Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Casting Processes Summary
Uploaded by
RajaSekarsajjaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Casting Processes Summary
Uploaded by
RajaSekarsajjaCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Casting Processes
Summary
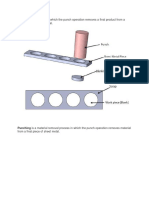
Green Sand Casting
Process
Sand, bonded with clay and water packed around
a wood or metal pattern
Pattern is removed and molten metal poured
On metal solidification, mold is broken & casting
removed
Advantages
Almost no size, shape, weight limitation
Low cost, Any metal can be cast.
2
Green Sand Casting
Limitations
Tolerances and surface finish are poorer than other
casting processes
Machining is often required
Slow production rate
Common Metals
Cast Iron, Steel, Aluminiumalloys, copper, Ni
Size Limit: 30g to 3000 kg
Thickness Limit: 0.25 cm any maximum
Draft Allowance: 1-3 deg
Surface Finish: 2.5 25 microns
Shell Mould Casting
Process
Sand coated with a thermosetting plastic resin is
dropped on to a heated metal pattern which cures
the resin
The shell segments striped from pattern and
assembled
After pouring molten metal, Shell broken away
Advantages
Faster production rate
High dimensional accuracy with smooth surface
3
Shell Mould Casting
Limitations
Requires expensive metal pattern
Thermosetting resin adds to cost
Limited part size
Common Metals
Cast Iron, Aluminiumalloys, copper
Size Limit: 30g to 10 kg
Thickness Limit: 0.15-0.6 (min)
Draft Allowance: 0.25 0.5 deg
Surface Finish: 0.3 4.0 microns
Investment Casting
Process
A refractory slurry is formed around a wax or plastic pattern
and allowed to harden.
Pattern is melted out and mold is baked
Molten metal poured and mold broken away from the
casting.
Advantages
Excellent Surface finish
High dimensional accuracy
No parting line & flash problems
Any intricate shape
4
Investment Casting
Limitations
Costly patterns and moulds
High labour cost
Limited Size
Common Metals
Steel, Aluminiumalloys, copper, precious metals
Size Limit: 3g to 5 kg
Thickness Limit: 0.06 cm
Draft Allowance: Zero
Surface Finish: 1.3 4.0 microns
Die Casting
Process
Molten metal injected into closed metal dies under
pressure (10-175 MPa)
Pressure maintained during solidification
Dies separated to eject casting
Cores must be simple and retractable
Advantages
Extremely smooth surface
Excellent dimensional accuracy
Rapid production rate
Good product tensile strength
5
Die Casting
Limitations
High initial die cost
Limited to high fluidity non-ferrous metals
Limited part size
Porosity may be problem
Common Metals
Aluminiumalloys, Zinc, Magnesium, Cu & Tin alloys
Size Limit: 30g to 7 kg
Thickness Limit: 0.75 mm
Draft Allowance: 2 deg
Surface Finish: 1 2.5 microns
Centrifugal Casting
Process
Molten metal is introduced into a rotating sand,
metal, or graphite mold and held against the mold
wall by centrifugal force until it solidifies.
Advantages
Produce wide range of cylindrical parts
Good dimensional accuracy
Good soundness and cleanliness
6
Centrifugal Casting
Limitations
Shape is limited
Expensive spinning equipment
Common Metals
Iron, Steel, Aluminiumalloys, Cu, and Ni
Size Limit: upto 3m dia and 15m length
Thickness Limit: 2.5 - 125 mm
Draft Allowance: 10 mm/m
Surface Finish: 2.5 12.5 microns
You might also like
- Sample Basic Computation - Rule 7&8Document20 pagesSample Basic Computation - Rule 7&8Udielh Velez100% (1)
- 1 First Fence StaadDocument8 pages1 First Fence StaadSiva JaseNo ratings yet
- Sacs Manual - Psi-PileDocument65 pagesSacs Manual - Psi-PileChristian Ammitzbøll0% (1)
- Society of American Silversmiths - PUK Pulse Arc Welders Reviewed, PUK04 ReviewDocument120 pagesSociety of American Silversmiths - PUK Pulse Arc Welders Reviewed, PUK04 ReviewCristal Murano100% (1)
- Agate Value, Price, and Jewelry InformationDocument7 pagesAgate Value, Price, and Jewelry Informationasset68No ratings yet
- Permanent Mold CastingDocument15 pagesPermanent Mold CastingEka RosmitaliaNo ratings yet
- CH 7-Methods of CastingDocument44 pagesCH 7-Methods of CastingGosaye DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Permanent Mold CastingDocument3 pagesPermanent Mold CastingNirav patelNo ratings yet
- Casting ProcessDocument53 pagesCasting ProcessSenthilKumar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- 3475331Document41 pages3475331Nguyen Trong TanNo ratings yet
- Permanent Mold CastingDocument10 pagesPermanent Mold Castingroronoa zoroNo ratings yet
- Mold CastingDocument55 pagesMold CastingSumit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Types of CastingDocument14 pagesTypes of CastingRamoji Aditya Chary100% (1)
- 2 - 2 Fundamentals of CastingDocument172 pages2 - 2 Fundamentals of CastingColorgold BirlieNo ratings yet
- Simple Pewter Casting PDFDocument5 pagesSimple Pewter Casting PDFJanFNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting & FormingDocument47 pagesMetal Casting & FormingMuzammil Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Making Your Own TubingDocument17 pagesMaking Your Own TubingGiNo ratings yet
- MOULDINGDocument35 pagesMOULDINGsumitNo ratings yet
- Gold Jewellery Casting Technology Design and Defects EliminationDocument7 pagesGold Jewellery Casting Technology Design and Defects EliminationReinol Eko SianturiNo ratings yet
- Foundry Manual02Document82 pagesFoundry Manual02Mohammad Namazi100% (2)
- Enme 331-Fundamentals of CastingDocument48 pagesEnme 331-Fundamentals of CastingAhmed AbdulrhmanNo ratings yet
- Sess 9 (Ceramic Mould - Pressure Die Casting - Centrifugal Casting)Document7 pagesSess 9 (Ceramic Mould - Pressure Die Casting - Centrifugal Casting)Prakash RagupathyNo ratings yet
- CastingDocument19 pagesCastingjoyhjones100% (7)
- Metal CastingDocument84 pagesMetal CastingmaniprofmechNo ratings yet
- Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, LonereDocument36 pagesDr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, LonereNikhil PawarNo ratings yet
- Casting Procedures and Casting DefectsDocument70 pagesCasting Procedures and Casting DefectsRohan Grover100% (1)
- Sand Casting and Other Casting ProcessesDocument74 pagesSand Casting and Other Casting ProcessesRashid KareemNo ratings yet
- 307151why You Really Need Ks925 JewelryDocument2 pages307151why You Really Need Ks925 Jewelrylaine685eNo ratings yet
- Casting, Welding, Machine Tools, Material SC PDFDocument240 pagesCasting, Welding, Machine Tools, Material SC PDFSanjay Kajal0% (1)
- Soldering and Brazing ProcessesDocument11 pagesSoldering and Brazing ProcessesAdiNo ratings yet
- EnvisionTEC Lost Wax Casting GuideDocument7 pagesEnvisionTEC Lost Wax Casting GuidedbpeNo ratings yet
- Casting, Forming & WeldingDocument90 pagesCasting, Forming & WeldingmahdiNo ratings yet
- Welding ShopDocument13 pagesWelding ShopAliNo ratings yet
- Metal CoastingDocument20 pagesMetal CoastingPranay Gaddam0% (1)
- Design Sand Casting Class IDocument23 pagesDesign Sand Casting Class Iiamajith123No ratings yet
- Kevin O'Dwyer: Metal in and Out of Time by John K Grande. Metalsmith Magazine 2013Document4 pagesKevin O'Dwyer: Metal in and Out of Time by John K Grande. Metalsmith Magazine 2013kodwyerdesignNo ratings yet
- The Pocket FoundryDocument6 pagesThe Pocket FoundryNatalie WyattNo ratings yet
- Ingot StructureDocument5 pagesIngot StructureklawsisNo ratings yet
- How To Solder Silver - 8 Steps (With Pictures) - WikiHowDocument3 pagesHow To Solder Silver - 8 Steps (With Pictures) - WikiHowtigerlo75No ratings yet
- Foundry ToolsDocument5 pagesFoundry ToolsChristian VicenteNo ratings yet
- Stir Casting MethodDocument5 pagesStir Casting Methodsatish448No ratings yet
- The Lost-Wax Casting Process-Down To Basics: ConceptDocument3 pagesThe Lost-Wax Casting Process-Down To Basics: ConceptRizuanul Arefin EmonNo ratings yet
- Metalcastingprocess 110925103638 Phpapp02 PDFDocument51 pagesMetalcastingprocess 110925103638 Phpapp02 PDFramesh tNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Sand CastingDocument6 pagesDifferent Types of Sand CastingAlok NayakNo ratings yet
- Metalsmithing Lesson PlanpdfDocument6 pagesMetalsmithing Lesson Planpdfapi-217892973No ratings yet
- Metal Spinning For Woodturners: James ThurmanDocument5 pagesMetal Spinning For Woodturners: James ThurmanJose Luis Araoz Platero OrfebreNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting Design: Mold and Gating System Design, Directional Solidification, and TroubleshootingDocument7 pagesMetal Casting Design: Mold and Gating System Design, Directional Solidification, and TroubleshootingzidaaanNo ratings yet
- Precision Investment Casting - Sumangal CastingDocument3 pagesPrecision Investment Casting - Sumangal Castingsumangal castingNo ratings yet
- Casting ProcessesDocument18 pagesCasting ProcessesvelavansuNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Metal Casting ProcessDocument261 pagesUnit-1 Metal Casting ProcessDharun PrakashNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Sheet MetalDocument13 pagesLecture 6 Sheet MetalmuzahedsirNo ratings yet
- FMP 221 Lecture 10 and 11Document44 pagesFMP 221 Lecture 10 and 11SarojKumarSinghNo ratings yet
- Process of Jewelry Manufacturing - CastingDocument3 pagesProcess of Jewelry Manufacturing - CastingS Sonia100% (1)
- Japanese SawDocument4 pagesJapanese SawtazzorroNo ratings yet
- Casting ProcessesDocument20 pagesCasting ProcessesVv4HNo ratings yet
- Casting ProceduresDocument91 pagesCasting ProceduresAziz Ahmed100% (1)
- MT 1 PatternDocument8 pagesMT 1 PatternRavasaheb BholeNo ratings yet
- Doming Silver BeadsDocument96 pagesDoming Silver BeadsJamie HallNo ratings yet
- Copper Work: A Text Book for Teachers and Students in the Manual ArtsFrom EverandCopper Work: A Text Book for Teachers and Students in the Manual ArtsNo ratings yet
- Disston Lumberman Handbook - Containing A Treatise Of The Construction Of Saws And How To Keep Them In OrderFrom EverandDisston Lumberman Handbook - Containing A Treatise Of The Construction Of Saws And How To Keep Them In OrderNo ratings yet
- Heavy Vehicle Dynamics Comparison Between Leaf Spring HydropneumaticDocument7 pagesHeavy Vehicle Dynamics Comparison Between Leaf Spring HydropneumaticRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Coating PerformanceDocument14 pagesEvaluation of Coating PerformanceRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Hydro Pneumatic DamperDocument6 pagesHydro Pneumatic DamperRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Carbon It RidingDocument3 pagesCarbon It RidingRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Nitro - CarburizingDocument9 pagesNitro - CarburizingRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Tubular Piston RodsDocument1 pageTubular Piston RodsRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Disc Spring SheetDocument2 pagesDisc Spring SheetRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Raw 4x4 BrochureDocument1 pageRaw 4x4 BrochureRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Leaf Spring CatalogueDocument1 pageLeaf Spring CatalogueRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- PTFE Piston RingsDocument21 pagesPTFE Piston RingsRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Automobile Industry in PPT Ankit KumarDocument60 pagesAutomobile Industry in PPT Ankit Kumarkumaripm33% (3)
- Where The Graphs Come FromDocument7 pagesWhere The Graphs Come FromRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- PTFE Piston RingsDocument21 pagesPTFE Piston RingsRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Shock Absorber Performance Test Rig: Ubique SystemsDocument1 pageShock Absorber Performance Test Rig: Ubique SystemsRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- JRZ Suspension EngineeringDocument25 pagesJRZ Suspension EngineeringRajaSekarsajja100% (1)
- 3-D Measurements On PistonsDocument4 pages3-D Measurements On PistonsRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Damping Force at Zero Velocity ExplainedDocument6 pagesDamping Force at Zero Velocity ExplainedRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Guide To Dyno GraphsDocument10 pagesGuide To Dyno GraphsRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Mistakes in AuditDocument4 pagesMistakes in AuditRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Supergas SpringsDocument2 pagesSupergas SpringsRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Cyclic WeatheringDocument8 pagesCyclic WeatheringRajaSekarsajjaNo ratings yet
- Suspension Design Rajeev - MokashiDocument16 pagesSuspension Design Rajeev - MokashiJatin351100% (1)
- Mechanics of Materials: Pure BendingDocument45 pagesMechanics of Materials: Pure BendingKhaNsa'a ZaNo ratings yet
- SHWSC Specifications Update June 2016Document83 pagesSHWSC Specifications Update June 2016Mohamed MansoorNo ratings yet
- SPG CAL 50 008 A4 Calculation Genset FoundationDocument11 pagesSPG CAL 50 008 A4 Calculation Genset FoundationOmar PerpatihNo ratings yet
- BM 3.2.11 LRFD Slab Bridge DesignDocument25 pagesBM 3.2.11 LRFD Slab Bridge DesignshafiullahNo ratings yet
- House Design and Floor Plan Cost - HapphoDocument5 pagesHouse Design and Floor Plan Cost - HapphoWelkin SkyNo ratings yet
- Local Checks 1Document85 pagesLocal Checks 1Alphyl BalasabasNo ratings yet
- Glamping Pods A (Layouts & Costings)Document15 pagesGlamping Pods A (Layouts & Costings)rajnish kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ExercisesDocument4 pagesChapter 2 ExercisesMaxNo ratings yet
- How To Primary Beam Is Rested On Secondary Beam How To Define in Staad ProDocument4 pagesHow To Primary Beam Is Rested On Secondary Beam How To Define in Staad ProseshukvsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Passive Fire Fighting SystemDocument18 pagesLecture 4 - Passive Fire Fighting SystemMuhammad FakhriNo ratings yet
- Functional Stability PileDocument8 pagesFunctional Stability PileEudkrenutNo ratings yet
- CEX 5231 Ass 3 2015 - 2016Document2 pagesCEX 5231 Ass 3 2015 - 2016MufeesNo ratings yet
- Steel Connections: Detailed ReportDocument9 pagesSteel Connections: Detailed ReportMahesh MNo ratings yet
- New Master Slide Project ReportingDocument102 pagesNew Master Slide Project ReportingdinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Outline: CE 134-Design of Reinforced Concrete StructuresDocument14 pagesChapter 8 Outline: CE 134-Design of Reinforced Concrete StructuresJerome FabreroNo ratings yet
- Cement Slurry Laboratory TestingDocument5 pagesCement Slurry Laboratory TestingalizareiforoushNo ratings yet
- MME 2260 Lab 3Document7 pagesMME 2260 Lab 3johnNo ratings yet
- SCHEDULE Level 2 NewDocument24 pagesSCHEDULE Level 2 NewGerald Jhon DadolNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationDocument15 pagesNew Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationSonika PatelNo ratings yet
- Terms Used in RoofDocument2 pagesTerms Used in Roofrahul_5587_265238786No ratings yet
- e2mdlCsm3A Rev1122Document16 pagese2mdlCsm3A Rev1122Pkk Siam Rayong co-saleNo ratings yet
- PAH 2016 Chapter 7 Rev 00 (Clean) - 161229 PDFDocument381 pagesPAH 2016 Chapter 7 Rev 00 (Clean) - 161229 PDFKHMHNNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete I - 2013-2014Document188 pagesReinforced Concrete I - 2013-2014alaa4altaie75% (4)
- 【Compiled】New Manual ModifiedDocument198 pages【Compiled】New Manual ModifiedRahul NundlallNo ratings yet
- Tension and Compression in TrussesDocument10 pagesTension and Compression in TrussespoojapavithranNo ratings yet
- Application of STATICSDocument3 pagesApplication of STATICSChristian SumanguidNo ratings yet
- Vertical Vessel AISCDocument9 pagesVertical Vessel AISCRajveer SinghNo ratings yet