Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction to Theoretical Linguistics
Uploaded by
Ade KolcsarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Theoretical Linguistics
Uploaded by
Ade KolcsarCopyright:
Available Formats
An Introduction to
LINGUISTICS
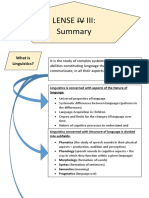
Main topics:
The role and position of THEORETICAL
LINGUISTICS in the mainstream linguistic research
Sub-areas of THEORETICAL LINGUISTICS
Main methods and approaches in the linguistic
research
Language levels and language units
Preliminary points:
1.What is Linguistics?
What is it concerned with?
What are its main methods of investigation?
2. What is language? How are natural languages
structured? What functions do they serve?
3. What is the relationship between language and
culture?
LINGUISTICS
Theoretical
linguistics
Applied
linguistics
Empirical
linguistics
1
What is linguistics?
... a science concerned with the study of
human, natural language.
What is language?
... a system of linguistic signs.
... a collection of units/items which
combine in order to create larger
meaningful units.
By and large, natural languages can be
investigated from two perspectives:
C
A B
D
(cf. Saussure 1916)
=
SYNCHRONY vs. DIACHRONY
language-state language evolution
synchronic linguistics diachronic linguistics
(cf. Saussure, 1916)
MACROLINGUISTICS
MACROLINGUISTICS
Sociolinguistics
Psycholinguistics
Neuro-psycholinguistics
Ethnolinguistics
Linguistic anthropology
Computational linguistics
Philosophy of language
etc.
Is linguistics the only science investigating language?
Theoretical
linguistics
phonetics
lexicology
semantics
morphology
syntax
stylistics
pragmatics
MICROLINGUISTICS
What is linguistics?
... a science concerned with the study of
human, natural language.
Language
non-human human
natural artificial
(e.g. Esperanto,
Volapk, the sign
language, codes,
etc.)
What is theoretical linguistics?
... a branch of linguistics which focuses
on the laws, principles, and mechanisms
underlying natural languages, in general.
2
3
Research methodology
non-specific: observation, inductive
methods, experiments, etc.
specific: the comparative method, the
immediate constituent analysis, linguistic
reconstruction, etc.
Language levels
vocabulary
syntax
morphology
phono-
logy
Language units
Phonology
segmental & suprasegmental units (e.g.
phonemes)
Morphology
morphemes, words
Syntax
words, phrases (syntagmata), clauses &
sentences
Vocabulary
words, affixes
Language functions
Leechs (1974) representation of the language functions
What is the relationship between
LANGUAGE and CULTURE?
c u l t u r e
objective subjective
LINGUISTIC LAWS: A BIRDS EYE VIEW
Diversification vs. Unification
Growth vs. Economy
Concrete to Abstract
Lexical to Grammatical
???
You might also like
- Foundations of Language Development: A Multidisciplinary ApproachFrom EverandFoundations of Language Development: A Multidisciplinary ApproachNo ratings yet
- Applied Linguistics to Foreign Language Teaching and LearningDocument26 pagesApplied Linguistics to Foreign Language Teaching and LearningXarvey MerchanNo ratings yet
- Week 1 An Introduction To The CourseDocument17 pagesWeek 1 An Introduction To The CourseZeineb AyachiNo ratings yet
- UGC MHRD ePG Pathshala Subject English LinguisticsDocument11 pagesUGC MHRD ePG Pathshala Subject English Linguisticskushi100% (1)
- Week 1 An Introduction To The CourseDocument17 pagesWeek 1 An Introduction To The CourseZeineb AyachiNo ratings yet
- GEEG 04 Block 01Document37 pagesGEEG 04 Block 01Dr Abdus SattarNo ratings yet
- LinguisticsDocument12 pagesLinguisticsAngelica MalpayaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PPT Linguistics Vs Applied LinguisticsDocument56 pagesUnit 1 PPT Linguistics Vs Applied LinguisticsPatrickXavierNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Theoretical and Applied LinguisticsDocument8 pagesComparison of Theoretical and Applied LinguisticsSabrina BadalovaNo ratings yet
- What is language? Key linguistic conceptsDocument36 pagesWhat is language? Key linguistic conceptsraushanNo ratings yet
- An Outline of History of Linguistics 1Document24 pagesAn Outline of History of Linguistics 1Yára LevyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LinguisticsDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Linguisticsnava anggri100% (4)
- 1) Language and Linguistics. Psychic DistanceDocument7 pages1) Language and Linguistics. Psychic DistanceАндрій ВолошинNo ratings yet
- LinguisticsDocument5 pagesLinguisticssami karemNo ratings yet
- Lense Iv Iii:: What Is Linguistics?Document5 pagesLense Iv Iii:: What Is Linguistics?Matt SalvaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linguistics Prelimenary Lessons LinguisticsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Linguistics Prelimenary Lessons Linguisticspheobe saludes100% (1)
- What Is Linguistics?Document3 pagesWhat Is Linguistics?BachaNo ratings yet
- Linguistic Theories, Branches and FieldsDocument13 pagesLinguistic Theories, Branches and FieldsChaima GuezzziNo ratings yet
- Written Report Contrasting Linguistics and Linguistic AnthropologyDocument15 pagesWritten Report Contrasting Linguistics and Linguistic AnthropologyIvy Baltazar Dela PuntaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LinguisticsDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Linguisticsselef12340% (1)
- Theoritical and Applied LinguisticDocument6 pagesTheoritical and Applied LinguisticOdonkz Forrealracingtiga100% (2)
- Scope LiDocument9 pagesScope Lirabin dasNo ratings yet
- What is Linguistics? An IntroductionDocument2 pagesWhat is Linguistics? An IntroductionBlanca Edith Lopez CabreraNo ratings yet
- Applied LinguisticsDocument27 pagesApplied LinguisticsjammurlammerNo ratings yet
- Current Research Topics in LinguisticsDocument16 pagesCurrent Research Topics in LinguisticsKarolina YakymenkoNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Theoretical and Applied LinguisticsDocument8 pagesComparison of Theoretical and Applied LinguisticsSabrina BadalovaNo ratings yet
- Dragusin LLS An 3 Sem 1 Linguistic Units Sinteze Curs PDFDocument13 pagesDragusin LLS An 3 Sem 1 Linguistic Units Sinteze Curs PDFRazvan VlagioiuNo ratings yet
- Part I, Lesson IIDocument5 pagesPart I, Lesson IIGomer Jay LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Linguistics Book Summary for Third Stage StudentsDocument44 pagesLinguistics Book Summary for Third Stage StudentsZahraa KhalilNo ratings yet
- Applied LinguisticsDocument15 pagesApplied LinguisticsAbdullah NaeemNo ratings yet
- Linguistics 1ST NotesDocument5 pagesLinguistics 1ST NotesEve RulonaNo ratings yet
- Basic linguistics topics under 40 charsDocument23 pagesBasic linguistics topics under 40 charsManuel J. Degyan60% (5)
- 0Document3 pages0Mohamed SahraouiNo ratings yet
- LinguisticsDocument23 pagesLinguisticsEzekiel D. Rodriguez92% (12)
- General Linguistics1 2Document37 pagesGeneral Linguistics1 2nancyzhyklnNo ratings yet
- SEMANA 1 MergedDocument295 pagesSEMANA 1 MergedLeancastNo ratings yet
- Subject Matter of LinguisticDocument7 pagesSubject Matter of LinguisticlovelifedianaNo ratings yet
- Linguistics S2 P2Document3 pagesLinguistics S2 P2ChakibNo ratings yet
- Diss (Linguistics)Document12 pagesDiss (Linguistics)Cristine SibuaNo ratings yet
- The Scientific Study of Language and CommunicationDocument18 pagesThe Scientific Study of Language and CommunicationAgus Aby AchaechiNo ratings yet
- Linguistics and Its BranchesDocument12 pagesLinguistics and Its BranchesGulfam Riaz100% (1)
- Linguistics - Module 1Document28 pagesLinguistics - Module 1Gerlyn Dangel100% (2)
- The Basics of Applied LinguisticsDocument102 pagesThe Basics of Applied LinguisticsJ G100% (2)
- Unit 1 Introduction To LinguisticsDocument6 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To LinguisticsRamanakumar Mohan100% (1)
- Linguistics 181006080848Document64 pagesLinguistics 181006080848James Alexander DezaNo ratings yet
- GL. Assignment by Muhammad Sanwal KhanDocument4 pagesGL. Assignment by Muhammad Sanwal KhanMuhammad SanwalNo ratings yet
- LinguisticsDocument11 pagesLinguisticsAntoneth AlviolaNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Applied LinguisticsDocument79 pagesThe Basics of Applied LinguisticsMai Mowafy100% (2)
- The Branches of LinguisticsDocument6 pagesThe Branches of Linguisticsyeseniacampos0314No ratings yet
- Language LinguisticsDocument35 pagesLanguage LinguisticsScholar Winterflame100% (1)
- Makalah LinguistikDocument9 pagesMakalah Linguistikyujinamo85No ratings yet
- Seminar 4Document10 pagesSeminar 4Gulzat KussepovaNo ratings yet
- Language and Linguistics 2Document40 pagesLanguage and Linguistics 2Sirikan SriwisanNo ratings yet
- Inglisuri Filoloiggis Shesavali, 1 (2) LeqciaDocument33 pagesInglisuri Filoloiggis Shesavali, 1 (2) LeqciamariamNo ratings yet
- Resumen para Linguistica 27-06Document15 pagesResumen para Linguistica 27-06Lou ClarkNo ratings yet
- Definition and Scope of Linguistics ExplainedDocument4 pagesDefinition and Scope of Linguistics ExplainedLee RaddNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "Perspective On Language" By Esteban Palací: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "Perspective On Language" By Esteban Palací: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- ReconstructionDocument6 pagesReconstructionVrinda DhongleNo ratings yet
- Sleepy Hollow - Cricket Collection 274 (Cross Stitch Chart)Document15 pagesSleepy Hollow - Cricket Collection 274 (Cross Stitch Chart)Ade Kolcsar100% (4)
- LexicografieDocument31 pagesLexicografieAde KolcsarNo ratings yet
- Cooking The Costco WayDocument274 pagesCooking The Costco Waysazkha2100% (3)
- The Scarlet LetterDocument5 pagesThe Scarlet LetterAde KolcsarNo ratings yet
- Cultural Studies Course 2Document29 pagesCultural Studies Course 2Ade KolcsarNo ratings yet
- Cultural Studies Course 4Document24 pagesCultural Studies Course 4Ade KolcsarNo ratings yet
- Cultural Studies Lecture 7 IDENTITYDocument23 pagesCultural Studies Lecture 7 IDENTITYAde KolcsarNo ratings yet
- Curs 3Document23 pagesCurs 3Ade KolcsarNo ratings yet
- Custom ReportDocument11 pagesCustom ReportAde KolcsarNo ratings yet
- Curs 2Document13 pagesCurs 2Ade KolcsarNo ratings yet
- Curs 1Document20 pagesCurs 1Ade KolcsarNo ratings yet
- Criticism 5.04Document1 pageCriticism 5.04Ade KolcsarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Racial Inequality - Norton AugustDocument46 pagesChapter 14 - Racial Inequality - Norton AugustAde KolcsarNo ratings yet
- Chief SeattleDocument3 pagesChief SeattleRaquel IngramNo ratings yet
- Bibliography Literary CriticismDocument1 pageBibliography Literary CriticismAde KolcsarNo ratings yet
- Chief SeattleDocument3 pagesChief SeattleRaquel IngramNo ratings yet
- Brussels Cambridge Esol Teacher Support ProgrammeDocument6 pagesBrussels Cambridge Esol Teacher Support ProgrammeAde KolcsarNo ratings yet
- Arhire 2Document10 pagesArhire 2Ade KolcsarNo ratings yet
- Arhire 1Document12 pagesArhire 1Ade KolcsarNo ratings yet
- Enneagram Personality Test ReportDocument18 pagesEnneagram Personality Test ReportCarmen NeacsuNo ratings yet
- D. Implementing Family Nursing Care PlanDocument17 pagesD. Implementing Family Nursing Care PlanWilma BeraldeNo ratings yet
- Students' Positive Perception of English for Self-ExpressionDocument24 pagesStudents' Positive Perception of English for Self-Expressionochay1806No ratings yet
- Deep Work: "Productivity Is About Depth of Work, Not Amount of Time"Document15 pagesDeep Work: "Productivity Is About Depth of Work, Not Amount of Time"Jenil RitaNo ratings yet
- CCAT - Measure cognitive aptitude with Criteria's Cognitive Aptitude TestDocument2 pagesCCAT - Measure cognitive aptitude with Criteria's Cognitive Aptitude TestOscarNo ratings yet
- SASMO 2017 SASMO 2017: Nathan Verel SetiawanDocument15 pagesSASMO 2017 SASMO 2017: Nathan Verel SetiawanTedy Zainul ArifinNo ratings yet
- This Content Downloaded From 88.197.46.154 On Mon, 21 Jun 2021 07:52:39 UTCDocument21 pagesThis Content Downloaded From 88.197.46.154 On Mon, 21 Jun 2021 07:52:39 UTCTasos TravasarosNo ratings yet
- RubricsDocument44 pagesRubricsAnisha msNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Versus Clinical Reasoning Versus Clinical JudgmentDocument3 pagesCritical Thinking Versus Clinical Reasoning Versus Clinical JudgmentWinda ArfinaNo ratings yet
- Vygotsky, L. (1965) - Psychology and Localization of FunctionsDocument6 pagesVygotsky, L. (1965) - Psychology and Localization of FunctionsVictor Contreras CabreraNo ratings yet
- Peningkatan Keterbukaan Diri (Self-Disclosure) Dengan Teknik Petak Johari Melalui Bimbingan Kelompok Di Sma Negeri 2 Di Kota Bengkulu Kelas X Mipa FDocument13 pagesPeningkatan Keterbukaan Diri (Self-Disclosure) Dengan Teknik Petak Johari Melalui Bimbingan Kelompok Di Sma Negeri 2 Di Kota Bengkulu Kelas X Mipa Fnorma asmilasihNo ratings yet
- Summary Recommendations From Dementia Driving Guidelines 2014Document1 pageSummary Recommendations From Dementia Driving Guidelines 2014avneesh.n.nzNo ratings yet
- Csi Scoring KeyDocument2 pagesCsi Scoring Keymaryam sherazNo ratings yet
- Principles and Theories of Learning and MotivationDocument6 pagesPrinciples and Theories of Learning and MotivationCharnievelle Catarata GranadoNo ratings yet
- Psych Assertions Reason Q AnalysisDocument5 pagesPsych Assertions Reason Q Analysisphanishashidhar100% (4)
- Manifest RealityDocument2 pagesManifest RealityFLOWNo ratings yet
- 07 StrategiesDocument13 pages07 StrategiesJonathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Summative 1.1Document3 pagesChapter 1 Summative 1.1Julieve A. Vistar0% (1)
- The Mental Status ExaminationDocument10 pagesThe Mental Status ExaminationSalvara Jane DanielNo ratings yet
- Personalized Curriculum Design May Be Imperative For Individuals With Heterogeneous Mathematics Capabilities: A Learning Trajectory Case StudyDocument40 pagesPersonalized Curriculum Design May Be Imperative For Individuals With Heterogeneous Mathematics Capabilities: A Learning Trajectory Case StudySafia Fatima MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- What Are False MemoriesDocument6 pagesWhat Are False MemoriesAnthonette EstigoyNo ratings yet
- Sensory Processing For High SchoolDocument6 pagesSensory Processing For High SchoolRaghaveni RVNo ratings yet
- The Independence of Positive and Negative Affect Diener 85Document13 pagesThe Independence of Positive and Negative Affect Diener 85Trihantoko SaputroNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Learning To Be A Better StudentDocument27 pages3.1 Learning To Be A Better StudentApufwplggl JomlbjhfNo ratings yet
- Simple Vak QuestionnaireDocument6 pagesSimple Vak Questionnairer3belzNo ratings yet
- Gagnes Nine Events InstructionDocument3 pagesGagnes Nine Events InstructionBernadette AragonNo ratings yet
- 1) What Are The 3 Areas of Philosophy?Document3 pages1) What Are The 3 Areas of Philosophy?Joyce Nesamoney SanthosamNo ratings yet
- Performance and Affects in Group Problem-SolvingDocument9 pagesPerformance and Affects in Group Problem-SolvingMaylin Loyola AyqueNo ratings yet
- Oppotunity Identification Skill T4Document36 pagesOppotunity Identification Skill T4Khairun Nasuha bt Mohamad TahirNo ratings yet
- WAIS-IV Index Scores and InterpretationDocument6 pagesWAIS-IV Index Scores and InterpretationChris BernardoNo ratings yet