Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Theorist
Uploaded by
Sugar Capule - ManuelCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Theorist
Uploaded by
Sugar Capule - ManuelCopyright:
Available Formats
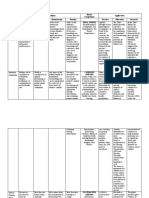
Nursing Theorist NURSING PERSON ENVIRONMENT HEALTH
1. F. Nightingale
Environmental Theory
Modern Nursing
resp. to others health Patient; control envt to
enhance recovery
Elements external to
& w/c affect the
health of sick
Being well(using every power to
full extent)
2. E. Wiedenbach
Helping Art of Clinical
Nx.
There is a pt. who needs
her help
When impeded strives by
his own efforts to achieve
such states
May prod. obstacles The rel. among nursing, pt., &
need for help imply health-
related concerns
3. V. Henderson
14 Basic Human
Needs
Assist indvl sick or well
that he will perform
unaided
Gain independence
ASAP
Needs assistance; mind and
body are inseparable pt., &
family viewed as a unit
External influence
affecting life and
development of an
organism
(Principles & Practice of Nx.)
Pt. ability to perform 14
components of nx care unaided
4. F.G. Abdellah
21 Nx. Problems
Nursing as a Problem
Solving process
Care of society sick or
well
A helping profession
Having physical, emotional,
& sociological needs
Create/maintain a
therapeutic
environment
(pt.- centered approaches to
nx)
State that is mutually exclusive
of illness
5. J. Watson
Transpersonal Caring
Concerned w/ health
promotion, restoration,
& illness prevention
- - Unity & harmony w/in the mind
body & soul & assisted w/ the
degree of congruence b/w the
self as perceived & the self as
experience
6. P. Benner
Novice to Expert
Caring rel.
Enabling condition of
connection & concern
Believe that thee are
significant aspects that
make up a person
Referred as situations Health: what can be assessed
Well-being: human experience
of health or wholeness
7. M. Levine
Conservation Model
Influence, adaptation
Human interaction
Participate on pts. envt
Holistic being
Wholeness is integrity
We live our lives
We are active
participants in it
Socially determined by the
ability to fxn in a reasonably
mal manner
8. Martha Rogers
Unitary Human Being
Both science & an art As an open system on
continuous process that is
the envt
Irreducible pan
dimensional field
identified by pattern &
manifesting char. Diff.
from those of the
parts
Uses the passive health to
symbolize wellness & the
absence of dse or major illness
9. Dorothy Johnson
Behavioral System
Model
7 Subsystems
External force acting to
preserve the orgn of the
pts. behavior helping the
pt. while the pt. is under
stress
As a behavioral system w/
patterned, repetitive, &
purposeful ways of
behaving that linked person
to envt
Factors not part of the
indvl behavioral
system
An elusive, dynamic state
influenced by biological, psych,
& social factors
Desired value by health
professionally
10. S.C. Roy
Adaptation Model
A profession focuses on
human life process &
patterns for ind., family,
group & society as a
whole
Humas are holistic, adoptive
systems describe as a
whole w/ parts that fxn as
unity for some purpose
All the conditions
affecting development
and behavior of
persons or group
A state & process of being and
becoming integrated & whole
person
11. B. Neuman
Systems Model
Concerned w/ the whole
person
May be ind., family, group,
community or social issue
All int. and ext. factors Continuum of wellness to
illness
12. I. King
Goal Attainment
Help indvl maintain
their health so they can
their roles
- Ways human being
interact w/ their envt
A dynamic state in life cycle
Interference to life cycle
(illness)
13. H. Peplau
Psychodynamic Nx
A significant, therapeutic
interpersonal process
In terms of a man
Lives in an unstable
equilibrium
Forces outside the
organism & in the
context of culture
Forward movement of
personality & other ongoing
humanprocess
14. I.J. Oralando
Nx. Process Theory
Distinct profession that
fxns automatically
Persons have verbally &
nonverbally
When cant meet their need
they become distressed
Doesnt define
Assume that when
theres nx-pt.
interaction they have
immediate interaction
Freedom of mental/physical
discomfort & feelings of
adequacy & well-being
contributed to health
15. J. Travelbee
Human to human
Rel. model
Assist ind., family or
comm.. to cope the
exp.erience of illness
suffering
A human being
Unique irreplaceable indvl
- Subjective: physical, emotional,
spiritual
Objective: measured by
physical exam
16. M. Leininger
Culture Care
Humanistic & scientific
profession
Culturally based &
consider w/ the needs &
values of pts.
Thus believed to be caring &
capable of being concerned
about
Totality of an
event/situation
State of well being that is
defined thru cultures
17. R.M. Rizzoparse
Human Becoming
Unique to medicine
Unique service to
mankind
Universe inseparable
& irreducible
18. M. Newman
Model of Health
Help clients recognize
theirown patterns by
forming rel. w/ clients
Identified by indvl pattern
of consciousness
Beyond the conscious
of the indvl
Fusion of dse & nondse
Can be regarded as the evolving
pattern of the person & the
envt
Ongoing process of expanding
consciousness
You might also like
- Margaret A. NewmanDocument7 pagesMargaret A. NewmanMarde Cabucos Phillip Bonachita100% (2)
- Nursing Theorists SummaryDocument4 pagesNursing Theorists SummaryChi Bie100% (3)
- Summary of Theoretical Foundations of NursingDocument6 pagesSummary of Theoretical Foundations of Nursinghans_manalo100% (5)
- Metaparadigm in NursingDocument3 pagesMetaparadigm in NursingJenno Ray SenalNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing - Basic ConceptsDocument83 pagesFundamentals of Nursing - Basic ConceptsDarell M. Book100% (7)
- Health Assessment in NursingDocument4 pagesHealth Assessment in NursingKiara Ash BeethovenNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Foundations in Nursing First Semester SY 2021 - 2022 Dr. Elena M. ValdezDocument36 pagesTheoretical Foundations in Nursing First Semester SY 2021 - 2022 Dr. Elena M. ValdezRednax 0912No ratings yet
- Development of Nursing TheoriesDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Nursing TheoriesBasil Hameed AmarnehNo ratings yet
- Notes on Nursing - What It Is, and What It Is Not: With a Chapter From 'Beneath the Banner, Being Narratives of Noble Lives and Brave Deeds' by F. J. CrossFrom EverandNotes on Nursing - What It Is, and What It Is Not: With a Chapter From 'Beneath the Banner, Being Narratives of Noble Lives and Brave Deeds' by F. J. CrossNo ratings yet
- Femoral Neck FractureDocument21 pagesFemoral Neck FractureSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing: ReviewerDocument20 pagesFundamentals of Nursing: ReviewerRjhay14100% (2)
- Theoretical Foundations of Nursing ReviewerDocument4 pagesTheoretical Foundations of Nursing ReviewerCharles Malcolm DalugdugNo ratings yet
- Summary of Nursing TheoriesDocument2 pagesSummary of Nursing TheoriesAngel Garcia Carbajal100% (3)
- Nursing TheoriesDocument7 pagesNursing TheoriesemsdaxxNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Nursing Theories With Concept AnalyzationDocument164 pagesCompilation of Nursing Theories With Concept AnalyzationPatrick PantuaNo ratings yet
- TFN TheoriesDocument3 pagesTFN TheoriesAngel JuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Scholarliness in NursingDocument12 pagesLecture 1 - Scholarliness in NursingCanary KhailNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Foundation of Nursing OverviewDocument3 pagesTheoretical Foundation of Nursing OverviewDing TanNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Foundation in NursingDocument5 pagesTheoretical Foundation in NursingMichaella Mae LaurestaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Foundation in Nursing 1Document57 pagesTheoretical Foundation in Nursing 1Sandra Reyes CervantesNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment NCM 101 Lec Learning MatDocument5 pagesHealth Assessment NCM 101 Lec Learning MatSheen CatayongNo ratings yet
- What Is A Theory?Document51 pagesWhat Is A Theory?Ca SobrementeNo ratings yet
- Theorists Phil BarkerDocument12 pagesTheorists Phil BarkerAlleah Mendoza100% (1)
- History of NursingDocument50 pagesHistory of NursingMichael GustiloNo ratings yet
- TheoristDocument130 pagesTheoristLucelle MacahiligNo ratings yet
- Technological Nursing As Caring by Rozzano C. Locsin Who Is Dr. Locsin?Document5 pagesTechnological Nursing As Caring by Rozzano C. Locsin Who Is Dr. Locsin?Bang Chan's Abs100% (1)
- Community Health NursingDocument93 pagesCommunity Health NursingKristaMaeC.LazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoristDocument103 pagesNursing TheoristVenice Joy Toledo-Malonzo,RN100% (5)
- Summary of Nursing TheoriesDocument5 pagesSummary of Nursing Theoriesrain ricamaraNo ratings yet
- Session 1 - Nurses Role in Health AssessmentDocument16 pagesSession 1 - Nurses Role in Health AssessmentCres Padua Quinzon100% (3)
- Nursing Philosophy UpdatedDocument9 pagesNursing Philosophy Updatedapi-581236671No ratings yet
- St. Anthony'S College - Nursing Department: Theoretical Foundations in NursingDocument86 pagesSt. Anthony'S College - Nursing Department: Theoretical Foundations in NursingCandido Kenneth JohnNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theorist Madeleine LeiningerDocument25 pagesNursing Theorist Madeleine Leiningerapi-240550685No ratings yet
- CHN NotesDocument7 pagesCHN NotesAnvi Turingan PedronanNo ratings yet
- Theory of Interpersonal RelationsDocument12 pagesTheory of Interpersonal RelationsjebashanthiniNo ratings yet
- Core Competencies Under The 11 Key Areas of ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesCore Competencies Under The 11 Key Areas of ResponsibilitiesJohnjohn MateoNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing ProcessDocument35 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Processdave100% (1)
- An Analysis of Roy's Adaptation Model Used in A Psych WardDocument9 pagesAn Analysis of Roy's Adaptation Model Used in A Psych WardAstrid LaverdeNo ratings yet
- TFN - Faye Glenn AbdellahDocument3 pagesTFN - Faye Glenn AbdellahRyneil AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Prelim TFNDocument5 pagesPrelim TFNjokazelNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument52 pagesFundamentals of NursingRegie Rose Luna100% (1)
- Health Care Ethics.w1Document10 pagesHealth Care Ethics.w1Roshin TejeroNo ratings yet
- Dorothea OremDocument6 pagesDorothea OremRen0607100% (2)
- Nursing ProcessDocument68 pagesNursing ProcessSareno PJhēaNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment Reviewer (Prelims)Document9 pagesHealth Assessment Reviewer (Prelims)Frances Nicole Flores100% (1)
- Human Becoming TheoryDocument3 pagesHuman Becoming Theoryflo_lamontagne100% (1)
- Orem's Self-Care Deficit TheoryDocument6 pagesOrem's Self-Care Deficit TheoryMary ShiksNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument11 pagesFundamentals of Nursinggladysbj1367% (3)
- Evolution of Nursing TheoriesDocument20 pagesEvolution of Nursing TheoriesKhibul LimNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Nursing Theories - PowerpointDocument122 pagesEvolution of Nursing Theories - PowerpointLea Lovelle Malabanan100% (2)
- Health Education TransDocument10 pagesHealth Education TransPia Gabrielle Cabatana100% (1)
- Context-Environment To Which Nursing Act Takes Place Content - Subject of Theory Process - Method by Which Nurse Acts in Nursing Theory NursingDocument22 pagesContext-Environment To Which Nursing Act Takes Place Content - Subject of Theory Process - Method by Which Nurse Acts in Nursing Theory NursingShyenNo ratings yet
- CHED Memorandum Order # 5 (2008)Document121 pagesCHED Memorandum Order # 5 (2008)wiredpsyche100% (69)
- Humanism, Nursing, Communication and Holistic Care: a Position Paper: Position PaperFrom EverandHumanism, Nursing, Communication and Holistic Care: a Position Paper: Position PaperNo ratings yet
- Sociology: An Introduction for Nurses, Midwives and Health VisitorsFrom EverandSociology: An Introduction for Nurses, Midwives and Health VisitorsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Handbook for Student Nurses, 201819 edition: Introducing key issues relevant for practiceFrom EverandA Handbook for Student Nurses, 201819 edition: Introducing key issues relevant for practiceNo ratings yet
- Imci 2Document39 pagesImci 2Sugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- NCP TetanusDocument2 pagesNCP TetanusSugar Capule - Manuel0% (1)
- OsteoDocument3 pagesOsteoSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- NCP Copd AirwayDocument2 pagesNCP Copd AirwaySugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyRespiDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyRespiSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- MMDSTDocument69 pagesMMDSTSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument1 pageMuscular SystemSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Glasgow Coma ScaleDocument3 pagesGlasgow Coma ScaleLanie Reyes de Guzman0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury: Philippine Orthopedic Center Group1 Section B "Reydi Badi"Document11 pagesSpinal Cord Injury: Philippine Orthopedic Center Group1 Section B "Reydi Badi"Sugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Poc ScoliosisDocument20 pagesPoc ScoliosisSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- PocDocument7 pagesPocSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Thromboangiitis Obliterans: Also Known AsDocument7 pagesThromboangiitis Obliterans: Also Known AsSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- GliclazideDocument8 pagesGliclazideSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Pott's DiseaseDocument8 pagesPott's DiseaseLorebell100% (2)
- Cancer NursingDocument208 pagesCancer NursingSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Particular CancersDocument8 pagesParticular CancersSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- Mini Mental State ExaminationDocument4 pagesMini Mental State ExaminationSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis HerpetiformisDocument11 pagesDermatitis HerpetiformisSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- GliclazideDocument8 pagesGliclazideSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Lapchole InstDocument4 pagesLapchole InstSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- 3A Non Therapeutic CommDocument11 pages3A Non Therapeutic CommSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Background of The Study (Imci) Nora Paps REVISEDDocument2 pagesBackground of The Study (Imci) Nora Paps REVISEDSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CKDDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CKDSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument11 pagesCholelithiasisSugar Capule - Manuel100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Middle Childhood Fact SheetDocument2 pagesMiddle Childhood Fact Sheetapi-252472215No ratings yet
- English: Quarter 3 - Module 21 Polite Expressions: Offering HelpDocument22 pagesEnglish: Quarter 3 - Module 21 Polite Expressions: Offering HelpSilverangel GayoNo ratings yet
- Collaborative Research Project SyllabusDocument3 pagesCollaborative Research Project SyllabusCameron BeyerNo ratings yet
- Level 2 Unit 3: Biographical Recount: Warm-UpDocument4 pagesLevel 2 Unit 3: Biographical Recount: Warm-UpAndrea BarrosoNo ratings yet
- Word-GrammarDocument3 pagesWord-GrammarMargielynNo ratings yet
- DLL Compound InterestDocument4 pagesDLL Compound InterestJose BenaventeNo ratings yet
- I.I The Background of The StudyDocument7 pagesI.I The Background of The StudytanbaroNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire - 1 Occupational Stress IndexDocument7 pagesQuestionnaire - 1 Occupational Stress IndexAnonymous kkl2AvNo ratings yet
- Essay Quality PDFDocument3 pagesEssay Quality PDFsachingoel1No ratings yet
- Samson StreetDocument58 pagesSamson Streetgbenga isaacNo ratings yet
- StrategicDocument26 pagesStrategicaljeanb_210% (1)
- Self-Taught Learning: Implementation Using MATLABDocument42 pagesSelf-Taught Learning: Implementation Using MATLABbodgergely100% (1)
- Ways of Expressing Future TimeDocument4 pagesWays of Expressing Future TimeAndreia MihailaNo ratings yet
- E - Value-Ate: Justine Revilla Mirando BSE-SCI A2020Document3 pagesE - Value-Ate: Justine Revilla Mirando BSE-SCI A2020Andrea MacasinagNo ratings yet
- HOMEROOM DLLweek-1-2Document3 pagesHOMEROOM DLLweek-1-2Gerald Rosario FerrerNo ratings yet
- Online Classes As New Normal Education During Pandemic, Its Challenges and Benefits On Criminology Student in Tomas Claudio CollegesDocument12 pagesOnline Classes As New Normal Education During Pandemic, Its Challenges and Benefits On Criminology Student in Tomas Claudio CollegesJohnpatrick DejesusNo ratings yet
- Prelim Eng Major 3 Structure of EnglishDocument3 pagesPrelim Eng Major 3 Structure of EnglishBill Russell CecogoNo ratings yet
- CBLM On Participate in Workplace CommuniDocument97 pagesCBLM On Participate in Workplace Communiwewe.trillanesNo ratings yet
- 10 Tips For Improving Your Oral PresentationsDocument2 pages10 Tips For Improving Your Oral PresentationsAngélica Osorio CastilloNo ratings yet
- Flower Life CycleDocument7 pagesFlower Life CyclelightranchNo ratings yet
- Hasok Chang Philosophical Grammar of Scientific PracticeDocument19 pagesHasok Chang Philosophical Grammar of Scientific PracticeItzcoatl Torres AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Appreciation Letter To Principal From TeacherDocument3 pagesAppreciation Letter To Principal From Teacherhenrymbaji0No ratings yet
- WHLP Format 2021-2022Document1 pageWHLP Format 2021-2022Mark Owen BaldoNo ratings yet
- Topic 01 - Introduction To ORDocument29 pagesTopic 01 - Introduction To ORimran_chaudhryNo ratings yet
- Task-Based Approach. Anzid MohammedDocument23 pagesTask-Based Approach. Anzid MohammedAnzid Mohammed100% (1)
- STS - Unit 1 - Lesson 1Document6 pagesSTS - Unit 1 - Lesson 1Chris MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Unpacking The Self LESSON 1: The Physical SelfDocument2 pagesUnpacking The Self LESSON 1: The Physical SelfWALLANG, Nicol B.No ratings yet
- Copc Syllabus Tem 305 QamDocument6 pagesCopc Syllabus Tem 305 QamJerome OrateNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Cognitive EngineeringDocument39 pagesChapter 5 - Cognitive EngineeringBaraa AbeadNo ratings yet
- Q3 ReyesPauline.Document3 pagesQ3 ReyesPauline.sarang kmmnskNo ratings yet