Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Optical and Microwave Lab Manuual
Uploaded by
ManiKandanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Optical and Microwave Lab Manuual
Uploaded by
ManiKandanCopyright:
Available Formats
EC2402 OPTICAL COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING
UNIT I INTRODUCTION 9
Introduction, Ray theory transmission- Total internal reflection-Acceptance angle
Numerical aperture Skew rays Electromagnetic mode theory of optical propagation
EM waves modes in Planar guide phase and group velocity cylindrical fibers
SM fibers.
UNIT II TRANSMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF OPTICAL FIBERS 9
Attenuation Material absorption losses in silica glass fibers Linear and Non linear
Scattering losses - Fiber Bend losses Midband and farband infra red transmission
Intra and inter Modal Dispersion Over all Fiber Dispersion Polarization- non linear
Phenomena. Optical fiber connectors, Fiber alignment and Joint Losses Fiber Splices
Fiber connectors Expanded Beam Connectors Fiber Couplers.
UNIT III SOURCES AND DETECTORS 9
Optical sources: Light Emitting Diodes - LED structures - surface and edge emitters,
mono and hetero structures - internal - quantum efficiency, injection laser diode
structures - comparison of LED and ILD
Optical Detectors: PIN Photo detectors, Avalanche photo diodes, construction,
characteristics and properties, Comparison of performance, Photo detector noise -Noise
sources , Signal to Noise ratio , Detector response time.
UNIT IV FIBER OPTIC RECEIVER AND MEASUREMENTS 9
Fundamental receiver operation, Pre amplifiers, Error sources Receiver Configuration
Probability of Error Quantum limit.
Fiber Attenuation measurements- Dispersion measurements Fiber Refractive index
profile measurements Fiber cut- off Wave length Measurements Fiber Numerical
Aperture Measurements Fiber diameter measurements.
UNIT V OPTICAL NETWORKS 9
Basic Networks SONET / SDH Broadcast and select WDM Networks
Wavelength Routed Networks Non linear effects on Network performance
Performance of WDM + EDFA system Solitons Optical CDMA Ultra High Capacity
Networks.
TOTAL : 45 PERIODS
TEXT BOOKS
1. Optical Fiber Communication John M. Senior Pearson Education Second
Edition. 2007
2. Optical Fiber Communication Gerd Keiser Mc Graw Hill Third Edition. 2000
REFERENCES
1. J.Gower, Optical Communication System, Prentice Hall of India, 2001
2. Rajiv Ramaswami, Optical Networks , Second Edition, Elsevier , 2004.
3. Govind P. Agrawal, Fiber-optic communication systems, third edition, John Wiley
& sons, 2004.
4. R.P. Khare, Fiber Optics and Optoelectronics, Oxford University Press, 2007.
EC2305 TRANSMISSION LINES AND WAVEGUIDES
UNIT I FILTERS 9
The neper - the decibel - Characteristic impedance of Symmetrical Networks Current
and voltage ratios - Propogation constant, - Properties of Symmetrical Networks - Filter
fundamentals Pass and Stop bands. Behaviour of the Characteristic impedance.
Constant K Filters - Low pass, High pass band, pass band elimination filters - m -
derived sections Filter circuit design Filter performance Crystal Filters.
UNIT II TRANSMISSION LINE PARAMETERS 9
A line of cascaded T sections - Transmission lines - General Solution, Physical
Significance of the equations, the infinite line, wavelength, velocity, propagation,
Distortion line, the telephone cable, Reflection on a line not terminated in Zo, Reflection
Coefficient, Open and short circuited lines, Insertion loss.
UNIT III THE LINE AT RADIO FREQUENCY 9
Parameters of open wire line and Coaxial cable at RF Line constants for dissipation -
voltages and currents on the dissipation less line - standing waves nodes - standing
wave ratio - input impedance of open and short circuited lines - power and impedance
measurement on lines / 4 line, Impedance matching single and double-stub
matching circle diagram, smith chart and its applications Problem solving using Smith
chart.
UNIT IV GUIDED WAVES BETWEEN PARALLEL PLANES 9
Application of the restrictions to Maxwells equations transmission of TM waves
between Parallel plans Transmission of TE waves between Parallel planes.
Transmission of TEM waves between Parallel planes Manner of wave travel.
Velocities of the waves characteristic impedance Attenuators
UNIT V WAVEGUIDES 9
Application of Maxwells equations to the rectangular waveguide. TM waves in
Rectangular guide. TE waves in Rectangular waveguide Cylindrical waveguides. The
TEM wave in coaxial lines. Excitation of wave guides. Guide termination and resonant
cavities.
L: 45, T: 15, TOTAL= 60 PERIODS
TEXT BOOK
1. John D.Ryder, "Networks, lines and fields", Prentice Hall of India, 2nd Edition, 2006.
REFERENCES
1. E.C.Jordan, K.G. Balmain: E.M.Waves & Radiating Systems, Pearson Education,
2006.
2. Joseph Edminister, Schaums Series, Electromegnetics, TMH, 2007.
3. G S N Raju, Electromagnetic Field Theory and Transmission Lines, Pearson
Education, 2006.
EC2405 OPTICAL & MICROWAVE LAB L T P C 00 32
MICROWAVE EXPERIMENTS:
1. Reflex Klystron Mode characteristics
2. Gunn Diode Characteristics
3. VSWR, Frequency and Wave Length Measurement
4. Directional Coupler Directivity and Coupling Coefficient S parameter
measurement
5. Isolator and Circulator S - parameter measurement
6. Attenuation and Power measurement
7. S - matrix Characterization of E-Plane T, H-Plane T and Magic T.
8. Radiation Pattern of Antennas.
9. Antenna Gain Measurement
OPTICAL EXPERIMENTS:
1. DC characteristics of LED and PIN Photo Diode.
2. Mode Characteristics of Fibers
3. Measurement of Connector and Bending Losses.
4. Fiber Optic Analog and Digital Link
5. Numerical Aperture Determination for Fibers
6. Attenuation Measurement in Fibers
You might also like
- Anna University 7th Sem SyllabusDocument5 pagesAnna University 7th Sem Syllabusamit8634No ratings yet
- Wireless Communication Systems and StandardsDocument10 pagesWireless Communication Systems and StandardsAbdul HaiyumNo ratings yet
- Speech Processing and Recognition SystemsDocument6 pagesSpeech Processing and Recognition SystemsJothiEeshwarNo ratings yet
- EC2305 Transmission Lines & Waveguides TheoryDocument1 pageEC2305 Transmission Lines & Waveguides TheoryVinayNo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines and Fields SyllabusDocument1 pageTransmission Lines and Fields SyllabusNaveen YannamaniNo ratings yet
- EC I, Nba 1Document4 pagesEC I, Nba 1Sudha PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- Be Ece 7th Semester Syllabus For Regulation 2008Document11 pagesBe Ece 7th Semester Syllabus For Regulation 2008tannamalaiNo ratings yet
- ECE 7th Sem R2008Document29 pagesECE 7th Sem R2008rajasekarkprNo ratings yet
- SECA 1701Document2 pagesSECA 1701Venkata naga Sai VarunNo ratings yet
- RF and Microwave Engineering Lab GuideDocument5 pagesRF and Microwave Engineering Lab GuidejuliaNo ratings yet
- Ec8751 Optical Communication LTPC3003 ObjectivesDocument2 pagesEc8751 Optical Communication LTPC3003 ObjectivesJAGAN SUBRAMANINo ratings yet
- Ec6702 Optical Communication and Networks L T P C 3 0 0 3Document2 pagesEc6702 Optical Communication and Networks L T P C 3 0 0 3YAMINI D SDECT013No ratings yet
- Ec2403 RF and Microwave EngineeringDocument2 pagesEc2403 RF and Microwave EngineeringsophialeebanNo ratings yet
- Yellow Indicates Anna University Syllabus. Red Indicates The Additional Topics AddedDocument3 pagesYellow Indicates Anna University Syllabus. Red Indicates The Additional Topics AddedS SIVAKUMARNo ratings yet
- Anna University Tiruchirappalli Tiruchirappalli - 620 024: Regulations 2007 SylllabusDocument31 pagesAnna University Tiruchirappalli Tiruchirappalli - 620 024: Regulations 2007 SylllabusDSV210512No ratings yet
- Syllabus 5TH SemDocument7 pagesSyllabus 5TH SemarivasanthNo ratings yet
- VII Sem Syllabus 2021-2022231121032932Document18 pagesVII Sem Syllabus 2021-2022231121032932Anand TiwariNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communication Course OverviewDocument2 pagesOptical Fiber Communication Course OverviewM Madhu MaliniNo ratings yet
- Ec 1211 Electronic Devices j3 0 0 100Document4 pagesEc 1211 Electronic Devices j3 0 0 100Preethi RanganathanNo ratings yet
- Ece202 Transmission-lines-And-fields TH 1.00 Ac16Document1 pageEce202 Transmission-lines-And-fields TH 1.00 Ac16netgalaxy2010No ratings yet
- TLRF What To StudyDocument1 pageTLRF What To StudyDhanaraj PNo ratings yet
- Department of Ece, Adhiparasakthi College of Engineering, KalavaiDocument27 pagesDepartment of Ece, Adhiparasakthi College of Engineering, Kalavaijayj_5No ratings yet
- Optical NWDocument1 pageOptical NWSpandan SinhaNo ratings yet
- Hand Book Fiber Optic Communications by Joseph C. Palais 5th Edition-LibreDocument253 pagesHand Book Fiber Optic Communications by Joseph C. Palais 5th Edition-LibreKed Llango100% (3)
- EC6702 Optical Communication and NetworksDocument1 pageEC6702 Optical Communication and NetworksSurendhar SNo ratings yet
- Ec6702 - OcnDocument1 pageEc6702 - OcnSurendhar SNo ratings yet
- EMFT, TL & Waveguides and AWPDocument4 pagesEMFT, TL & Waveguides and AWPpawansvsuNo ratings yet
- Pre-Phd ECE SyllabusDocument53 pagesPre-Phd ECE SyllabusVivekananda NareddulaNo ratings yet
- 359 - EC8651 Transmission Lines and RF Systems - Anna University 2017 Regulation SyllabusDocument2 pages359 - EC8651 Transmission Lines and RF Systems - Anna University 2017 Regulation SyllabuskiziNo ratings yet
- Moe SyllabusDocument2 pagesMoe SyllabusparthiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Ec6702 - Ocn SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabus Ec6702 - Ocn SyllabusSurendhar SNo ratings yet
- Dr.K. Anitha - Optical CommunicationDocument117 pagesDr.K. Anitha - Optical Communicationjohnsai003No ratings yet
- Ec2402 Optical Communication and Networking L T P C 3 0 0 3Document2 pagesEc2402 Optical Communication and Networking L T P C 3 0 0 3Shaiju RajanNo ratings yet
- Comm SysDocument46 pagesComm Syssuresh_1989No ratings yet
- Ec8751 Optical Communication L T P C 3 0 0 3Document2 pagesEc8751 Optical Communication L T P C 3 0 0 3santhosh sekarNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication: EC8751 - OC 11Document30 pagesOptical Communication: EC8751 - OC 11BinoStephenNo ratings yet
- Ug 3rd Year Physics SyllabusDocument10 pagesUg 3rd Year Physics SyllabusAjaikumarNo ratings yet
- OcnDocument2 pagesOcnRaji SharmiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: 3 1 0 Unit Topics Lectures I 8Document1 pageSyllabus: 3 1 0 Unit Topics Lectures I 8Vibhor BhardwajNo ratings yet
- 361 - EC8751 Optical Communication - Anna University 2017 Regulation SyllabusDocument2 pages361 - EC8751 Optical Communication - Anna University 2017 Regulation SyllabusPoonguzhaliNo ratings yet
- Ec8751 Optical CommunicationDocument2 pagesEc8751 Optical Communicationthiruvengadam cNo ratings yet
- Ec010 505 Applied Electromagnetic TheoryDocument2 pagesEc010 505 Applied Electromagnetic Theorywalternampimadom100% (1)
- EMI Measurement TechniquesDocument2 pagesEMI Measurement Techniquesjebi.lee449No ratings yet
- Optical CommunicationsDocument1 pageOptical CommunicationsLakshmiNarayana Reddy BynagariNo ratings yet
- Microwave EngineeringDocument2 pagesMicrowave Engineeringசுந்தர் சின்னையா0% (9)
- Antenna & Wave PropagationDocument3 pagesAntenna & Wave PropagationShakshi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- M.tech. (RF & Microwave Engineering)Document37 pagesM.tech. (RF & Microwave Engineering)sultan1786No ratings yet
- Transmission Lines and WaveguidesDocument1 pageTransmission Lines and WaveguidesKarthikeyan_Go_95250% (1)
- RGPV EC 7th Syllabus 2011Document13 pagesRGPV EC 7th Syllabus 2011Amish VyasNo ratings yet
- 20EC215 MOC SyllabusDocument2 pages20EC215 MOC SyllabusSanjay Pandi SNo ratings yet
- TLW SyllabusDocument1 pageTLW SyllabusankurwidguitarNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication SyllabusDocument2 pagesOptical Communication Syllabuskrishna_ScrbidNo ratings yet
- Microwave and Radar Engineering-Pcec 4101Document2 pagesMicrowave and Radar Engineering-Pcec 4101Dr-Harish Chandra Mohanta0% (1)
- ElectiveDocument35 pagesElectivekalpana kcNo ratings yet
- B.tech ECE Third Semester SyllabusDocument10 pagesB.tech ECE Third Semester Syllabusteranon978No ratings yet
- Ec403 Transmission Lines and Networks: Objective of The CourseDocument1 pageEc403 Transmission Lines and Networks: Objective of The CourseBiswajit SarkarNo ratings yet
- Optical Characterization of Semiconductors: Infrared, Raman, and Photoluminescence SpectroscopyFrom EverandOptical Characterization of Semiconductors: Infrared, Raman, and Photoluminescence SpectroscopyNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to the Theory of Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Theory of Microwave CircuitsK. KurokawaNo ratings yet
- 2009 ESC Guidelines On EndocarditisDocument45 pages2009 ESC Guidelines On EndocarditisDaondy Friarsa SoehartoNo ratings yet
- 20 N 60 C 3Document13 pages20 N 60 C 3rashidmirzaNo ratings yet
- Comparison Study of Conventional Hot-Water and Microwave Blanching at Different Timetemperaturepower Combinations On The Quality of Potatoes.Document72 pagesComparison Study of Conventional Hot-Water and Microwave Blanching at Different Timetemperaturepower Combinations On The Quality of Potatoes.DavldSmith100% (1)
- DUB01CB Eng PDFDocument4 pagesDUB01CB Eng PDFAnonymous hj273CMNo ratings yet
- 2nd - Science-Second-Quarter-Week-1Document37 pages2nd - Science-Second-Quarter-Week-1Arlene AranzasoNo ratings yet
- Abbey Pain Scale assessment toolDocument2 pagesAbbey Pain Scale assessment toolMuhammad RezgiaNo ratings yet
- CIVL-365 Tutorial 8 SolutionDocument3 pagesCIVL-365 Tutorial 8 SolutionIvsNo ratings yet
- Clay ShonkwilerDocument9 pagesClay ShonkwilerJeoff Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica Cat. Bard 36kbtu Act.Document15 pagesFicha Tecnica Cat. Bard 36kbtu Act.Jehison M Patiño TenorioNo ratings yet
- Limbah PabrikDocument2 pagesLimbah Pabrikindar dewaNo ratings yet
- Purification of Morphologically and Functionally Intact Human Basophils To Near HomogeneityDocument9 pagesPurification of Morphologically and Functionally Intact Human Basophils To Near HomogeneitySinaí GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Approach To Malabsorption (SANJAY)Document58 pagesApproach To Malabsorption (SANJAY)Sanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Mouse Deer and TigerDocument2 pagesMouse Deer and Tigeralan.nevgan100% (1)
- Syllabi - EE 5004 - Power ElectronicsDocument2 pagesSyllabi - EE 5004 - Power ElectronicsKalum ChandraNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Effects of VitaminsDocument21 pagesNutrition Effects of Vitaminsblessed cccNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet - MSDS: Section 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocument5 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet - MSDS: Section 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationPubcrawlNo ratings yet
- Integrating Kuleana Rights and Land Trust PrioritesDocument50 pagesIntegrating Kuleana Rights and Land Trust PrioritesKeala Rodenhurst-JamesNo ratings yet
- Difference Between AerospaceDocument2 pagesDifference Between AerospaceSyawalMaulanaNo ratings yet
- Shariff NDocument4 pagesShariff NKruu ChinnuNo ratings yet
- Assignment #1: 1 HgjyygbykvrfDocument1 pageAssignment #1: 1 HgjyygbykvrfJuan Sebastian ArangoNo ratings yet
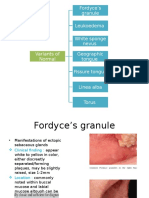
- Variants of NormalDocument9 pagesVariants of NormalFaizah HannyNo ratings yet
- VGHV NBV GH fc7fvbn BN NGCJHGDocument16 pagesVGHV NBV GH fc7fvbn BN NGCJHGRahul GNo ratings yet
- Modicon TM172PDG42R DatasheetDocument14 pagesModicon TM172PDG42R DatasheetRonnie SolomonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Machinery PrinciplesDocument27 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Machinery PrinciplesYousab CreatorNo ratings yet
- @MedicalBooksStore 2016 AntibioticDocument349 pages@MedicalBooksStore 2016 Antibioticant bee100% (1)
- KTS - Sarao.bakus Temple of Eternal FiireDocument176 pagesKTS - Sarao.bakus Temple of Eternal FiireK.T.S. SaraoNo ratings yet
- Operator Manual T2100-ST2 - ST1Document50 pagesOperator Manual T2100-ST2 - ST1Nurul FathiaNo ratings yet
- B.pharm Course Handbook 2017 18Document74 pagesB.pharm Course Handbook 2017 18Md RaquibNo ratings yet
- Warhammer 40k Kroot VehiclesDocument2 pagesWarhammer 40k Kroot VehiclesJoseph RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Ch1 PDFDocument54 pagesCh1 PDFChristian Jegues100% (2)