Professional Documents
Culture Documents
W5 Warehouse
Uploaded by
elfaziaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
W5 Warehouse
Uploaded by
elfaziaCopyright:
Available Formats
3/10/2014
1
Warehouse management
(Manajemen Pergudangan)
Week 5
Storage Fundamentals in Inventory
Strategy
4-37
P
L
A
N
N
I
N
G
O
R
G
A
N
I
Z
I
N
G
C
O
N
T
R
O
L
L
I
N
G
Transport Strategy
Transport fundamentals
Transport decisions
Customer
service goals
The product
Logistics service
Ord . proc. & info. sys.
Inventory Strategy
Forecasting
Inventory decisions
Purchasing and supply
scheduling decisions
Storage fundamentals
Storage decisions
Location Strategy
Location decisions
The network planning process
P
L
A
N
N
I
N
G
O
R
G
A
N
I
Z
I
N
G
C
O
N
T
R
O
L
L
I
N
G
Transport Strategy
Transport fundamentals
Transport decisions
Customer
service goals
The product
Logistics service
Ord . proc. & info. sys.
Inventory Strategy
Forecasting
Inventory decisions
Purchasing and supply
scheduling decisions
Storage fundamentals
Storage decisions
Location Strategy
Location decisions
The network planning process
3/10/2014
2
Why firm need storage and material
handling?
11-38
Do firm really need storage and
material handling as a part of the
Logistics system?
Storage is an economic convenience not
a necessity
Inventory to improve supply and
demand coordinations warehouse
and material handling are needed
maintaining inventories
Reasons for storage
11-39
To reduce transportation-production costs
To coordinate supply and demand
To assist in the production process
To assist in the marketing process
3/10/2014
3
Transportation-production costs
reductions
11-40
Ship Direct
from Plant
Ship through 35
warehouses
Change in
costs
Production costs
500,000 425,000 -75,000
Transportation costs
- To warehouse
0 50,000 50,000
- To local area
250,000 100,000 -150,000
Warehouse costs
0 75,000 75,000
Total
750,000 650,000 -100,000
Coordination of supply and demand
Food, beverage and cigarette
Steel industry
11-41
3/10/2014
4
Production needs
Warehousing may be part of the production
process
Wine, cheeses
Cigarette
11-42
Marketing considerations
Warehousing is needed to deliver rapidly to the
customers and improve customer services (out of
stock)
11-43
3/10/2014
5
Storage functions
Holding
Consolidation
Break-bulk
Mixing (merge in translit)
11-44
Consolidation
warehouse
A
A B C D
B
C
D
Manufacturer A
Manufacturer B
Manufacturer C
Manufacturer D
10,000 lb.
8,000 lb.
15,000 lb.
7,000 lb.
40,000 lb.
Customer
Consolidation Warehouse
Similar to a merge-in-
transit facility
3/10/2014
6
Storage Cost Savings
Direct shipments to customers
MANUFACTURER
SHIPPING
WEIGHT
(lb.)
LTL RATE TO
CUSTOMER COST
A 10,000 $2.00/cwt. $200
B 8,000 1.80 133
C 15,000 3.40 510
D 7,000 1.60 112
Total $966
Storage Cost Savings (Contd)
Shipments through a distribution center
MANUFACTURER
SHIPPING
WEIGHT (lb.)
LTL RATE TO
DISTRIBUTION
CENTER
TOTAL LTL
A 10,000 $0.75
$75
B 8,000 0.60
48
C 15,000 1.20
180
D 7,000 0.50
35
Total 40,000
DISTRIBUTION
WAREHOUSE CHARGE
TL RATE FROM
DISTRIBUTION
WAREHOUSE TO
CUSTOMER TOTAL TL COST
$10 $1.00/cwt. $100 $185
8 1.00 80 136
15 1.00 150 345
7 1.00 70 112
$778
11-9
3/10/2014
7
Distribution
warehouse
Manufacturer Customer B
Customer C
Customer A
Low rate TL
shipment
LTL
Distribution, Break Bulk, or Pool Point
Warehouse
Warehouse may or
may not hold
inventories
Distribution
warehouse
Manufacturer B
Customer Y
Customer X
Product B
Product Mixing
Manufacturer A
Manufacturer C
3/10/2014
8
Warehouse functions
as buffer stock to anticipate fluctuations
/uncertainties demands
to consolidate transportations for economic scale
to minimise response time for demand fulfillments
to keep quality and safety of raw
material/parts/finished products that are stored
Storage functions are performed in an attempt to
reduce transportation, production, and purchasing
costs, which justify their added expense.
Storage alternatives
Ownership
Leasing
Rental
In-transit
11-51
3/10/2014
9
Types of Warehouse (types of products)
raw materials
finished goods
supplies
repair/spare parts
Arnold and Chapman 2008
Types of Warehouse (types of level)
Main warehouse
Consumable Item Storage
Critical item storage
Cool room
Secondary warehouse
Customs Process Storage
Empty basket storage
Chemical Storage
Temporary storage
Lube oil storage
Drilling and Completion Storage
Pipe yard
Case in oil company
3/10/2014
10
Types of Warehouse (flows)
Mixing or consolidation warehouse
Breakbulk warehouse
Drilling and Completion Storage
3/10/2014
11
Pipe Yard
Manufacturer A
Manufacturer A & B
Manufacturer A, B & C
Manufacturer A, B, C & D
P
e
r
c
e
n
t
a
g
e
o
f
u
s
a
b
l
e
w
a
r
e
h
o
u
s
e
c
a
p
a
c
i
t
y
Time, months
Balancing the Load on a Public
Warehouse
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
J F M A M J J A S O N D
Ballou (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
3/10/2014
12
Space Comparison
Ownership alternative
Less expensive under high utilization
High degree of control over operations
Benefits of real estate ownership
Space may be converted to uses other than storage
Rental alternative
No fixed investment
Lower cost under seasonal or low utilization of an owned facility
Location flexibility
Ballou (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
Ballou (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
A Low Throughput, Holding Warehouse
Semipermanent
storage bay
Product
Inbound and
outbound
3/10/2014
13
Semi-permanent
storage bay
Product
Order picking and product mixing bays
I
n
b
o
u
n
d
O
u
t
b
o
u
n
d
A
B
C
D
C A
Replenishment
Order-picking
route
A High Throughput, Distribution
Warehouse
Ballou (2004) Prentice Hall, Inc.
END
You might also like
- A Storage and Material Handling Ballou11Document19 pagesA Storage and Material Handling Ballou11Uttkarsh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Warehousing DecisionsDocument34 pagesWarehousing DecisionschiragNo ratings yet
- Total Cost AnalysisDocument10 pagesTotal Cost Analysisayane_sendoNo ratings yet
- Ballou 03Document18 pagesBallou 03brunomarinoneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 WarehousingDocument52 pagesLesson 2 WarehousingSilvi MustikawatiNo ratings yet
- Storage and Handling Decisions ChapterDocument26 pagesStorage and Handling Decisions ChapterRandy YanNo ratings yet
- WarehousingDocument41 pagesWarehousingutkarsh kumarNo ratings yet
- John Darlington - VATX - 10 TOCPA - Feb 2014 - India - FINDocument67 pagesJohn Darlington - VATX - 10 TOCPA - Feb 2014 - India - FINJelena FedurkoNo ratings yet
- 04 A SCM Mod E 2014 v1Document38 pages04 A SCM Mod E 2014 v1mansie139No ratings yet
- Racking SystemDocument76 pagesRacking SystemmlogvijayNo ratings yet
- Consolidation WarehousingDocument22 pagesConsolidation WarehousingJoshua AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Ballou 01Document25 pagesBallou 01rajuahmedt100% (1)
- Designing The Distribution Network in A Supply ChainDocument67 pagesDesigning The Distribution Network in A Supply ChainkristianNo ratings yet
- JLV - PD06-5 Logistics and The Supply Chain - Movement of Goods AssignmentDocument9 pagesJLV - PD06-5 Logistics and The Supply Chain - Movement of Goods AssignmentjannickvyNo ratings yet
- DHL Supply ChainDocument28 pagesDHL Supply ChainJohn Chauca100% (1)
- Warehouse ManagementDocument28 pagesWarehouse ManagementRavi Singh100% (2)
- Making SAP Work For Your Supply Chain: Tuesday 11 September 2012Document65 pagesMaking SAP Work For Your Supply Chain: Tuesday 11 September 2012vgahrinNo ratings yet
- Kuliah - 10 Dan 11 Logistics-Warehousing1Document67 pagesKuliah - 10 Dan 11 Logistics-Warehousing1Syukri SyahabNo ratings yet
- Logistics Management: Warehousing Customer Service Material HandlingDocument35 pagesLogistics Management: Warehousing Customer Service Material HandlingGanesh GunjalNo ratings yet
- New Zealand All Natural Ice Cream (NAN)Document16 pagesNew Zealand All Natural Ice Cream (NAN)Ashish MohiteNo ratings yet
- Module 5.session 29-31. WarehousingDocument21 pagesModule 5.session 29-31. WarehousingAshish AimaNo ratings yet
- Design Opt Unit-3Document35 pagesDesign Opt Unit-3JayaprasannaNo ratings yet
- DHL PDFDocument28 pagesDHL PDFbhatiaharryjassiNo ratings yet
- Procurement CH 5Document55 pagesProcurement CH 5KalkidanNo ratings yet
- PPP SCM Chapter1 (Supply Chain Management)Document29 pagesPPP SCM Chapter1 (Supply Chain Management)Mahfuz Raihan100% (1)
- Supply Chain Management: Facility LocationDocument32 pagesSupply Chain Management: Facility LocationkoolyarNo ratings yet
- 2 LogisticsDocument24 pages2 LogisticsViki ChandranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Warehousing 97 03 FormatDocument20 pagesChapter 3 Warehousing 97 03 Formatnikita sharmaNo ratings yet
- Ballou 09Document105 pagesBallou 09Andrew RhoNo ratings yet
- Pallet Standardisation in FMCG IndustryDocument5 pagesPallet Standardisation in FMCG IndustryVirendra Vaswani100% (1)
- Distribution and Fulfillment Centers: by Dr. Albert TanDocument56 pagesDistribution and Fulfillment Centers: by Dr. Albert TanlimyisyuenNo ratings yet
- WarehousingDocument47 pagesWarehousingTonyo LinaNo ratings yet
- Total Cost of Ownership of Car ModelsDocument33 pagesTotal Cost of Ownership of Car ModelsC100% (1)
- Warehousing Basics ExplainedDocument31 pagesWarehousing Basics ExplainedSneha RMNo ratings yet
- Case Study Brief 2022Document9 pagesCase Study Brief 2022Tannusha BasaboinaNo ratings yet
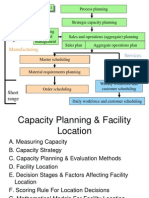
- Strategic capacity planning and facility location optimizationDocument59 pagesStrategic capacity planning and facility location optimizationprateekgenext9754No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Managing Inventory Flows in The Supply Chain4962Document70 pagesChapter 6 Managing Inventory Flows in The Supply Chain4962Sanjay UkalkarNo ratings yet
- Applying Lean Concepts-Wp PDFDocument6 pagesApplying Lean Concepts-Wp PDFEdgar PedrazaNo ratings yet
- WAREHOUSING BENEFITSDocument8 pagesWAREHOUSING BENEFITSHarshNo ratings yet
- Evidence 4 SummaryDocument8 pagesEvidence 4 SummaryPoly CancinoNo ratings yet
- DHL's Use of E-Business StandardsDocument15 pagesDHL's Use of E-Business StandardsNivedita Sharma100% (1)
- Long Range Intermediate Range: ManufacturingDocument59 pagesLong Range Intermediate Range: ManufacturingManal VermaNo ratings yet
- Shell PennzoilDocument39 pagesShell PennzoilNadia HachkiNo ratings yet
- Warehouse Management SystemDocument82 pagesWarehouse Management SystemElyaas Zerdi91% (11)
- BatDocument14 pagesBatnakibosmanNo ratings yet
- An Insight: Logistics in SCMDocument81 pagesAn Insight: Logistics in SCMSagarika Roy0% (1)
- Distribution StrategiesDocument7 pagesDistribution StrategiesSai Dheerendra PalNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Lean Manufacturing PrinciplesDocument24 pagesIntroduction to Lean Manufacturing PrinciplesCosmin RaducanuNo ratings yet
- Bis Corporation Network Planning CaseDocument19 pagesBis Corporation Network Planning CaseAbhishek Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle Kaizen TCDocument71 pagesProduct Life Cycle Kaizen TCLorie Grace LagunaNo ratings yet
- Expert Insight: Optimizing Warehouse Facility DesignDocument4 pagesExpert Insight: Optimizing Warehouse Facility DesignMd Abdullah Al ArmanNo ratings yet
- Warehouse ManagementDocument8 pagesWarehouse ManagementPrakhar SharmaNo ratings yet
- LOGMGT SUPPLYCHAIN OVRVDocument80 pagesLOGMGT SUPPLYCHAIN OVRVBradley FernandesNo ratings yet
- Maritime Transport Part4 9781789662467Document22 pagesMaritime Transport Part4 9781789662467Filiz MizrakNo ratings yet
- IB-int Log1Document41 pagesIB-int Log1vivek_antilNo ratings yet
- Reducing logistics costs through strategic decision makingDocument16 pagesReducing logistics costs through strategic decision makingGajendra BeheraNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Refinery Relocation Projects: 5-Phases of Project ManagementFrom EverandPetroleum Refinery Relocation Projects: 5-Phases of Project ManagementNo ratings yet
- Capital Equipment Purchasing: Optimizing the Total Cost of CapEx SourcingFrom EverandCapital Equipment Purchasing: Optimizing the Total Cost of CapEx SourcingNo ratings yet
- Physical Distribution and Logistics Concepts ExplainedDocument108 pagesPhysical Distribution and Logistics Concepts ExplainedAzhar HussainNo ratings yet
- USPSDocument18 pagesUSPSSamuel100% (2)
- Agri Supply ChainDocument249 pagesAgri Supply ChainAlok P SinghNo ratings yet
- Oracle Shipping Software - Oracle Multi Carrier ShippingDocument2 pagesOracle Shipping Software - Oracle Multi Carrier ShippingshipconsoleNo ratings yet
- Walmart Supply ChainDocument35 pagesWalmart Supply ChainYassine Chakrad0% (1)
- Effective Price Benchmarking With LTL's Most Popular Base RateDocument12 pagesEffective Price Benchmarking With LTL's Most Popular Base RateDeepak MishraNo ratings yet
- What Does Fedex Deliver?Document17 pagesWhat Does Fedex Deliver?duckythiefNo ratings yet
- Supplier Shipping User GuideDocument33 pagesSupplier Shipping User GuideAndreea Popescu100% (2)
- Senior Logistics Executive in Dallas TX Resume Thomas JonesDocument3 pagesSenior Logistics Executive in Dallas TX Resume Thomas JonesThomasJones1No ratings yet
- Asom PPT - Fedex FinalDocument15 pagesAsom PPT - Fedex FinalSaptarshi SarkarNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Performance Final ProjectDocument27 pagesSupply Chain Performance Final Projectpktun0% (1)
- Maintenance Cost Reduction Project: Solving Problems With Labor and Maintenance CostsDocument24 pagesMaintenance Cost Reduction Project: Solving Problems With Labor and Maintenance CostsTee YeesiangNo ratings yet
- Cross Docking Functionality in SAP ECC 6Document3 pagesCross Docking Functionality in SAP ECC 6Pranaya Barik100% (3)
- 03 PickupserviceWSDLGuide - v2014Document168 pages03 PickupserviceWSDLGuide - v2014agsvdaNo ratings yet
- FED EX Service Guide 2017Document198 pagesFED EX Service Guide 2017surfing77100% (1)
- D4169 16Document17 pagesD4169 16Alevj Db88% (17)
- Vivek Ranjan Das - CV - 0717 PDFDocument1 pageVivek Ranjan Das - CV - 0717 PDFVivek Ranjan DasNo ratings yet
- Truck Terms GlossaryDocument15 pagesTruck Terms GlossaryJIMJEO100% (1)
- VRL 2015Document112 pagesVRL 2015Jupe JonesNo ratings yet
- Network PlanningDocument59 pagesNetwork PlanningVignesh ManickamNo ratings yet
- Transport Fundamentals & ModesDocument40 pagesTransport Fundamentals & ModesNashphapaKanchanamuntanaNo ratings yet
- Sanga E-Transportation Product Marketing PlanDocument29 pagesSanga E-Transportation Product Marketing PlanraiderNo ratings yet
- D4169-16 - Cargo - TranspDocument36 pagesD4169-16 - Cargo - TranspRajeshNo ratings yet
- Walmart's Retail LinkDocument9 pagesWalmart's Retail LinkVedNo ratings yet
- Purchasing Lecture For SCM Class 1Document42 pagesPurchasing Lecture For SCM Class 1aamirjewaniNo ratings yet
- ISTA GuidelinesDocument16 pagesISTA GuidelinestairelkNo ratings yet
- SAP For Logistics Service Provider ManagingDocument16 pagesSAP For Logistics Service Provider ManagingSuryanarayana TataNo ratings yet
- 2006 09 ArmstrongAssociates Whos Who INTL Vol 1Document189 pages2006 09 ArmstrongAssociates Whos Who INTL Vol 1patel_dipesh_p6019No ratings yet
- General Freight Trucking Business PlanDocument37 pagesGeneral Freight Trucking Business Planlorenneth67% (3)
- Logistic Management of Gati: Submitted By:-Vinay TiwariDocument24 pagesLogistic Management of Gati: Submitted By:-Vinay Tiwarivtiwari2No ratings yet