Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cloud Computing and Its Applications
Uploaded by
Kavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cloud Computing and Its Applications
Uploaded by
Kavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamCopyright:
Available Formats
OVERCOMING NETWORK SECURITY VULNERABILITIES IN CLOUD
COMPUTING
ABSTRACT
In this modern technologies world
everything becomes very vast and more
reliable .We makes our documentation on
one pc and we can access and get this on
other system but this can be happened with
the help of internet. The rapid
improvement of the capacity of online
connectivity gave birth to cloud
computing. Data and processes could be
done online without the need of any local
software or client. As long as the user
knows the process and has the right
security credentials, he could access the
system and make the necessary changes,
but there are major challenges and security
issues in cloud computing that makes
accessing somewhat difficult. In this paper
we are giving a introduction to cloud
computing and discussing and overcome
this security issues that being coming in
cloud computing applications.
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 Cloud Computing
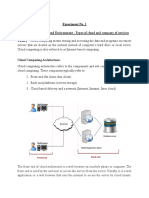
It simply, means "Internet
Computing." The Internet is commonly
visualized as clouds; hence the term cloud
computing for computation done through
the Internet. With Cloud Computing users
can access database resources via the
Internet from anywhere, for as long as they
need, without worrying about any
maintenance or management of actual
resources. Besides, databases in cloud are
very dynamic and scalable. Cloud
computing is unlike grid computing, utility
computing, or autonomic computing. In
fact, it is a very independent platform in
terms of computing. The best example of
cloud computing is Google Apps where
any application can be accessed using a
browser and it can be deployed on
thousands of computer through the
Internet.
1.2 Types of cloud computing services
IT people talk about three different
kinds of cloud computing, where different
services are being provided for you.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
means you're buying access to raw
computing hardware over the Net, such as
servers or storage. Since you buy what you
need and pay-as-you-go, this is often
referred to as utility computing. Ordinary
web hosting is a simple example of IaaS,
you pay a monthly subscription or a per-
megabyte/gigabyte fee to have a hosting
company serves up files for your website
from their servers.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
means you use a complete application
running on someone else's system. Web-
based email and Google Documents are
perhaps the best-known examples. Zoho is
another well-known SaaS provider
offering a variety of office applications
online.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) means
you develop applications using Web-based
tools so they run on systems software and
hardware provided by another company.
Force.com (from salesforce.com) and the
Google App Engine are examples of PaaS.
1.3 Type of clouds:
Public cloud:
A public cloud is one based on the
standard cloud computing model, in which
a service provider makes resources, like
applications and storage, available to the
general public over the Internet. Cloud
services may be free or offered on a pay-
per-usage model.
The main benefits of using a public cloud
service are:
1. Easy and inexpensive set-up because
hardware, application and bandwidth costs
are covered by the provider.
2. Scalability to meet needs.
3. No wasted resources
Private cloud:
Private cloud (also called internal cloud or
corporate cloud) is a marketing term for a
proprietary computing architecture that
provides hosted services to a limited
number of people behind a firewall.
Hybrid cloud:
A hybrid cloud environment consisting of
multiple internal and/or external providers
will be typical for most enterprises. It is a
cloud computing environment in which an
organization provides and manages some
resources in-house and has others provided
externally. For example, an organization
might use a public cloud service, such as
Amazon's Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
for general computing but store customer
data within its own data center.
2. SOLUTION OF SECURITY ISSUES
IN CLOUD COMPUTING
As new technologies emerge, they
often tend to build on the success of
previous developments. Cloud computing
and storage, benefit from years of
development and testing of large scale
infrastructure. The most important take
away is cloud storage is for everyone and
every organization. From big to small,
groups to individual, the use of grid
infrastructure can be deployed for
maximum return and efficiency. In
response, Stone soft has identified five
ways IT teams can protect themselves
against cloud security threats and attacks,
while helping ensure the success of their
cloud computing strategies. They include:
2.1 Federated ID
Inherent in a cloud computing
environment is the need for workers to log
into multiple applications and services.
This presents a formidable security pitfall,
as organizations may lose control over
their ability to ensure strong authentication
at the user level. To mitigate this risk,
organizations need single sign-on
capabilities such as those provided by
the Stone Gate SSL VPN that enable
users to access multiple applications and
services, including those located outside of
the organization in the public cloud,
through a single login. With this ability,
organizations can streamline security
management and ensure strong
authentication within the cloud.
2.2 Always-on Connectivity
When the majority of an
organizations critical business data is
stored in the cloud, network downtime can
shut down business operations. Access to
cloud services must be always available,
even during maintenance, thus requiring
high availability technologies and
capabilities such as active clustering,
dynamic server load balancing and ISP
load balancing within the network
infrastructure. Organizations should seek
technologies that are built into their
network solutions, rather than purchase
them as standalone products to ensure
effectiveness, ease of management and
reduced network costs.
2.3 Multi-layer Inspection
The rise of the cloud computing
environment and increased sophistication
of threats has created a need for a proper
layered defense comprised of perimeter
protection and intrusion detection and
prevention capabilities within the network.
Rather than implementing first-generation
firewalls to protect the cloud at the
perimeter, Stone soft recommends the
deployment of virtual next generation
firewall appliances like the Stone Gate
Virtual Next Gen Firewall that integrate
advanced firewall and IPS capabilities for
deep traffic inspection. This will allow
organizations to inspect all levels of
traffic, from basic Web browsing to peer-
to-peer applications and encrypted Web
traffic in the SSL tunnel. Additional IPS
appliances should be implemented to
protect networks from internal attacks that
threaten access to the cloud.
2.4 Centralized Management:
Human error is still the greatest
network security threat facing both
physical and virtual computing
environments. As companies deploy
additional network devices to secure their
virtual networks, they exponentially
increase this risk as device management,
monitoring and configuration become
more tedious and less organized. For this
reason, Stone soft recommends companies
use a single management console to
manage, monitor and configure all devices
physical, virtual and third-party.
2.5 Virtual Desktop Protection
More and more organizations are
deploying virtual desktops to realize the
cost and administration benefits. However,
these desktops are just as if not more
vulnerable than their physical counterparts.
To adequately protect virtual desktops,
organizations should isolate them from
other network segments and implement
deep inspection at the network level to
prevent both internal and external threats.
Those organizations should deploy a
multi-pronged approach to security by
implementing IPS technology that
prevents illegal internal access, protects
the clients from malicious servers, as well
as providing secure remote access
capabilities through IP sec or SSL VPN
that protects against unauthorized external
access.
2.6 Data storage Location
Cloud compliance is difficult
because you do not know where you data
are located. Not only does an organization
not know what is being done with its data,
it may not even know who the providers
are. Cloud computing models ignore these
problems and make compliance and
verification of compliance difficult.
2.7 Security and privacy
First among cloud computing data
storage issues is security and privacy In
fact, Software as a Services (SaaS)
provider may be relying on other external
providers for its backbone, infrastructure,
and data storage. Cloud vendor uses
encryption for securing data at rest and in
transit. The cloud service provider should
encrypt data on storage devices at all times
in order to prevent data breaches.
Companies have to make sure that their
data is protected when transmitted over the
Internet by always being encrypted and
authenticated by the cloud provider.
3. CLOUD COMPUTING
APPLICATIONS
The applications of cloud
computing are practically limitless. With
the right middleware, a cloud computing
system could execute all the programs a
normal computer could run. There are
some benefits and applications in cloud
computing that makes it different from
other concepts:
3.1 Clients would be able to access their
applications and data from anywhere at
any time. They could access the cloud
computing system using any computer
linked to the Internet. Data wouldn't be
confined to a hard drive on one user's
computer or even a corporation's internal
network.
3.2 It could bring hardware costs down.
Cloud computing systems would reduce
the need for advanced hardware on the
client side. You wouldn't need to buy the
fastest computer with the most memory,
because the cloud system would take care
of those needs for you. Instead, you could
buy an inexpensive computer terminal.
The terminal could include a monitor,
input devices like a keyboard and mouse
and just enough processing power to run
the middleware necessary to connect to the
cloud system. You wouldn't need a large
hard drive because you'd store all your
information on a remote computer.
3.3 Corporations that rely on computers
have to make sure they have the right
software in place to achieve goals. Cloud
computing systems give these
organizations company-wide access to
computer applications. The companies
don't have to buy a set of software or
software licenses for every employee.
Instead, the company could pay a metered
fee to a cloud computing company.
3.4 Servers and digital storage devices take
up space. Some companies rent physical
space to store servers and databases
because they don't have it available on site.
Cloud computing gives these companies
the option of storing data on someone
else's hardware, removing the need for
physical space on the front end.
3.5 Corporations might save money on IT
support. Streamlined hardware would, in
theory, have fewer problems than a
network of heterogeneous machines and
operating systems.
3.6 If the cloud computing system's back
end is a grid computing system, then the
client could take advantage of the entire
network's processing power. Often,
scientists and researchers work with
calculations so complex that it would take
years for individual computers to complete
them. On a grid computing system, the
client could send the calculation to the
cloud for processing. The cloud system
would tap into the processing power of all
available computers on the back end,
significantly speeding up the calculation.
4. Conclusion:
Cloud computing is a better
concept because we can access our files,
images and anything through the internet,
but there are some security issues in using
these applications .We have to overcome
these security issues and after this we can
used any cloud computing applications
thats makes cloud computing better
option.
5. REFRENCES
[1]
http://blog.animoto.com/2008/04/21/amaz
on-ceo-jeff-bezos-onanimoto/
[2]
searchcloudcomputing.techtarget.com/defi
nition/cloud-computing
[3] www.infoworld.com/.../cloud-
computing/what-cloud-computing
[4] Let it rise A special report on
corporate IT, The Economist, October
25th, 2008
[5] Jeff Cogswell, RightScale eases
developing on Amazon EC2 eweek.com,
October 21st, 2008
[6] Peter Wayner, Cloud versus cloud A
guided tour of Amazon,
[7] Google, AppNexus and GoGrid,
InfoWorld, July 21, 2008
[8] James Staten, Is Cloud Computing
Ready for the Enterprise?
[9] Forrester Report, March 7, 2009.
You might also like
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Real World Challenges of Cloud ComputingDocument23 pagesReal World Challenges of Cloud ComputingVarsha PrabhuNo ratings yet
- cloud computing AUDocument11 pagescloud computing AUTHANGA DURAINo ratings yet
- Unit 1stDocument11 pagesUnit 1stAmanNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: NAME:-Mohsin Qayyum A Morning) SUBMITTED TO: - Sir Muhammed Waseem Subject: - MisDocument6 pagesCloud Computing: NAME:-Mohsin Qayyum A Morning) SUBMITTED TO: - Sir Muhammed Waseem Subject: - MisMohsin QayyumNo ratings yet
- Unit I Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument36 pagesUnit I Introduction To Cloud Computingkomalpopatshinde2345No ratings yet
- Part B ETIDocument10 pagesPart B ETISoNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument3 pagesCloud ComputingThinh Le VietNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual CloudDocument49 pagesLab Manual CloudTed Breaker0% (1)
- Cloud Computing: Presented By: Nirjala HadaDocument18 pagesCloud Computing: Presented By: Nirjala HadaNirjala HadaNo ratings yet
- ETI Micro Project Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesETI Micro Project Cloud ComputingSheshrao LandgeNo ratings yet
- Anurag CC LAB File CompleteDocument27 pagesAnurag CC LAB File CompleteBaby SauravNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument17 pagesCloud ComputingFLAMENo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument117 pagesCloud ComputingElder Castro100% (1)
- Unit 1Document13 pagesUnit 1Bnod MsraNo ratings yet
- Cloud computing: Moving IT out of the officeFrom EverandCloud computing: Moving IT out of the officeBCS, The Chartered Institute for ITNo ratings yet
- Rsa SecurityDocument6 pagesRsa SecuritySumana SikdarNo ratings yet
- Security Issues in Cloud Computing and Risk Assessment: Darshan R, Smitha G RDocument6 pagesSecurity Issues in Cloud Computing and Risk Assessment: Darshan R, Smitha G RInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument64 pagesUntitledlekhaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Guide: Types, Benefits & How It WorksDocument40 pagesCloud Computing Guide: Types, Benefits & How It WorksHimanshu SoniNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing IEEE PaperDocument4 pagesCloud Computing IEEE PaperAsrar Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Problem Definition: Implementing Digital Signature With RSA To The Data On CloudDocument22 pagesProblem Definition: Implementing Digital Signature With RSA To The Data On CloudHamid HaqaniNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing TDocument6 pagesCloud Computing TROW OF 2 GONo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar ReportJp Sahoo0% (1)
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar Reportshinchan noharaNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar Reportshinchan noharaNo ratings yet
- Cloud: Get All The Support And Guidance You Need To Be A Success At Using The CLOUDFrom EverandCloud: Get All The Support And Guidance You Need To Be A Success At Using The CLOUDNo ratings yet
- CC Security in Cloud Computing - 1Document67 pagesCC Security in Cloud Computing - 1PANDYA CHITRANGDANo ratings yet
- Introduction to Cloud Computing FundamentalsDocument24 pagesIntroduction to Cloud Computing FundamentalsJacebh NikhNo ratings yet
- Cloud 1Document7 pagesCloud 1vikram kumar jonnalagaddaNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument4 pagesCloud ComputingChuru iddyNo ratings yet
- Hilcoe School of Computer Science and Technology: Meron Teshome / Am9943Document14 pagesHilcoe School of Computer Science and Technology: Meron Teshome / Am9943Meron TeshomeNo ratings yet
- CC Lab FileDocument42 pagesCC Lab FileRitika SinghNo ratings yet
- Name: Anujkumar Sinh ROLL NO: 2105 Subject: Internet Technology CODE: CSC104Document4 pagesName: Anujkumar Sinh ROLL NO: 2105 Subject: Internet Technology CODE: CSC104Anuj SinghNo ratings yet
- Jimma Institute of Technology: Cloud Computing Unit - 1: Cloud Computing FundamentalsDocument18 pagesJimma Institute of Technology: Cloud Computing Unit - 1: Cloud Computing FundamentalsdagneNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocument17 pagesWhat Is Cloud ComputingVictor ImarhiagbeNo ratings yet
- PR-114 AllDocument13 pagesPR-114 AllseemaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: - BY Banu Pooja Kannikanti 17H71A05C4Document19 pagesCloud Computing: - BY Banu Pooja Kannikanti 17H71A05C4Bhavana GummaNo ratings yet
- Two Cloud ArchitectureDocument44 pagesTwo Cloud ArchitecturegomathiNo ratings yet
- My Seminar Report On Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesMy Seminar Report On Cloud ComputingKevin NettarNo ratings yet
- Project 12Document15 pagesProject 12Ahmed Al-mohammdiNo ratings yet
- What is Cloud ComputingDocument29 pagesWhat is Cloud ComputingTarik ShethNo ratings yet
- Research On Cloud Computing Security Problem and Strategy: Wentao LiuDocument4 pagesResearch On Cloud Computing Security Problem and Strategy: Wentao LiuRahul BangaNo ratings yet
- CC 1Document58 pagesCC 1VISHNU VASHISHTHNo ratings yet
- PR 114Document4 pagesPR 114seemaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing JUNE 2022Document12 pagesCloud Computing JUNE 2022Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: A Security Concern: MBA (Marketing) SEM II IMS, Lucknow UniversityDocument12 pagesCloud Computing: A Security Concern: MBA (Marketing) SEM II IMS, Lucknow UniversityShadaab AlamNo ratings yet
- Enterprise CloudDocument5 pagesEnterprise CloudadiraihajaNo ratings yet
- CC Lab 1 Roll No. 10Document15 pagesCC Lab 1 Roll No. 10Revathi DusaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing OverviewDocument23 pagesCloud Computing OverviewpallaviNo ratings yet
- Ex No. 2 Title: Installation and Configuration of Own Cloud Theory: What Is Cloud Computing?Document7 pagesEx No. 2 Title: Installation and Configuration of Own Cloud Theory: What Is Cloud Computing?William Jacob Ekow SamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 New Trends in MISDocument31 pagesLecture 4 New Trends in MISmaryallaine02No ratings yet
- Final MaterialDocument63 pagesFinal MaterialAyman AwadNo ratings yet
- Cloud_Computing_Tutorials.Document3 pagesCloud_Computing_Tutorials.daniloorestmarijaniNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Notes For BSC and BCADocument48 pagesCloud Computing Notes For BSC and BCAPvlsowjanya100% (3)
- AssignmentDocument12 pagesAssignmentChaithu GowdruNo ratings yet
- Assignment On: by Pragya Chakshoo (4067) To Prof. Narender Singh ChauhanDocument10 pagesAssignment On: by Pragya Chakshoo (4067) To Prof. Narender Singh ChauhanPragya ChakshooNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Security TechniquesDocument8 pagesCloud Computing Security TechniquesVinod NaiduNo ratings yet
- Detailed Overview of Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesDetailed Overview of Cloud ComputingAravind Kumar CSNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Risks and ServicesDocument9 pagesCloud Computing Risks and ServicesSelormNo ratings yet
- SSLC MarchApril RetotalResultsDocument199 pagesSSLC MarchApril RetotalResultsKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- Objective: This Unit Discusses About The Analysis and Performance Measure of DataDocument1 pageObjective: This Unit Discusses About The Analysis and Performance Measure of DataKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Design and DevelopmentDocument1 pageEmbedded Systems Design and DevelopmentKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- RawDocument5 pagesRawKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Design and DevelopmentDocument1 pageEmbedded Systems Design and DevelopmentKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- DS ManualDocument96 pagesDS ManualKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- DS ManualDocument96 pagesDS ManualKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- Sri Balaji Chockalingam Engineering College Data Structures CIA TestDocument1 pageSri Balaji Chockalingam Engineering College Data Structures CIA TestKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- Measurouting: A Framework For Routing Assisted Traffic MonitoringDocument2 pagesMeasurouting: A Framework For Routing Assisted Traffic MonitoringKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- 1Document9 pages1Kavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- HashDocument1 pageHashKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- Temperature StandardsDocument1 pageTemperature StandardsKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- Password HackingDocument60 pagesPassword HackingKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- A Novel Approach For Enhanced Network Security Along With Information SecurityDocument1 pageA Novel Approach For Enhanced Network Security Along With Information SecurityKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- 1Document9 pages1Kavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- Security Challenges in Mobile SystemsDocument1 pageSecurity Challenges in Mobile SystemsKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- 1Document9 pages1Kavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Provide Department-Wise Details Separately As Enclosure I. SpaceDocument11 pagesLaboratory: Provide Department-Wise Details Separately As Enclosure I. SpaceKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- Pondicherry Central University Computer Science Database Management SystemsDocument7 pagesPondicherry Central University Computer Science Database Management SystemsKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- Pondicherry University ATM Management System Project Report UML DiagramsDocument13 pagesPondicherry University ATM Management System Project Report UML DiagramsKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- Pondicherry Central University Computer Science Database Management SystemsDocument7 pagesPondicherry Central University Computer Science Database Management SystemsKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- 2marks Q &ADocument28 pages2marks Q &AKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- C EssentialsDocument45 pagesC EssentialssuchitraprasannaNo ratings yet
- Cse SyllabusDocument10 pagesCse SyllabusGurudeepakk RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- Building Domain Specific Dictionaries of Verb-Object Relation From Source CodeDocument8 pagesBuilding Domain Specific Dictionaries of Verb-Object Relation From Source CodeKavinhariharasudhan SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- David Sosa - The Import of The Puzzle About BeliefDocument31 pagesDavid Sosa - The Import of The Puzzle About BeliefSr. DanieoNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Design Modification for Medical ImagingDocument6 pagesOptical Fiber Design Modification for Medical ImagingNAJMILNo ratings yet
- 7949 37085 3 PBDocument11 pages7949 37085 3 PBAman ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- FeminismDocument8 pagesFeminismismailjuttNo ratings yet
- Traditional Training TechniquesDocument13 pagesTraditional Training TechniquesRachana PradeepNo ratings yet
- 11 - Chapter 5 PDFDocument35 pages11 - Chapter 5 PDFlouisNo ratings yet
- Curriculum VitaeDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitaebtk_20No ratings yet
- Variable frequency drives for electric submersible pumpsDocument34 pagesVariable frequency drives for electric submersible pumpshermit44535No ratings yet
- 103EXP3 SpectrophotometerDocument5 pages103EXP3 SpectrophotometeralperlengerNo ratings yet
- Differential Aptitude TestsDocument2 pagesDifferential Aptitude Testsiqrarifat50% (4)
- Understanding PerformanceDocument65 pagesUnderstanding PerformanceClaudia AfinekNo ratings yet
- The STP Guide To Graduate Student Training in The Teaching of PsychologyDocument101 pagesThe STP Guide To Graduate Student Training in The Teaching of PsychologyNeilermindNo ratings yet
- Construction Vibrations and Their Impact On Vibration-Sensitive FacilitiesDocument10 pagesConstruction Vibrations and Their Impact On Vibration-Sensitive FacilitiesKwan Hau LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Ibrahim A. MistrahNo ratings yet
- The Confidence Myth and What It Means To Your Career: by Tara MohrDocument4 pagesThe Confidence Myth and What It Means To Your Career: by Tara MohrdargeniNo ratings yet
- Space Systems and Space Subsystems Fundamentals Course Sampler 140211082630 Phpapp02Document42 pagesSpace Systems and Space Subsystems Fundamentals Course Sampler 140211082630 Phpapp02danielNo ratings yet
- Pagdaragdag (Adding) NG Bilang Na May 2-3 Digit Na Bilang Na May Multiples NG Sandaanan Antas 1Document5 pagesPagdaragdag (Adding) NG Bilang Na May 2-3 Digit Na Bilang Na May Multiples NG Sandaanan Antas 1Teresita Andaleon TolentinoNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Arithmetic Reasoning Practice Test 1Document7 pagesASVAB Arithmetic Reasoning Practice Test 1ASVABTestBank100% (2)
- Standard Test Method For Impact Resistance D2794Document3 pagesStandard Test Method For Impact Resistance D2794vasu_suvaNo ratings yet
- Manage Faisalabad WasteDocument2 pagesManage Faisalabad WasteUsama SanaullahNo ratings yet
- COM295r3 Communication Process WorksheetDocument2 pagesCOM295r3 Communication Process Worksheetfa1therrNo ratings yet
- SplunkCloud-6 6 3-SearchTutorial PDFDocument103 pagesSplunkCloud-6 6 3-SearchTutorial PDFanonymous_9888No ratings yet
- Managing Change Leading TransitionsDocument42 pagesManaging Change Leading TransitionsSecrets26No ratings yet
- Syllabus in Study and Thinking SkillsDocument5 pagesSyllabus in Study and Thinking SkillsEnrique Magalay0% (1)
- Personal Philosophy of Education-Exemplar 1Document2 pagesPersonal Philosophy of Education-Exemplar 1api-247024656No ratings yet
- JCL RefresherDocument50 pagesJCL RefresherCosta48100% (1)
- Proposal LayoutDocument11 pagesProposal Layoutadu g100% (1)
- Vblock® Systems Password ManagementDocument22 pagesVblock® Systems Password ManagementVakul BhattNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database Utilities OverviewDocument6 pagesOracle Database Utilities OverviewraajiNo ratings yet