Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer
Uploaded by
Sunsong31Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer
Uploaded by
Sunsong31Copyright:
Available Formats
13.
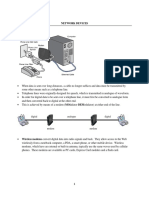
10 Network Devices
Modem(Modulation/Demodulation):
a) A computer peripheral that allows you to connect and
communicate with other computers via telephone lines. It changes
digital signal into analog signal and vice versa for transmission over
telephone line.
b) Uses t hree types of modulation techniques for transmission of
data:
i) AM(Amplitude Modulation)
ii) FM(Frequency Modulation)
iii) PM(Phase Modulation)
c) Converts digital signals into A/F(Audio Frequency) tones which are
in the frequency range that the telephone lines can transmit.
d) Modems come in two varieties:
i) Internal Modems: fixed within the computer
ii) External Modems: connected as peripherals
RJ-45(Registered Jack-45)
a) Eight wire connector used to connect computer on LANs especially
Ethernet
b) Looks very much similar to the telephone wires connector but it is
wider than that.
Ethernet card
a) LAN architecture developed by Xerox Corp. and DEC and Intel.
b) Ethernet uses star or bus topologies and can support data transfer
rates up to 10 Mbps.
c) Contains connection for either coaxial or twisted pair cables or both.
Hub
a) Hardware device used to connect several computers together.
b) Similar to a concentrator a device that provides a central
connection point for cables from different points.
c) Hubs can be of two types-
i) Active hubs- electrically amplify the signals as it moves from
one connected device to another.
ii) Passive hubs- allow the signal to pass from one computer to
another without any change.
Switch
a) Used to segment networks into different subnetworks called
subnets or LAN Segment.
b) Responsible for filtering i.e. transforming data in a specific way and
forwarding packets.
c) Support any packet protocol.
Repeater
a) Device that amplifies and restores signals for long distance
transmission.
b) Two types :
i) Amplifier : merely amplifies the incoming signal(and any
concurrent noise) over the network.
ii) Signal repeater :collects inbound packets and then
transmits them as if they were starting from their source
station.
Bridge
a) A device that establishes an intelligent connection between two
local networks with same standard but with different types of
cables.
b) Smart enough to know which computers are on which side of
the bridge
Router
a) A Router is a network device that is used to separate different segments in a
network to improve performance and reliability. A router works like a bridge but
can handle different protocols.
b) Differs from a bridge in a way that former uses logical addresses and the latter
uses physical addresses.
Gateway
Gateway node often acts as a proxy server and a firewall.
A Gateway is a network device that connects dissimilar net-works. It establishes
an intelligent connection between a local network and external networks with completely
differently structures.
WiFi Card
An internal or external Local Area Network adapter with a built-in wireless radio
and antenna.
Allows you to setup your work station or home office with considering the
proximity or availability of hard line network access.
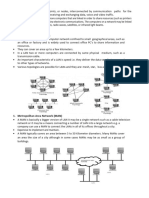
13.11 LAN Design
Network design problem consists of the following three general element :
Enviornment given- Location of hosts, servers, terminals, the projected traffics.
Performance constraints-Network reliability, traffic, throughput, and host/client computer
speeds.
Internetworking variables- Network topologies, and capacities.
>>>NOTE:- The 80-20 rule: in a properly designed small to medium-sized network
environment, 80 percent of the traffic on a given network segment is local (destined for a
target in the same work-group), and not more than 20 percent of the network traffic need
to move across a backbone (the spine that connects various segments or subnetworks)
LAN Design Faqs
1) When/ why hubs and switches are used?
Answer) Whenever one needs to form a network among multiples nodes network devices, a device
like hub or switch is needed.
2) How does a hub works?
Answer) Hub is a multiport repeater, which broadcasts all information to all other ports. It causes
unnecessary network traffic. Hence it is called non-intelligent or dump device. [You can think of a
hub as a dump postman who does not know the house number, so he goes to every house and asks
the owner if the letter is his?]
3) Why repeaters?
Answer) When a signal travels along a cable, the tends to lose strength. A repeater is a device that
boots or regenerates a networks signal as it passes through and rebroadcasts it.
4) When are repeaters required?
Answer) Repeaters are mainly used for extending the range when the total length of network cable
exceeds the standards set, for example, in fast Ethernet, this is 100 metres. And if you have to
connect two computers that are more than 100 metres apart you need repeater.
These days, there are wireless repeaters also available. Wireless repeaters extend the range of
wireless signals.
5) How does switch works?
Answer) A switch has same as that of a hubs- i.e., to connect multiple computers. But a switch is
a smart device (not dump as hub) .It can identify the intended destination ( use mail address for
this ) and send the information only to the target computer(s). [Here, a switch is like a smart
postman who knows the addresses of the recipients and goes only to the house where the letter
is to be delivered. ]
A switch does not share the media /bandwidth among all its connected computers.
No unnecessary traffic generated
Can send and receive information at the same time.
Switches, however, expensive than hubs.
HUB SWITCH
Repeats the incoming traffic to all
connections.
Sends traffic only to appropriate
connections.
Offer single lane connection, hence either
send or receive at a time.
Establishes two-lane communication,
facilitating send and receives at the same
time.
Shares bandwidth among its connection Does not share bandwidth, each connection
gets full bandwidth.
Inexpensive choice. Expansive than hubs.s
You might also like
- Short Stories For Children PDFDocument44 pagesShort Stories For Children PDFazhagaan100% (16)
- Dell EMC 2000 Networking 2020Document30 pagesDell EMC 2000 Networking 2020abdulmuizzNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Limited Power of Attorney: (Initial and Check The Box If Applicable)Document3 pagesLimited Power of Attorney: (Initial and Check The Box If Applicable)Sunsong31No ratings yet
- 67HM FZ3 PDFDocument24 pages67HM FZ3 PDFmarcio almeidaNo ratings yet
- Leader LDC-823A - ManualDocument16 pagesLeader LDC-823A - Manual김박사No ratings yet
- EP 301 - Computer Networking FundamentalsDocument18 pagesEP 301 - Computer Networking FundamentalsShazul Afizi Zulkiflee100% (1)
- Computer Networking Devices: Network Interface Card (NIC)Document9 pagesComputer Networking Devices: Network Interface Card (NIC)Kelvin KujoNo ratings yet
- DCN FileDocument50 pagesDCN FileArpit KumarNo ratings yet
- Drive Test Problems (Part 2)Document25 pagesDrive Test Problems (Part 2)Abdelrahman.Mostafa100% (7)
- Sicam Sat 1703 Acp - Rtu PDFDocument12 pagesSicam Sat 1703 Acp - Rtu PDFtdusko100% (2)
- Computer Network Notes Class 12Document13 pagesComputer Network Notes Class 12om100% (1)
- Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) Full TextDocument62 pagesAutomated Guided Vehicle (AGV) Full Textazriffaris100% (2)
- UNIT - 1 NW FundamentalsDocument72 pagesUNIT - 1 NW Fundamentalsyimanuel AdNo ratings yet
- Network Devices - PPSXDocument37 pagesNetwork Devices - PPSXMaricris Bejer LopezNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument15 pagesNetwork DevicesShilpa PutanikarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NetworkingDocument17 pagesIntroduction To NetworkingGraceNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks-Lab: Hareem Aslam Hareem - Aslam@pucit - Edu.pkDocument24 pagesComputer Networks-Lab: Hareem Aslam Hareem - Aslam@pucit - Edu.pkHareem AslamNo ratings yet
- CN Connecting DevicesDocument3 pagesCN Connecting DevicesLife SayingsNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Computer Networks: Types, Components & TopologiesDocument19 pagesIntroduction to Computer Networks: Types, Components & TopologiesscribdNo ratings yet
- Topic 6b Network Devices PDFDocument24 pagesTopic 6b Network Devices PDFTheo NdedaNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Notes Class 12Document14 pagesComputer Network Notes Class 12Mohit HoodaNo ratings yet
- ModemDocument24 pagesModemHrithik ReignsNo ratings yet
- AS CS Chapter 2 ContinuedDocument57 pagesAS CS Chapter 2 ContinuedPriyanka LaadNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument5 pagesNetwork DevicesPiyush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Study Major Network ComponentsDocument9 pagesStudy Major Network ComponentsSandip MouryaNo ratings yet
- Practical: 01 Aim: To Study Various Networking Components. Major Computer Network ComponentsDocument9 pagesPractical: 01 Aim: To Study Various Networking Components. Major Computer Network ComponentsSandip MouryaNo ratings yet
- Different Networking Devices: Passive Hub Active HubDocument9 pagesDifferent Networking Devices: Passive Hub Active HubRodryan Karl GarayNo ratings yet
- Network Devices ExplainedDocument20 pagesNetwork Devices Explainedsanamsuri369No ratings yet
- CPT 1Document184 pagesCPT 1Alan VikramNo ratings yet
- Network Devices: Modems, Switches, Routers, Bridges, Nics, HubsDocument28 pagesNetwork Devices: Modems, Switches, Routers, Bridges, Nics, HubsVensia MohammedNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NetworkDocument52 pagesFundamentals of Networkumurita37No ratings yet
- Lab Assignment: 3: Be 5 Section B Subject: CCNDocument6 pagesLab Assignment: 3: Be 5 Section B Subject: CCNIqraJahanNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument5 pagesNetwork Devicesmitalee2502No ratings yet
- Common Network Connectivity Devices ExplainedDocument5 pagesCommon Network Connectivity Devices ExplainedRenz Kenn BalagtasNo ratings yet
- XII - Computer Networks - NetworkDevicesDocument30 pagesXII - Computer Networks - NetworkDevicesLakshya NayakNo ratings yet
- G12AutumnQuiz1 Worksheet 1Document3 pagesG12AutumnQuiz1 Worksheet 1shrikant19829No ratings yet
- Components of Computer NetworksDocument7 pagesComponents of Computer NetworksLaurNo ratings yet
- Network Tools and Testing DevicesDocument9 pagesNetwork Tools and Testing DevicesCamilleNo ratings yet
- Networking DevicesDocument22 pagesNetworking DevicesAlexander PhiriNo ratings yet
- Distributed Communications SystemsDocument36 pagesDistributed Communications SystemsRavi AroraNo ratings yet
- Networking and Internetworking DevicesDocument21 pagesNetworking and Internetworking DevicesDip DasNo ratings yet
- Web Application Class XI Unit 1 NotesDocument14 pagesWeb Application Class XI Unit 1 NotesNaina Kanojia90% (10)
- Activity 5 CNDocument15 pagesActivity 5 CNshifa dafedarNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument27 pagesComputer NetworkAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- DCN LAB WORK ON NETWORK DEVICESDocument6 pagesDCN LAB WORK ON NETWORK DEVICESBalaram Pratap KotyadaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Physical LayerDocument29 pagesMODULE 1 Physical LayerAditya RanjanNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer Networking: ContentDocument42 pagesData Communication and Computer Networking: ContentMubaarak NuurNo ratings yet
- Network Types DevicesDocument4 pagesNetwork Types DevicesM.n KNo ratings yet
- CN Lab2 102117105Document9 pagesCN Lab2 102117105kavya aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Abhijay - CN EXP1 Network DevicesDocument11 pagesAbhijay - CN EXP1 Network Devicesshweta joshiNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument3 pagesNetwork DevicesNhyat SeatNo ratings yet
- Network Devices: Digital Digital AnalogueDocument6 pagesNetwork Devices: Digital Digital AnalogueAbygayle IveyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document9 pagesLesson 5Kean Rafael MarianoNo ratings yet
- Communication DevicesDocument22 pagesCommunication Deviceshadirehman488No ratings yet
- What Is A Network?Document9 pagesWhat Is A Network?amrit singhaniaNo ratings yet
- Networking Devices: 1. Network HubDocument3 pagesNetworking Devices: 1. Network HubSaurav PooniaNo ratings yet
- Netcom Lab Cat 1 20bci0115Document5 pagesNetcom Lab Cat 1 20bci0115Finance IEEE-SSITNo ratings yet
- Networking (26 09 2020)Document24 pagesNetworking (26 09 2020)jdubey4258No ratings yet
- There Are Different Types of Servers, For Example:: Prepared by MR: Hussain KDocument14 pagesThere Are Different Types of Servers, For Example:: Prepared by MR: Hussain Khussain korirNo ratings yet
- Notes On Computer NetworkDocument35 pagesNotes On Computer NetworkKailash Chand SharmaNo ratings yet
- Networks and The Effects of Using ThemDocument22 pagesNetworks and The Effects of Using ThemMohd RafeeqNo ratings yet
- Understanding Data Link Layer SwitchesDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Data Link Layer SwitchesReymond D. SeNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking Individual Assignments: Section:-"A"Document9 pagesComputer Networking Individual Assignments: Section:-"A"Abi DemNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Submitted By: Mr. Iqbal Isha Salhan Cse 4 SEM REGD. NO. 1407217Document27 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By: Mr. Iqbal Isha Salhan Cse 4 SEM REGD. NO. 1407217Gagandeep MehtaNo ratings yet
- Lec 15networking DevicesDocument33 pagesLec 15networking DevicesJyoti SinghNo ratings yet
- Networking Basics: Topologies, Switches, RoutersDocument50 pagesNetworking Basics: Topologies, Switches, RoutersDeepika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Social NDocument10 pagesSocial NSunsong31No ratings yet
- AnMock Poll CertificateDocument1 pageAnMock Poll CertificateSunsong31No ratings yet
- For Ma Tio N Onl Y: Biotechnology Use and Development Survey - 2005Document16 pagesFor Ma Tio N Onl Y: Biotechnology Use and Development Survey - 2005Sunsong31No ratings yet
- The Mass Media & The Youth: Shaping Attitudes, Values and ThinkingDocument24 pagesThe Mass Media & The Youth: Shaping Attitudes, Values and ThinkingSunsong31No ratings yet
- Ans1 The Prime Purpose of CDocument3 pagesAns1 The Prime Purpose of CSunsong31No ratings yet
- CH 12Document39 pagesCH 12Sunsong31No ratings yet
- CRM and Information Visualization: Data Mining and Campaign ManagementDocument66 pagesCRM and Information Visualization: Data Mining and Campaign ManagementSunsong31No ratings yet
- Question Spaces EnglishDocument3 pagesQuestion Spaces EnglishSunsong31No ratings yet
- Corrige ND UmDocument2 pagesCorrige ND UmSunsong31No ratings yet
- CWE SPL IV Detail - Advt - 17.09.2014 PDFDocument26 pagesCWE SPL IV Detail - Advt - 17.09.2014 PDFparagsavaneNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratios and Bank Financing: To Contact Your Local Ledgers Representative Please Call 1.888.470.0772 - 1Document9 pagesFinancial Ratios and Bank Financing: To Contact Your Local Ledgers Representative Please Call 1.888.470.0772 - 1Sanjay ShelarNo ratings yet
- By Nidhi Srivastava: Business Plan-Blue PrintDocument36 pagesBy Nidhi Srivastava: Business Plan-Blue PrintSunsong31No ratings yet
- Contact No Email ID: Candidate NameDocument4 pagesContact No Email ID: Candidate NameSunsong31No ratings yet
- Appeal and Revision in Taxation: Nidhi Srivastava Aashima Bhutani Divya Singh Tripti NegiDocument19 pagesAppeal and Revision in Taxation: Nidhi Srivastava Aashima Bhutani Divya Singh Tripti NegiSunsong31No ratings yet
- Greg Simons The Role of Media in A DemocracyDocument10 pagesGreg Simons The Role of Media in A DemocracySunsong31No ratings yet
- Civil Services Magazine DEC'14Document120 pagesCivil Services Magazine DEC'14Er RameshNo ratings yet
- 2005 Mta Ed Seminar PoserDocument58 pages2005 Mta Ed Seminar PoserSunsong31No ratings yet
- Brief History of Mass MediaDocument39 pagesBrief History of Mass MediaSunsong31No ratings yet
- Akshit Manhas 121001061645 Phpapp01Document37 pagesAkshit Manhas 121001061645 Phpapp01Sunsong31No ratings yet
- Catherine Murray Fall 2003: CMNS-130 C.A. MurrayDocument26 pagesCatherine Murray Fall 2003: CMNS-130 C.A. MurraySunsong31No ratings yet
- 9social Science Sample Papers 1Document20 pages9social Science Sample Papers 1Shanu PowerNo ratings yet
- RBI scam email promises ₹49 crore lottery winDocument3 pagesRBI scam email promises ₹49 crore lottery winSunsong31No ratings yet
- Learning Proverbs Using OFFICE Applications: Produced By: Hasanov Zahir Nurutdinov RuslanDocument23 pagesLearning Proverbs Using OFFICE Applications: Produced By: Hasanov Zahir Nurutdinov RuslanSunsong31No ratings yet
- Byju Hyd. Schedule - UpdatedDocument1 pageByju Hyd. Schedule - UpdatedSunsong31No ratings yet
- Mass MediaDocument30 pagesMass MediaSunsong31No ratings yet
- NET EXAM Paper 1Document27 pagesNET EXAM Paper 1shahid ahmed laskar100% (4)
- Government in Mizoram: Governor of Mizoram: Dr. Kamla BeniwalDocument2 pagesGovernment in Mizoram: Governor of Mizoram: Dr. Kamla BeniwalSunsong31No ratings yet
- Altera Cyclone IV FPGA C402 DocumentDocument17 pagesAltera Cyclone IV FPGA C402 DocumentJhonny ChiriNo ratings yet
- Understanding A Simple Operating System: Chapter 1: Starting Up SOS 3Document53 pagesUnderstanding A Simple Operating System: Chapter 1: Starting Up SOS 3mmxy_1No ratings yet
- MD06 TVInstruccionesDocument43 pagesMD06 TVInstruccionesDaniel RiberaNo ratings yet
- CXP-4MT-12: 4.3-10 Male Connector For 1/2" Annular CableDocument1 pageCXP-4MT-12: 4.3-10 Male Connector For 1/2" Annular CableCesar RinconNo ratings yet
- 02 - Dioda - Sedra4 Ch03Document97 pages02 - Dioda - Sedra4 Ch03Rizky WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Advance Smart Series Diagramas EsquematicosDocument12 pagesAdvance Smart Series Diagramas Esquematicosfredy ruiz0% (1)
- Man 1200S24Document14 pagesMan 1200S24RameshNo ratings yet
- HD Series™ High Performance Dish Antenna: Hdda5WDocument2 pagesHD Series™ High Performance Dish Antenna: Hdda5Wjavierdb2012No ratings yet
- Circuit Mate 9020 - 20 MHZ OscilloscopeDocument11 pagesCircuit Mate 9020 - 20 MHZ OscilloscopedecalusNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 4 - DC CircuitsDocument46 pagesLecture Notes 4 - DC CircuitsSharveen GopalNo ratings yet
- This Is Brochure-Trafo-Auto-Centrado-type-DryDocument1 pageThis Is Brochure-Trafo-Auto-Centrado-type-DryfendynovapamelaNo ratings yet
- PATH: P - MU0418A-MU0281/1D-V: Open - Dry - AreaDocument2 pagesPATH: P - MU0418A-MU0281/1D-V: Open - Dry - AreaAnjul RamachandranNo ratings yet
- MESH-2100 User ManualDocument2 pagesMESH-2100 User ManualCarlos Daniel CruzNo ratings yet
- SFS4525T N-Channel and P-Channel MOSFET DatasheetDocument2 pagesSFS4525T N-Channel and P-Channel MOSFET DatasheetAntonio Negrete100% (1)
- Radar Signal Detection Using TMS320C50Document82 pagesRadar Signal Detection Using TMS320C50mgitecetechNo ratings yet
- An Ultra-Low-Noise Electrical-Potential Probe For Human-Body ScanningDocument8 pagesAn Ultra-Low-Noise Electrical-Potential Probe For Human-Body ScanningIgnacy RogońNo ratings yet
- Arduino Controlled ATX Power SupplyDocument7 pagesArduino Controlled ATX Power Supplyolaolaolaola123No ratings yet
- AN010 Bias Web PubDocument7 pagesAN010 Bias Web PubGs SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Compare 22-32 inch LCD TVsDocument4 pagesCompare 22-32 inch LCD TVssuni80No ratings yet
- ANT-ATD451800-1774 DatasheetDocument2 pagesANT-ATD451800-1774 DatasheetАнтонNo ratings yet
- Tea 1601Document27 pagesTea 1601Leonel Edgardo MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Maxon 49-SX 2-Way Radio MANUALDocument16 pagesMaxon 49-SX 2-Way Radio MANUALRich RitterbuschNo ratings yet
- ACS800 ReadmeDocument4 pagesACS800 Readmeyasararafat1No ratings yet
- Hitachi L26A01 & L32A01 LCD TV SM - No - 0245E ServicemanualDocument68 pagesHitachi L26A01 & L32A01 LCD TV SM - No - 0245E ServicemanualJennySeifertsNo ratings yet
- 30V P-Channel MOSFET Technical DocumentDocument5 pages30V P-Channel MOSFET Technical DocumentYonatan RivadeneyraNo ratings yet