wood blocks under the bedpost.
In children who develop laryngospasm as a complication of anaesthesia during surgery, treatment usually involves moving t
head and neck to open the airway. It also involves using a machine (continuous positive airway pressure, or CPAP) to delive
air directly into the airway. Some children need to have a tube placed into the throat to assist with breathing.
View Article Sources
SOURCES:
GP Notebook: Laryngospasm
NHS Choices.
GI Motility Online: "Laryngeal and pharyngeal complications of gastroesophageal reflux disease."
Maceri, D, Zim, S Laryngoscope, 2001; vol. 111: pp. 1976-1979.
Hideto S Seiji N, Toshiaki Y Larynx Japan, 2002; vol. 14: pp. 25-28.
Burgoyne L, Anghelescu D Paediatric Anesthesia, 2008; vol. 18: pp. 297-302.
Medically Reviewed by Dr Rob Hicks on February 28, 2014
2014 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved.
From our sponsor
Anti-Blemish Solutions Clinical Clearing Gel
Starts working instantly to clear the appearance of
blemishes
Available at Boots and Boots.com
Buy now
Page 2of 2 Laryngospasm: Causes, symptoms and treatments
5/17/2014 http://www.webmd.boots.com/heartburn-gord/guide/laryngospasm-causes-symptoms-and-t...
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Research Essay Final OutlineDocument7 pagesResearch Essay Final Outlineapi-251704489No ratings yet
- The Best Diy Antenna For HDTV !!!..Document3 pagesThe Best Diy Antenna For HDTV !!!..VelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- TL-MR3020 V 1 User GuideDocument258 pagesTL-MR3020 V 1 User GuideLynda MinarsihNo ratings yet
- Daily Calendar Nov 2015Document18 pagesDaily Calendar Nov 2015VelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- The Truth About ProteinDocument5 pagesThe Truth About ProteinVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- DIR-605L B1 QIG 032013 v2.1 (US)Document2 pagesDIR-605L B1 QIG 032013 v2.1 (US)atulkheraNo ratings yet
- Food Journal and Menu PlannerDocument1 pageFood Journal and Menu PlannerVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Daily Calendar Aug 2015Document19 pagesDaily Calendar Aug 2015VelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Thirukadaiyur - To Celebrate Shastiapthapoorthi at ThirukadaiyurShastipurthi, Ukradha Santhi, Sashtiyapthapoorthy, Bhimaradhashaanthi, Sadhabishegam, 60th Marriage, 70th Marriage, 80th MarriageDocument2 pagesThirukadaiyur - To Celebrate Shastiapthapoorthi at ThirukadaiyurShastipurthi, Ukradha Santhi, Sashtiyapthapoorthy, Bhimaradhashaanthi, Sadhabishegam, 60th Marriage, 70th Marriage, 80th MarriageVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- (GUIDE) Using CHKDSK To Fix A Corrupted SD Card - Android Forums at AndroidCentralDocument12 pages(GUIDE) Using CHKDSK To Fix A Corrupted SD Card - Android Forums at AndroidCentralVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Daily Calendar Oct 2015Document19 pagesDaily Calendar Oct 2015VelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- The Social DietDocument5 pagesThe Social DietVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Daily Calendar Dec 2015Document18 pagesDaily Calendar Dec 2015VelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Differences in Drinking WaterDocument6 pagesDifferences in Drinking WaterVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Food Labeling LiesDocument6 pagesFood Labeling LiesVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Stroke in The Young - The DRDocument13 pagesStroke in The Young - The DRVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Protein Powder Study Results - The DRDocument12 pagesProtein Powder Study Results - The DRVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Stroke Risk Printable Wa... Card - The DRDocument11 pagesStroke Risk Printable Wa... Card - The DRVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Breakfasts of The WorldDocument4 pagesBreakfasts of The WorldVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- FAQ - Root Canals - The DRDocument11 pagesFAQ - Root Canals - The DRVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Cook With Coca ColaDocument6 pagesCook With Coca ColaVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- 20 Surprisingly Good Sou... Otein - The DRDocument13 pages20 Surprisingly Good Sou... Otein - The DRVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Cankles Fact Sheet - The DRDocument12 pagesCankles Fact Sheet - The DRVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Compress - Homemade Herba..Document4 pagesCompress - Homemade Herba..VelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- A Health Inspector's Gui... G Out - The DRDocument12 pagesA Health Inspector's Gui... G Out - The DRVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- 10 Surprising Sources Of... Min C - The DRDocument10 pages10 Surprising Sources Of... Min C - The DRVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- How To Seal Travertine - ..Document4 pagesHow To Seal Travertine - ..VelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- A Health Inspector's Gui... G Out - The DRDocument12 pagesA Health Inspector's Gui... G Out - The DRVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- 10 Mental Tricks For A M... Rkout - The DRDocument12 pages10 Mental Tricks For A M... Rkout - The DRVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Cook With Coca ColaDocument6 pagesCook With Coca ColaVelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Wood Pellet Mill - Briqu..Document5 pagesWood Pellet Mill - Briqu..VelayuthamGunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Managing Chronic Neurologic Problems Like Parkinson's DiseaseDocument1 pageManaging Chronic Neurologic Problems Like Parkinson's DiseaseMeryPinkihanNo ratings yet
- Protozoan Parasites: Infective Stages, Transmission, DiseasesDocument3 pagesProtozoan Parasites: Infective Stages, Transmission, DiseasesPatrice Bianca SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Archive: Enterotoxemia (Overeating Disease) in Sheep and GoatsDocument4 pagesArchive: Enterotoxemia (Overeating Disease) in Sheep and GoatsErnesto VersailleNo ratings yet
- Aj CSF - Rhinorrhea - + - Nasal - Foreign - Body - + - Myiasis - + - ChoanalDocument63 pagesAj CSF - Rhinorrhea - + - Nasal - Foreign - Body - + - Myiasis - + - ChoanalTradigrade PukarNo ratings yet
- 2017 Understanding-Nystagmus v04Document48 pages2017 Understanding-Nystagmus v04Stephanie AureliaNo ratings yet
- Healthy Ways to Survive and Help Others in CrisisDocument91 pagesHealthy Ways to Survive and Help Others in CrisisfsimsdcNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument12 pagesLiver CirrhosisOm Pratap KurmiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Tyna MooreDocument91 pagesDr. Tyna MooreCaroline AloulNo ratings yet
- Transfusion - March April 1966 - Allen - Choice of Blood For Exchange TransfusionDocument3 pagesTransfusion - March April 1966 - Allen - Choice of Blood For Exchange TransfusionDR. KHANNo ratings yet
- CBU 5th Year Exam Paper 1 2017Document13 pagesCBU 5th Year Exam Paper 1 2017Homeground entertainment100% (3)
- Acute CholecystitisDocument28 pagesAcute CholecystitisWilfredo Mata JrNo ratings yet
- SKIN, HAIR, and NAILSDocument17 pagesSKIN, HAIR, and NAILSkhalidNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FluvoxamineDocument2 pagesDrug Study FluvoxamineAngeline de Gala0% (1)
- Clinical Review October 20 2017 - SHINGRIXDocument158 pagesClinical Review October 20 2017 - SHINGRIXPayneMaxNo ratings yet
- Priority Nursing Diagnosis Rationale: PrioritizationDocument3 pagesPriority Nursing Diagnosis Rationale: PrioritizationJan Lianne BernalesNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular SurgeryDocument2 pagesAbdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular SurgeryzipzipzipNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Period and ComplicationsDocument63 pagesPostpartum Period and ComplicationsSharmaineAnnePoliciosNo ratings yet
- Limb Defciency and Phantom Limb QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesLimb Defciency and Phantom Limb Questionnairenadia kurniaNo ratings yet
- Substance Abuse & PregnancyDocument2 pagesSubstance Abuse & PregnancyChelcee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Leukemia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument4 pagesLeukemia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYElle Rosales50% (2)
- Chapter 2 Respiratory AssessmentDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Respiratory AssessmentKathleen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Research Paper 22the Causes of The Increasing Anxiety Amongst The Grade 10 Student of Maligaya Highschool22 1Document3 pagesGroup 5 Research Paper 22the Causes of The Increasing Anxiety Amongst The Grade 10 Student of Maligaya Highschool22 1Lean De MesaNo ratings yet
- Measuring Disease As SGTDocument5 pagesMeasuring Disease As SGTItharshan Indreswaran33% (3)
- GOCABR ProtocolDocument5 pagesGOCABR Protocolnunuk wijayantiNo ratings yet
- Fat Embolism Syndrome: DescriptionDocument4 pagesFat Embolism Syndrome: DescriptionDayuKurnia DewantiNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation After Hip-Joint ReplacementDocument18 pagesRehabilitation After Hip-Joint ReplacementDenise De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Lipoma ExcisionDocument4 pagesLipoma ExcisionNikolaus TalloNo ratings yet
- Dynamicsofdiseasetransmission 160905060144Document33 pagesDynamicsofdiseasetransmission 160905060144Samjaisheel SamsonNo ratings yet
- Cvspa01 Hypertension and AthrosclerosisDocument8 pagesCvspa01 Hypertension and AthrosclerosisRobert So JrNo ratings yet